Over the years I have written on an assortment of methods for color separation in knits including DBJ, a summary post with links to previous shares: dbj-and-color-separations-some-previous-posts-links/
and in the-start-of-a-blog-index/
A variety of textures and patterns may be used to achieve fabrics that are very different in appearance, using a very simple pattern along with cam button or lock setting changes. The first chart was generated at that time using Intwined Pattern Studio, a program that for a time appeared to be very promising and then moved on to lack of updates for Mac making it useless in 2013, followed by none for Windows as well, with no successful use of it reported in forums in years, but one may still purchase it 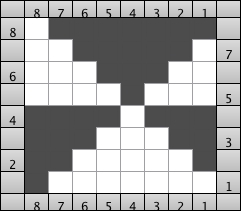 The manual color separation method for punchcard machines.
The manual color separation method for punchcard machines.
The elongated X2 repeat version of the triangle drawn in Gimp 

 As for more than 2 colors per row, performing the color separations may be achieved manually, various software is now available for performing the work in instants.
As for more than 2 colors per row, performing the color separations may be achieved manually, various software is now available for performing the work in instants.
Ayab offers an elegant color separation solution, heart-of-Pluto, that will knit single passes for each color per row on the front of the knit, resulting in 3 color patterns with limited design stretch, and no worries about the placement of one color over any stitches preceding it in the same color on the previous pass.
The difference in the same design being knit with the standard, elongated version, allowing for two passes with the same color before each color change and the Pluto version.  knit using img2track, the vertical stretch is manually set to X2,
knit using img2track, the vertical stretch is manually set to X2, 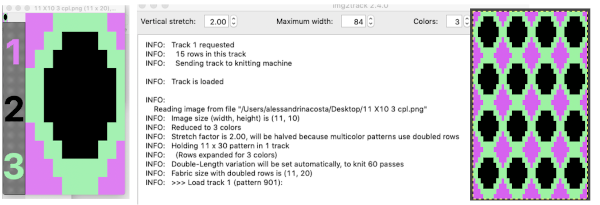 A “hack” 2021/01/24/img2track_multiple-colors-per-row-dbj-each-color-knitting-only-once/
A “hack” 2021/01/24/img2track_multiple-colors-per-row-dbj-each-color-knitting-only-once/
For more information on the various DAK separation charts and related swatches including limitations encountered, see post: DBJ, more than 2 colors per row 4
There is a Russian punchcard site that will allow entering personal repeats or selecting one from their extensive library, where it is possible to obtain related 2-color dbj separations as well. The punchcard color separation may be created manually, a slow process, while the punchcard templates in Dak are achieved with a few, quick clicks of a mouse. The repeat may be created as a graphic file, in my case a png created with Gimp, the elongation in Arah because Gimp fails to scale small repeats cleanly. The image may then be opened as a graphic file,
 stitch and row counts should match, and save the stp
stitch and row counts should match, and save the stp 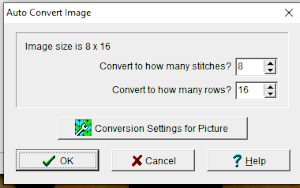
if experimenting with changing selections and this window appears it is OK to click on No  The separation methods in DAK:
The separation methods in DAK:
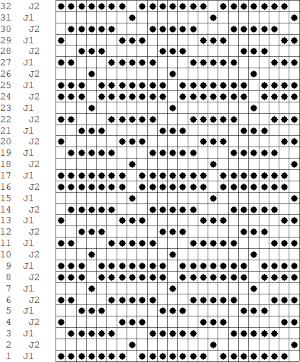
Method C separates each color row into separate rows of knitting, rows do not have to be repeated in pairs, and the double-length switch will need to be used in Japanese knitting machines 
![]() The elongated triangles repeat template is different from what would be produced with the above set at double length, may be used as is to produce a variety of fabrics including quilting
The elongated triangles repeat template is different from what would be produced with the above set at double length, may be used as is to produce a variety of fabrics including quilting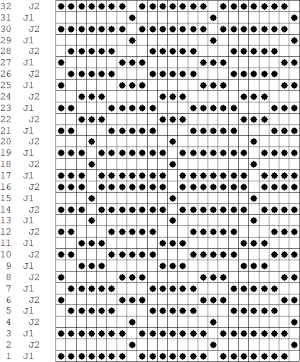 Yarn choice and design make a big difference. Here the yarn is far too thin, and the repeat too narrow in width, but the possible result is illustrated. The main bed is set to slip in both directions throughout. The ribber setting needs to slip in both directions for every other pair of rows. When the ribber slips, the main bed will knit the color that will create the pockets, where there are many single stitches selected here, the KC was set to KC1. When the color is changed and the ribber is set to knit again, stitches in that color will knit on both beds, sealing the fabric in those areas and forming a solid color background on the reverse side. Here the white forms the pockets, and the floats after a pair of passes are seen in this photo.
Yarn choice and design make a big difference. Here the yarn is far too thin, and the repeat too narrow in width, but the possible result is illustrated. The main bed is set to slip in both directions throughout. The ribber setting needs to slip in both directions for every other pair of rows. When the ribber slips, the main bed will knit the color that will create the pockets, where there are many single stitches selected here, the KC was set to KC1. When the color is changed and the ribber is set to knit again, stitches in that color will knit on both beds, sealing the fabric in those areas and forming a solid color background on the reverse side. Here the white forms the pockets, and the floats after a pair of passes are seen in this photo. 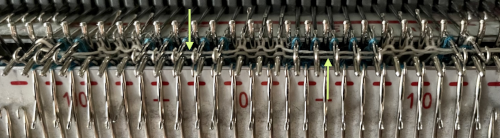 Because the yarn is so thin there is a considerable grin through on both sides, the areas marked with arrows indicate where the white pockets were lightly stuffed with yarn ends
Because the yarn is so thin there is a considerable grin through on both sides, the areas marked with arrows indicate where the white pockets were lightly stuffed with yarn ends 
![]() For a review of quilting on machines including Passap see 2018/02/15/revisiting-machine-knit-quilting/, and using a second knit carriage with a modified sinker plate for knitting stitches on main bed only, making ribber settings fixed throughout, and allowing for tension adjustments for each color yarn.
For a review of quilting on machines including Passap see 2018/02/15/revisiting-machine-knit-quilting/, and using a second knit carriage with a modified sinker plate for knitting stitches on main bed only, making ribber settings fixed throughout, and allowing for tension adjustments for each color yarn.
Methods A and B are both used in Japanese machines when each color is intended to be knit for 2 rows with color changes on the left.
Method A works on pairs of rows. If the pattern does not consist of identical pairs of rows there are likely to be yarn error messages that resolve when the design is lengthened in height X2.
The original triangle elongated to 8X16 
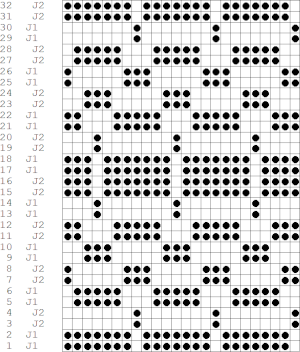 If pngs are created outside the program, they may be doubled in length unless the repeat is designed that way.
If pngs are created outside the program, they may be doubled in length unless the repeat is designed that way.  The associated menu options in Dak when the plan is to work in double jacquard
The associated menu options in Dak when the plan is to work in double jacquard 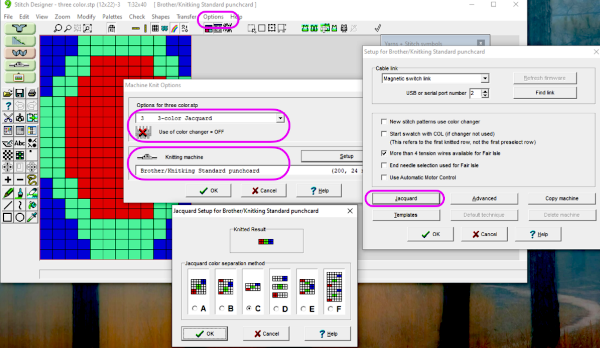 How the different jacquard setups process the specific repeats:
How the different jacquard setups process the specific repeats:
Method B creates the same separation as the default built-in KRC one in Japanese electronics. If knitting DBJ it may be used with DAK if the pattern is downloaded as fair isle but the machine will then need to be set for dbj. If additional colors are used, pairs of rows will follow a single pass for color1. The print preview templates, if generated within the stitch count restriction for use on punchcards, may be used as guides for punching the required holes, this would be the card for that 8X8 triangle repeat, a tad shy of the recommended 36 rows, 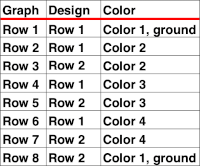
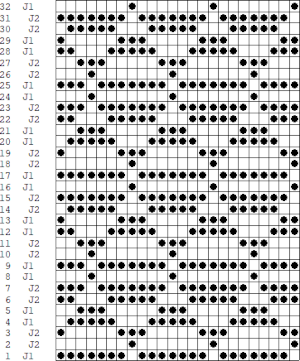 Passap card reader techniques saved from long ago experiments.
Passap card reader techniques saved from long ago experiments.  Other separation methods in the Passap are handled by the console with the entry of specific knitting technique numbers.
Other separation methods in the Passap are handled by the console with the entry of specific knitting technique numbers.
That said, the DAK color separation is applicable for printing reader templates if still using Passap E6 reader cards or punching for the Duo with Deco.
Method C see the top of the post
Method D separates each color into a separate reader card and is used to download to the Silver Reed PEI or the Passap E6, appears to use superimposing of layers, and matches method 4 in my post.
Method E is suitable for machines with a color changer on each side, like the Brother CK 35. It works on pairs of rows and separates each row into a pass with each color. A 3-color jacquard would have six passes with colors separated as follows: 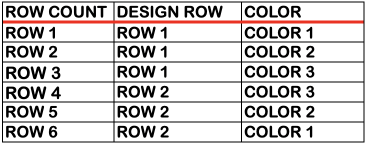 Method F is a Half-Milano separation. Each pattern row is separated into a pair of passes for each color, but the second row for each color has no patterning, so the ribber stitches only knit as the carriage returns to the left side, a possible way of creating repeats for drop stitch lace on Brother machines.
Method F is a Half-Milano separation. Each pattern row is separated into a pair of passes for each color, but the second row for each color has no patterning, so the ribber stitches only knit as the carriage returns to the left side, a possible way of creating repeats for drop stitch lace on Brother machines. 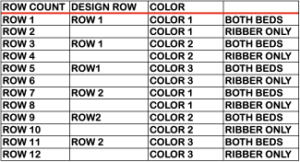 The elongated triangle template was split into 2 pages for viewing, they are combined in this image
The elongated triangle template was split into 2 pages for viewing, they are combined in this image 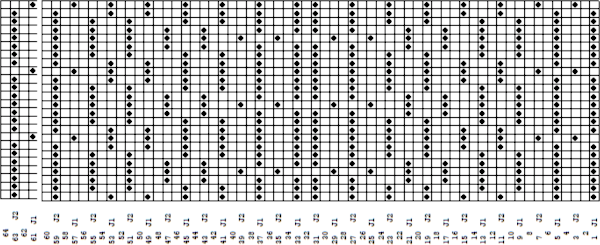 This may be the associated Passap Reader technique, but I have no way to test it
This may be the associated Passap Reader technique, but I have no way to test it 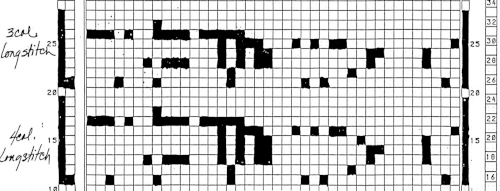 Processing the template using numbers: a table is created twice the length of the 8X16 triangle repeat, followed by hiding the 32 odd-numbered rows, positioned in front of the scaled punchcard template, stitch markings are traced
Processing the template using numbers: a table is created twice the length of the 8X16 triangle repeat, followed by hiding the 32 odd-numbered rows, positioned in front of the scaled punchcard template, stitch markings are traced 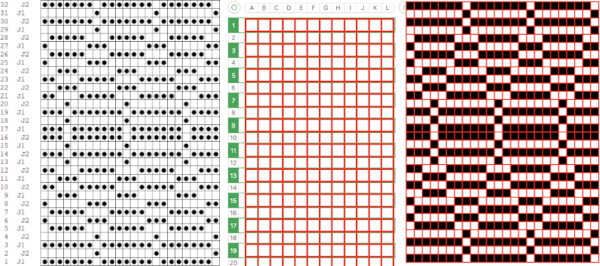 the rows are then unhidden, the repeat is checked, matched here to the F jacquard separation in Dak
the rows are then unhidden, the repeat is checked, matched here to the F jacquard separation in Dak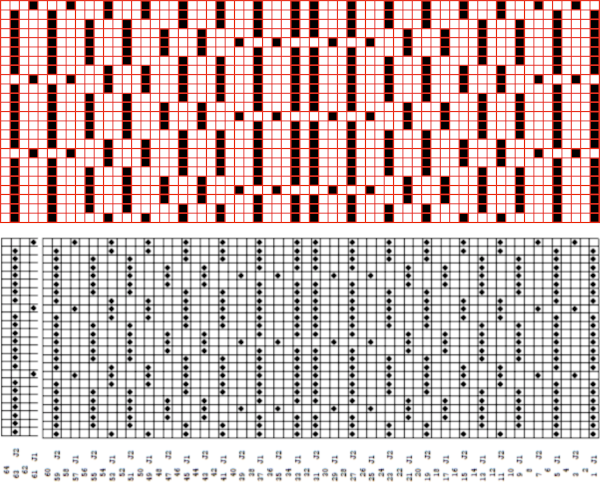 The numbers table is processed in Gimp to obtain the png for knitting the now 24X64 pattern
The numbers table is processed in Gimp to obtain the png for knitting the now 24X64 pattern ![]() Proof of concept swatches: the long stitch in 2 colors,
Proof of concept swatches: the long stitch in 2 colors,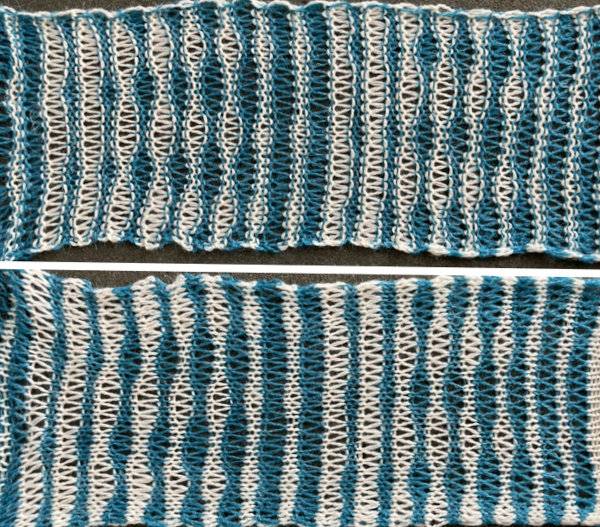  and the pattern executed as a tubular FI knit: I had yarn issues, hence the dropped stitches. Both swatches were knit to approximately the same point in the pattern repeats, there are obvious quality differences in width and length. In tubular knits, there are differences in the width and height of the knit on each side. The front is a slip stitch with floats, drawing the fabric in, while the ribber knits every stitch every other row. With a good choice of yarn and pattern, loosening the tension on the top bed may ease this problem. As often happens, casting on and binding off need special considerations ie to allow for any fabric stretch when off the machine or to leave a tubular knit open at either or both ends if that is the goal. More info on tubular knits including on Passap
and the pattern executed as a tubular FI knit: I had yarn issues, hence the dropped stitches. Both swatches were knit to approximately the same point in the pattern repeats, there are obvious quality differences in width and length. In tubular knits, there are differences in the width and height of the knit on each side. The front is a slip stitch with floats, drawing the fabric in, while the ribber knits every stitch every other row. With a good choice of yarn and pattern, loosening the tension on the top bed may ease this problem. As often happens, casting on and binding off need special considerations ie to allow for any fabric stretch when off the machine or to leave a tubular knit open at either or both ends if that is the goal. More info on tubular knits including on Passap DAK has been a purchase made out of curiosity, and my use of it has been very limited since my designing needs are met by using other programs that are free to users and generate and accept files in multiple formats, while the Brother Knitleader or even simple use of the magic formula solves knitting any desired shape in any gauge.
DAK has been a purchase made out of curiosity, and my use of it has been very limited since my designing needs are met by using other programs that are free to users and generate and accept files in multiple formats, while the Brother Knitleader or even simple use of the magic formula solves knitting any desired shape in any gauge.
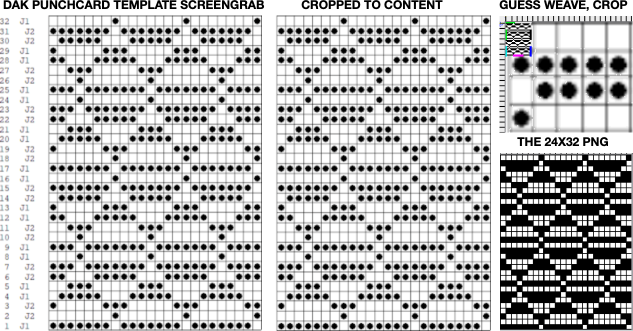
That said, if one can generate the templates produced in DAK, the screengrab of the result may be used to generate a PNG with ArahPaint using the weave-from-grid feature that is then knit-ready on any electronic machine able to accept downloads. The method is far quicker than using Numbers and Gimp. 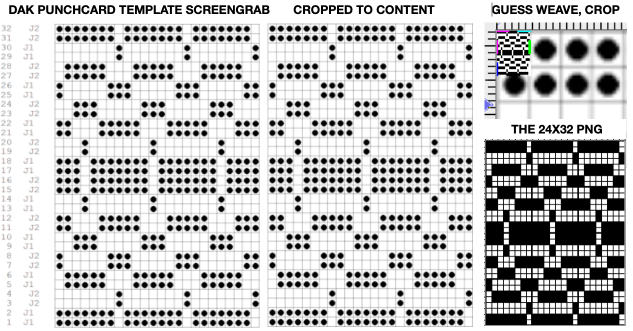
![]()
![]()