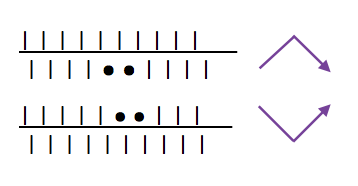
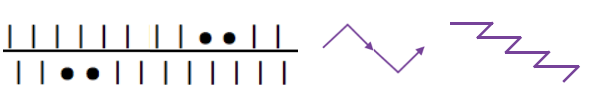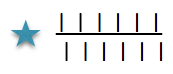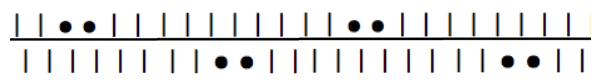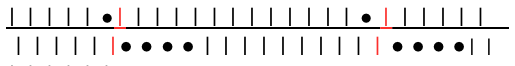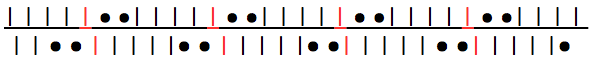RIBBED, FOLDING PLEATS result from varying the needle arrangement on both beds, usually in every needle rib. As with any knit fabric, the knit piece will fold toward the purl side along the length of the piece, not away from it. The bend can be put permanently into the fabric by leaving one or more consecutive needles on the same bed out of work. The non-working needle(s) will create a narrow vertical column of stocking stitch on the opposite bed which will roll itself toward its purl surface. By spacing the groups of non-working needles alternately between the beds, the fabric will immediately fold into pleats when taken off the machine. The same principle could be applied to hand knitting. The symbols: black dots indicate needles out of work, purple arrows the direction of the fold in the resulting fabric, and the needles in work on either bed, or any machine.
Sharp angles occur when there are enough needles in work on both beds to allow the fabric to fold over itself crisply before it is forced by the next group of out-of-work needles to fold once again in the opposite direction
 alternating direction of folds to create sharp or knife pleats
alternating direction of folds to create sharp or knife pleats
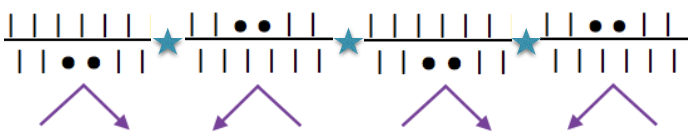
repeat the above configuration across the needle bed, going as narrow or as wide as desired, the series of pleats will face in one direction. Crystal pleats are very fine knife pleats often seen in sewing tuxedo shirts
double sharp or box pleats are a variation where the direction of every other pleat is reversed, extra stitch groups may be added between pleats to vary their spacing. The pleats are folded away from each other on the outside of the garment. Inverted box pleats are the same as a box pleat, but face inside the garment
added stitch group represented by a star, stitch count varied to suit
fold up as
accordion sharp pleats out of work needles evenly staggered on both beds
fold up as
Putting out-of-work needles on one bed close to out-of-work needles on the other will not allow the fabric to fold over completely before reversing direction, and will result in rounded or rolled, rather than sharp pleats. There should be one full needle rib stitch between needles out of work, highlighted below in red. Repeating the same selection results in rolled single pleats
fold up as
double rolled pleats mirror needle groups
fold up as![]()
in accordion rolled OOW needles are spaced evenly on both beds
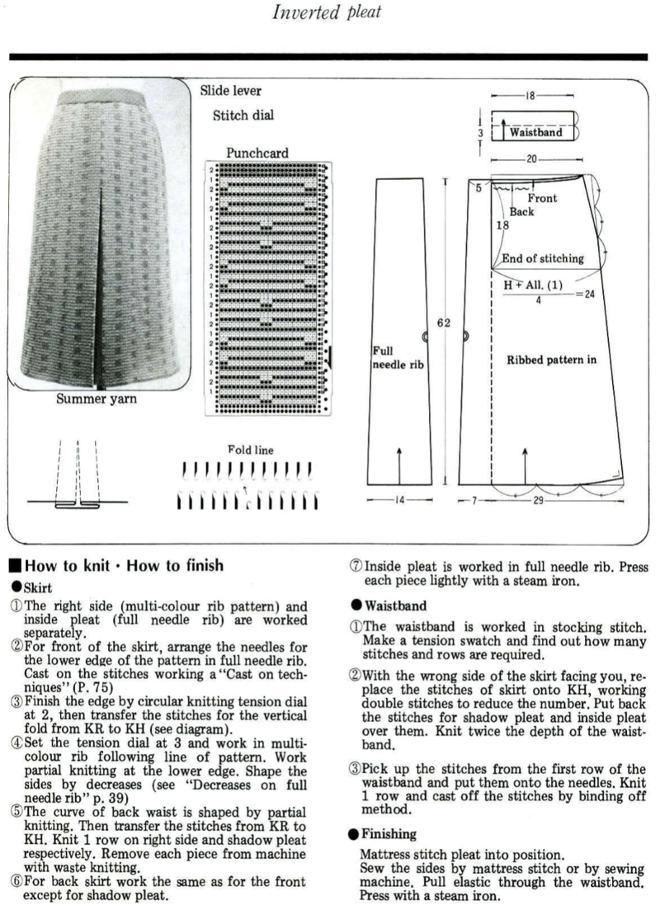
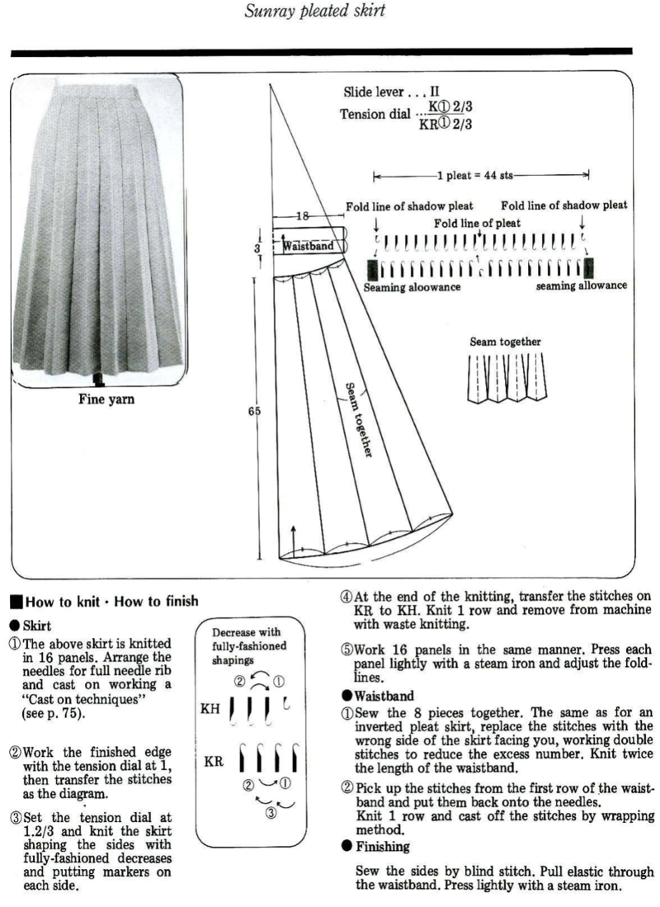
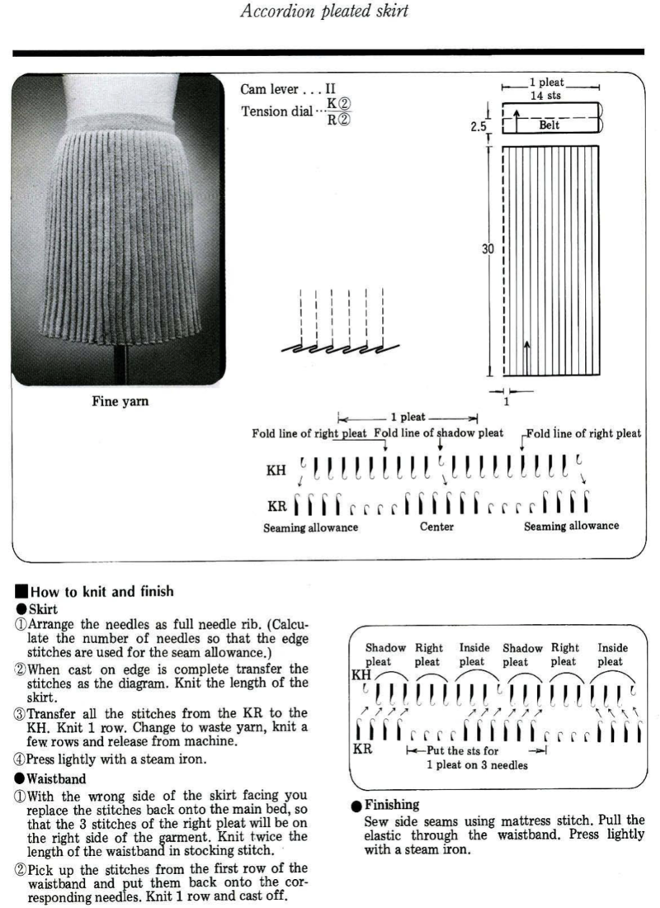
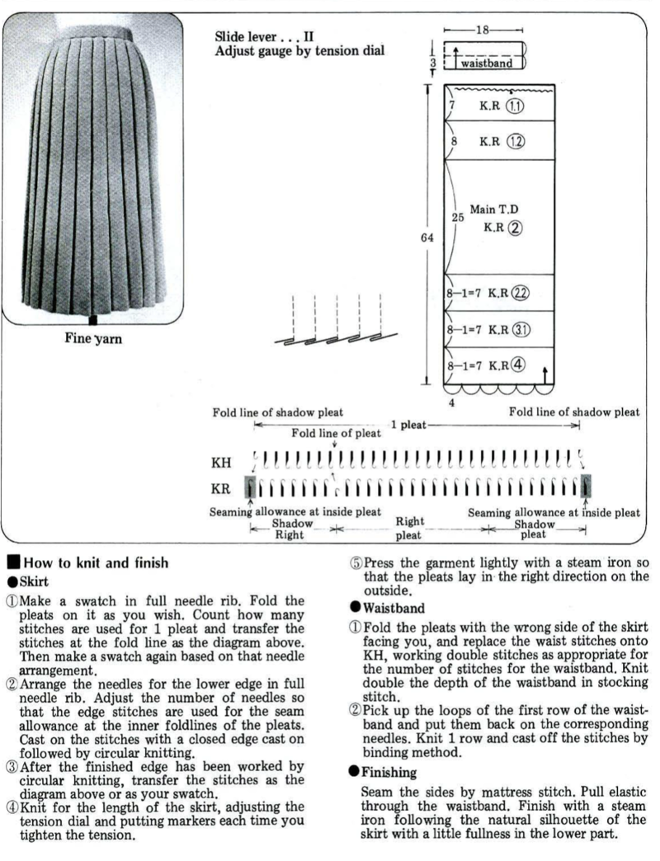
Types of pleats, their width, spacing, and mixing with stretches of every needle rib, may be used in whole garments or garment details ie cuffs, peplums, single-fold large pleats in skirts and jackets, etc.
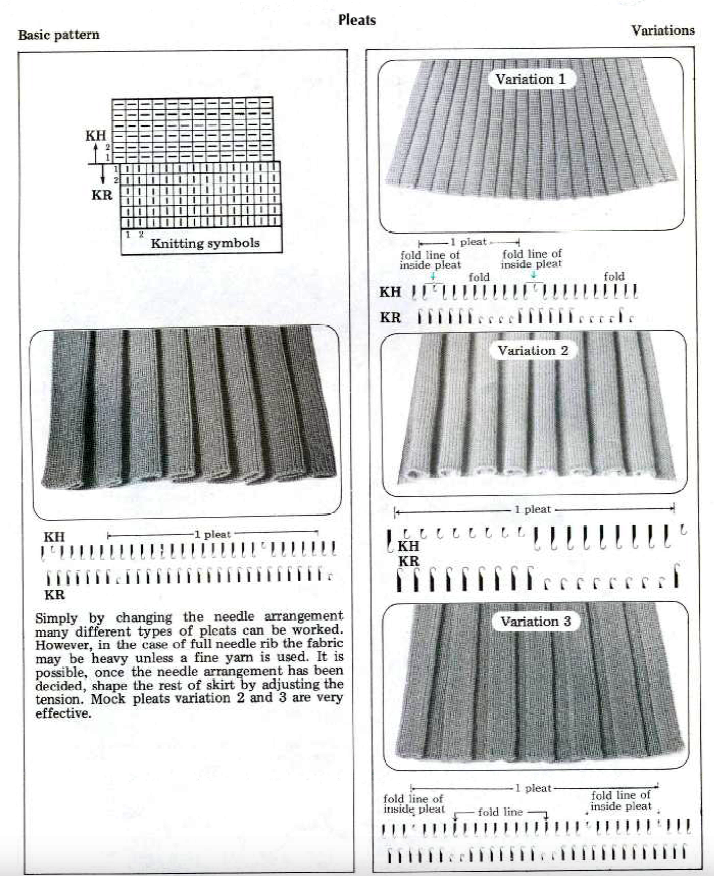
Brother Ribber Techniques Book page 37 illustration
Some considerations:
Normal shaping procedures are not practical in these fabrics. Tension changes are used from loose to tight to achieve shaping from wider at the bottom to narrower at the top, requiring extended swatches. The larger the finished items, such as skirts, produce more predictable results if the test swatch is a large one. A minimum of 100 rows for gauging is recommended. A test segment is made for each tension change. Swatches should be allowed to rest after being treated like the finished garment will be: blocked, pressed, washed, etc., then hung vertically and allowed to rest. After deciding the length, 2-4 inches need to be subtracted from the desired measurement to allow for the “drop” that is likely in the finished piece over time.
The fabric may look a bit different on one side than the other, either works as the exterior of the piece and is a matter of preference.
These are knits where the clicks between numbers on tension dials on machines come into use. In addition to the usual gauge calculations for knitting garments, a bit more math is needed.
The number of needles used needs to be divisible by the number of stitches used for any pleat.
Joining on inner folds rather than outer ones produces better results. Having an extra stitch at joining edges, with seaming using half a stitch on each side, will keep pleat widths constant.
The larger the pleat, the more bulk is created. Most skirts will require 3 panels with one seam worn on the center back. Yokes may be added to decrease bulk rather than having pleats meet at the waistline.
Ribbers on Japanese machines tend to knit tighter than main beds. At times an increase of 2 tension numbers may be required to get stitch sizes created by both beds to approach being equal. The other factor to consider is that the wider the plain knit vertical portion of the pleats, for stitches to knit off properly, the more tension needs to approach the # used to knit the same yarn in stocking stitch on the respective single bed. Tolerance varies between machines.
Experimentation is needed even before knitting the large swatches. It pays to be familiar with both your ribber and your yarn before trying these fabrics and to keep good notes.
Folded / true pleats occur when the groups of NOOW (needles out of work) that make the fold lines are spaced far enough apart so that the underlap of the pleat is quite wide. Rolled/ mock pleats occur when the groups of NOOW that form the fold lines are fairly close together. Stockinette/rib combinations: vertical columns of stocking stitches are created, sometimes combined with ribbed ones. The fabric lies flat and does not fold.
Double jacquard is usually an every-needle rib fabric, so pleats can be created in conjunction with it, even planned to occur within specific areas of the design repeat. Consider yarn weight and backing technique in planning for drape.
A series of needle arrangements to try, including one worked on every other needle, which requires the pitch change from P to H. Charts were created as combined tables using Mac Numbers 5/2018
More from the Brother Ribber Techniques Book pp 108-112
Review of terms often used: full pitch = the needles of one bed are exactly opposite the needles of the other bed. Passap = racking handle up. Half pitch = the needles of one bed are directly opposite the gate pegs of the opposite bed. Passap = racking handle down. FNR: full needle rib = within the working area all needles on both beds are in working position, with the beds set at half-pitch. 1X1 rib set up= within the work area every other needle on both beds is in work in alternating positions, ribber set to full pitch. Tubular cast-on is often used for fabrics of this type, in both FNR and 1X1 rib setups.
“True” pleats have three components: the face, the fold-over or turn back, and the underside; they are formed by folding a piece of knitted fabric over. “Mock pleats” are produced by varying stitch patterns. Sometimes the terms S and Z are used in reference to how the pleat folds, with S pleats pointing the right and Z pointing to the left. The fold-over bulk is something that needs to be planned or even compensated for when creating garments ie such as skirts, where yokes are often added to minimize bulk at the waist and hips.
Studio tips and techniques #36, by Terry Burns, is now available for free download online and begins to cover Double bed pleated skirts tt-36-double_bed_skirts