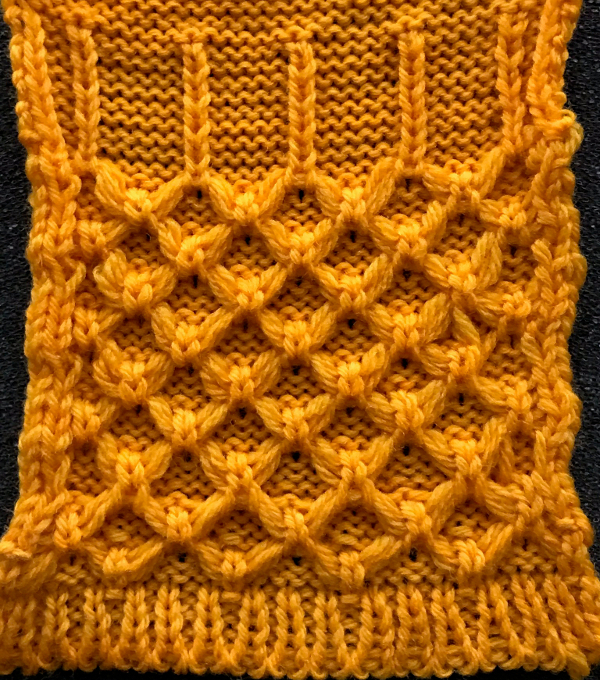
A recent Pinterest post got me searching out some of the fabrics in this group. In hand knitting, floats creating the butterflies/ bowknots are usually apparent on the knit side. For two such patterns please see http://www.knittingstitchpatterns.com/2014/11/butterfly-bowknots.html
http://www.knittingstitchpatterns.com/2015/04/butterfly.html

https://handlife.ru/vazanie/obemnyy-uzor.html caught my attention. Here we have a combination of knit and purl stitches, with floats formed on the purl side, making the fabric or a “cousin” of it possible on the machine  This is my first experiment with gathered slip stitch floats on the purl side of the knit. To begin, this chart indicates one punchcard pattern’s full repeat in width. Four repeats in length would be required (the punchcard minimum repeat in length to achieve smooth continuous card feeding is 36 rows). Punch out blue squares, leaving white ones unpunched. A single repeat (outlined in black, 8 stitches by 12 rows) is for use in electronic patterning, where one may alternately draw or program white squares, then use color reverse. The red line represents 0 needle position in Brother KM
This is my first experiment with gathered slip stitch floats on the purl side of the knit. To begin, this chart indicates one punchcard pattern’s full repeat in width. Four repeats in length would be required (the punchcard minimum repeat in length to achieve smooth continuous card feeding is 36 rows). Punch out blue squares, leaving white ones unpunched. A single repeat (outlined in black, 8 stitches by 12 rows) is for use in electronic patterning, where one may alternately draw or program white squares, then use color reverse. The red line represents 0 needle position in Brother KM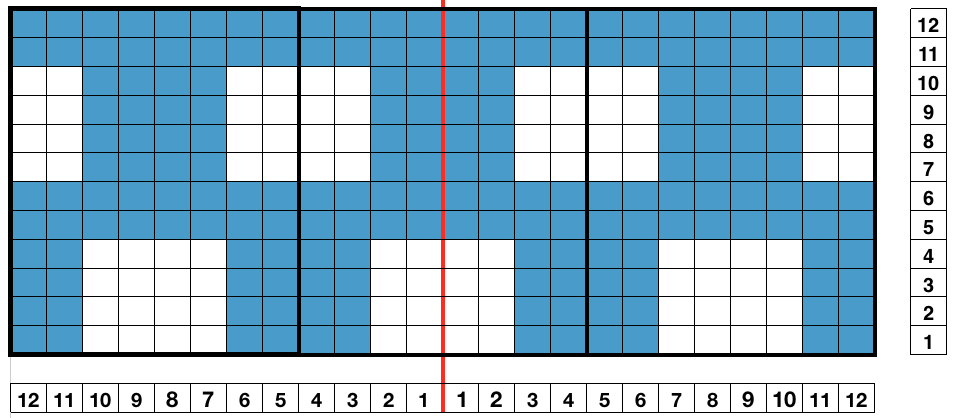
Pitch on H5, ribber needles are centered between main bed ones, so the “knot” width, represented by white squares, can be even in number. Begin with the first needle left of 0 (red line) in the work position, continue across ribber bed with every 4th needle in work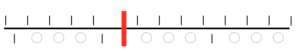
The main bed knits in a slip stitch pattern for 4 rows, then knits 2 rows across all stitches. Floats are created every blank row throughout, composing the knots or butterflies. The ribber is set to knit (N,<–>N, will pick up stitches only on selected needles.
The fabric is a slip stitch one, so it will be short and narrow. That is something to be considered when planning cast on, bind off, and beginning and ending edges of the piece.
In Japanese machines, a ribber comb is recommended. If casting on the single bed, start with waste yarn, poke the comb through that, and proceed as you would for any other rib fabric.
My sample is knit on a 910, with white squares drawn. This is what happens when you forget to color reverse. The all-blue squares now became “white”, so those 2 rows were slipped, not knit, bringing float repeats closer together the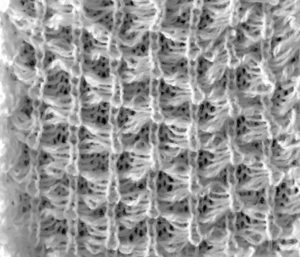 result with color reverse
result with color reverse 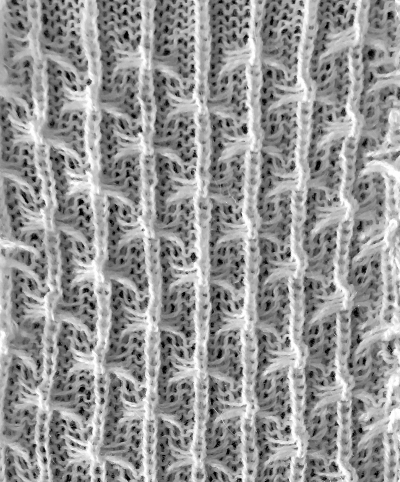 working out a mylar, electronic (unless DM 80 40 stitch width is in use) repeat for a variation of the fabric knit single bed. The stitch count is odd, allowing for a center stitch manipulation. KCI is used to make certain the first and last needles knit on each side. Floats created close to edges may be left without hooking them up. The fabric separates slightly along the “bowknot” edges
working out a mylar, electronic (unless DM 80 40 stitch width is in use) repeat for a variation of the fabric knit single bed. The stitch count is odd, allowing for a center stitch manipulation. KCI is used to make certain the first and last needles knit on each side. Floats created close to edges may be left without hooking them up. The fabric separates slightly along the “bowknot” edges 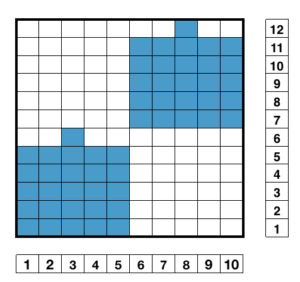 because color-reverse is used, blue squares in chart slip, create floats
because color-reverse is used, blue squares in chart slip, create floats  when Rows 6 and 12 are reached respectively, that single square becomes a non- selected needle, and pick up those floats with any preferred tool
when Rows 6 and 12 are reached respectively, that single square becomes a non- selected needle, and pick up those floats with any preferred tool  lift them up and onto that single non selected needle, push that needle out to hold
lift them up and onto that single non selected needle, push that needle out to hold
 with the next pass the single needle and loops knit off together and become part of the alternating all knit block in the design
with the next pass the single needle and loops knit off together and become part of the alternating all knit block in the design
 the swatches are knit in a 2/15 wool, the fabric might be better served using a thicker yarn. Here the “blocks” creating “floats” are side by side
the swatches are knit in a 2/15 wool, the fabric might be better served using a thicker yarn. Here the “blocks” creating “floats” are side by side

For another single bed cousin in different weight yarn, please see the previous post

Fabrics worked on the single bed with groups of pulled-up stitches on the purl side will have some distortion of the stocking stitch side depending on the weight of yarn used, the number of rows hooked up, and stitch type. Working on the opposite bed to create the floats produces a more balanced fabric.
My charts often evolve. This may be done on graph paper if there is no access to the software. I began adding a space between each block, thinking about those knit stitches I wanted to create on the purl ground, hooking stitches up on red squares 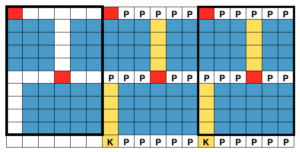 adding border stitches, and more theory on the placement of stitch type
adding border stitches, and more theory on the placement of stitch type
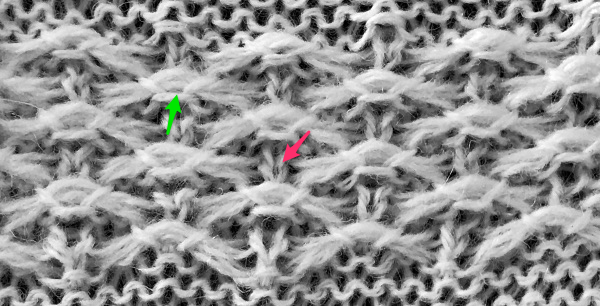
 the result places “knit” stitches in the center of butterfly (magenta arrow), not at its sides, and I see and extra purl stitch (green arrow). Multiple stitch-wide borders create unwanted floats on one side
the result places “knit” stitches in the center of butterfly (magenta arrow), not at its sides, and I see and extra purl stitch (green arrow). Multiple stitch-wide borders create unwanted floats on one side
 back to the drawing board and working things out first as a hand technique
back to the drawing board and working things out first as a hand technique
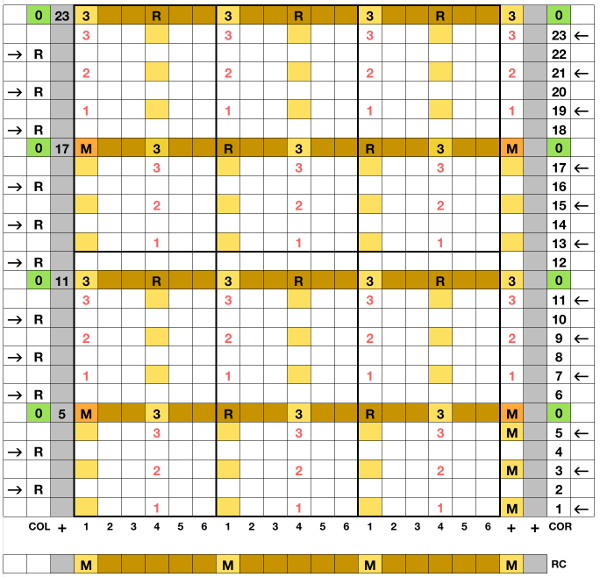 I began with my carriage on the right (COR), after setting up the repeat on a multiple of 6 stitches +3 as indicated above. The last stitch on either side on both beds is never transferred, and the short loops of every other set (rows 5 and 17 in the chart) are not hooked up. This will produce a slightly rolled edge on each side. The larger number of border stitches becomes problematic. The photos were taken while knitting 2 different swatches, so needle tape markings are not the same in all photos. To produce the circular knit, opposite part buttons are pushed in so with carriage on the right (COR), the settings would be
I began with my carriage on the right (COR), after setting up the repeat on a multiple of 6 stitches +3 as indicated above. The last stitch on either side on both beds is never transferred, and the short loops of every other set (rows 5 and 17 in the chart) are not hooked up. This will produce a slightly rolled edge on each side. The larger number of border stitches becomes problematic. The photos were taken while knitting 2 different swatches, so needle tape markings are not the same in all photos. To produce the circular knit, opposite part buttons are pushed in so with carriage on the right (COR), the settings would be
Cast on in any preferred method, ending with all stitches on the ribber  Configure main bed needles as illustrated in a stand-alone setup row at the bottom of the chart
Configure main bed needles as illustrated in a stand-alone setup row at the bottom of the chart  With carriages traveling from right to left, the main bed knits on those single needles, creating floats between them and the ribber slips. When carriages travel from left to right, only the ribber knits, and the main bed slips. Here the carriages have traveled to the left, and back to the right
With carriages traveling from right to left, the main bed knits on those single needles, creating floats between them and the ribber slips. When carriages travel from left to right, only the ribber knits, and the main bed slips. Here the carriages have traveled to the left, and back to the right
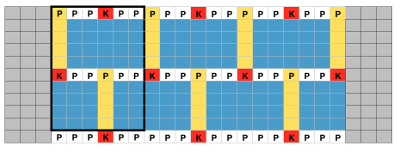
 With row counter (RC) set to 000 at the start of the knit, hand techniques occur on RC 5, 11, 17, 23, 29, and so on. Hooking up loops and transferring stitches between beds always occur with carriages on the left (COL). On those rows, the floats are hooked up on the center needle of the 5 empty groups. In this photo, the ribber is dropped to show what is happening on each bed. The last stitches on each bed are not moved, and those short floats, when created on completion of alternate repeat top halves, are not hooked up
With row counter (RC) set to 000 at the start of the knit, hand techniques occur on RC 5, 11, 17, 23, 29, and so on. Hooking up loops and transferring stitches between beds always occur with carriages on the left (COL). On those rows, the floats are hooked up on the center needle of the 5 empty groups. In this photo, the ribber is dropped to show what is happening on each bed. The last stitches on each bed are not moved, and those short floats, when created on completion of alternate repeat top halves, are not hooked up  after the three floats have been hooked up, with COL each time, the in-between main bed stitches are transferred back down to ribber
after the three floats have been hooked up, with COL each time, the in-between main bed stitches are transferred back down to ribber COL: be sure when hooking up floats that all in the series are picked up. The space between the beds is fairly narrow, and the tool used is purely preference-based. Shifting the main bed needles forward will provide a visual check for loop count as you go. I bring needles with multiple loops out to hold before transferring to the ribber, and then also the transferred stitches on the ribber out to hold to ensure they will all knit on the next pass from left to right. Patterning occurs on every 6th needle on both beds, except border stitch groups
COL: be sure when hooking up floats that all in the series are picked up. The space between the beds is fairly narrow, and the tool used is purely preference-based. Shifting the main bed needles forward will provide a visual check for loop count as you go. I bring needles with multiple loops out to hold before transferring to the ribber, and then also the transferred stitches on the ribber out to hold to ensure they will all knit on the next pass from left to right. Patterning occurs on every 6th needle on both beds, except border stitch groups
 this is the needle arrangement/position in my final swatch, knit in 2/8 wool, COR
this is the needle arrangement/position in my final swatch, knit in 2/8 wool, COR
So what can be automated in the process? The knit bed needs to work the stitches that form floats every other row, while the card or mylar need to advance every row. Trying patterns out as an all-hand technique helps determine tolerance on the part of the machine and the degree of patience available. With thinner yarn, the fabric would be more compressed, and maneuvering stitches more frequently to achieve similar finished size knits, so I switched to a thicker yarn. I found more than 3 rows of floats were too hard for me to manage successfully. “Air knitting” to determine the placement of knitting on any bed before patterning helps determine the number of needles in use, especially if edge needle placement or count matters: here is the first pass using my mylar  eliminating needles to any desired width, leaving only one needle in work on each side of selected needle each bed for this fabric
eliminating needles to any desired width, leaving only one needle in work on each side of selected needle each bed for this fabric  reducing main bed count so only one needle is left on either side of a selected one
reducing main bed count so only one needle is left on either side of a selected one  that needle (green arrow, gets transferred down to ribber
that needle (green arrow, gets transferred down to ribber  now the number of needles involved on both beds is evident on both beds
now the number of needles involved on both beds is evident on both beds
 While knitting in the pattern the ribber pitch is set on P (point to point) to keep stitches on opposing beds centered (P pitch also makes it easier to transfer directly from one bed to the other). If the cast-on is for every other needle rib with stitches then transferred between beds for pattern knitting set up, the cast-on and all rib rows need to be knit in H pitch, with a switch to P for transfers and knitting in pattern to be completed. With the first row set up on the selected segment of the needle bed, there are additional steps to take.
While knitting in the pattern the ribber pitch is set on P (point to point) to keep stitches on opposing beds centered (P pitch also makes it easier to transfer directly from one bed to the other). If the cast-on is for every other needle rib with stitches then transferred between beds for pattern knitting set up, the cast-on and all rib rows need to be knit in H pitch, with a switch to P for transfers and knitting in pattern to be completed. With the first row set up on the selected segment of the needle bed, there are additional steps to take.
This is my working repeat. Since it is 6 stitches wide, it could be worked out on a punchcard, punching out all black squares. On my mylar, I marked yellow squares only, with no color reverse
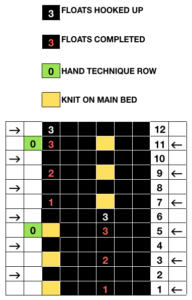 To work consistently with the method described in the larger chart, the first row was manually set up on both beds preparing for the pattern with COL: change knob set to KCII (cancel end needle selection, not every needle in work on the main bed), KC set to slip <–>, so non selected needles slip with each pass of the carriages, advancing the mylar or card one row. The ribber set to N/N or as below will knit from left to right. Pre-selection row is made traveling to the right, ribber only knits
To work consistently with the method described in the larger chart, the first row was manually set up on both beds preparing for the pattern with COL: change knob set to KCII (cancel end needle selection, not every needle in work on the main bed), KC set to slip <–>, so non selected needles slip with each pass of the carriages, advancing the mylar or card one row. The ribber set to N/N or as below will knit from left to right. Pre-selection row is made traveling to the right, ribber only knits
With COR: set RC (row counter) to 000. Make certain proper part (slip) buttons are engaged. MB knits in the pattern based on selected needles, ribber knits when moving from left to right. The fabric is tubular Hand techniques will now also occur when carriages are on the left, on RC 5, 11, etc as described in the hand technique chart, on rows with no needle selection. As in hand tech, transfers and multiple loops containing needles are brought out to hold before moving the carriages from left to right and selecting the needles for the next set of floats with that same pass.
Hand techniques will now also occur when carriages are on the left, on RC 5, 11, etc as described in the hand technique chart, on rows with no needle selection. As in hand tech, transfers and multiple loops containing needles are brought out to hold before moving the carriages from left to right and selecting the needles for the next set of floats with that same pass.
This is my resulting fabric, hand tech shown, the short mylar test above was cropped 