A Facebook group query brought up the possibility of creating cables in an “easier, quicker” way than by crossing stitches by hand. Over the years different authors have suggested a “sewn” method for pulling stocking stitch columns together in order to achieve the cabled effect. The illustrations are usually of the work done on a ribbed fabric, but it also may be achieved in simple stocking stitch, with ladders marking the edges of the mock cable, and providing a visual line to follow and count spaces when smocking the fabric up. The width of each column, the yarn fiber content, and personal preferences will determine the success” of the results.
I was reminded of “magic cables”, a technique made popular years ago in a copyrighted pattern series by Ricky Mundstock, ie this one from 1969 (illustrated online). The concept originated in a Japanese publication years before, relies on hooking up tuck loops to create the cable-like effects.  I tend not to knit from published patterns, set out to understand what makes the fabric work in theory, and then sort out whether I have other preferences of my own for creating it. I began to experiment with a totally random tuck card. Tuck is chosen for the background because it is short and fat, giving the taller all knit rows for the “cables” the possibility of an additional gather, adding to their depth. I chose a purely random repeat, which is a good way to start for DIY if hesitant about the process. White squares will not be selected, will tuck for 2 rows, have a knit stitch (black dot in card) on each side of them. Max on Brother, unless using very thing yarn would be white bars single square in width, 4 rows in height (yes, there can be exceptions on rare occasions)
I tend not to knit from published patterns, set out to understand what makes the fabric work in theory, and then sort out whether I have other preferences of my own for creating it. I began to experiment with a totally random tuck card. Tuck is chosen for the background because it is short and fat, giving the taller all knit rows for the “cables” the possibility of an additional gather, adding to their depth. I chose a purely random repeat, which is a good way to start for DIY if hesitant about the process. White squares will not be selected, will tuck for 2 rows, have a knit stitch (black dot in card) on each side of them. Max on Brother, unless using very thing yarn would be white bars single square in width, 4 rows in height (yes, there can be exceptions on rare occasions)
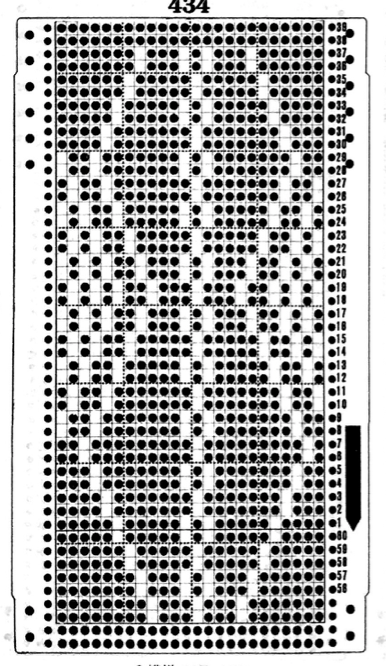 The card is cropped to the 24 X 44 stitch in width and height for the repeat to be worked in electronics. The area colored blue on the far right indicates possible all knit rows for hooking up “cables” during knitting, mustard color indicates ladders created by an out of work needle on each side of the central, all knit column. The ladders make it easier to identify each all knit column. The tape over holes idea does not work for masking a punchcard since that blue area would need to be all punched holes. The tape over would result in “unpunched” ones.
The card is cropped to the 24 X 44 stitch in width and height for the repeat to be worked in electronics. The area colored blue on the far right indicates possible all knit rows for hooking up “cables” during knitting, mustard color indicates ladders created by an out of work needle on each side of the central, all knit column. The ladders make it easier to identify each all knit column. The tape over holes idea does not work for masking a punchcard since that blue area would need to be all punched holes. The tape over would result in “unpunched” ones.
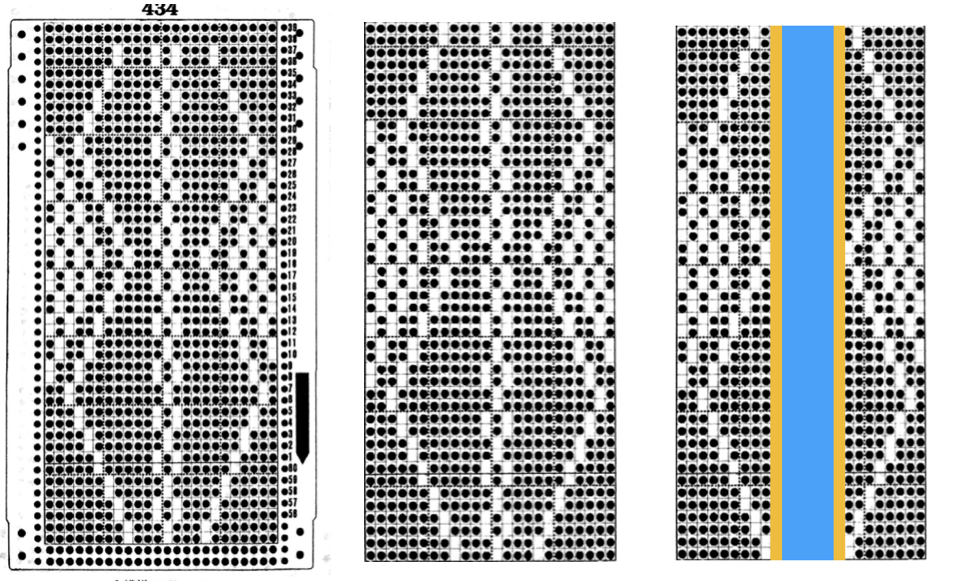 This takes the revised card single repeat and indicates some quick possibilities for altering it
This takes the revised card single repeat and indicates some quick possibilities for altering it 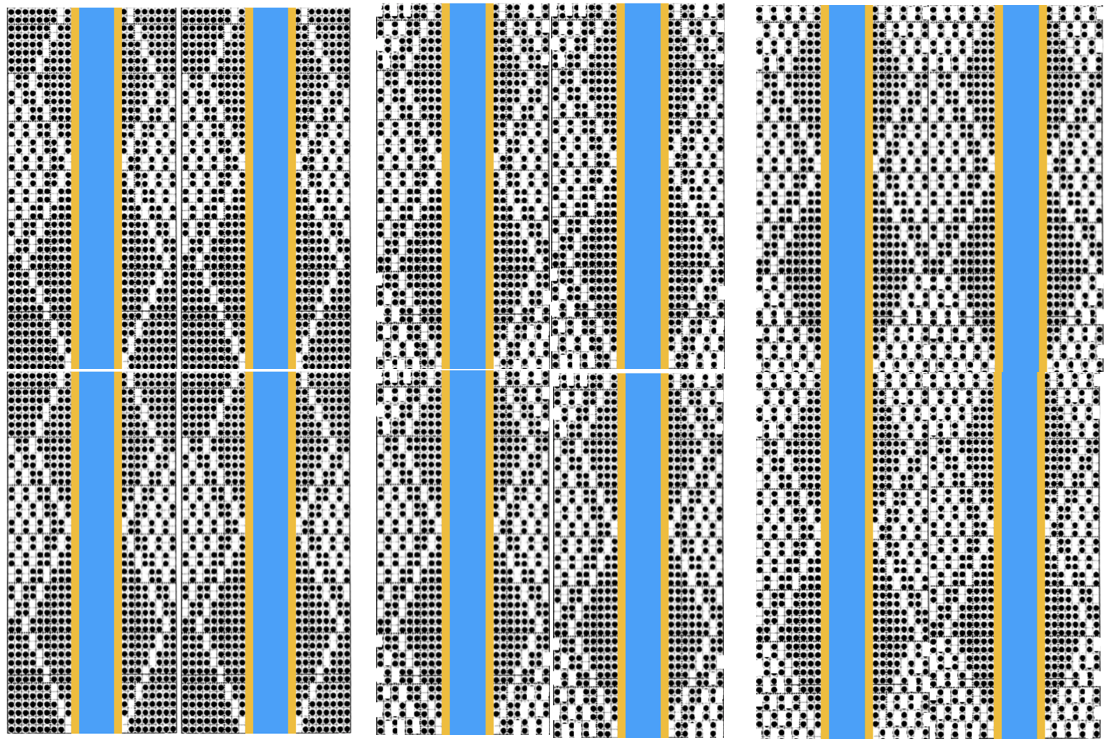 I added 2 more stitches to establish a slightly different pattern. The grab form my work in Numbers was then opened in gimp and scaled to 26X44 for the possible knitting pattern. If working with black and white squares, the image will need to be colored reverse for knitting. I abandoned this repeat for my final swatches in favor of keeping markers for hooking stitches up along the all knit column inside the ladders as opposed to the knit body of the remaining shapes.
I added 2 more stitches to establish a slightly different pattern. The grab form my work in Numbers was then opened in gimp and scaled to 26X44 for the possible knitting pattern. If working with black and white squares, the image will need to be colored reverse for knitting. I abandoned this repeat for my final swatches in favor of keeping markers for hooking stitches up along the all knit column inside the ladders as opposed to the knit body of the remaining shapes.  Here the non-selected needles are placed along the knit column itself, on alternating sides. The final repeat after correcting a pixel error I discovered while knitting:
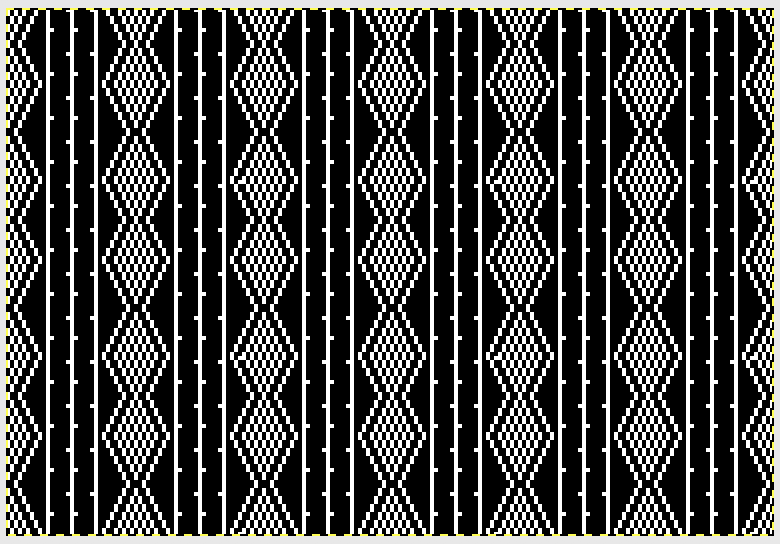
Here the non-selected needles are placed along the knit column itself, on alternating sides. The final repeat after correcting a pixel error I discovered while knitting: 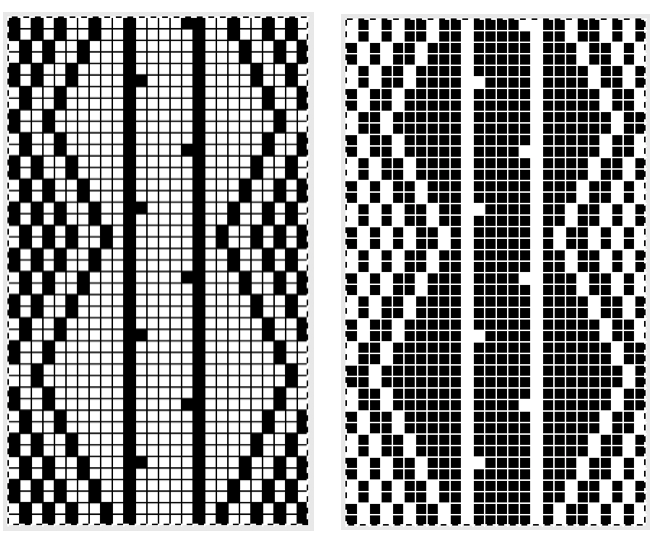 Ayab does not repeat across the horizontal row, each stitch in the width you are planning to knit needs to be programmed. For a test swatch, I decided to work with programmed 72 stitches (knit on fewer). This would be the downloadable file
Ayab does not repeat across the horizontal row, each stitch in the width you are planning to knit needs to be programmed. For a test swatch, I decided to work with programmed 72 stitches (knit on fewer). This would be the downloadable file![]()
magnified and gridded to visually check again prior to knitting it 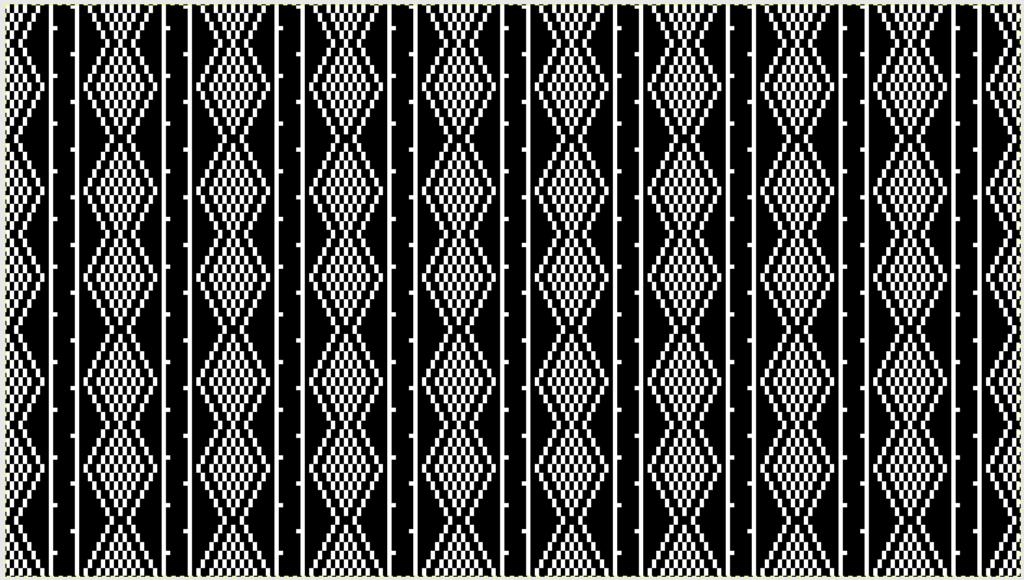 This is what is seen by the knitter when the image is loaded,
This is what is seen by the knitter when the image is loaded,  but any image loaded is automatically flipped/ mirrored horizontally by the software. Direction may not matter in the overall pattern, but here we have needles out of work, which if selected on the basis of what is seen as opposed to what is knit, would be in the wrong location. The first preselection row is also only possible from left to right. The easiest way to empty the proper needles is to do transfers after that row, to either side, restoring needle selection prior to continuing to knit. Also, since there are needles out of work, end needle selection is canceled (KCII).
but any image loaded is automatically flipped/ mirrored horizontally by the software. Direction may not matter in the overall pattern, but here we have needles out of work, which if selected on the basis of what is seen as opposed to what is knit, would be in the wrong location. The first preselection row is also only possible from left to right. The easiest way to empty the proper needles is to do transfers after that row, to either side, restoring needle selection prior to continuing to knit. Also, since there are needles out of work, end needle selection is canceled (KCII).
In my first swatch, I tried the idea of hooking up stitches in opposite directions, but was not pleased with the result, wanted to reduce the amount of hand manipulation involved. In the later swatch, I hooked up every other selection onto the same side. Arrows here indicate the direction, not the proper needle position.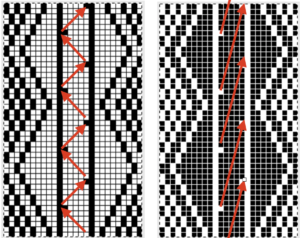
Alternating side hooking up with some yarn and needle change issues. 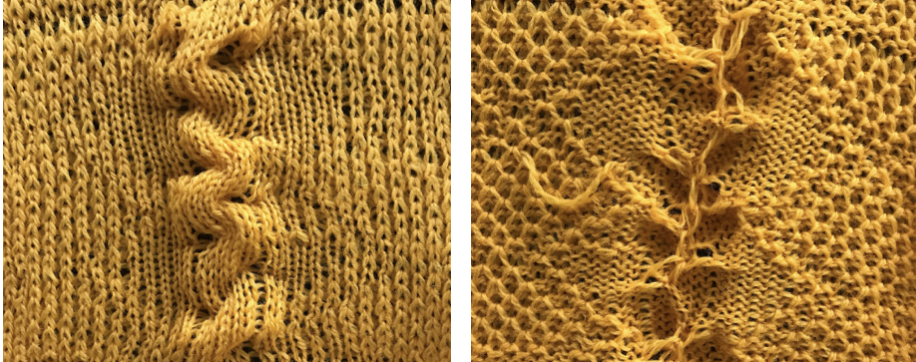 Hooking up to one side only was quicker to execute and appeared more pleasing to me. Both swatches had blips from an errant pixel.
Hooking up to one side only was quicker to execute and appeared more pleasing to me. Both swatches had blips from an errant pixel.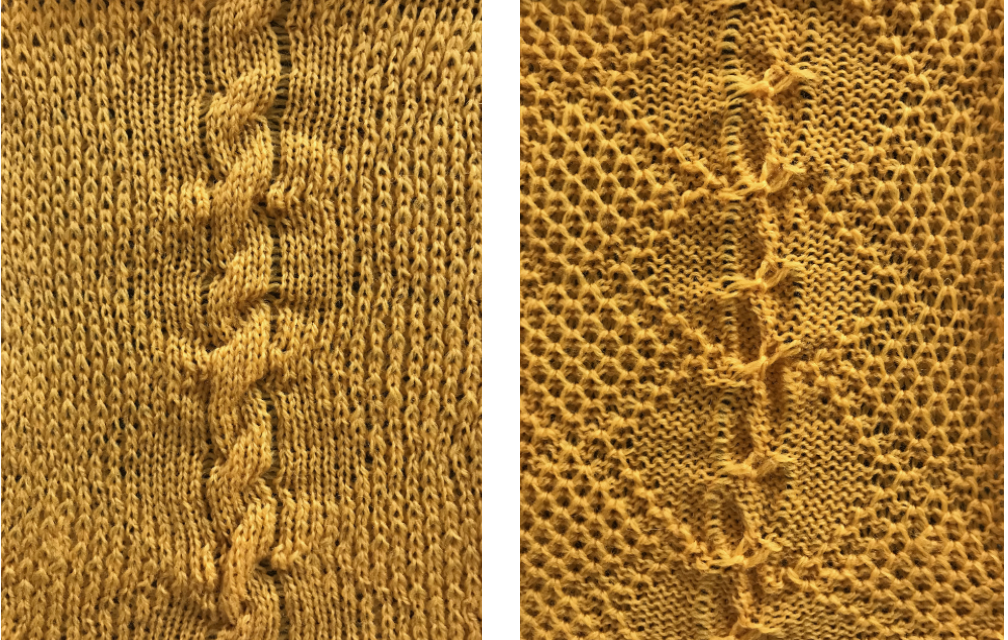  Steps in knitting the above fabric. The actual knitting will happen with what is shown as the repeat with white pixels on the dark ground, seen looking at the center vertical all knit column of the repeat when knitting the fabric. Allow the non-selected needle on the left side of the column to tuck, providing a marking row for picking up stitches, knit until the needle on the right side of the column is not selected. Prior to knitting across that row pick up the tucked loop and stitch on the left side
Steps in knitting the above fabric. The actual knitting will happen with what is shown as the repeat with white pixels on the dark ground, seen looking at the center vertical all knit column of the repeat when knitting the fabric. Allow the non-selected needle on the left side of the column to tuck, providing a marking row for picking up stitches, knit until the needle on the right side of the column is not selected. Prior to knitting across that row pick up the tucked loop and stitch on the left side
 Lift both loops up onto the non selected needle on the right side of the column, bring that needle all the way out to hold (three yarn loops in the hook)
Lift both loops up onto the non selected needle on the right side of the column, bring that needle all the way out to hold (three yarn loops in the hook) 
Continue knitting until the next non-selected needle in the column appears once again on the right, pick up from below the left marking spot, and repeat. For DIY insert all knit columns on your chosen repeat and proceed as above.
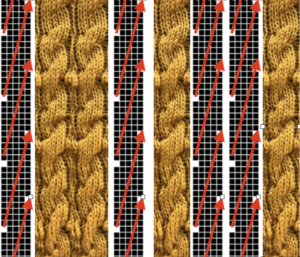
Visualizing possibilities: chart for side by side columns actions on the purl side is shown. The black columns with arrows coupled with photos show the direction of the hook-ups in the back, purl side of the fabric, and potential “cables” as seen on the knit side using the column repeat illustrated above. 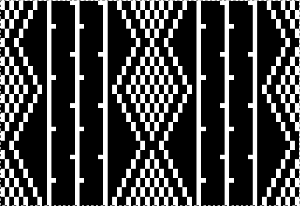
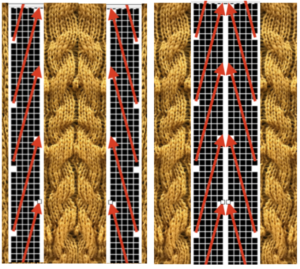
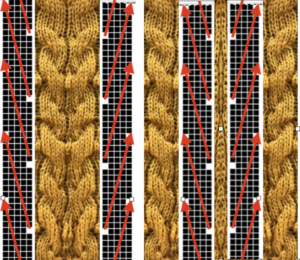 This is a garter stitch version found on Pinterest
This is a garter stitch version found on Pinterest