There has been a resurgence of interest in this stitch in the FB machine knitting group and discussion exploring a variety of methods for creating it. The inspiration, taken from a commercial sweater-knit:  For some single-color variations see Bowknot/ Butterfly stitch on the machine and No longer a mystery pattern.
For some single-color variations see Bowknot/ Butterfly stitch on the machine and No longer a mystery pattern.
I program repeats whenever possible, and find it useful in eliminating errors, particularly in longer pieces. My first experiments for this fabric were conducted using the fair isle setting, which is essentially a slip stitch automatically working 2 colors with each pass of the knit carriage single bed.
Slip stitch patterns with hand-transferred stitches, single bed explores some of the methods for bringing slip stitch floats to the knit side of these fabrics, which is part of the hand techniques necessary to achieve the colored versions. As with any knit fabric yarn qualities, color contrasts, and tolerance for proper stitch formation are all variables.
For vertical columns in 2 colors, it is only necessary to program a single, fixed row with a punchcard or electronic, or choose any pixel-based repeat akin to this with full pairs of alternating stripes. I like to plan with selected needles at each end of the sample 
![]() With the machine set to FI, needles not selected will knit a ground color, while selected needles will knit the color in the B feeder. It is easier to manipulate the slip stitch floats from purl to knit side if working in the non-selected groups of needles. Having the columns in odd numbers of stitches makes it easier to handle steps that require finding the center needle in each group if one is wanting to maintain symmetry. In my first test, I manipulated only the selected groups of needles to work the float movements, leaving the floats from the other color undisturbed, which makes the process far more convoluted than it needs to be. In this and the subsequent sample, I manipulated the left and right-hand pairs of floats moving them to the front of the knit, leaving the choice of what to do with the remaining center floats. In A they were brought up on top of the center needle in E position before knitting the next row. In B they are lifted into the hook of the needle and brought out to the B position so that the stitch is knit in color 1, while in C the remaining single stitch floats are simply left alone. In a couple of spots the yarn split, getting hooked up creating bleed-through, and what would result in an issue if that happened on the group of floats that were to be moved.
With the machine set to FI, needles not selected will knit a ground color, while selected needles will knit the color in the B feeder. It is easier to manipulate the slip stitch floats from purl to knit side if working in the non-selected groups of needles. Having the columns in odd numbers of stitches makes it easier to handle steps that require finding the center needle in each group if one is wanting to maintain symmetry. In my first test, I manipulated only the selected groups of needles to work the float movements, leaving the floats from the other color undisturbed, which makes the process far more convoluted than it needs to be. In this and the subsequent sample, I manipulated the left and right-hand pairs of floats moving them to the front of the knit, leaving the choice of what to do with the remaining center floats. In A they were brought up on top of the center needle in E position before knitting the next row. In B they are lifted into the hook of the needle and brought out to the B position so that the stitch is knit in color 1, while in C the remaining single stitch floats are simply left alone. In a couple of spots the yarn split, getting hooked up creating bleed-through, and what would result in an issue if that happened on the group of floats that were to be moved. 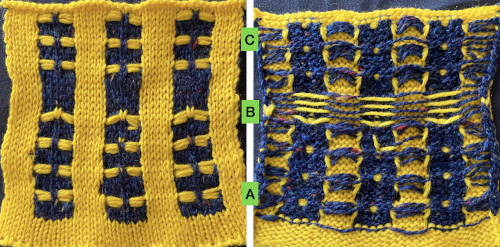 As stated, the process is easier and quicker working on non-selected groups. Above, the yellow yarn was thicker than the blue. To maintain proper color selection in the non-selected column, the center needle needs to remain in the B position, with the slipped stitch forming floats below it before the next row knits. If the needle is brought out to E, it will knit in the contrast color, forming floats in that color on the purl side, and a knit stitch in what was planned as an all-solid column on the knit. The results are seen at the top of the first sequence in the swatch. I chose to limit my number of floats to 4 to keep the process manageable, moved stitches on the left of the center needle to the front of the knit, and then followed with those to its right. One of the many things to explore in hand technique fabrics is finding a way to handle tools that may be more comfortable than others, practicing on single blocks of color first can help establish that. Below both yarns are equal in weight and thinner. The floats formed by the color in the B feeder are also hooked up on the center needle in each vertical group in that color, forming a pattern on the purl side as well.
As stated, the process is easier and quicker working on non-selected groups. Above, the yellow yarn was thicker than the blue. To maintain proper color selection in the non-selected column, the center needle needs to remain in the B position, with the slipped stitch forming floats below it before the next row knits. If the needle is brought out to E, it will knit in the contrast color, forming floats in that color on the purl side, and a knit stitch in what was planned as an all-solid column on the knit. The results are seen at the top of the first sequence in the swatch. I chose to limit my number of floats to 4 to keep the process manageable, moved stitches on the left of the center needle to the front of the knit, and then followed with those to its right. One of the many things to explore in hand technique fabrics is finding a way to handle tools that may be more comfortable than others, practicing on single blocks of color first can help establish that. Below both yarns are equal in weight and thinner. The floats formed by the color in the B feeder are also hooked up on the center needle in each vertical group in that color, forming a pattern on the purl side as well. 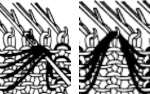 The needle position for selection for B feeder yarn also needs to be maintained. Bringing the needle out to E ensures it will knit on the next pass. In both of my tests, the slip stitch floats on the knit side lie more horizontally than the lifted-up floats on the purl.
The needle position for selection for B feeder yarn also needs to be maintained. Bringing the needle out to E ensures it will knit on the next pass. In both of my tests, the slip stitch floats on the knit side lie more horizontally than the lifted-up floats on the purl. 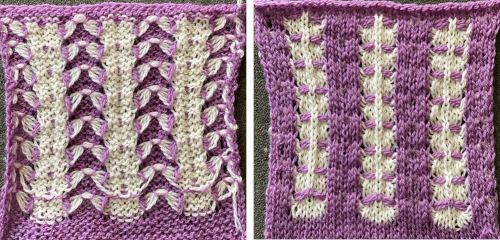 Other ways of working the fabric, along with a history of the FB thread offered by Claudia Scarpa including a single bed slip stitch version with an English downloadable PDF http://ratatatata.it/dragonfly/.
Other ways of working the fabric, along with a history of the FB thread offered by Claudia Scarpa including a single bed slip stitch version with an English downloadable PDF http://ratatatata.it/dragonfly/.
Her youtube video illustrates a different way of managing floats than mine.
JuliKnit offers 2 videos knit on Silver Reed 1, and 2. Both are knit using the ribber, the first method uses holding to gather loops on each of the beds, and the second begins to address automation for needle selection on the top bed using DAK, with the selection on the ribber remaining manual. The stitch illustrations generated in DK offer knit stitch simulations such as these 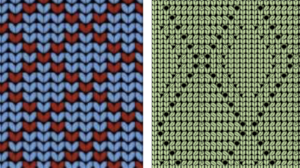 Executing her versions on a Brother machine requires some interpretation. The fabric is constructed using the ribber in conjunction with the main bed. The vertical columns are 5 stitches wide.
Executing her versions on a Brother machine requires some interpretation. The fabric is constructed using the ribber in conjunction with the main bed. The vertical columns are 5 stitches wide.
Colors are worked one at a time. If a color changer is to be used, an even number of rows would be required for each pattern segment. For 4 floats followed by an all-knit row, the repeat would be 5 rows high, so one consideration would be operating with the second color from the right, requiring free passes. Studio machines release the top of the knit carriage at an angle from the bottom, so that explains the move seen in the video for the carriage to be moved to the right. Brother machines use the slip stitch setting in either or both directions, to achieve that. Using both buttons avoids any confusion. All needles in use must be in the B position for the “free pass” to avoid dropped stitches. The number of rows gets adjusted in the videos eventually to 6.
When working on the top bed, the ribber is set to slip both ways.
For those unfamiliar with Studio settings a brief review: the Studio SRP60N ribber introduced the option for knitting emulating the lili selection in Brother. 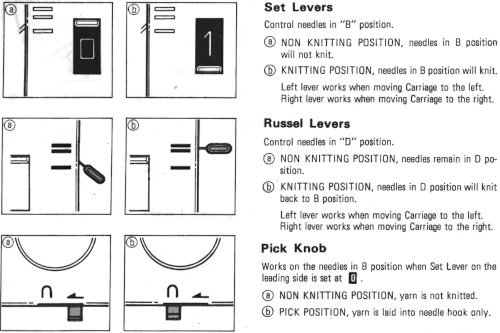 The grey plastic piece on the left of the studio ribber, the autoset lever, when cleared would essentially duplicate setting Brother levers to slip manually in both directions, clearing it again would return it to knit.
The grey plastic piece on the left of the studio ribber, the autoset lever, when cleared would essentially duplicate setting Brother levers to slip manually in both directions, clearing it again would return it to knit. 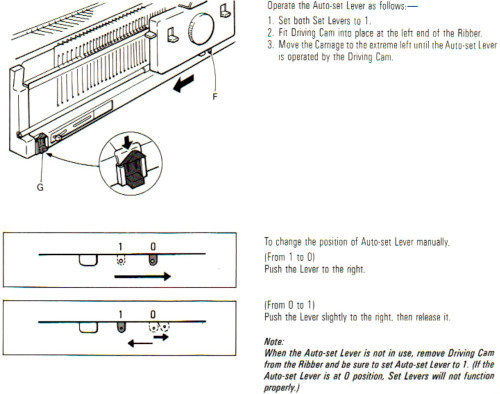 Cast on either EON or EN rib. Transfer needles in a 5X5 rib beginning and ending with a single needle in work on the ribber on the far left and right, setting up the initial needle arrangement for the fabric. Black dots represent needles in work on both beds, and the red ones the initial needles that will be worked in the holding position on the top bed.
Cast on either EON or EN rib. Transfer needles in a 5X5 rib beginning and ending with a single needle in work on the ribber on the far left and right, setting up the initial needle arrangement for the fabric. Black dots represent needles in work on both beds, and the red ones the initial needles that will be worked in the holding position on the top bed. ![]() The video knits each color for an even number of rows. Bring the first and last needle into work on the ribber before knitting each row. The remaining stitches are knit only on the main bed. The knit carriage is set to knit, the ribber to slip in both directions. Pick up the chosen color on the left, and knit for an odd number of rows, when the carriages are on the right, push held needles back to work position so they will knit on the pass back to the color changer. The ribber knits the next color. A review of the Brother ribber carriage for those not familiar with it
The video knits each color for an even number of rows. Bring the first and last needle into work on the ribber before knitting each row. The remaining stitches are knit only on the main bed. The knit carriage is set to knit, the ribber to slip in both directions. Pick up the chosen color on the left, and knit for an odd number of rows, when the carriages are on the right, push held needles back to work position so they will knit on the pass back to the color changer. The ribber knits the next color. A review of the Brother ribber carriage for those not familiar with it 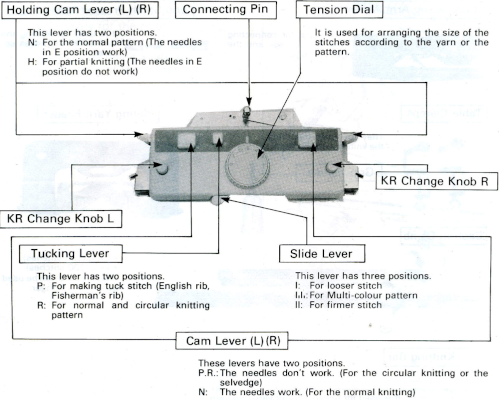 COL: the main bed will now slip in both directions, set it accordingly. The ribber only knits. The center needle on the top bed that held the butterflies is transferred down to the ribber, illustrated in the red dots over black ones. The center needles in the blank areas on the ribber, blue dots, are brought up to hold, the ribber levers are set to knit in both directions, holding levers are set to hold in both directions as well,
COL: the main bed will now slip in both directions, set it accordingly. The ribber only knits. The center needle on the top bed that held the butterflies is transferred down to the ribber, illustrated in the red dots over black ones. The center needles in the blank areas on the ribber, blue dots, are brought up to hold, the ribber levers are set to knit in both directions, holding levers are set to hold in both directions as well, ![]() knit for an odd number of rows, with carriages on the right, push held needles back to work position so they will knit on the pass back to the color changer. COL: the knit carriage changes back to knit settings, and the ribber slip setting in both directions is restored. The center stitches that formed ribber butterflies are transferred up to the top bed, and needles at the center of the blank areas on the top bed are brought out to hold. The color is changed, and the process begins again.
knit for an odd number of rows, with carriages on the right, push held needles back to work position so they will knit on the pass back to the color changer. COL: the knit carriage changes back to knit settings, and the ribber slip setting in both directions is restored. The center stitches that formed ribber butterflies are transferred up to the top bed, and needles at the center of the blank areas on the top bed are brought out to hold. The color is changed, and the process begins again. ![]() My first efforts were met with dropped stitches after a few rows and expletives. My second effort fared no better, I simply could not avoid dropped stitches on either bed, perhaps because of my yarn choice and the small tension it required. Working on the single bed once more, using the slip stitch setting and knitting one color at a time, I achieved a fabric more similar to the original photograph. The chart reflects the number of needles in my test swatch, with a 2 knit stitch border added on each side
My first efforts were met with dropped stitches after a few rows and expletives. My second effort fared no better, I simply could not avoid dropped stitches on either bed, perhaps because of my yarn choice and the small tension it required. Working on the single bed once more, using the slip stitch setting and knitting one color at a time, I achieved a fabric more similar to the original photograph. The chart reflects the number of needles in my test swatch, with a 2 knit stitch border added on each side  Each color knits for 4 rows. At the end of each 4-row sequence, the non-selected needles allow for manipulation of the floats.
Each color knits for 4 rows. At the end of each 4-row sequence, the non-selected needles allow for manipulation of the floats. 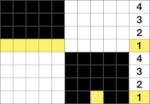 The transfers in the piece begin on row 5. Before the next row is knit in the alternate color, the slip stitch floats are reconfigured, bringing stitches 1 and 2, 4 and 5 in each group to the knit side of the fabric, leaving the center floats undisturbed.
The transfers in the piece begin on row 5. Before the next row is knit in the alternate color, the slip stitch floats are reconfigured, bringing stitches 1 and 2, 4 and 5 in each group to the knit side of the fabric, leaving the center floats undisturbed.  Bring the whole group out to the E position so they will form knit stitches with the first row of contrast as the carriage moves to the right.
Bring the whole group out to the E position so they will form knit stitches with the first row of contrast as the carriage moves to the right.  Knit 4 rows. The carriage will once again be on the left unless 2 carriages are in use from opposite sides. The center needle in each group of 5 will be left unselected.
Knit 4 rows. The carriage will once again be on the left unless 2 carriages are in use from opposite sides. The center needle in each group of 5 will be left unselected.  Lift floats up onto that center needle, and bring it out to E position so that it will form a knit stitch in the next color to be used.
Lift floats up onto that center needle, and bring it out to E position so that it will form a knit stitch in the next color to be used.  The final result is closer to the original
The final result is closer to the original