A “how might this be done challenge” of late re this fabric brought to mind racked patterns for chevrons, both vertical and horizontal, and the possibility of producing them on home knitting machines.  To review some of the principles in racking in both Brother and Passap knitting machines: the pitch is the distance between each needle groove along the needle bed is sometimes also referred to as gauge. The size varies between machine brands and types of machines. For example, the Brother bulky has a 9 mm pitch, the Passap a 5 mm one; the larger the pitch number, the thicker the yarn that may be used.
To review some of the principles in racking in both Brother and Passap knitting machines: the pitch is the distance between each needle groove along the needle bed is sometimes also referred to as gauge. The size varies between machine brands and types of machines. For example, the Brother bulky has a 9 mm pitch, the Passap a 5 mm one; the larger the pitch number, the thicker the yarn that may be used.
Full pitch lines up needles and gate pegs (or channels) on both beds directly opposite each other. To knit patterns in full pitch, the rule is that for every needle in the working position on the main bed, the corresponding needle on the opposite bed must be out of work, and vice versa. This setting is never used when groups of all needles are in work on both beds. Stitch patterns using this setting are designed to have opposite needles in work on either bed at any one time, but not both at once. The number of maximum needles in use for ribs on both beds will usually total 200 (4.5 mm machines), and the setting accommodates yarns thicker than when every needle is in use.
In half-pitch both bed needles are now offset by half a position, centering them between each other. The full complement of needles for possible use now is potentially 400 (4.5 mm machines); the setting accommodates thinner yarns than one might use on the single bed.
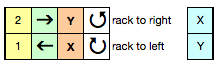
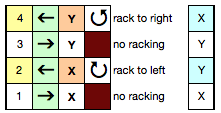
The half pitch lever on Brother may be moved from P to H to change alignments. In Passap the racking handle may be used in an up or down position to do so. The racking or swing lever allows the ribber bed to be swung one full pitch to the right or to the left in a series of stepped moves. The racking handle on Brother machines is located on the left-hand side of the ribber bed. Racking swing indicator positions are numbered 0-10. When the racking indicator has been moved over to the next number, this means the ribber has moved by one full pitch. With the swing indicator at 5, both beds will be centered opposite each other, the usual position. Starting points may vary when racking is used in patterns. Beds cannot be racked with needles in holding, as needles will then crash into each other. It is always a good idea to check ribber alignment before tackling more complex, double bed fabrics. In Passap the racking indicator is situated above the racking handle, and arrows indicate the direction of the last movement. The scale at the top of the front bed shows the possible racking movements from a center point of 0 to 3 to either to right or left of center. I chose to place numbers below the factory ones on the machine from 0 to 7, finding that method easier to follow, since I do not rely on built-in patterns and racking prompts from the console. For the purposes of these swatches, I am reverting to the factory indicators.
In the Passap system, the racking handle has 2 main positions: up, and down. When the racking handle is up needles are directly opposite each other (P pitch in Brother), when it is down the needles are between each other on opposing beds (H on Brother). There are some racking handle positions at different parts of the “clock” that are recommended when using some of the Passap accessories.
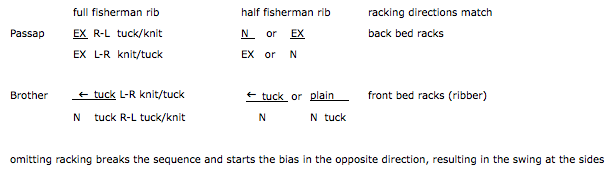
Regardless of machine brand needles have 3 basic functions: knit, slip (do not knit), tuck (gather loops). Passap pushers have 3 positions: work, rest, and out of work. When a pusher is in the up position the corresponding needle will knit no matter what the setting on the pattern dial. This is the equivalent of having needle pre-selection on Brother, but forgetting to change cam buttons from the normal knit setting. When a pusher is at rest it will slip or tuck depending on lock setting to AX, DX, or FX (in Brother these would be needles not selected, in B position). If locks are set to C, E, or G, the pushers have no effect on the needles. Pusher positions may be changed manually, automatically by arrow keys (back lock Passap, lili buttons, and lever Brother ribber), automatically by readers whether electronic or punchcard on both brands in the Brother main bed or front bed Passap are in use. NO pushers are used in N (double or single bed plain knit), CX (tubular), EX (double bed, tuck).
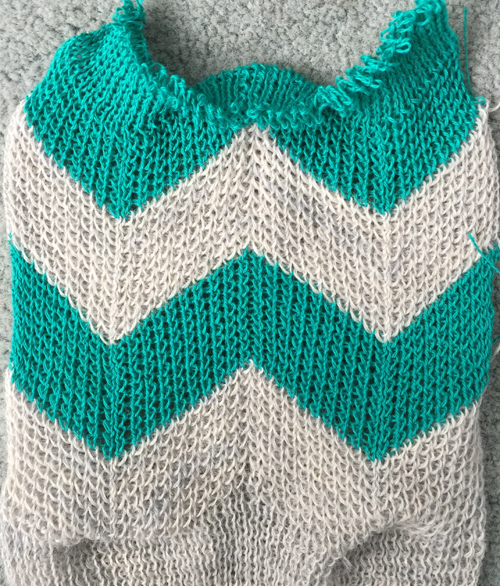
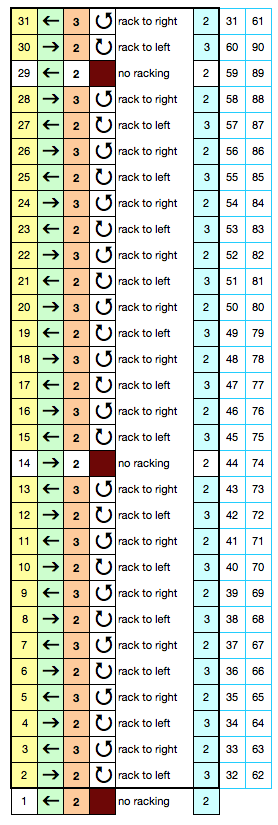
I personally find racking easier in terms of the numbering in Brother brand machines. For these samples, however, I chose to work on my E 6000. Adding tuck to the mix creates more textured surfaces, and a half or full fisherman’s rib where every needle tucks, then knits as the carriage reverses direction on either single or both beds, is a place to start. I have written previously on tracking brother racking sequences using a punchcard numbering system. If no other pattern is used on the main or front beds, needle and pusher selection might be used to track the racking position there as well. These fabrics require concentration. In terms of chevrons, both horizontal and vertical may be produced. Some published sources include a youtube video by Diana Sullivan, knit on a Japanese machine, and a baby blanket in full fisherman rib knit on the Duo 80. The version below is my half fisherman adaptation of the latter. The photos illustrate both sides of the fabric. The racking is done by moving a single of each of only 2 positions to the right or to the left. Single (or multiple, odd-numbered) rows at the end of each sequence place the carriage at its start on the opposite side, rather than altering the numbered sequences as in the Diana video. I began my fabric on Passap racking position 2, to the right of 0, locks set at KX, N, first and last needle in work on the front bed. The back bed tucks every needle right to left, knits them left to right. There is a slight difference in texture between the 2 sides of the fabric.


activate row counter after CX rows in the cast on, with locks on left, so knitting the racked pattern begins with locks on Right, RC on 1. Below is my working “cheat sheet”
For scales and chevrons on Brother machines please see 2018/07/19/more-scales-and-chevrons-in-ribbed-racked-4-fabrics/
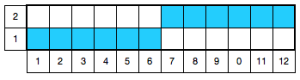
 this fabric is produced in conjunction with a pattern repeat using the principle that black squares knit (pushers up, needles preselected), white squares tuck (pushers down, needles not selected), the repeat is 12 stitches wide, 2 rows high; it is possible to have 6 stitches tucking side by side because this is an every needle rib, and there will be a knit stitch on the opposite bed anchoring down each tuck loop
this fabric is produced in conjunction with a pattern repeat using the principle that black squares knit (pushers up, needles preselected), white squares tuck (pushers down, needles not selected), the repeat is 12 stitches wide, 2 rows high; it is possible to have 6 stitches tucking side by side because this is an every needle rib, and there will be a knit stitch on the opposite bed anchoring down each tuck loop one color half fisherman side 2
one color half fisherman side 2 2 color setting, color changes every 2 rows, side 1, thinner yarn
2 color setting, color changes every 2 rows, side 1, thinner yarn side 2
side 2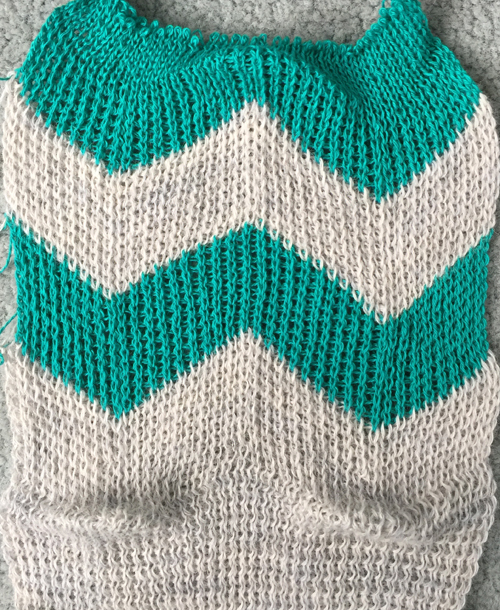
 side two
side two  back to vertical: full fisherman with color changes every 2 rows, side one
back to vertical: full fisherman with color changes every 2 rows, side one  side 2, with a few stitches knit off issues
side 2, with a few stitches knit off issues 
 same fabric with color change every 2 rows
same fabric with color change every 2 rows