Recently there have been many questions in FB forums about incorporating text in knits. The techniques can vary depending on available tools. The most basic method is entering vowel and consonant shapes dot by dot in paint programs, with each dot becoming a pixel or punched hole in the final image. There are many free downloadable fonts for personal use that produce images that can fairly easily be translated this way, among them:
https://www.fontspace.com/munro-font-f14903
https://www.1001fonts.com/subway-ticker-font.html
https://www.1001fonts.com/01-digit-font.html
https://www.1001fonts.com/loud-noise-font.html
https://www.1001fonts.com/arcade-font.html
https://www.1001fonts.com/mobile-font-font.html
Knit stitch shaped units
https://www.fontspace.com/xmas-sweater-stitch-font-f28134https://www.fontspace.com/christmas-jumper-font-f21275
https://www.fontspace.com/knitfont-font-f6001
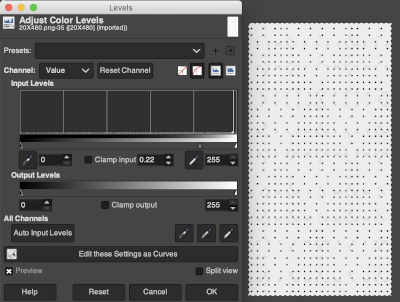
Notes on using GIMP update for Mac 2019, I had a quick FB share for a first exploration using Gimp:
“I have not previously put much effort into using text in gimp. A quick start: image 200X200,1800 magnification view grid, snap to grid, work in RGB mode, not indexed,
turn off anti-aliasing, it wants to smooth edges. Caution should be exercised when using antialiasing on images that are not in RGB color space. It is an effect used to smooth edges in bitmapped images and will blur the edge pixels to transparency.
In this instance, ultimately working in lo-res black and white for downloads, you want to keep the jaggies, not average them out.
I believe Passap actually has a built-in command to “smooth edges” in images downloaded into it. I have always preferred manipulating the images myself rather than relying on software to do it for me.
Start with a font size of 12 in the chosen font, and increase the font size if letters are too close together, the result is easily changed to black to make it ready for downloads, obviously not an answer for tiny letters. My capitals are font size 12, and the other 3 words size 16 to maintain spacing between the letters”
 Getting a bit more methodical,
Getting a bit more methodical,
info from the Gimp manual: Text management, Text tool
In addition, there are good online videos on this topic, but they are intended for use in much larger canvases, often using 150-200 as the font size, whereas in knitting that is likely the limit of our canvas size when planning for programming the full needle bed.
I am working on a Mac. From Windows tutorials found on Youtube, it appears there still are differences in some of the content and optics between the two platforms. A note: version 2.10.34, 2023 begins to incorporate some of the Windows commands in the Mac version.
Gimp is the only program that I personally prefer and use dark mode. To change the app’s appearance, the selections for dark, gray, or light themes may be made by choosing system preferences, then clicking on the theme, and selecting from options available on the right  a partial illustration of changes in the grey and light themes
a partial illustration of changes in the grey and light themes Text may be activated by choosing text in the image/ tools menu
Text may be activated by choosing text in the image/ tools menu  by clicking on the tool icon A in the toolbox
by clicking on the tool icon A in the toolbox  or by using t as the keyboard shortcut, then clicking anywhere on the canvas.
or by using t as the keyboard shortcut, then clicking anywhere on the canvas.
Click on the fonts button Aa to open the font selector
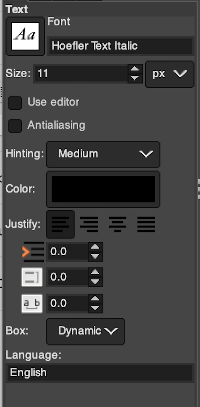 At the top of the Text tool dialog, the current Text Size, 11 in above, is shown in either pixels or points. A pixel is the smallest component in a bitmap image, and all measures in pixels depend on the screen resolution. A point is a fixed value, one inch is the same as 72 points. Standard screen resolution is often 72 pixels per inch, in which case text in pixels will be the same size as text measured in points.
At the top of the Text tool dialog, the current Text Size, 11 in above, is shown in either pixels or points. A pixel is the smallest component in a bitmap image, and all measures in pixels depend on the screen resolution. A point is a fixed value, one inch is the same as 72 points. Standard screen resolution is often 72 pixels per inch, in which case text in pixels will be the same size as text measured in points.
You may also type in the name of the font you wish to use,  choosing from installed fonts. Text editing can happen by selecting buttons here or with direct on-canvas editing by making the changes within the semi-transparent floating toolbox on the canvas itself.
choosing from installed fonts. Text editing can happen by selecting buttons here or with direct on-canvas editing by making the changes within the semi-transparent floating toolbox on the canvas itself.
If you prefer to work with dockable dialogues go to and choose Windows, Dockable Dialogs, Fonts, and options will appear on the right 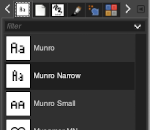 As long as a text box is active, making another selection from the fonts menu will instantly change the box content, creating a preview each time.
As long as a text box is active, making another selection from the fonts menu will instantly change the box content, creating a preview each time.
As mentioned, Antialiasing is best turned off when not in RGB color mode
Hinting “Uses the index of adjustment of the font to modify characters in order to produce clear letters in small font sizes” is helpful in lo-res text intended for knitting 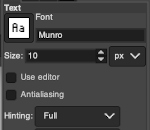 Color default is black, click in the box beside Color selection and a dialogue selection box appears for changing it
Color default is black, click in the box beside Color selection and a dialogue selection box appears for changing it 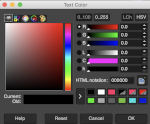 The choices listed at Gimp.org for text directions include the standard right to left, left to right as in most languages, and the following for vertical text
The choices listed at Gimp.org for text directions include the standard right to left, left to right as in most languages, and the following for vertical text  After the text is entered on the canvas, right-click on the inside of the text box to change text direction
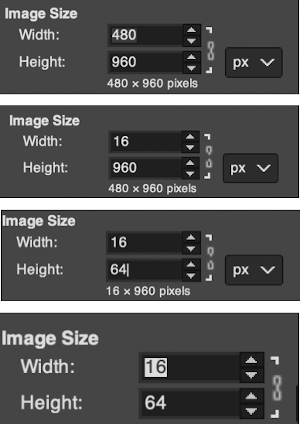
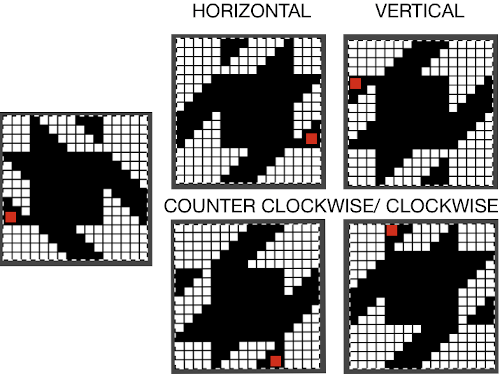
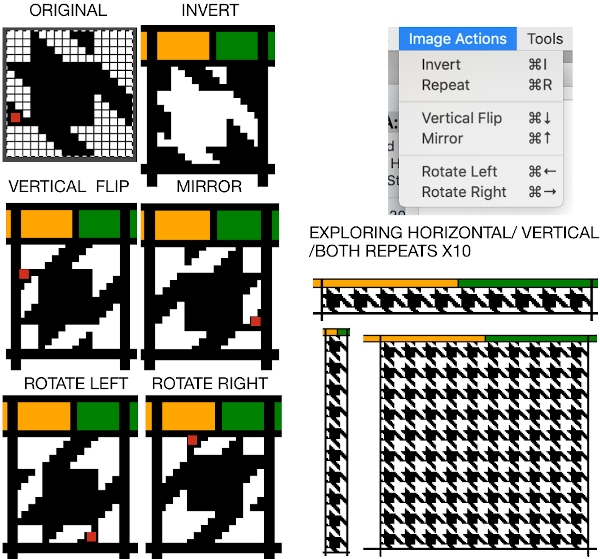
After the text is entered on the canvas, right-click on the inside of the text box to change text direction 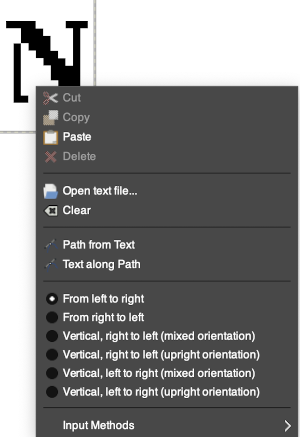 It is not necessary to work with the layers menu to start with. It is possible to “wing it” to get a starting sense of the process. Scaling and transformations are available, starting on a canvas size less than 200X200 based on needle counts on a standard km providing an ample field on which to play. If the intent is to change the direction of all the entered text, Image/transform may be used. Entering the same text in the same font size in an altered direction can change the overall pixel counts
It is not necessary to work with the layers menu to start with. It is possible to “wing it” to get a starting sense of the process. Scaling and transformations are available, starting on a canvas size less than 200X200 based on needle counts on a standard km providing an ample field on which to play. If the intent is to change the direction of all the entered text, Image/transform may be used. Entering the same text in the same font size in an altered direction can change the overall pixel counts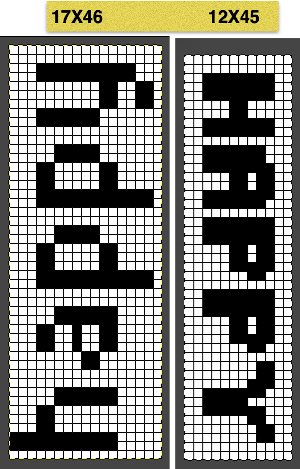
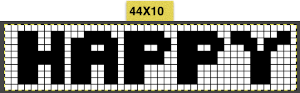 After the chosen text is placed change its mode from RGB to B/W indexed, then crop the image to your chosen size. Export.bmp, the result loaded into img2track and Ayab
After the chosen text is placed change its mode from RGB to B/W indexed, then crop the image to your chosen size. Export.bmp, the result loaded into img2track and Ayab
 For a different way to edit, choose Image/Flatten and individual components may be reconfigured on a new canvas to a very different size. This file is now 68 stitches wide, rather than 144
For a different way to edit, choose Image/Flatten and individual components may be reconfigured on a new canvas to a very different size. This file is now 68 stitches wide, rather than 144 
 The usual text alignment rules apply in text boxes as well, left to right
The usual text alignment rules apply in text boxes as well, left to right  using the return key, double-clicking in the box will highlight each letter and activate view grid should you wish to count pixels in each
using the return key, double-clicking in the box will highlight each letter and activate view grid should you wish to count pixels in each ![]() Text center-aligned
Text center-aligned
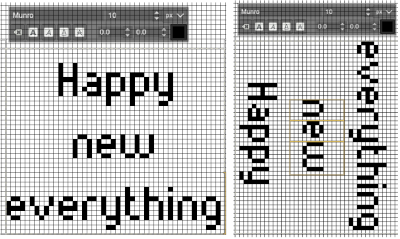 Getting more control of the process: after the text tool is highlighted and clicking anywhere on your canvas two things appear automatically. The four little boxes represent the text box, which is dynamic by default and grows in size to accommodate typed text. Anytime you click on the canvas a new text box is created.
Getting more control of the process: after the text tool is highlighted and clicking anywhere on your canvas two things appear automatically. The four little boxes represent the text box, which is dynamic by default and grows in size to accommodate typed text. Anytime you click on the canvas a new text box is created.
To change the size of the text box and you want the text to fit in a specific area, click and drag on one of the lower, small exterior boxes, and release. The box then becomes fixed, and the text will move automatically to the next line and is placed according to alignment settings. If the bottom of the text is cut off, click and drag on that small square on the bottom corner or the bottom line of the text box shape to expand its size to include it in full.
Double-click on a line of text to reveal those outlines around each letter or click and drag right or left on full words for editing. Click on a single letter space to delete it. Repeat if needed, type in the new letter(s) for a spelling correction or word change.
If following Windows instructions, it is helpful to know the comparable Mac commands ![]() pictured here on the bottom left of the Mac onscreen keyboard
pictured here on the bottom left of the Mac onscreen keyboard ![]() Use the option key and click on the canvas, and drag to place the text box on any specific area, or also to move all content in an existing text box, choose the move tool
Use the option key and click on the canvas, and drag to place the text box on any specific area, or also to move all content in an existing text box, choose the move tool  then click on any letter within the text box and drag and place. Random placement in the text box will move the whole layer
then click on any letter within the text box and drag and place. Random placement in the text box will move the whole layer 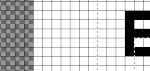 The spacing between the lines and between the letters may be adjusted as well. Clicking on the arrows to change the values here is one option, negative or positive numbers may be used
The spacing between the lines and between the letters may be adjusted as well. Clicking on the arrows to change the values here is one option, negative or positive numbers may be used 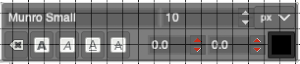 or what appeared easier to me, the same may be done here
or what appeared easier to me, the same may be done here  A sample of adjustments in line spacing
A sample of adjustments in line spacing  Very small fonts are likely not to have any room for decreased spacing in the between letters in strings of text.
Very small fonts are likely not to have any room for decreased spacing in the between letters in strings of text.
A reminder before converting to .png for download
flatten image
convert mode to indexed B/W
crop content to the desired size
export as .png
Font: mazeletter
final image loaded into img2track and Ayab ![]()
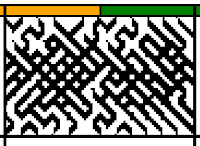

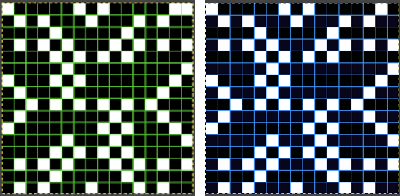
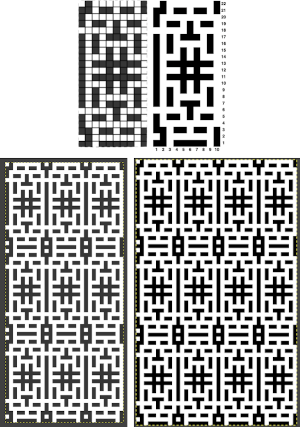
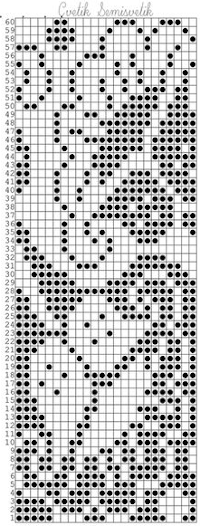 The units in many such illustrations are not square, and the goal is to end up with a PNG where each square unit represents one stitch, one row.
The units in many such illustrations are not square, and the goal is to end up with a PNG where each square unit represents one stitch, one row.
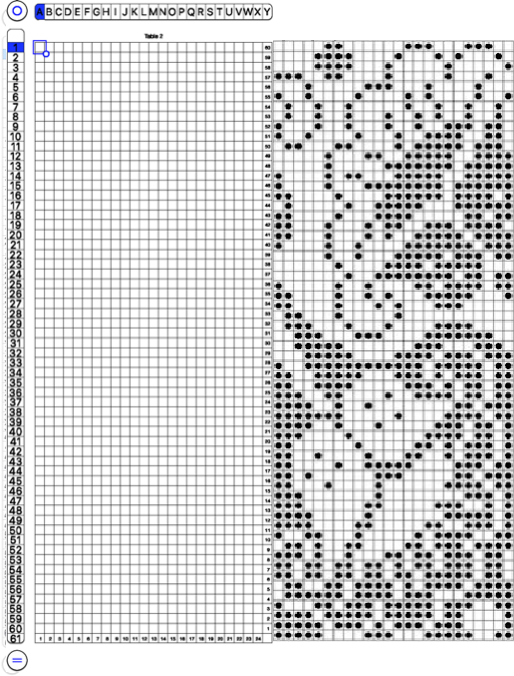
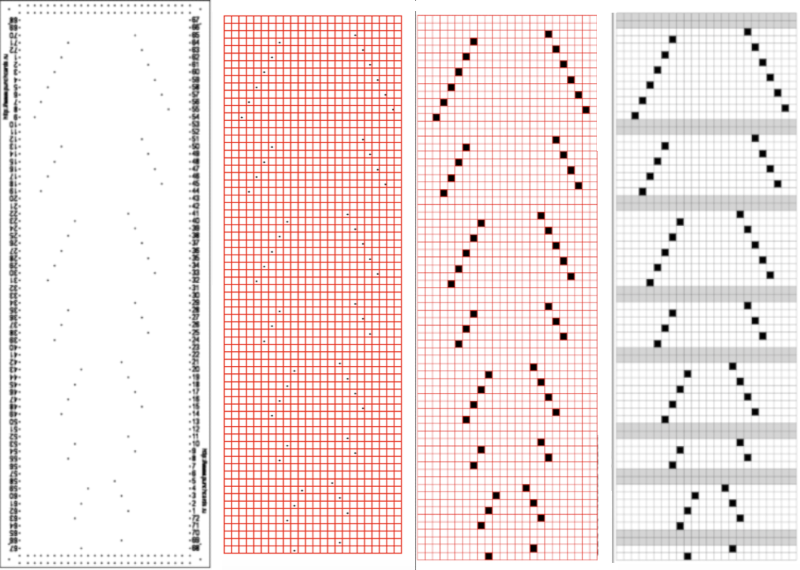
 and alter the cell borders to a bright, contrasting color. I chose red, 3-point thickness.
and alter the cell borders to a bright, contrasting color. I chose red, 3-point thickness. 
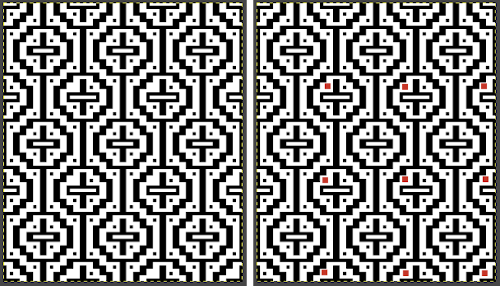
 Copy and paste the completed table. Make certain there is a different color cell in any white squares at the far corners of the image, in this case, upper right and upper left (yellow), remove cell borders
Copy and paste the completed table. Make certain there is a different color cell in any white squares at the far corners of the image, in this case, upper right and upper left (yellow), remove cell borders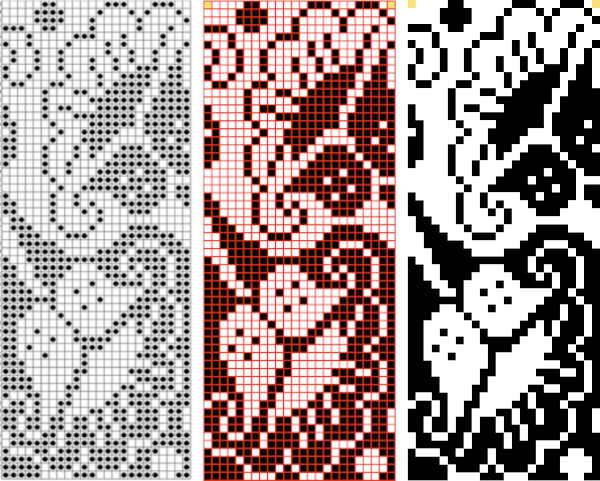 



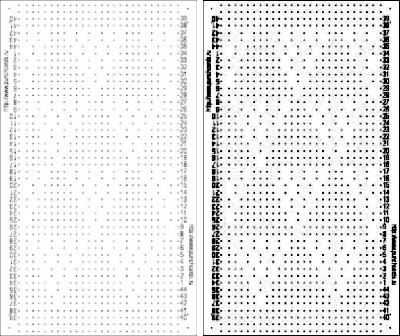
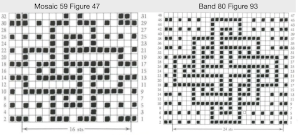
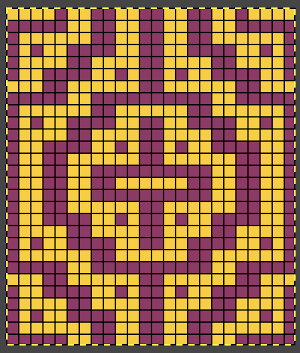
 Proceed as for the first image, being mindful of an unnecessary row at the bottom. The saved image can be tweaked in size by turning off Constrain Proportions and adjusting values for width and height for proper placement under the table grid. It soon becomes evident that the card is composed of smaller repeat segments, which in turn can be copied and pasted making for quicker work in filling in the whole punchcard row requirement.
Proceed as for the first image, being mindful of an unnecessary row at the bottom. The saved image can be tweaked in size by turning off Constrain Proportions and adjusting values for width and height for proper placement under the table grid. It soon becomes evident that the card is composed of smaller repeat segments, which in turn can be copied and pasted making for quicker work in filling in the whole punchcard row requirement. 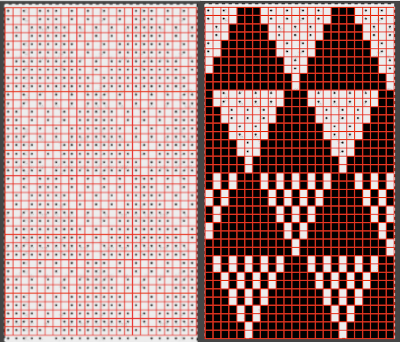 Check the repeat alignment by tiling it.
Check the repeat alignment by tiling it. 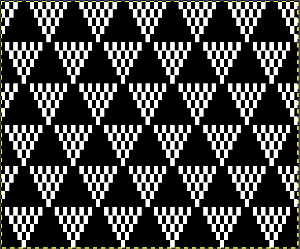 The smallest adjusted electronic repeat, 12X20 pixels.
The smallest adjusted electronic repeat, 12X20 pixels. 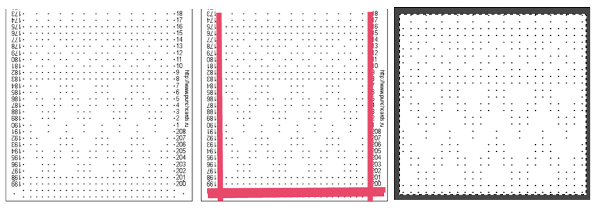 The converted, partial punchcard repeat
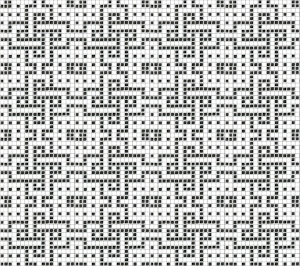
The converted, partial punchcard repeat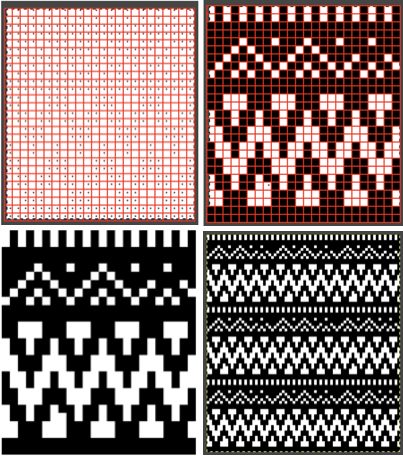  2023: ArahPaint‘s weave from grid tool makes working with the full repeat possible. The final repeat was cropped by 2 rows at the top to 24X206 to avoid a 4-row solid color line produced when the original was tiled vertically.
2023: ArahPaint‘s weave from grid tool makes working with the full repeat possible. The final repeat was cropped by 2 rows at the top to 24X206 to avoid a 4-row solid color line produced when the original was tiled vertically.

 if used, will change the numbering on the side of the card, but not the design content
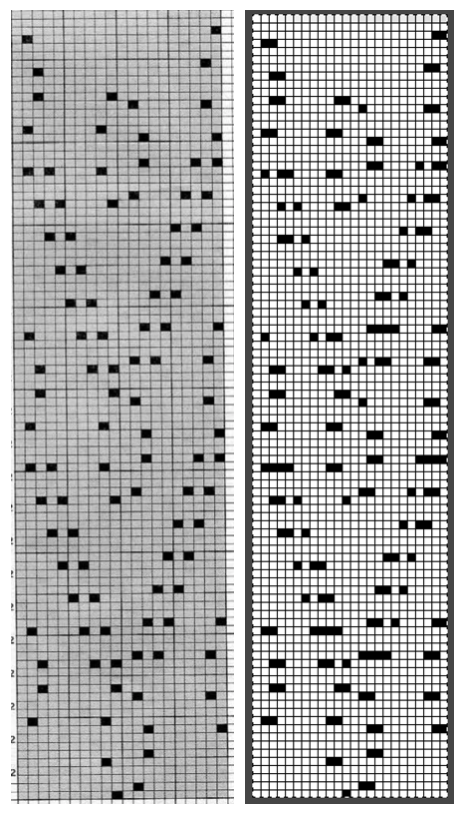
if used, will change the numbering on the side of the card, but not the design content 
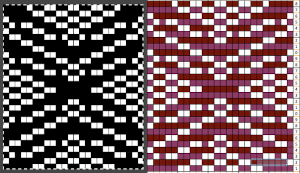
 In the past I have found lace repeats, in particular, to be particularly cranky when scaled down in Gimp due to the paucity of black cells. After the above steps, I decided to try color invert, resize, and color invert again, which in this instance, produced what appears to be an accurate repeat. Of course, the final png is likely to need mirroring for use in some electronic models
In the past I have found lace repeats, in particular, to be particularly cranky when scaled down in Gimp due to the paucity of black cells. After the above steps, I decided to try color invert, resize, and color invert again, which in this instance, produced what appears to be an accurate repeat. Of course, the final png is likely to need mirroring for use in some electronic models 
 2023: a different approach:
2023: a different approach: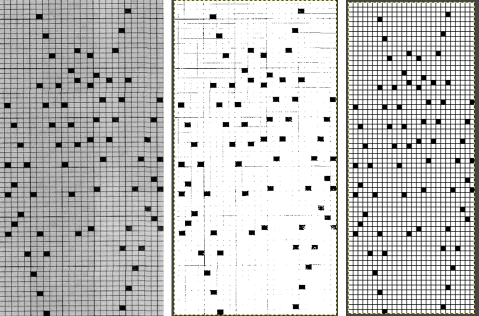
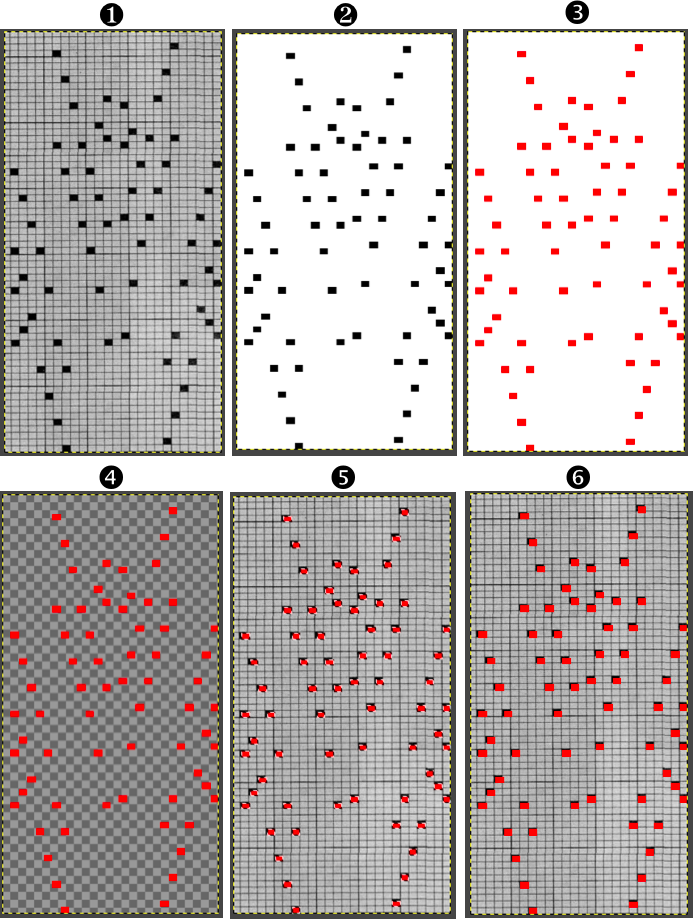




 The working design repeat is 16X16. Create a new table that is 16 cells wide, twice its height, 32. While holding down the command key, select all the odd-numbered rows planned for the final chart repeat, any errors can be corrected by clicking again on the same spot, still holding the key down. The process may be done in steps, releasing the key in between selecting groups
The working design repeat is 16X16. Create a new table that is 16 cells wide, twice its height, 32. While holding down the command key, select all the odd-numbered rows planned for the final chart repeat, any errors can be corrected by clicking again on the same spot, still holding the key down. The process may be done in steps, releasing the key in between selecting groups 
 Fill in cells the chosen 2 colors
Fill in cells the chosen 2 colors 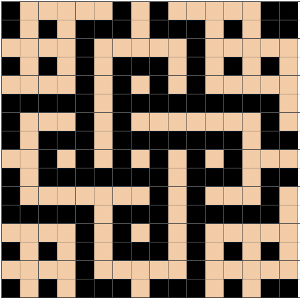


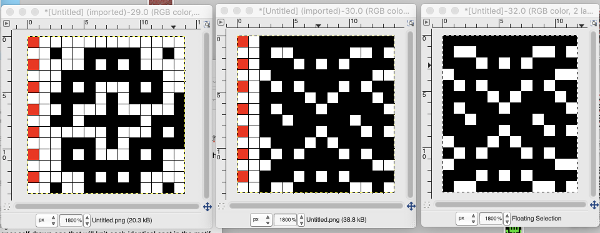
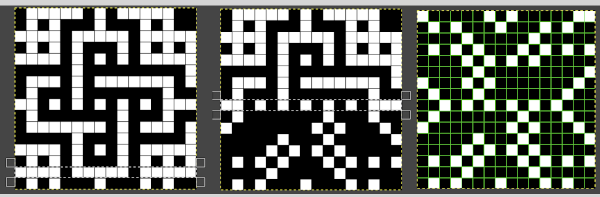

 will swap black and white cells in that row. Continue the process on every other row. It is not necessary to select the tool each time, as you advance and select the next row, the one just left remains briefly outlined in white dashes, making it easier to advance correctly in the design.
will swap black and white cells in that row. Continue the process on every other row. It is not necessary to select the tool each time, as you advance and select the next row, the one just left remains briefly outlined in white dashes, making it easier to advance correctly in the design.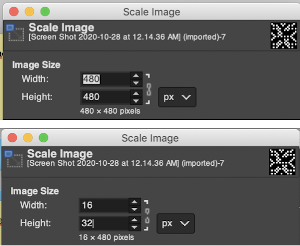
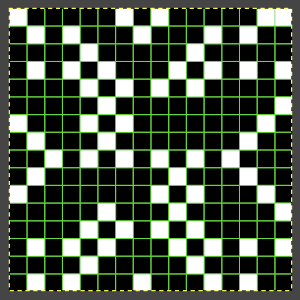 This repeat posed by a quandary. The file may be used as-is and doubled in length after download. For doubling the height in Numbers, prior to importing the final screengrab into gimp, please see post:
This repeat posed by a quandary. The file may be used as-is and doubled in length after download. For doubling the height in Numbers, prior to importing the final screengrab into gimp, please see post:  and
and 
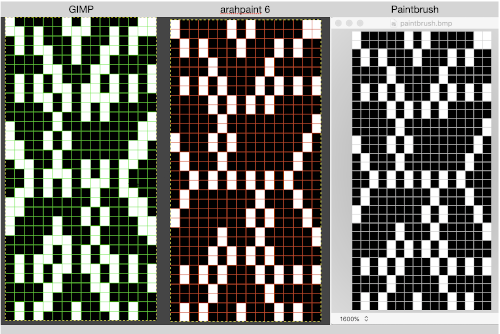







 adapted for maze knitting, eliminating long floats, to be lengthened to double-height
adapted for maze knitting, eliminating long floats, to be lengthened to double-height 

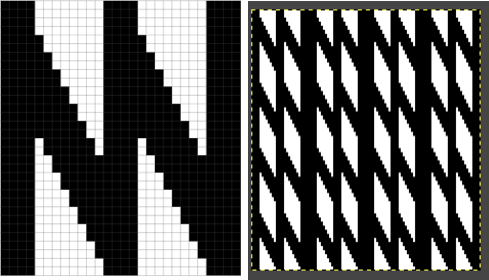
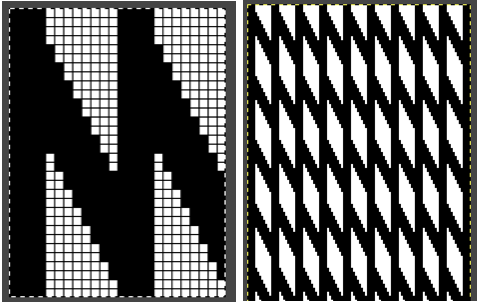
 Using the maze generator by
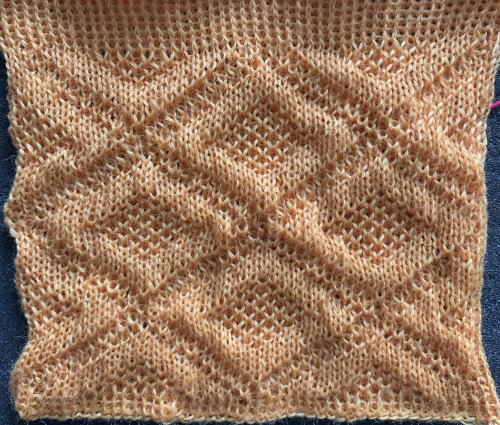
Using the maze generator by 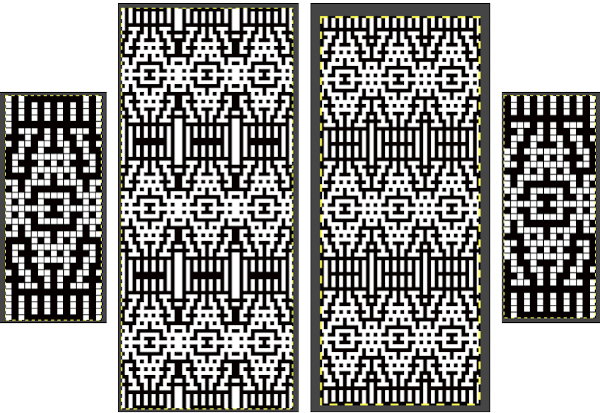 The proof of concept swatch for the version on the right, knit in tuck stitch
The proof of concept swatch for the version on the right, knit in tuck stitch  the double-length BMP ready for knitting, 14X68
the double-length BMP ready for knitting, 14X68
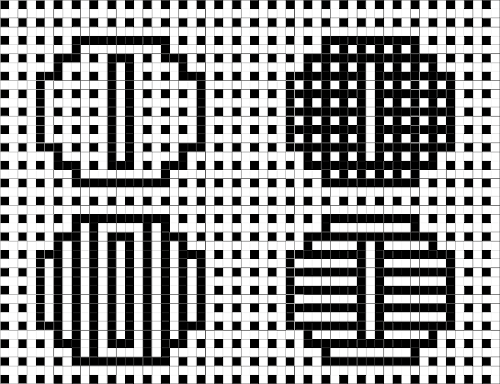


 If numbers are your preference, with a bit of playing around digits may be adjusted in width and height
If numbers are your preference, with a bit of playing around digits may be adjusted in width and height 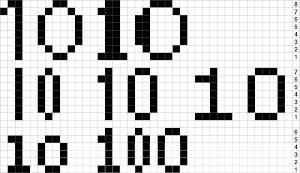 going a bit bolder, the 8 individual letters as numbers could repeat horizontally across each design row.
going a bit bolder, the 8 individual letters as numbers could repeat horizontally across each design row. 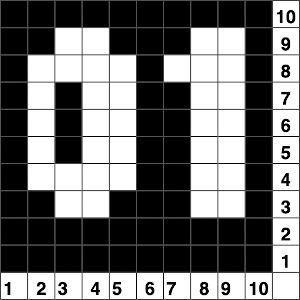 A repeat for the letter AX2 planned for the first segment of an 82 stitch wide scarf,
A repeat for the letter AX2 planned for the first segment of an 82 stitch wide scarf, 
 G carriages may be used to knit the same patterns in knit and purl stitch combinations.
G carriages may be used to knit the same patterns in knit and purl stitch combinations. 

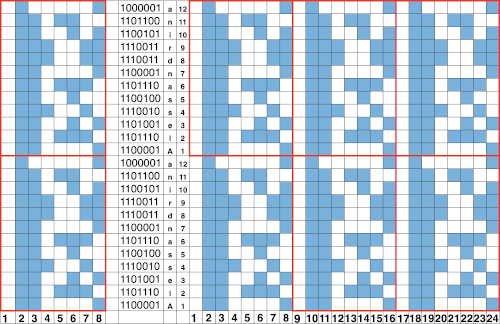
 The suitable dbj separation is the one where each color in each row knits for 2 rows, whether performed by hand, using the 3 colors per row separation in img2track or the default separation in Passap. The Ayab HOP separation is awesome, works for any 3 color design with as little elongation as possible, but is not suited for this purpose. How-tos for DIY separations and their automated versions by programs for knitting more than 2 colors per row have been discussed in other posts.
The suitable dbj separation is the one where each color in each row knits for 2 rows, whether performed by hand, using the 3 colors per row separation in img2track or the default separation in Passap. The Ayab HOP separation is awesome, works for any 3 color design with as little elongation as possible, but is not suited for this purpose. How-tos for DIY separations and their automated versions by programs for knitting more than 2 colors per row have been discussed in other posts.
 A similar process on the Passap allows for playing easily with both racked colors because of the possible arrow and pusher settings on the back bed, but on Brother, this would require hand selection on the ribber on every row or a specific color separation for needle selection on the top bed
A similar process on the Passap allows for playing easily with both racked colors because of the possible arrow and pusher settings on the back bed, but on Brother, this would require hand selection on the ribber on every row or a specific color separation for needle selection on the top bed Seeking automation, keeping things simple, here is a basic zigzag pattern in a repeat also executable on punchcard machines. The ribber is now set to knit throughout (N/N), the main bed to slip in both directions. End needle selection must be canceled when using the slip setting selectively or when working patterning with needles completely out of work
Seeking automation, keeping things simple, here is a basic zigzag pattern in a repeat also executable on punchcard machines. The ribber is now set to knit throughout (N/N), the main bed to slip in both directions. End needle selection must be canceled when using the slip setting selectively or when working patterning with needles completely out of work 
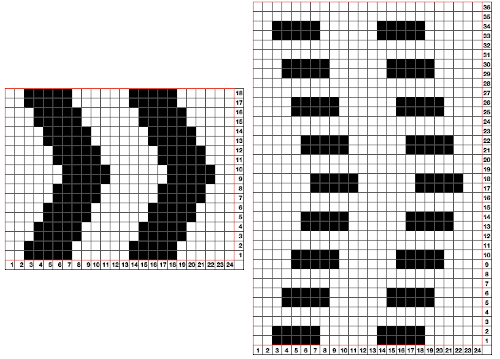
 The process using 3 colors: the patterning color will be knit on needles preselected on the top bed. As shaping is about to begin, in this pattern, one needle preselected out indicates the location for an “increase”, one preselected back to B position a decrease
The process using 3 colors: the patterning color will be knit on needles preselected on the top bed. As shaping is about to begin, in this pattern, one needle preselected out indicates the location for an “increase”, one preselected back to B position a decrease  To perform the decrease, using a double eye tool to transfer the B position stitch down onto the ribber needle adjacent to the first needle in D position on the top bed
To perform the decrease, using a double eye tool to transfer the B position stitch down onto the ribber needle adjacent to the first needle in D position on the top bed



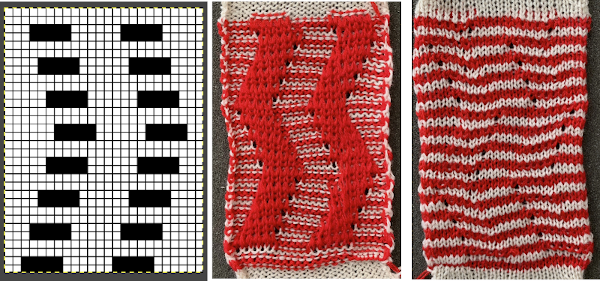
 The repeat and the knit shown on both sides:
The repeat and the knit shown on both sides: 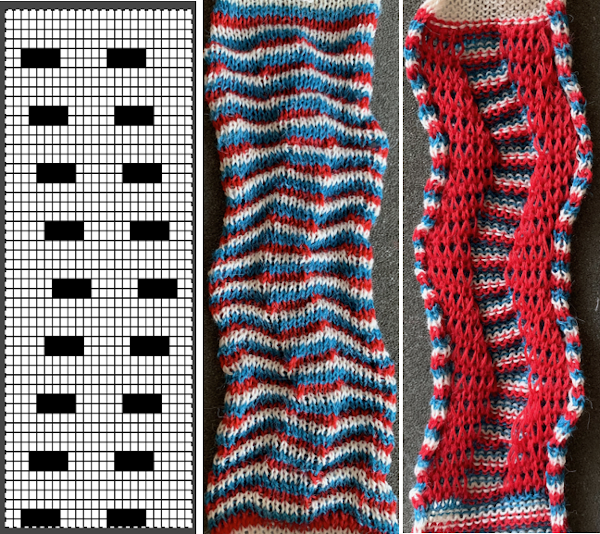 Comparing the 2 color and 3 color versions: aside from the obvious increase in length, note that the slipped segments in red on the 3 color swatch are now composed of longer stitches since they are held for 2 additional rows, and the overall fabric is more puckered than the 2 color version. The curling at the sides is the nature of edge stitches, especially if the yarn used is wool. At times that may be used intentionally, as a decorative edge.
Comparing the 2 color and 3 color versions: aside from the obvious increase in length, note that the slipped segments in red on the 3 color swatch are now composed of longer stitches since they are held for 2 additional rows, and the overall fabric is more puckered than the 2 color version. The curling at the sides is the nature of edge stitches, especially if the yarn used is wool. At times that may be used intentionally, as a decorative edge.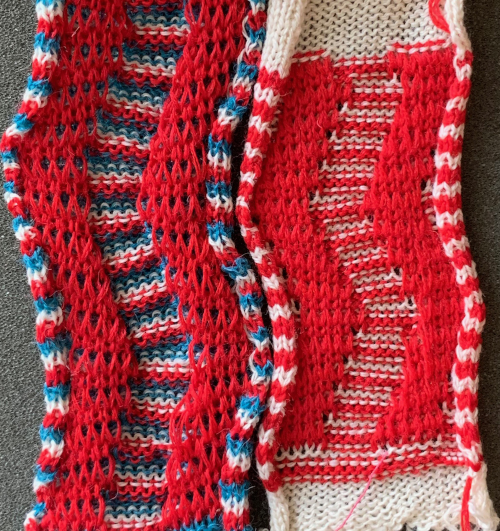
 Using the same color separation as for the simple zig-zag shape, the design is expanded to include knit bed rows that will be skipped completely, resulting in the ribber alone knitting in the second color for those rows. It is now twice as long as the original, 24X64
Using the same color separation as for the simple zig-zag shape, the design is expanded to include knit bed rows that will be skipped completely, resulting in the ribber alone knitting in the second color for those rows. It is now twice as long as the original, 24X64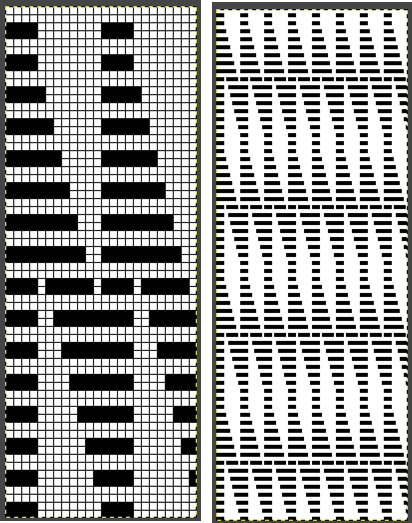 The planned proof of concept added a 4 stitch border on the right for a 28 stitch swatch centered with 14 stitches either side of 0. Tiling the repeat X2 again in height made it easier for me to plan how to manage transfers to expose the varying stripes in the ground. Visual comparison to the movement in the inspiration knit:
The planned proof of concept added a 4 stitch border on the right for a 28 stitch swatch centered with 14 stitches either side of 0. Tiling the repeat X2 again in height made it easier for me to plan how to manage transfers to expose the varying stripes in the ground. Visual comparison to the movement in the inspiration knit:  As the number of needles in work on either of the 2 beds is increased, it is likely tension or yarn changes may be required. The first preselection row is from the right, toward the color changer. The stitches on the non selected needles are transferred to the bottom bed
As the number of needles in work on either of the 2 beds is increased, it is likely tension or yarn changes may be required. The first preselection row is from the right, toward the color changer. The stitches on the non selected needles are transferred to the bottom bed 
 with the color change, only preselected needles will knit on both the top and bottom beds moving to the right
with the color change, only preselected needles will knit on both the top and bottom beds moving to the right  and will do so again on the return to the left while preselecting an all blank row
and will do so again on the return to the left while preselecting an all blank row  on the next pass to the right only the ribber knits in the ground color;
on the next pass to the right only the ribber knits in the ground color; 


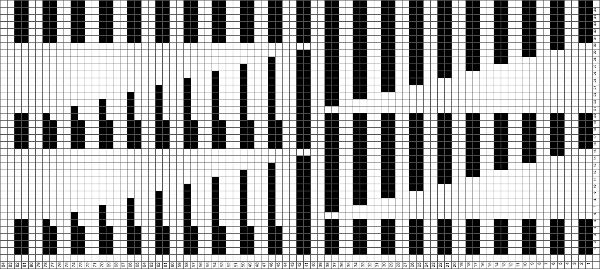
 Back to the drawing board in order to reduce the number of hand manipulations involved, with a shift in the center transition, the repeat in my spreadsheet is now 24 stitches wide, plus an additional 4 stitch border, and gets marked up with colors. I prefer to program the width of my knitting as opposed to a single repeat for all over patterning
Back to the drawing board in order to reduce the number of hand manipulations involved, with a shift in the center transition, the repeat in my spreadsheet is now 24 stitches wide, plus an additional 4 stitch border, and gets marked up with colors. I prefer to program the width of my knitting as opposed to a single repeat for all over patterning 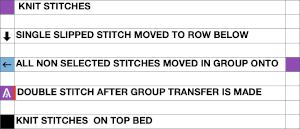
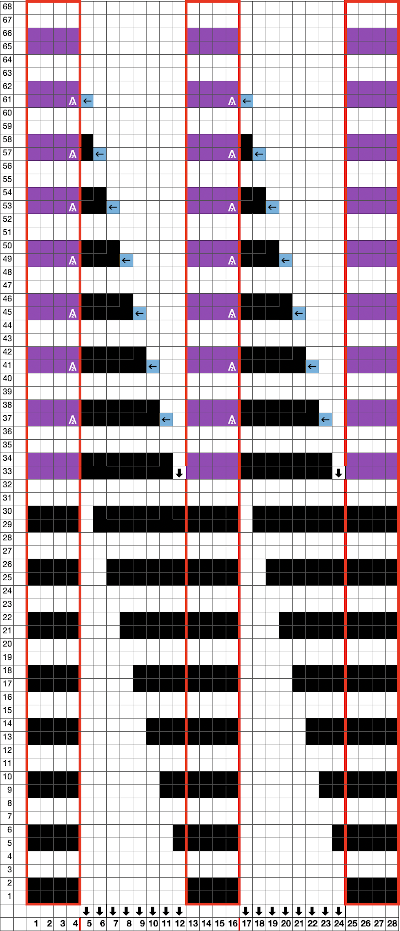
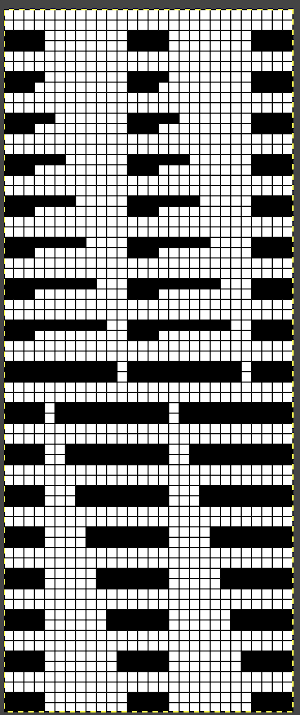 The choice can be made based upon the preference of moving stitch groups to the right or to the left with the horizontal direction of the repeat adjusted for your KM model or software used.
The choice can be made based upon the preference of moving stitch groups to the right or to the left with the horizontal direction of the repeat adjusted for your KM model or software used. 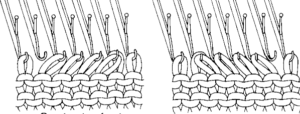 I planned the transfers in this swatch toward the color changer after picking up the proper color, white, and before knitting the next row using it. The 930 png:
I planned the transfers in this swatch toward the color changer after picking up the proper color, white, and before knitting the next row using it. The 930 png: 
 When the top of the repeat is reached, row 68, the only needles selected will be those of the 4 stitch vertical columns and the design repeat will return to its start
When the top of the repeat is reached, row 68, the only needles selected will be those of the 4 stitch vertical columns and the design repeat will return to its start My proof of concept swatch is 3.75 inches wide
My proof of concept swatch is 3.75 inches wide 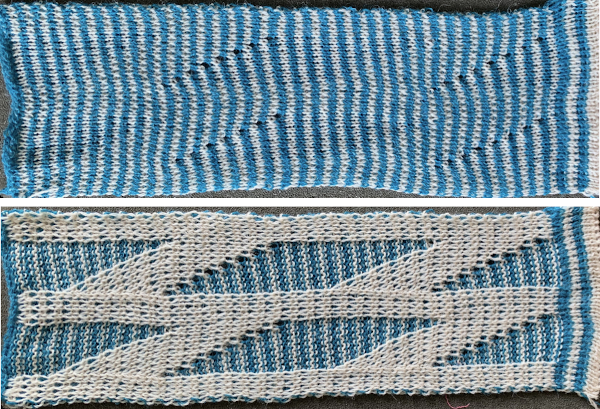 The inspiration sweater was knit using a wider repeat and significantly thicker yarn, reflected here in the small number of repeats composing the sweater body front
The inspiration sweater was knit using a wider repeat and significantly thicker yarn, reflected here in the small number of repeats composing the sweater body front 
 The off white yarn used here was the same thickness but not fiber content as in the previous swatch, 2/18 wool-silk vs Australian wool in the former. It is not as smoothly spun. The result shows an interesting similarity in length, though there are 16 additional rows in the pattern repeat. This time I programmed my repeat for stitch transfers on the knit bed to move away from the color changer.
The off white yarn used here was the same thickness but not fiber content as in the previous swatch, 2/18 wool-silk vs Australian wool in the former. It is not as smoothly spun. The result shows an interesting similarity in length, though there are 16 additional rows in the pattern repeat. This time I programmed my repeat for stitch transfers on the knit bed to move away from the color changer.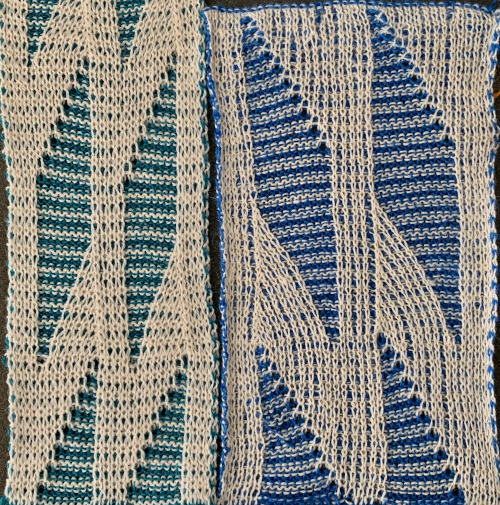  Eliminating the border on one side, a double repeat (30 stitches) measure 4 inches in width. To put the difference in scale to the sweater in perspective, an oversize garment with 40 inches in chest diameter would require 20 inches in width for the front piece. Ten single repeats, as opposed to the inspiration’s sweater 4, bring the total required the number of stitches to 150. With the added border of 5 stitches for matching side edges, the fabric is in the realm of possibility for producing a garment on the home knitting machine. My tension was set at 3/3 for all the swatches, with some teasing required on occasion to encourage stitches on the main bed to knit off properly. Ribber height adjustment can also have an effect on those numbers. I tend to do all my knitting with the slide lever in the center position. The double 30X84 repeat with no added border
Eliminating the border on one side, a double repeat (30 stitches) measure 4 inches in width. To put the difference in scale to the sweater in perspective, an oversize garment with 40 inches in chest diameter would require 20 inches in width for the front piece. Ten single repeats, as opposed to the inspiration’s sweater 4, bring the total required the number of stitches to 150. With the added border of 5 stitches for matching side edges, the fabric is in the realm of possibility for producing a garment on the home knitting machine. My tension was set at 3/3 for all the swatches, with some teasing required on occasion to encourage stitches on the main bed to knit off properly. Ribber height adjustment can also have an effect on those numbers. I tend to do all my knitting with the slide lever in the center position. The double 30X84 repeat with no added border

 There have previous posts on automated lace edging on Brother machines, ie
There have previous posts on automated lace edging on Brother machines, ie 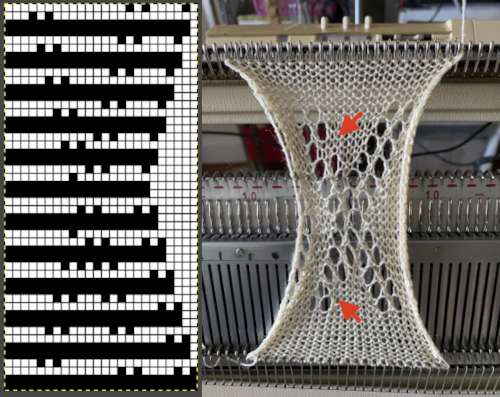

 The Studio cam settings
The Studio cam settings 



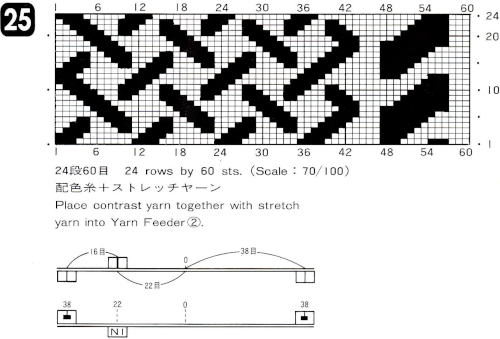
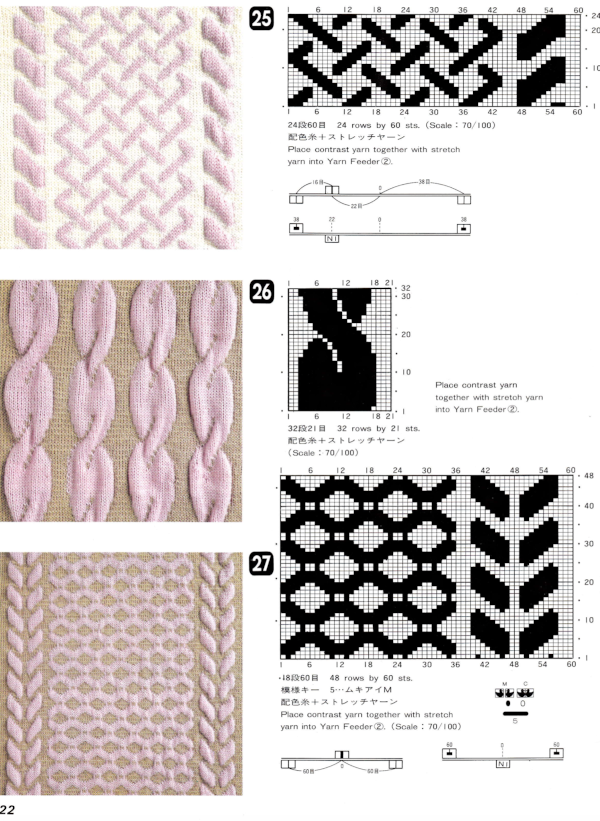
 25: the original provided was 60X24, here it is adjusted to a full size 76X24
25: the original provided was 60X24, here it is adjusted to a full size 76X24
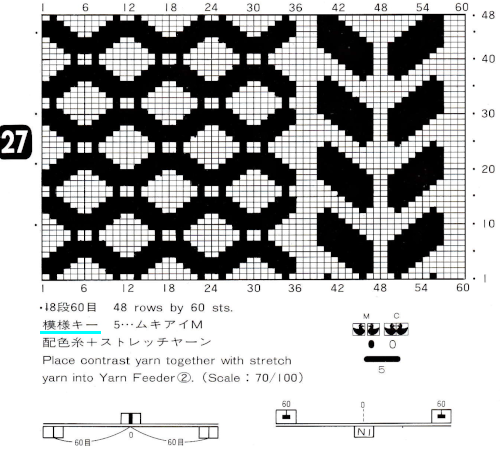
 28: the repeat provided was 60X84, here it is adjusted to a full size 120X84
28: the repeat provided was 60X84, here it is adjusted to a full size 120X84
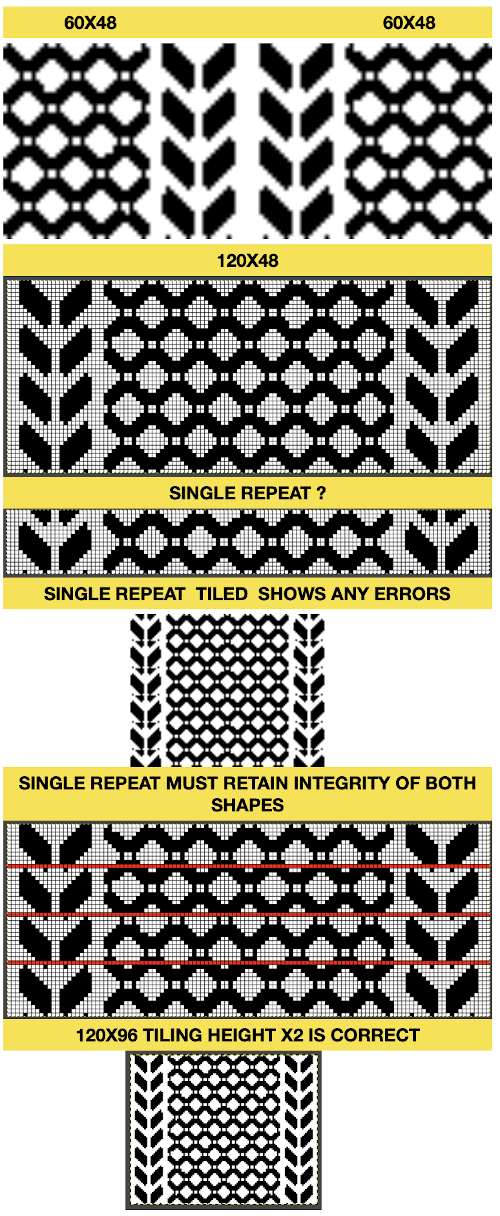
 tiled X2 in height to check for proper alignment
tiled X2 in height to check for proper alignment 

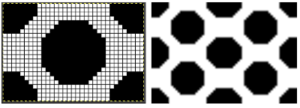 Increments in height need to happen at sequences of 2 rows each, so the design was then doubled in height, resulting in a scaled image now 33 stitches by 46 rows in height, with a planned horizontal repeat X2 = 66. Note: the sidebar offers start and end needles are given for pattern placement on the needle bed. Sampling may occur on fewer stitches than that. Since the number of repeats programmed to add up to an even number and center alignment is chosen, the number of needles is even on each side of 0.
Increments in height need to happen at sequences of 2 rows each, so the design was then doubled in height, resulting in a scaled image now 33 stitches by 46 rows in height, with a planned horizontal repeat X2 = 66. Note: the sidebar offers start and end needles are given for pattern placement on the needle bed. Sampling may occur on fewer stitches than that. Since the number of repeats programmed to add up to an even number and center alignment is chosen, the number of needles is even on each side of 0.  In my second series of swatches, I decided to try for a smaller “circular” shape, with the repeat now measuring 15 wide by 20 high, and a planned horizontal repeat X3 = 45. If centered, the software places the odd number of needles on the right-hand side of 0.
In my second series of swatches, I decided to try for a smaller “circular” shape, with the repeat now measuring 15 wide by 20 high, and a planned horizontal repeat X3 = 45. If centered, the software places the odd number of needles on the right-hand side of 0. 
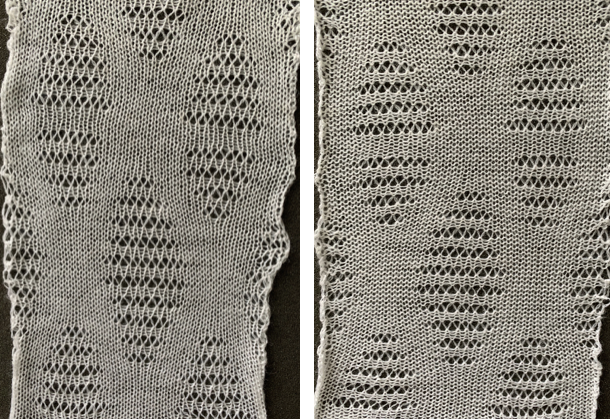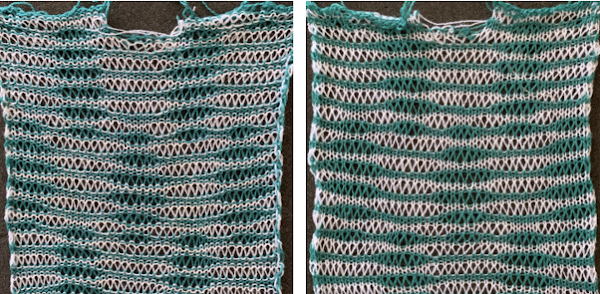

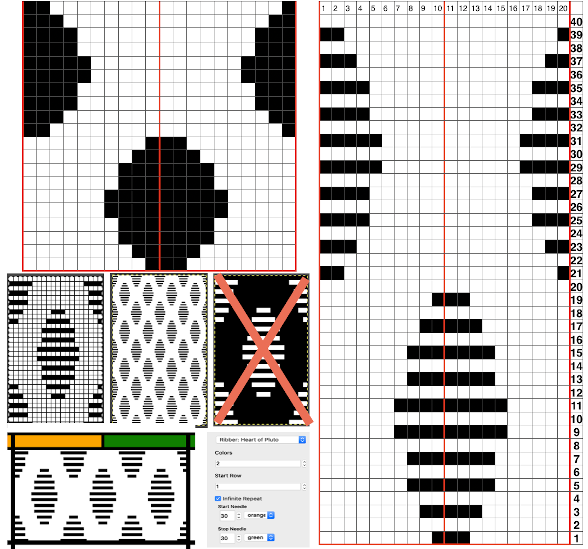
 The wider horizontal band of all knit stitches was due to operator error, happened when I pushed back preselection an extra time, resulting in the ribber only knitting extra rows. For the sake of added clarity, I have added color to the chart below, assigning yellow and grey to all-white design areas in the pattern. The black squares are what I choose to drop. For illustration purposes, this is only a segment of the repeat.
The wider horizontal band of all knit stitches was due to operator error, happened when I pushed back preselection an extra time, resulting in the ribber only knitting extra rows. For the sake of added clarity, I have added color to the chart below, assigning yellow and grey to all-white design areas in the pattern. The black squares are what I choose to drop. For illustration purposes, this is only a segment of the repeat. 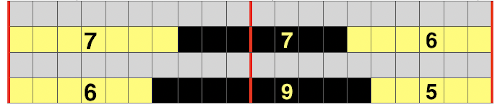



 drop the loops, return needles to B position. At this point, since all needles are in B a modified stitch ditcher may be used for 2 passes, dropping the loops on the first pass and returning the whole series back to B on the second.
drop the loops, return needles to B position. At this point, since all needles are in B a modified stitch ditcher may be used for 2 passes, dropping the loops on the first pass and returning the whole series back to B on the second. 
 COL: push all preselected needles back to B, as you knit back to the right the next group of white squares (yellow) in the next design row will be preselected
COL: push all preselected needles back to B, as you knit back to the right the next group of white squares (yellow) in the next design row will be preselected
 COL: knit to the right in order to form loops on the main bed, continue for the desired number of repeats and end as suggested for the two-color version.
COL: knit to the right in order to form loops on the main bed, continue for the desired number of repeats and end as suggested for the two-color version.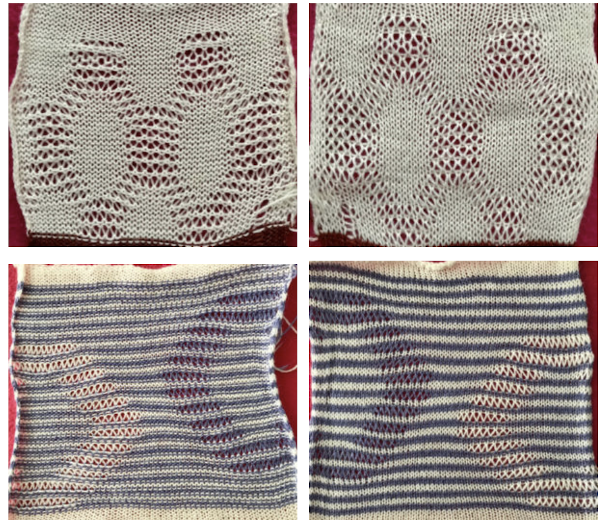

 The FI results are shown on the left, the first dbj test with lili buttons engaged and both carriages set to slip in both directions appear to the right. Note the difference in width and height of the resulting knit. The floats in FI are overlong, and there are some separation and lengthening of the stitches along the diagonal edges of the houndstooth shape
The FI results are shown on the left, the first dbj test with lili buttons engaged and both carriages set to slip in both directions appear to the right. Note the difference in width and height of the resulting knit. The floats in FI are overlong, and there are some separation and lengthening of the stitches along the diagonal edges of the houndstooth shape 
 The program does provide prompts as to which color should be picked up next, and clues as to where one is in the repeat, they are found at the bottom of the Ayab window. I happened to grab content with color B upcoming both times.
The program does provide prompts as to which color should be picked up next, and clues as to where one is in the repeat, they are found at the bottom of the Ayab window. I happened to grab content with color B upcoming both times. 
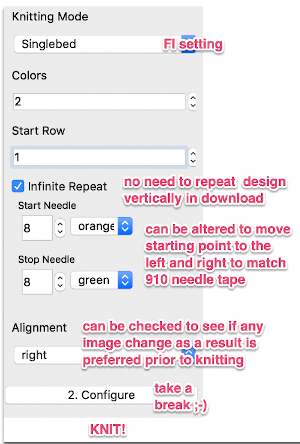
 When preparing images for download, they should be indexed to 3 colors
When preparing images for download, they should be indexed to 3 colors 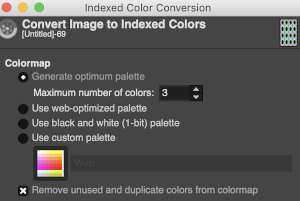
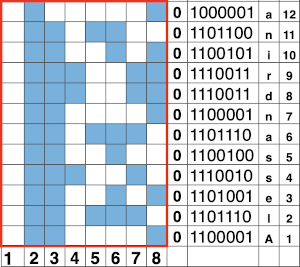
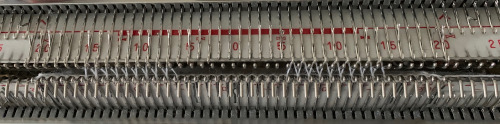
 It takes a while when knitting double bed knits before one can assess whether the results are correct in terms of patterning since the knit is hidden for some length as it drops between the beds. Because the Ayab prompts for color changes were altered sometimes when the carriage on the right, sometimes on the left, I dropped the first sample off after slightly more than one repeat, found its patterning to be correct, and that the prompts when on the color changer side for the following row to be knit from left to right were reliable, as shown in the knit swatches. In turn, I used an indexed greyscale image. The lettering on the right indicates where colors were placed following the give instructions, rather than where they were assigned in the original design. The manual states that the color sequence for the separation is: white, grey, black, gray, however, if the prompts for changing colors as given are followed, which is very valuable in tracking them, the knitting occurs in reverse order.
It takes a while when knitting double bed knits before one can assess whether the results are correct in terms of patterning since the knit is hidden for some length as it drops between the beds. Because the Ayab prompts for color changes were altered sometimes when the carriage on the right, sometimes on the left, I dropped the first sample off after slightly more than one repeat, found its patterning to be correct, and that the prompts when on the color changer side for the following row to be knit from left to right were reliable, as shown in the knit swatches. In turn, I used an indexed greyscale image. The lettering on the right indicates where colors were placed following the give instructions, rather than where they were assigned in the original design. The manual states that the color sequence for the separation is: white, grey, black, gray, however, if the prompts for changing colors as given are followed, which is very valuable in tracking them, the knitting occurs in reverse order. 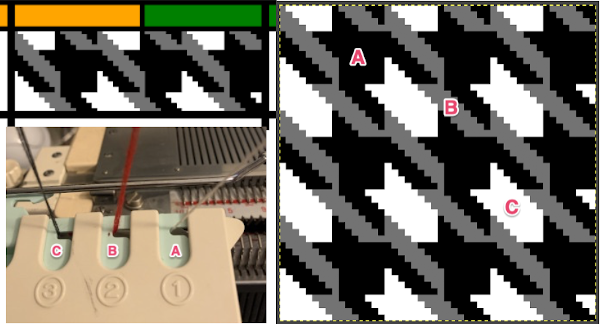 Knitting mode options for DBJ are listed below the single bed one,
Knitting mode options for DBJ are listed below the single bed one,  The main bed is set to slip in both directions, the ribber as well, with lili buttons engaged. The number of colors is not altered automatically by Ayab, the change needs to be made manually.
The main bed is set to slip in both directions, the ribber as well, with lili buttons engaged. The number of colors is not altered automatically by Ayab, the change needs to be made manually. 





 This was the set up in the color changer
This was the set up in the color changer 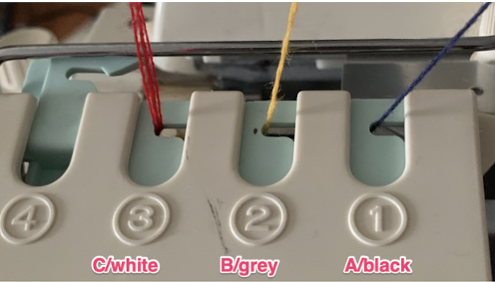


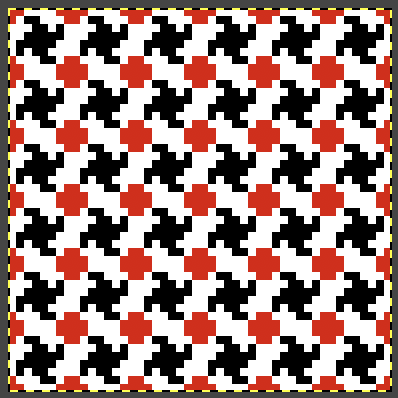
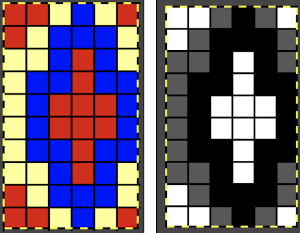
 Planned possible use of the middle color twice may be seen in this image
Planned possible use of the middle color twice may be seen in this image
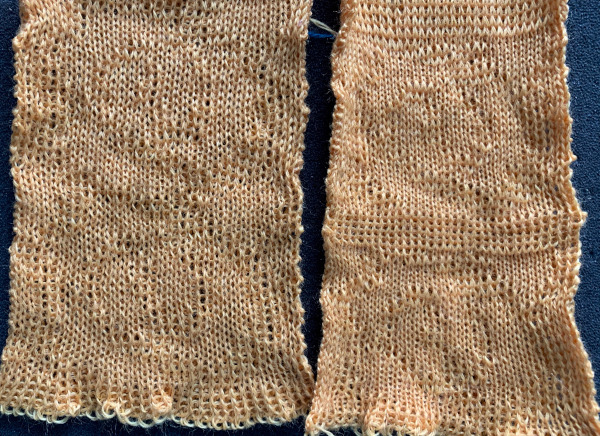

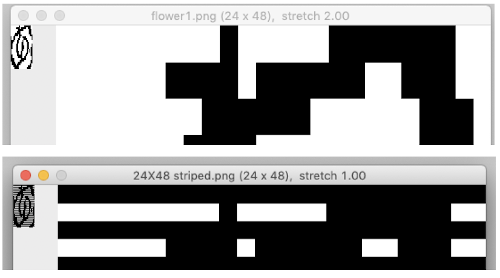


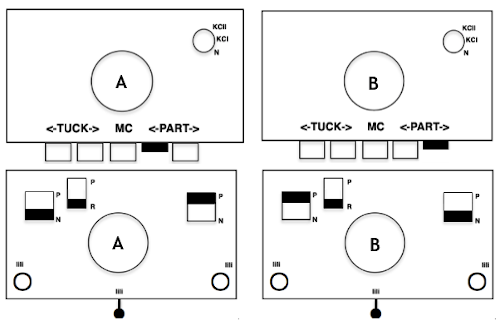



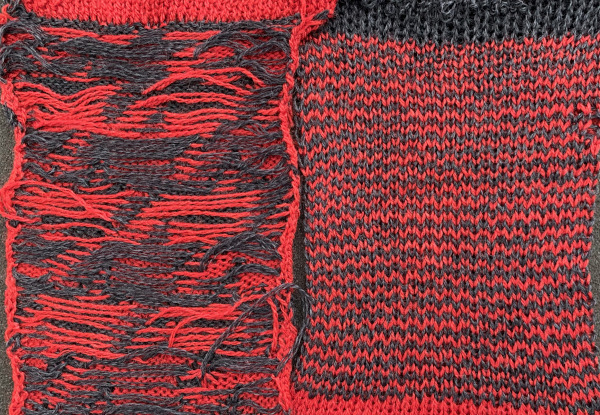
 The “striped” repeat produces essentially the same fabric. The knit carriage may be set to slip in both directions when using it since the row of all punched holes or black pixels will knit every stitch on every needle selected while in the previous samples the cam button set to knit in one direction performed that function regardless of any markings on the design repeat. The ribber is set to knit in one direction, slip in the other. Reversing sides for cam button settings produces the same fabric
The “striped” repeat produces essentially the same fabric. The knit carriage may be set to slip in both directions when using it since the row of all punched holes or black pixels will knit every stitch on every needle selected while in the previous samples the cam button set to knit in one direction performed that function regardless of any markings on the design repeat. The ribber is set to knit in one direction, slip in the other. Reversing sides for cam button settings produces the same fabric 

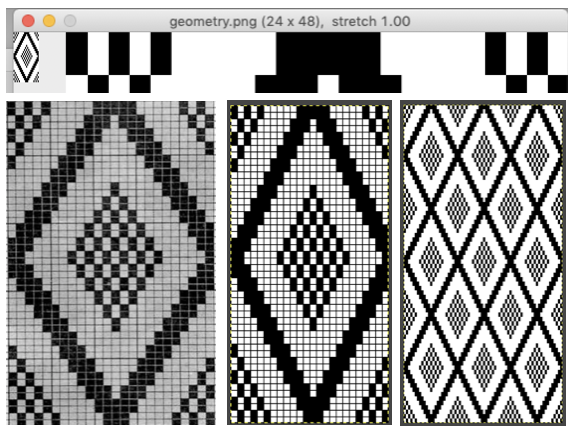
 The
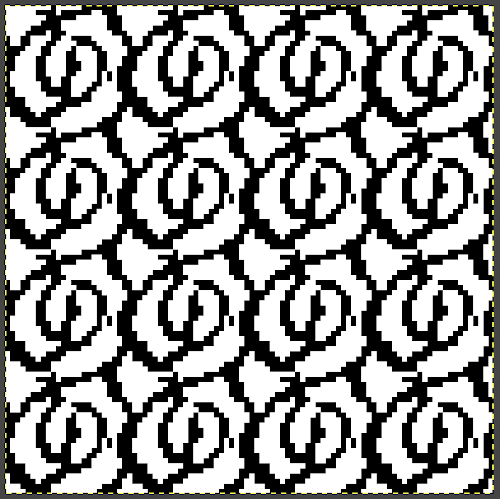
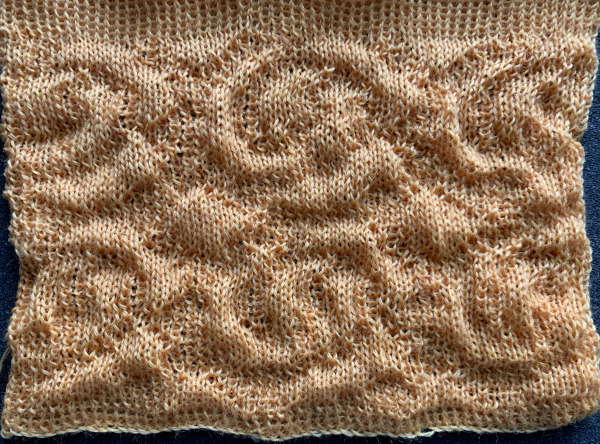
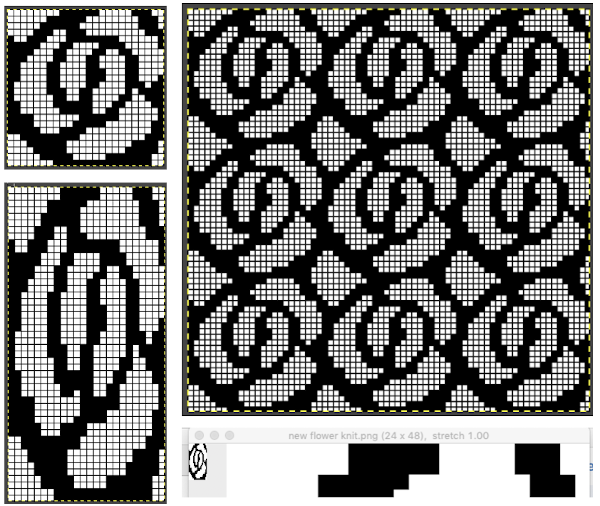
The  The repeat I chose is designated as suitable for the Garter Carriage. It is 24 stitches wide by 48 rows high, shown below as provided, charted in Gimp as .png for download, and tiled to help visualize how continuous repeats might line up. The image .png was downloaded with img2track to my 930, with a stretch factor of 1.0, retaining the original repeat size
The repeat I chose is designated as suitable for the Garter Carriage. It is 24 stitches wide by 48 rows high, shown below as provided, charted in Gimp as .png for download, and tiled to help visualize how continuous repeats might line up. The image .png was downloaded with img2track to my 930, with a stretch factor of 1.0, retaining the original repeat size

