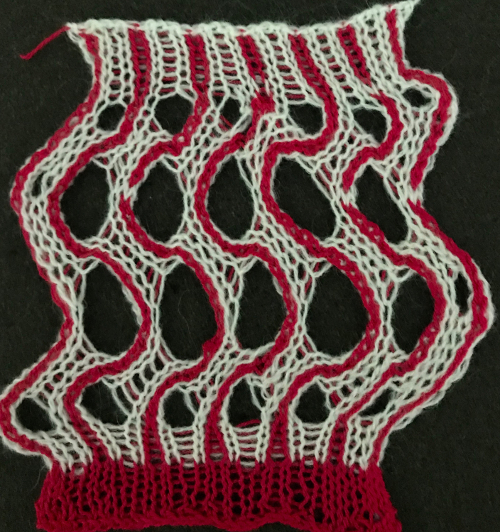
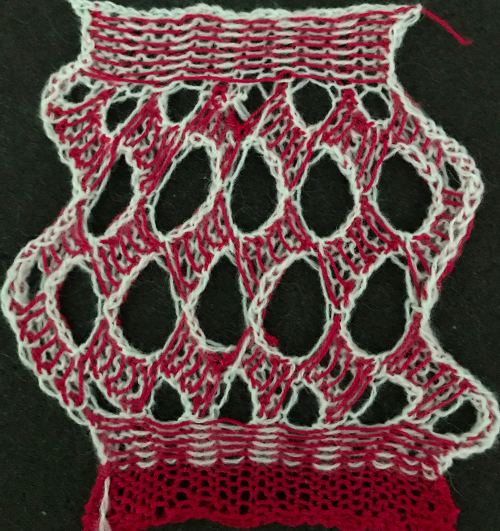
One is limited to imagination, skill, and patience when working short-rowed fabrics. The techniques may be used in borders, on isolated areas, symmetrically or not, and the yarn, in turn, may be able to be pressed, stiffened, felted (which minimizes any slits), or otherwise processed to achieve desired effects. The scale of the shapes affects both the final look and purpose. Development for large sculptural pieces is very different from that used if one is aiming toward a comfortable, perhaps even flattering variable in a garment, but both can blend for interesting one-offs or even collections.
The usual conventions apply: stitches are brought to hold opposite the carriage side, or floats will be created, indicated by yellow curved lines 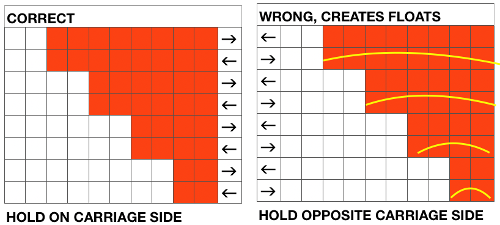 That is a rule that may be broken when planned angles require decreases every row, and a decision is made that such floats and their respective width are acceptable.
That is a rule that may be broken when planned angles require decreases every row, and a decision is made that such floats and their respective width are acceptable.
There are many more variations of the patterns I have previously referred to as “wisteria”. This is one, using different (2) width repeats in a systemic manner across a piece. I find myself going to a spreadsheet prior to any actual knitting nowadays. Low tech can achieve the same, and be as basic as colored pencils on graph paper. Representing actual rows knit would make for a very long chart. This is a compressed version with red representing rows knit on that portion of the needles in work, the other colors for each of the 7 and 9 stitch repeats respectively 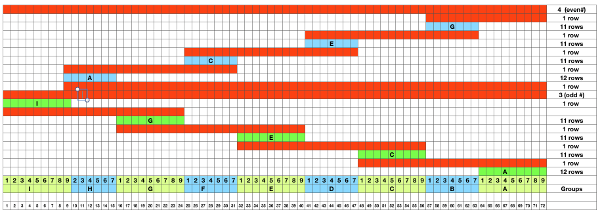 some sense of how repeats would line up, again not to proper scale
some sense of how repeats would line up, again not to proper scale  To knit: cast on and knit at least 4 rows on the desired width for the planned piece. I prefer to end COR, but directions could easily be reversed for a start from the opposite side.
To knit: cast on and knit at least 4 rows on the desired width for the planned piece. I prefer to end COR, but directions could easily be reversed for a start from the opposite side.
The row counter may be set to 0 and used for each segment, or the tripper for it can be turned off as preferred. With labor-intensive fabrics, I sometimes calculate based on a minimum number of repeats rather than row counts. The gauge can be even more difficult to calculate even if rows are tracked somehow. In addition, the choice of yarn, its weight, whether each segment is weighted down or not, and the tension in masts and carriages all can make the result uneven or harder to predict. The use of claw weights is a personal preference. I prefer to avoid them whenever possible. They can help control the length of the slits at their side(s), but sometimes distort the length of the knit stitch on either side of them. COR: set the carriage to hold, bring all the needles to the left of the first group of 9 needles to hold, knit 12 rows (even number), returning to the right.
COR: push back to knit groups B (7stitches ) and C (9 stitches) to the left of A into work
Knit one row to left
COL: bring A (9 stitches) and B (7 stitches) to the right of C out to hold, knit 11 (odd #) of rows on C, ending with COR once more (one row had already been knit on those stitches, so the total remains constant).
Repeat in groups of 3 as described in the last 2 steps across the row ending COL
Knit a few rows, ending COR
Bring the first group of 9 stitches on left out to hold, knit one row to left
Bring all stitches to the right of the first group of 7 stitches out to hold, knit 12 rows, ending COL
Bring the next two groups of 9 and 7 needles out to work, knit one row to the right
Bring the remaining stitches to the left of the new group of 7 out to hold, knit 11 rows (odd #), ending COL. Continue across row. At the end knit a few rows, ending once more on the right.
I found at least 3-4 rows were needed between sections of segments to achieve shapes that did not meet to create extended slits with threads across them and to achieve a look I preferred. In the interim, all knit rows could serve as the opportunity to add other stitch types or techniques including purl ridges on the knit side, which could be achieved easily enough with a G carriage, but may prove perilous with a garter bar.
The needle bed or the needle tape may be marked with a water-soluble pen between needle groups to help make tracking easier.
Proof of concept purl side  knit side
knit side  slightly scrunched up
slightly scrunched up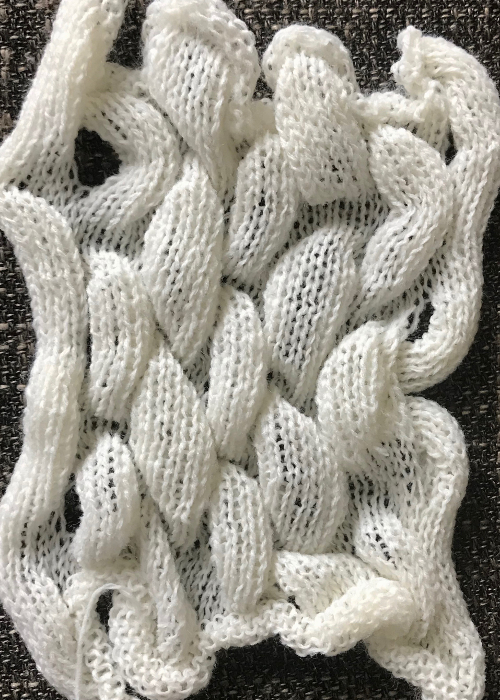  with a touch of steam and light pressing
with a touch of steam and light pressing 
Planning your own pattern in scaled-down numbers of stitches and rows is good practice, and may also lead to pleasant surprises. As with any test, keeping notes while in progress is well worth it. What may be obvious while knitting may escape recall after the fact. Then there are “little things” that factor in as well. For decades I knit on a 910 or a punchcard machine. On the 910 settings stay as preferred unless changed manually. In my electronic default, the repeat direction was set to be as seen on the knit side, on the punchcard, it is fixed as seen on the purl. At one point I received an orphaned, frozen 930 that I was able to get moving following online video advice. I have often forgotten to set the number one variation button or to change the default isolation to an all-over-one in knits where that mattered critically. If programming a repeat, the starting side for a preselection row matters, and it will change based on which side of the finished fabric reflects your planned motif.
The start of an idea with points to be considered, some observations, and questions  Working it out on a spreadsheet: arrows indicate the direction in which the carriage needs to be moving, I prefer to start COR, the image can be flipped horizontally for starting with COL. The repeat is outlined with a thick border, is too wide for automating for punchcard, but as hand technique variations can be endless. To produce longer slits and raised shapes, add an even number of rows to the red colored blocks, for more distance between raised motifs, add an even number of rows to the side to side all green areas, maintaining the directional arrows.
Working it out on a spreadsheet: arrows indicate the direction in which the carriage needs to be moving, I prefer to start COR, the image can be flipped horizontally for starting with COL. The repeat is outlined with a thick border, is too wide for automating for punchcard, but as hand technique variations can be endless. To produce longer slits and raised shapes, add an even number of rows to the red colored blocks, for more distance between raised motifs, add an even number of rows to the side to side all green areas, maintaining the directional arrows. 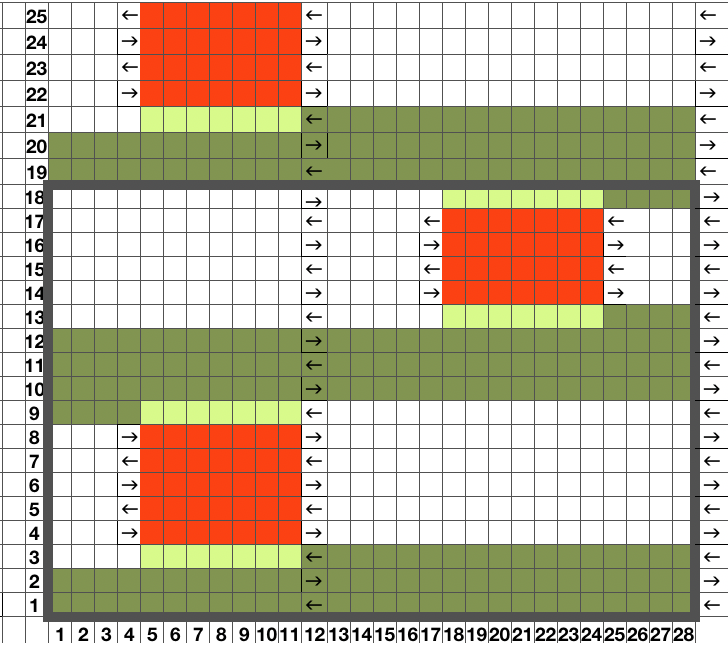 This is the isolated repeat for converting the pattern to a file suitable for download
This is the isolated repeat for converting the pattern to a file suitable for download 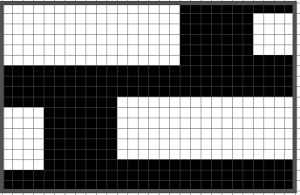 and its mirrored version for knitting from the opposite side
and its mirrored version for knitting from the opposite side  My test swatch was knit on the 930, using img2track. Because not every needle on the bed is in work throughout the knit, end needle selection must be canceled (KC II). The knit carriage after the preselection row is set to slip in both directions. Because only a few rows are knit on the red blocks in the chart, the result is subtle. The white yarn used in many of my tests happens to be a 2/24 acrylic, so on the too thin side, and likely to be well flattened if pressed.
My test swatch was knit on the 930, using img2track. Because not every needle on the bed is in work throughout the knit, end needle selection must be canceled (KC II). The knit carriage after the preselection row is set to slip in both directions. Because only a few rows are knit on the red blocks in the chart, the result is subtle. The white yarn used in many of my tests happens to be a 2/24 acrylic, so on the too thin side, and likely to be well flattened if pressed.
 Often, the edge stitches on the carriage side will tend to be a bit tighter than those formed away from it. The same repeat may be used to create very different fabrics. Eliminating the all knit columns on either side of the center produces a piece with “ruffles” on either side of the center as the outer edge of each shape is no longer anchored down. The principle was used in knitting “potato chip” scarves popular in both hand and machine knitting for a while. Having a repeat on one side of an all knit vertical strip creates a ruffled edging.
Often, the edge stitches on the carriage side will tend to be a bit tighter than those formed away from it. The same repeat may be used to create very different fabrics. Eliminating the all knit columns on either side of the center produces a piece with “ruffles” on either side of the center as the outer edge of each shape is no longer anchored down. The principle was used in knitting “potato chip” scarves popular in both hand and machine knitting for a while. Having a repeat on one side of an all knit vertical strip creates a ruffled edging. 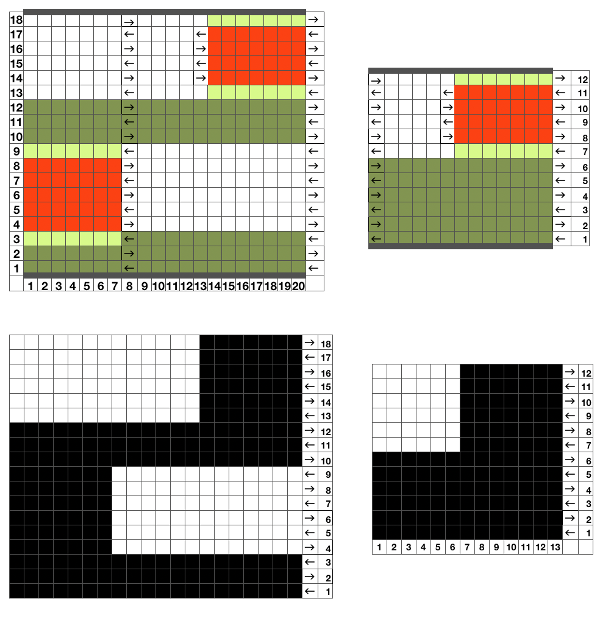
 Note the effect of the added all knit rows on the “wave” of the piece on the right.
Note the effect of the added all knit rows on the “wave” of the piece on the right.
Many patterns are published for hand knit variants as well, Lion Brand Yarns offers the opportunity for learning both knit and crochet stitches. Some patterns are free with login (website info access is also free). Here are 2 such designs with slits and bumps to the max The shapes for the “bumps” may be changed, moving away from rectangular formats. Small repeats are used for the purposes of illustration here, but they, in turn, may be scaled up, rendered asymmetrical, vary in placement, and more. My design steps began with this idea
The shapes for the “bumps” may be changed, moving away from rectangular formats. Small repeats are used for the purposes of illustration here, but they, in turn, may be scaled up, rendered asymmetrical, vary in placement, and more. My design steps began with this idea
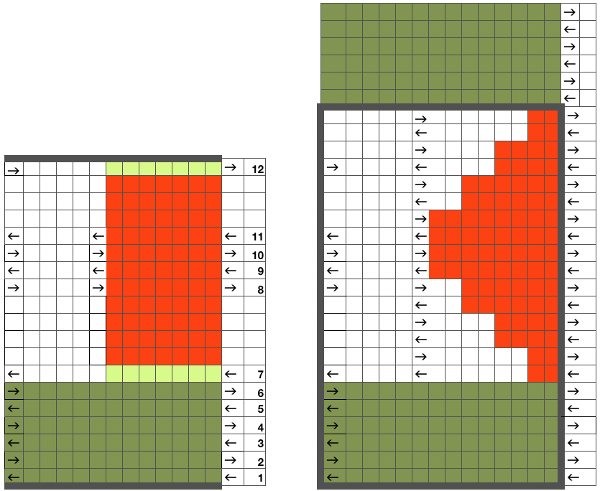 Following the goal to achieve bilateral placement along a central vertical knit strip, with vertical knit strip borders at either side, here shapes point in the same direction
Following the goal to achieve bilateral placement along a central vertical knit strip, with vertical knit strip borders at either side, here shapes point in the same direction
 Aiming for shapes pointing in opposite directions, following those arrows for “pretend knitting”, a repeat is highlighted with a dark border on the left, while to its right placement for extra rows of knitting is suggested (must be even numbers). The repeat is then isolated and “grabbed” for use in GIMP
Aiming for shapes pointing in opposite directions, following those arrows for “pretend knitting”, a repeat is highlighted with a dark border on the left, while to its right placement for extra rows of knitting is suggested (must be even numbers). The repeat is then isolated and “grabbed” for use in GIMP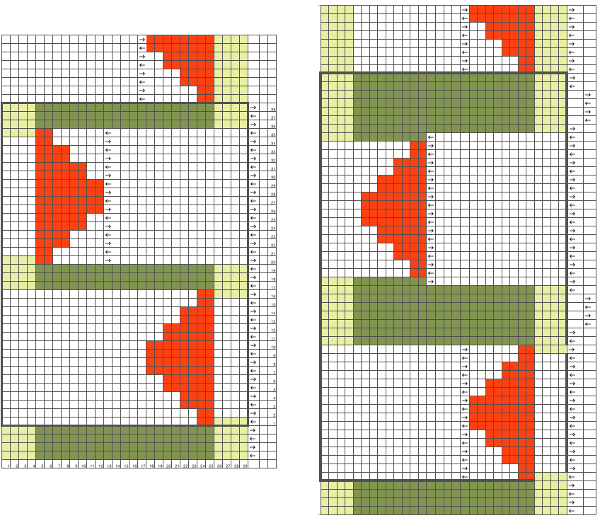
In Gimp the bucket fill was used to fill all colors to black, the image was converted to bitmap BW, scaled, and then knit. This feature changed in Gimp 2.10, requiring the use of the fuzzy select tool to achieve that goal. This is the final repeat used 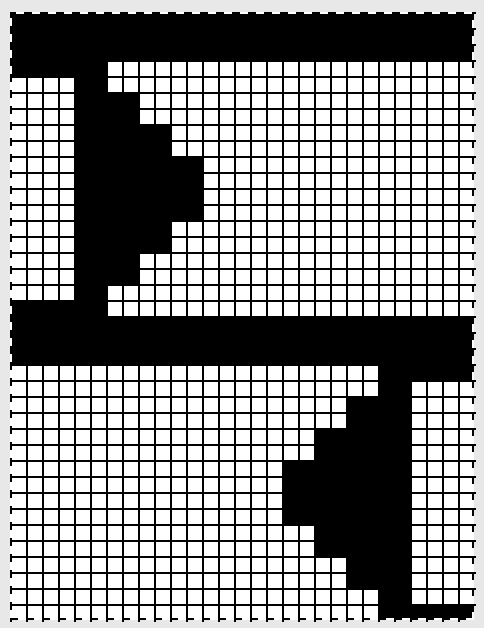 I ran into an interesting problem for the first time. I had entered the row and stitch counts on my chart, used those counts to scale the image used for my repeat down to size for knitting, kept getting floats where there should not have been any, could not understand what the error in the repeat might be. What was happening is that because of the wrong row number used in scaling, there was an extra pixel row in the first test swatches resulting in knitting errors. The final repeat is 29 stitches wide, 38 rows high. This is the resulting swatch
I ran into an interesting problem for the first time. I had entered the row and stitch counts on my chart, used those counts to scale the image used for my repeat down to size for knitting, kept getting floats where there should not have been any, could not understand what the error in the repeat might be. What was happening is that because of the wrong row number used in scaling, there was an extra pixel row in the first test swatches resulting in knitting errors. The final repeat is 29 stitches wide, 38 rows high. This is the resulting swatch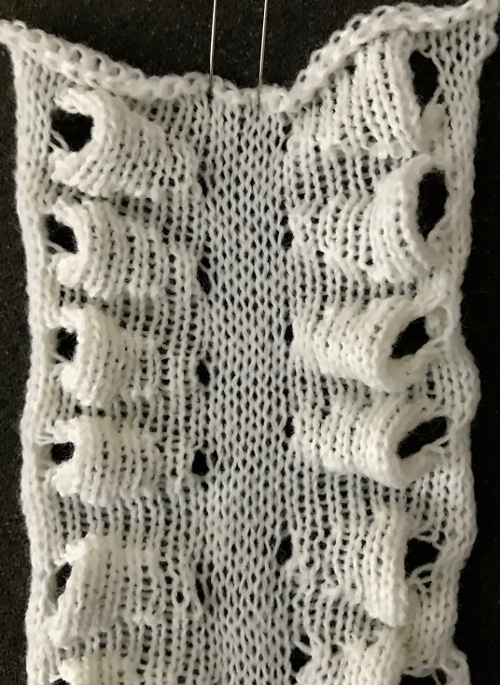
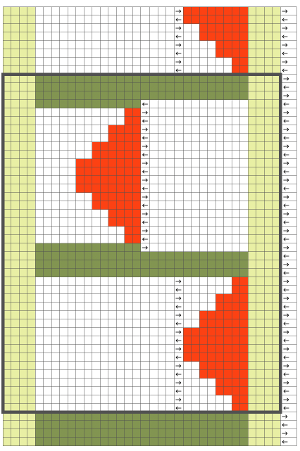
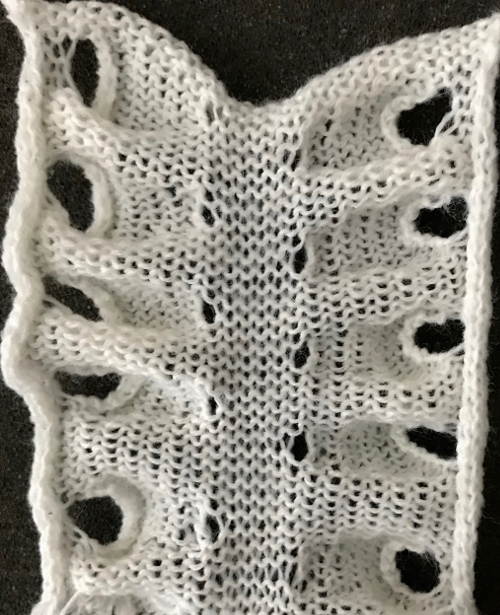 Once more, the repeat could be reduced down to eliminate side knit strips, or limit shapes to one side only for a one-sided ruffle. What about repeating the same slit horizontally across a row? Repeats become very long, arrows are intended again as guides in the knitting direction.
Once more, the repeat could be reduced down to eliminate side knit strips, or limit shapes to one side only for a one-sided ruffle. What about repeating the same slit horizontally across a row? Repeats become very long, arrows are intended again as guides in the knitting direction. 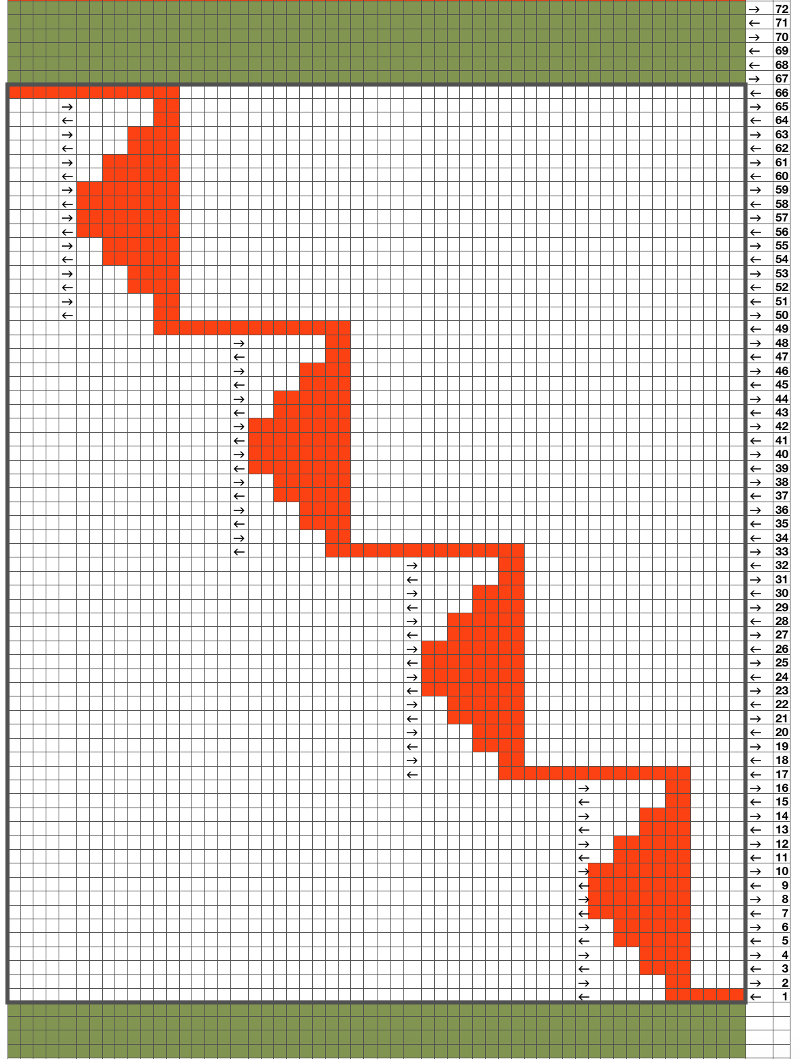 An even number of rows (green) at the end of the outlined repeat will return the carriage to begin knitting it from the right side once more. An odd number of rows added at its top will prepare for knitting the motifs beginning on the left.
An even number of rows (green) at the end of the outlined repeat will return the carriage to begin knitting it from the right side once more. An odd number of rows added at its top will prepare for knitting the motifs beginning on the left. 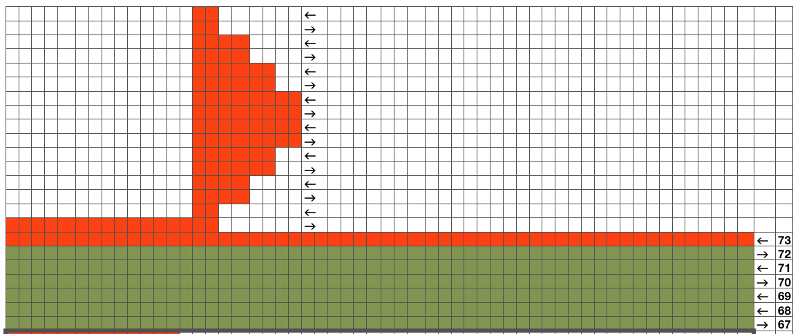 Again, motifs may be brought closer together, laid out directly above each other, in brick fashion, mirrored, or as otherwise desired. Adding rows at the center of the shape will make the “smaller” eyelets at the corner larger as well as the ones created by its outer edge. The possibilities are endless. If an automated slip stitch is used, it is the selected needles that knit. This is my final test repeat, flipped because I insist on forgetting to turn on the #1 variation button on my 930, and I like to begin sequences from the right.BringingB
Again, motifs may be brought closer together, laid out directly above each other, in brick fashion, mirrored, or as otherwise desired. Adding rows at the center of the shape will make the “smaller” eyelets at the corner larger as well as the ones created by its outer edge. The possibilities are endless. If an automated slip stitch is used, it is the selected needles that knit. This is my final test repeat, flipped because I insist on forgetting to turn on the #1 variation button on my 930, and I like to begin sequences from the right.BringingB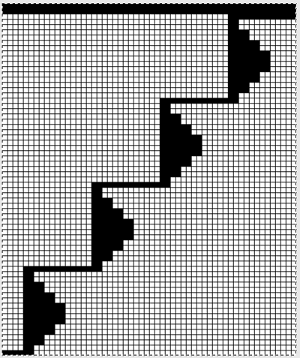 Pushing unwanted needle groups back to the D position will make them knit rather than being held, which is another way to vary the texture distribution across any single row
Pushing unwanted needle groups back to the D position will make them knit rather than being held, which is another way to vary the texture distribution across any single row It is possible to add color changes between or within pattern repeats as well as needles out of work.
It is possible to add color changes between or within pattern repeats as well as needles out of work.
A free pass may be made to the opposite side by bringing all needles out to hold, and once there, returning the next group of stitches to be knit into work. If electronics are in use for automated patterning, the carriage may be removed from the needle bed and brought to the other side before continuing. If a punchcard is in use, an odd number of rows will need to be programmed for one of the colors in order to maintain proper needle selection.
Repeats in the charts below are for illustration purposes, not fully worked out Adding color stripes, with or without ladders  Needles out of work with lateral transfers alternated with needles returned to work will add eyelets to the piece and allow for every needle stripes of colors (or plain knit). If a lot of eyelets created from needle transfers are in play, it may be necessary to change the direction of those transfers.
Needles out of work with lateral transfers alternated with needles returned to work will add eyelets to the piece and allow for every needle stripes of colors (or plain knit). If a lot of eyelets created from needle transfers are in play, it may be necessary to change the direction of those transfers. 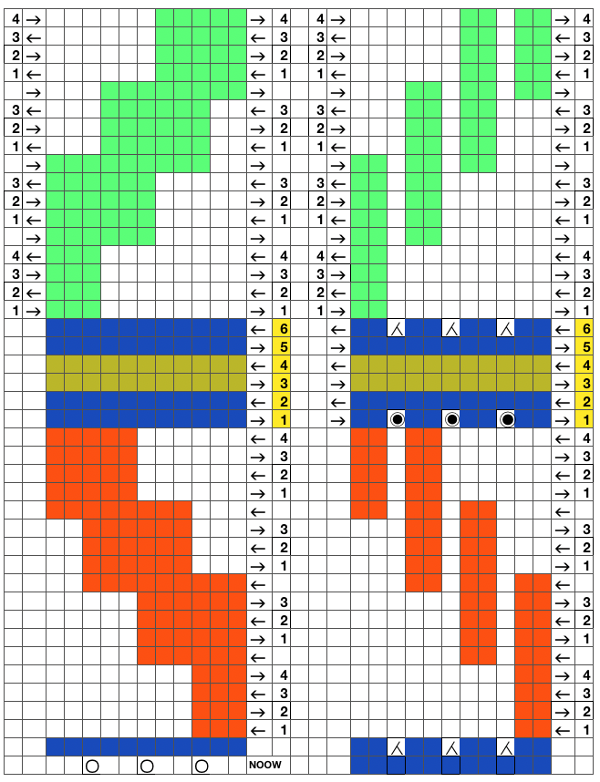 It is also possible to combine patterning and holding.
It is also possible to combine patterning and holding.
As needle groups are brought in to and out of the hold position, the needle selection must be maintained in order to keep correct patterning. There also seems to be a sweet spot in most machines for how far back a needle needs to be pushed for it not to “bounce” to an undesired position, thus picking up and knitting in the wrong color or dropping stitches off. Some variations are also found in how far the active knitting needs to be cleared with each carriage pass on each side. One row in my test swatch has obvious extra stitches in white, my feeder B color. I am not certain as to the cause.
The introduction of patterning adds yet another layer of complexity to track. Once again I am using 2/24 yarns.
