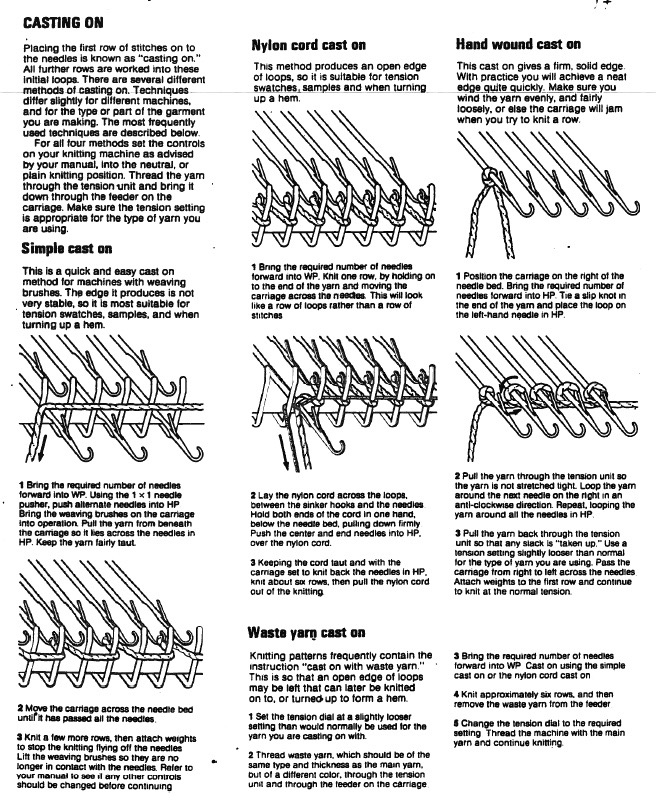
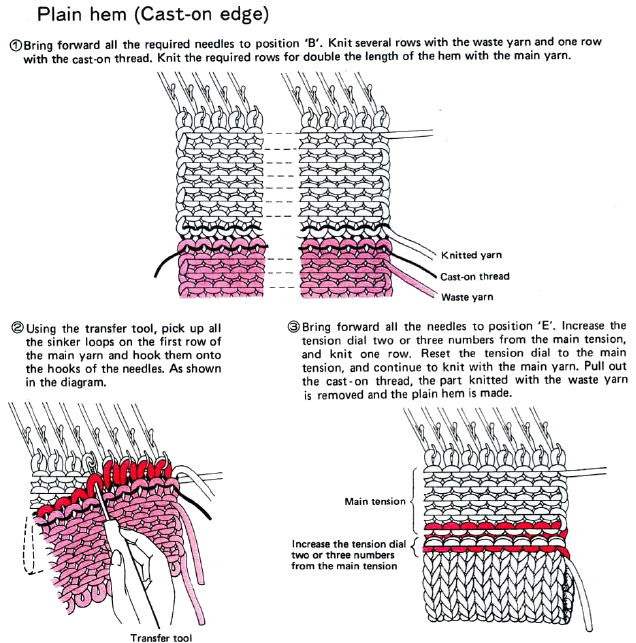
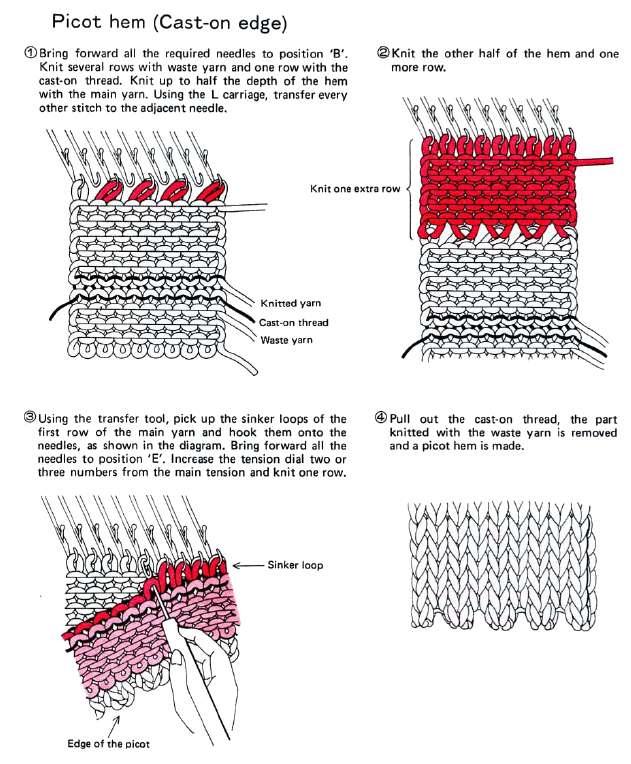
My first encounter using a ribber cast-on comb for open edge single bed knitting was in using the Passap machine. Its use for this purpose is possible on other brands as well. It provides an easy way to deal with waste yarn and weight application on ribbed fabrics. I like using ribber cast-on combs when knitting single-bed to distribute weight evenly across pieces if needed. A second comb may be inserted as the knitting grows. Weights may then be removed and moved up, and so on. Unevenly distributing weight causes elongated stitches in those areas, and makes shaped knitting unpredictable unless the ratio of weight to the width of knitting is maintained. Here the topic is using the ribber comb in single bed open cast-on and hanging hems.
My Japanese machines are used chiefly for the production of single bed items, so usually they are ribber free. Balancing the ribber on older KMs can be fussy, so once the ribber is up, working, and well-balanced, my recommendation is to leave it in place if it is going to be used on a regular basis.
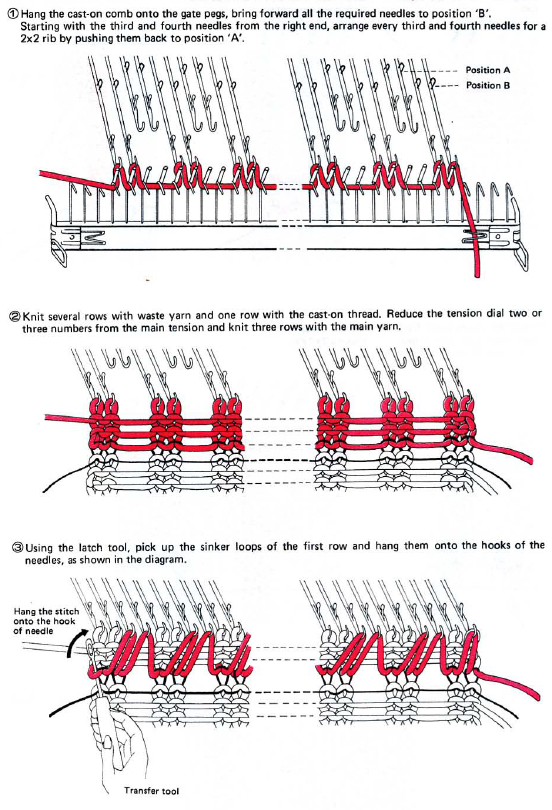
For this technique use a cast-on comb appropriate for your knitting machine’s gauge ie 4.5mm, 5mm, etc., the brand is not relevant, only tooth spacing is. It is possible to cut ribber cast on combs into different widths for use when knitting is planned on fewer stitches than those accommodated by their available commercial widths. In the yarn used in my swatches, I found knitting the first row at stocking stitch tension created large enough stitches for later picking up and hanging the hem. Test your yarn, if necessary use a looser tension for the “cast on” row, and evaluate any inside hem “drop” if a looser stitch size is used.
Remove the wire from the comb. Bring the comb up and between needles to be used, and re-insert the wire. Needles and latches will need to travel easily under the wire when the first knit row takes place. 
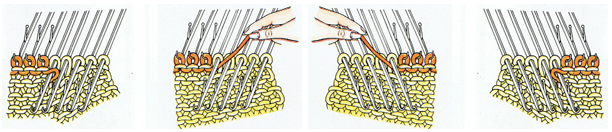
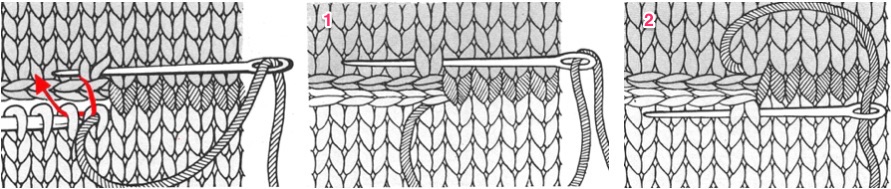
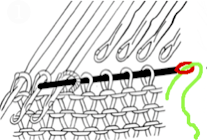
The knit carriage will not clear the comb properly because of the location of its brushes, etc. For the “cast on” row, exchange the sinker plate on your knit carriage for the arm normally used with the ribber. The first photo below shows the approximate location for the comb during the first knit row. Needles are centered between the teeth, and the teeth themselves line up with gate pegs. The comb needs to be manually held in place since there is no opposing bed in use to help balance it. The latter would ease the process in wider pieces of knitting. The ribber sinker plate has no brushes or wheels to anchor knitting on the knitting bed; any rows knit single bed using it, will need to have needles brought out to hold position prior to knitting each row for all stitches to be formed properly
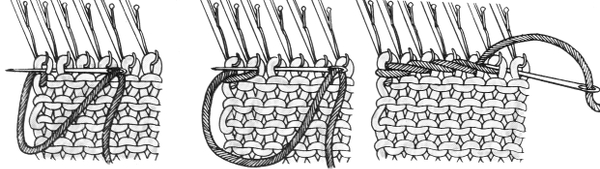
The comb in position:
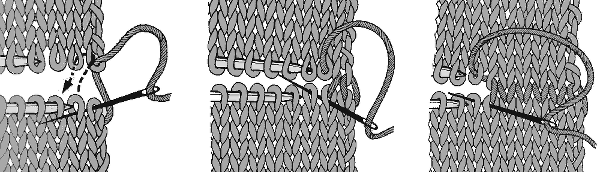
 a pass is made slowly with the ribber sinker plate in place
a pass is made slowly with the ribber sinker plate in place  the comb is dropped
the comb is dropped  bring all needles out to hold / E position
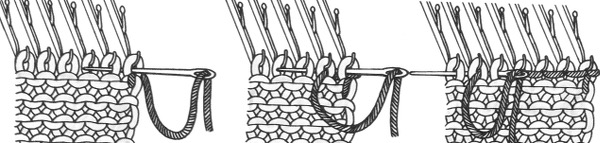
bring all needles out to hold / E position  knit one more row, return to the starting position
knit one more row, return to the starting position  change the ribber arm to the sinker plate for the knit carriage, and proceed with hem
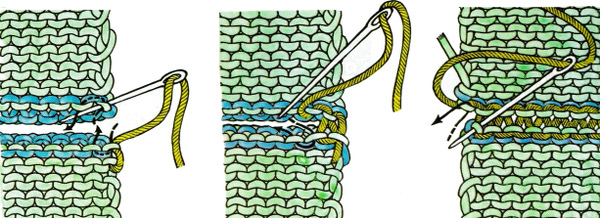
change the ribber arm to the sinker plate for the knit carriage, and proceed with hem  the comb will then need to be lifted up to close the hem
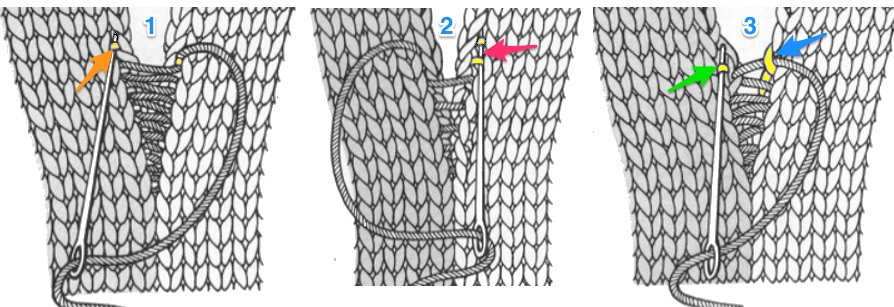
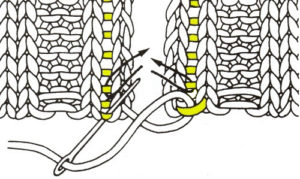
the comb will then need to be lifted up to close the hem  first rest a knitting needle or similar tool on the open hem
first rest a knitting needle or similar tool on the open hem  lift comb up enclosing knitting needle, add weights
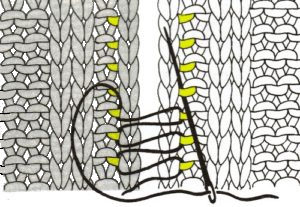
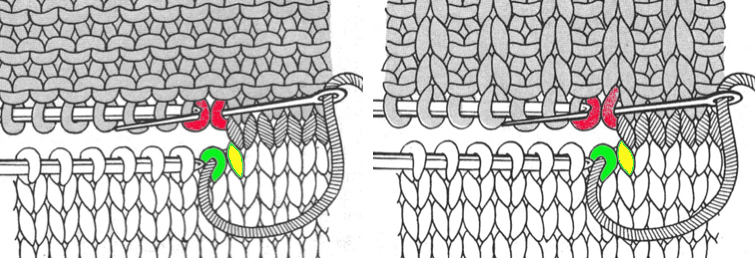
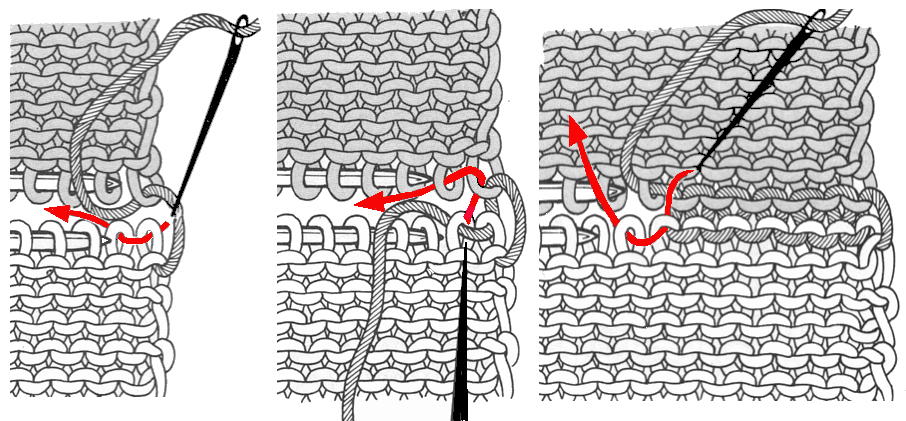
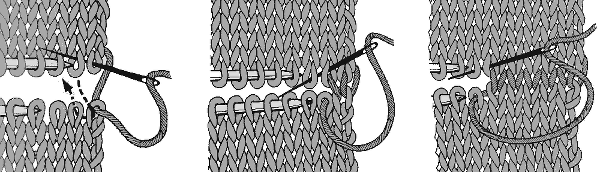
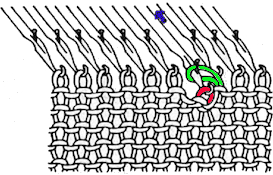
lift comb up enclosing knitting needle, add weights  lift comb perpendicular to needles, move it forward slightly for a better view of stitches
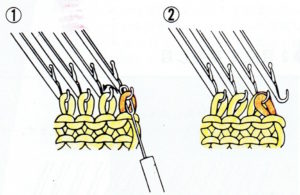
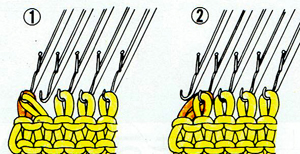
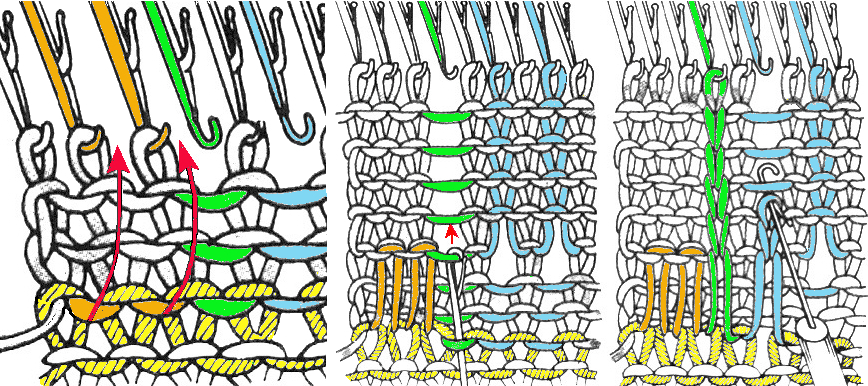
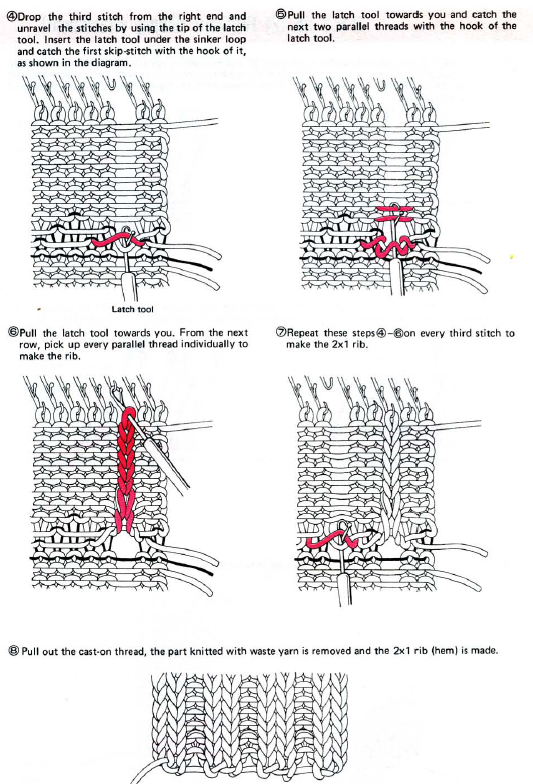
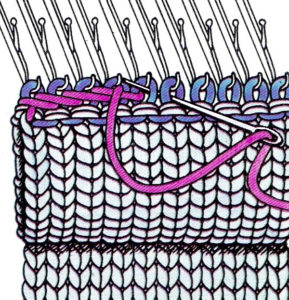
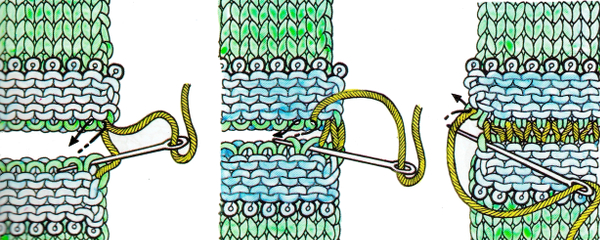
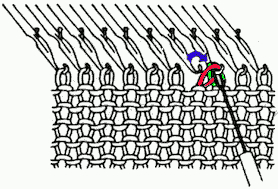
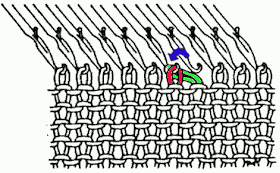
lift comb perpendicular to needles, move it forward slightly for a better view of stitches  needles (red dot) need to enter the stitches through their center (yellow highlight), not their side (orange highlight) or stitches will later drop; push needles through the center of each stitch on comb
needles (red dot) need to enter the stitches through their center (yellow highlight), not their side (orange highlight) or stitches will later drop; push needles through the center of each stitch on comb 
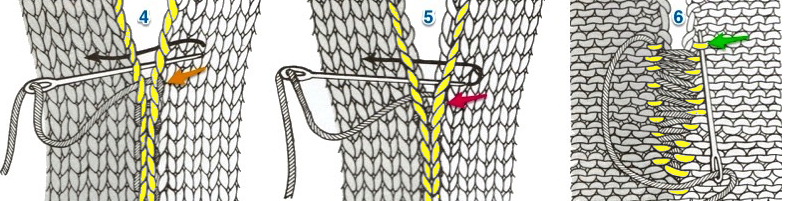
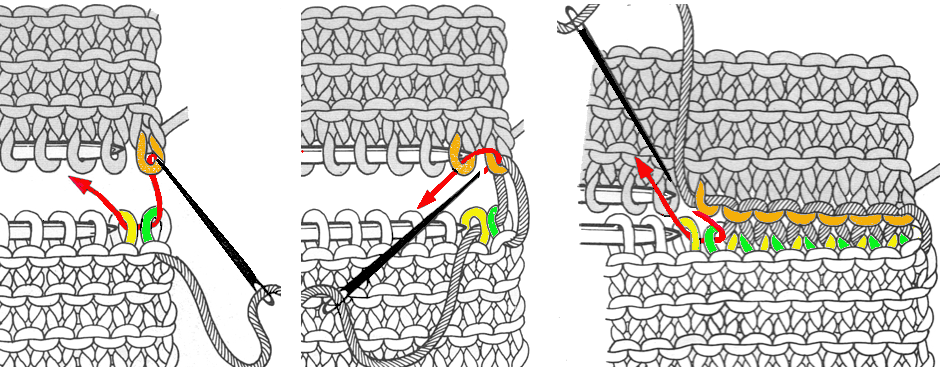
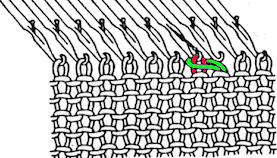
 continue across the bed
continue across the bed 

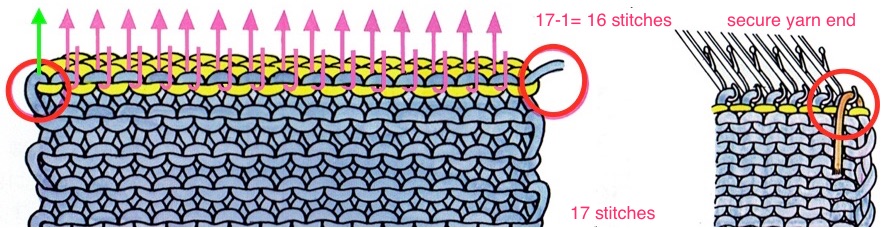
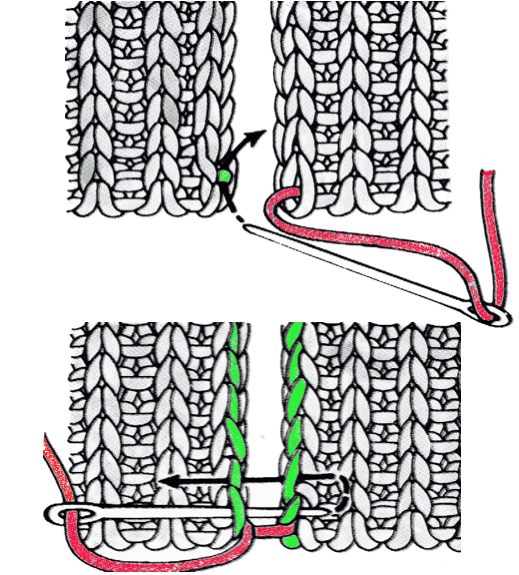
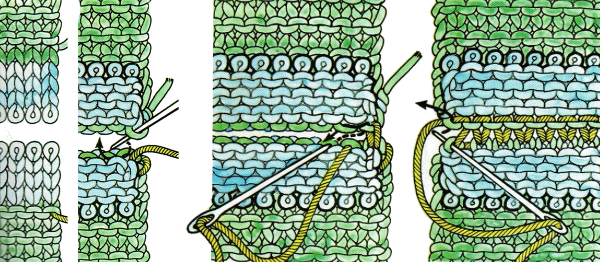
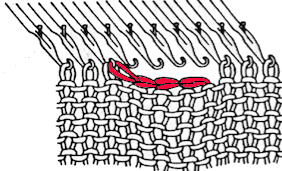
 remove the wire from the comb, lift it up and off
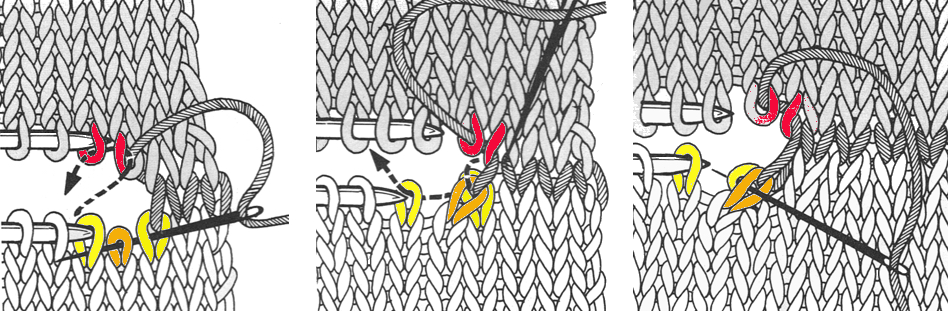
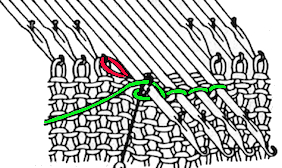
remove the wire from the comb, lift it up and off  remove weights and knitting needle; wrap the cut yarn end around the last needle on that side
remove weights and knitting needle; wrap the cut yarn end around the last needle on that side  pick up from the row below to fill in the “missing single stitch” on the opposite side
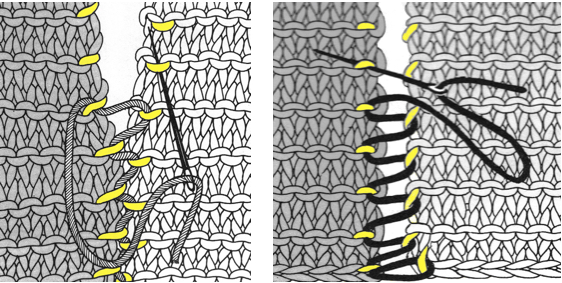
pick up from the row below to fill in the “missing single stitch” on the opposite side  complete the hem with looser joining row, return to standard tension, continue knitting
complete the hem with looser joining row, return to standard tension, continue knitting 
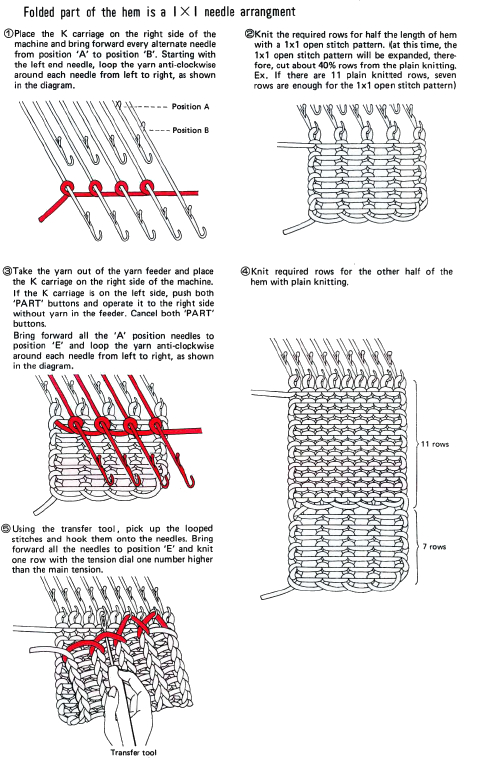
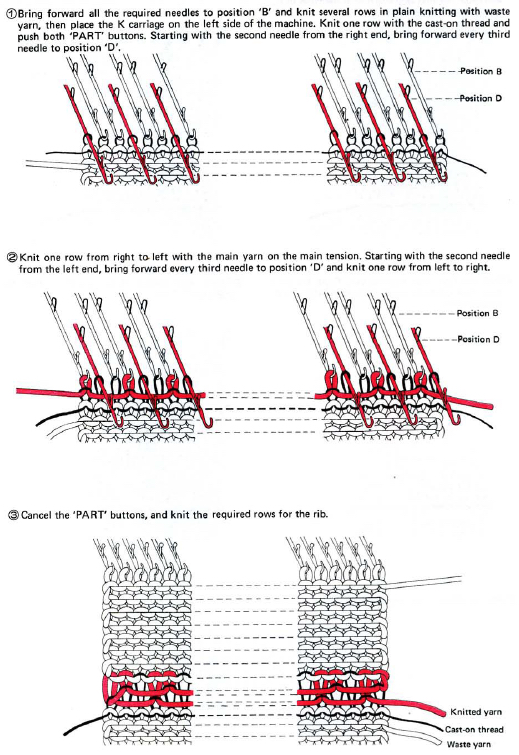
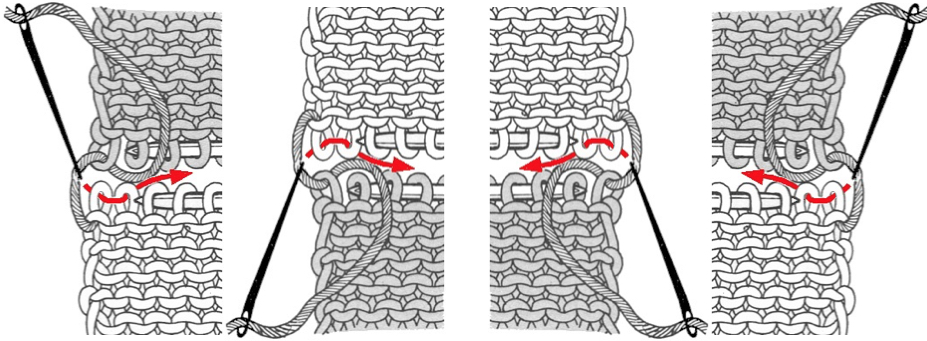
To achieve joining hems in this manner with the ribber in place, though possible on both beds, it is quickest to cast on the back bed (Passap) or on the knit bed (Brother, etc.). Hold the appropriate ribber comb with the bump(s) up facing you, so that the teeth line up as shown above, with the flow combs/ gate pegs, and the needled can come through the gaps. Leave the wire in, hold the bump(s) against the front bed/ ribber, and tilts the comb against the back/ knit bed. Hold the comb high enough to take the lock or carriage across. Take the locks/carriages across to the opposite side, drop the comb and weigh it, and knit 2 rows on Passap before using strippers. In Japanese kms drop the ribber, switch sinker plates, and continue to knit on the main bed.
“bump”: Passap comb “bumps”: Brother comb
“bumps”: Brother comb 
For other purposes and an edge similar to a “weaving cast on”executed on Japanese machines use EON for the “cast on row” and bring into work the rest of the needles prior to knitting the second row.
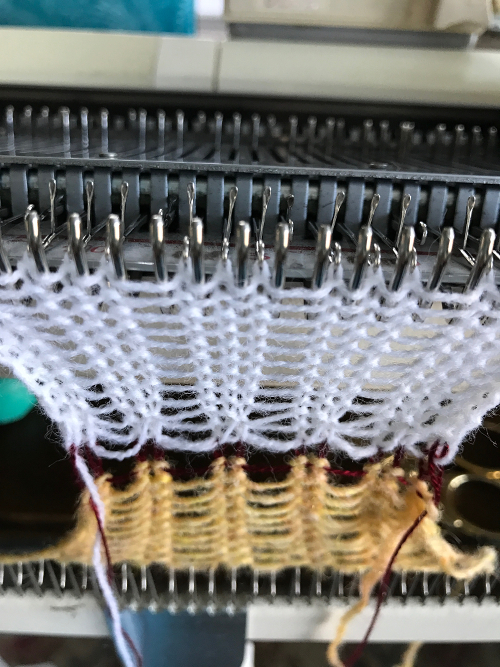






















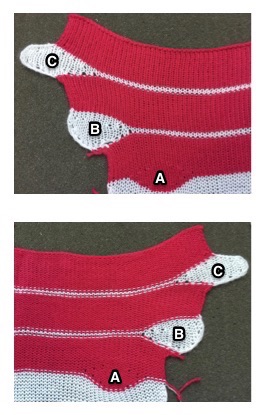
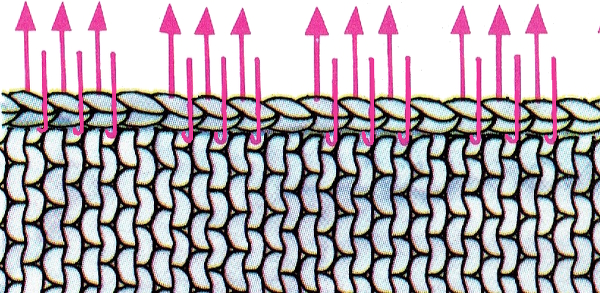
 open stitches to finished hem
open stitches to finished hem 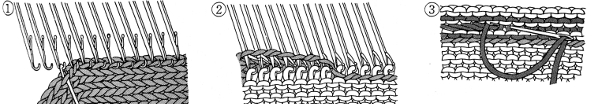
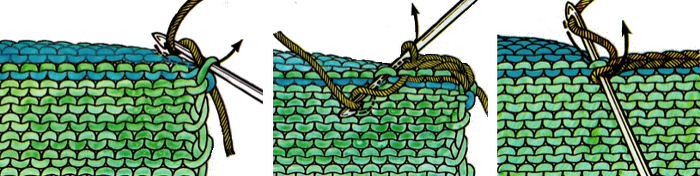

 1. mattress stitch, knit side out, one full stitch away from the edge, adding a second strand of yarn to finish the join
1. mattress stitch, knit side out, one full stitch away from the edge, adding a second strand of yarn to finish the join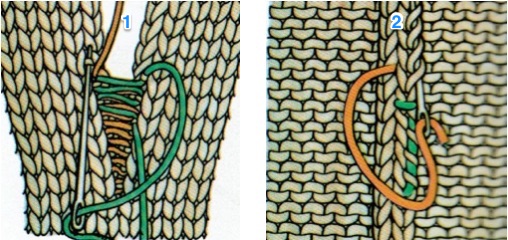
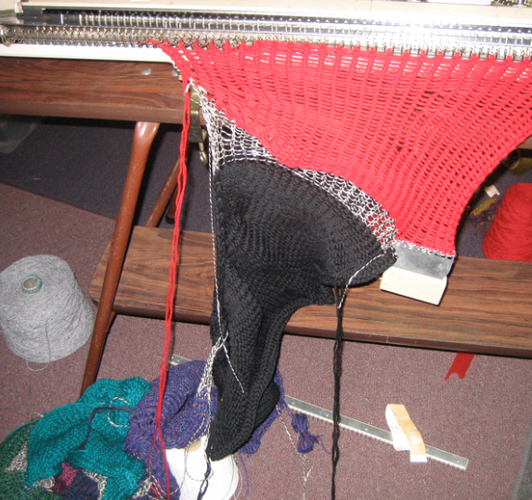
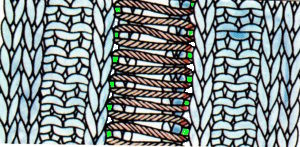
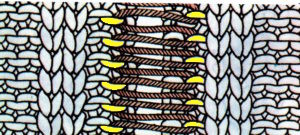



 for a sense of scale before felting
for a sense of scale before felting 
 My customer handout:
My customer handout: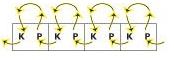



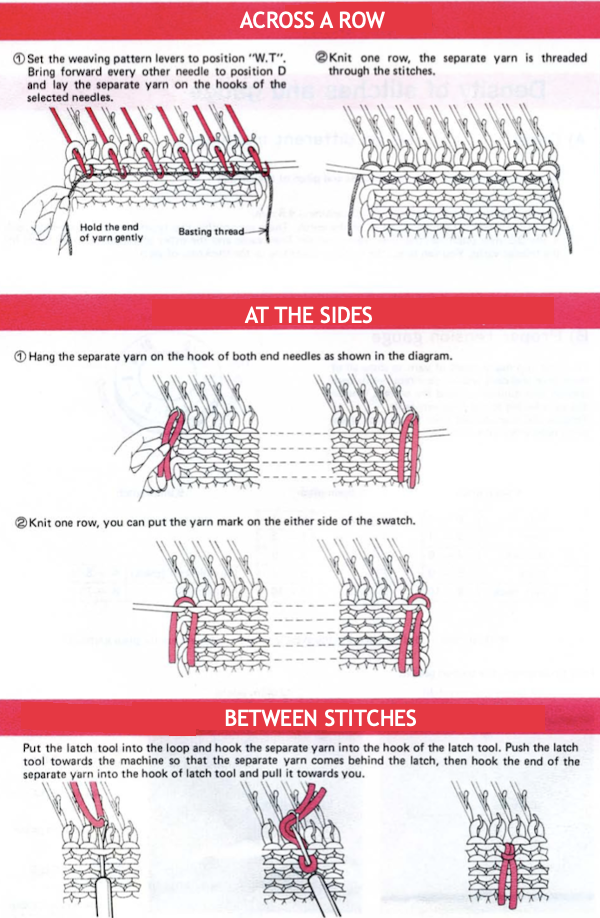
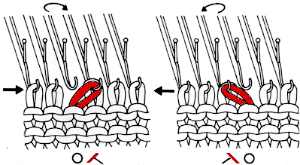
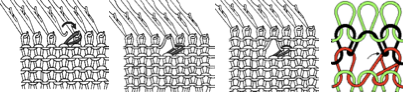
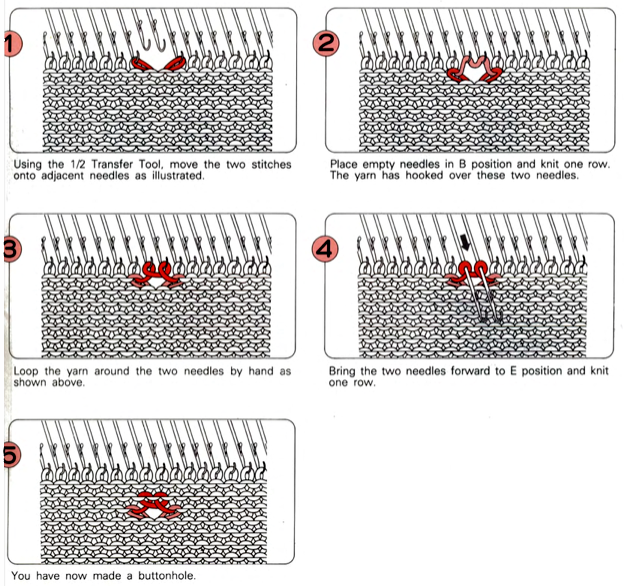
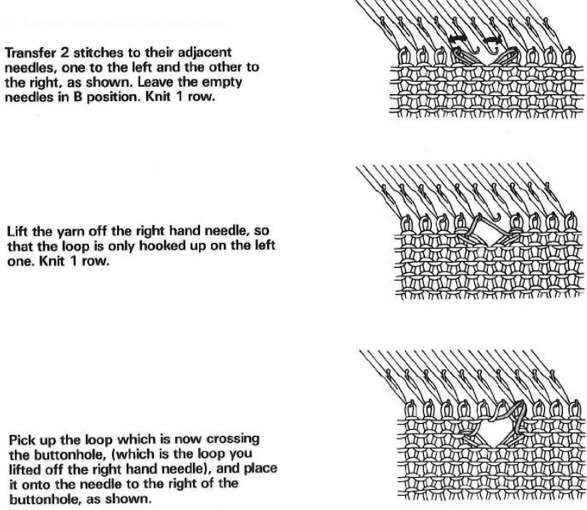
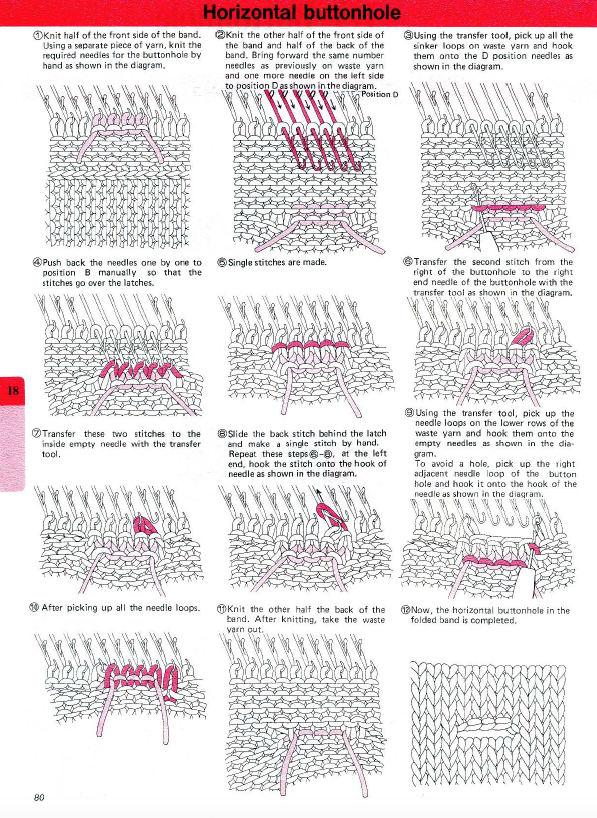











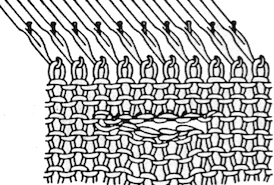

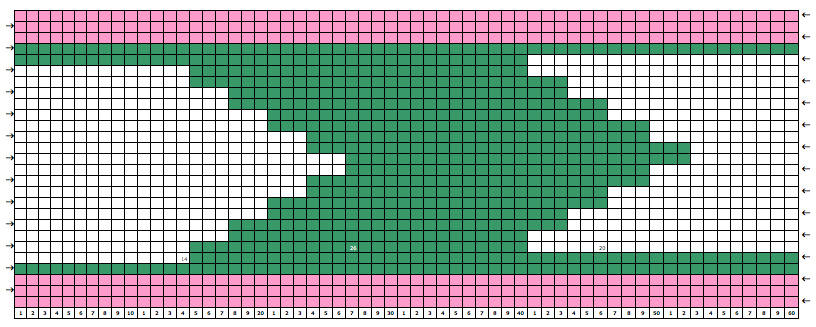
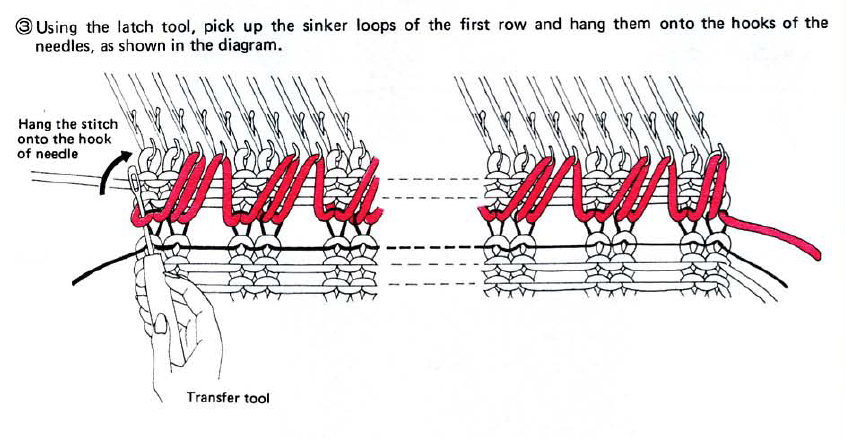
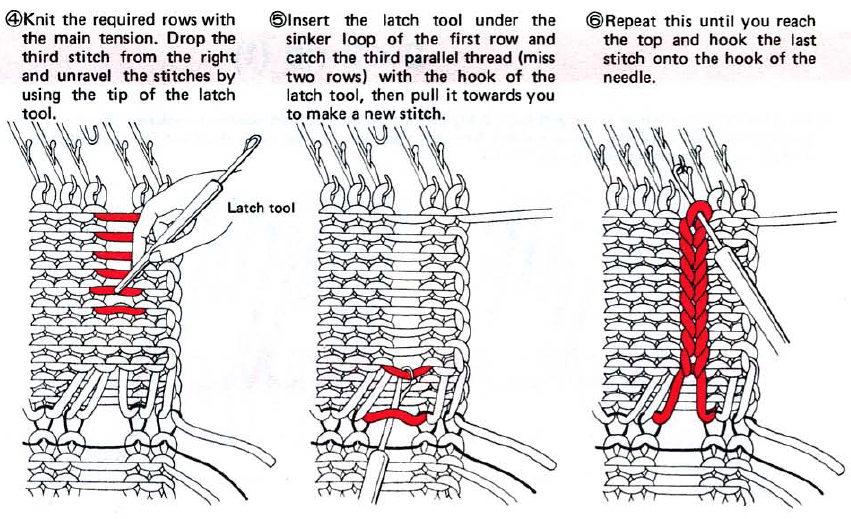
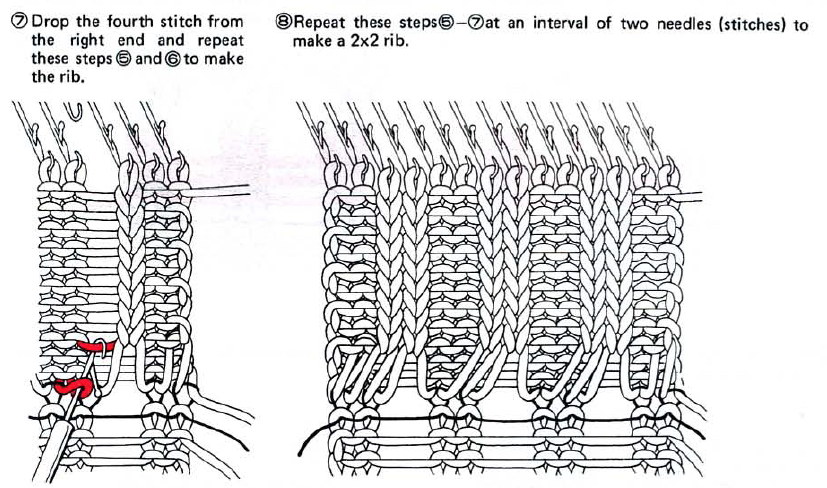
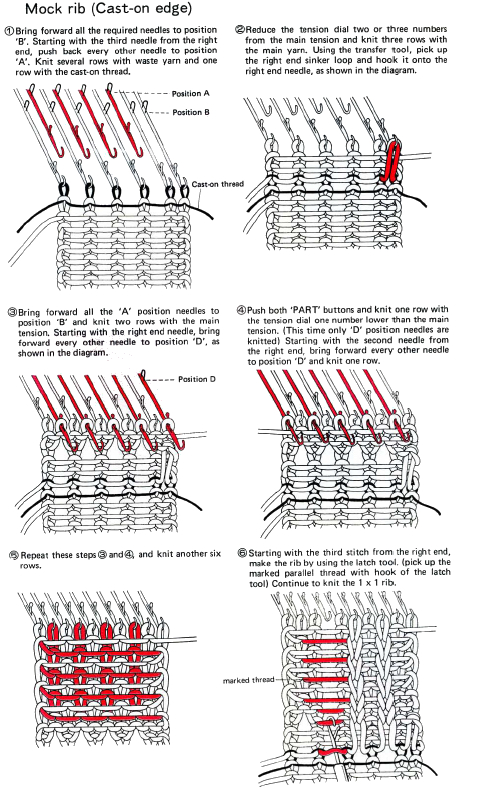
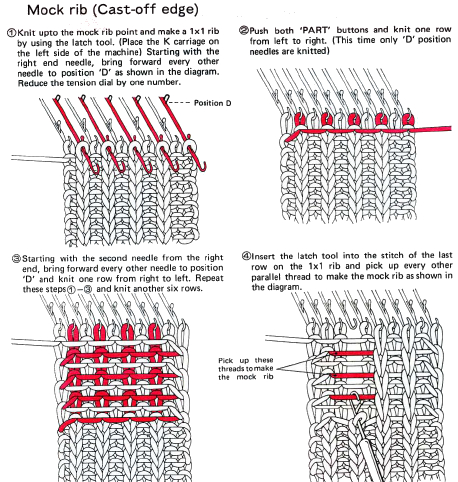
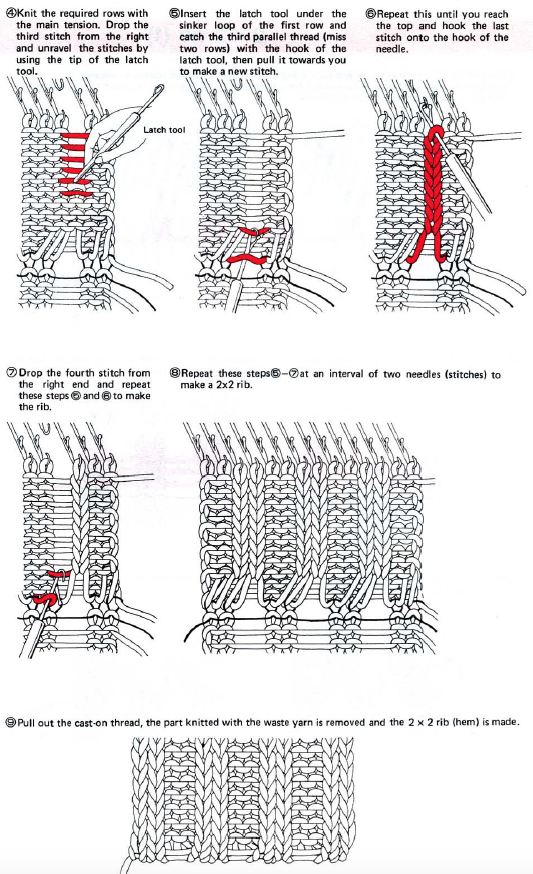
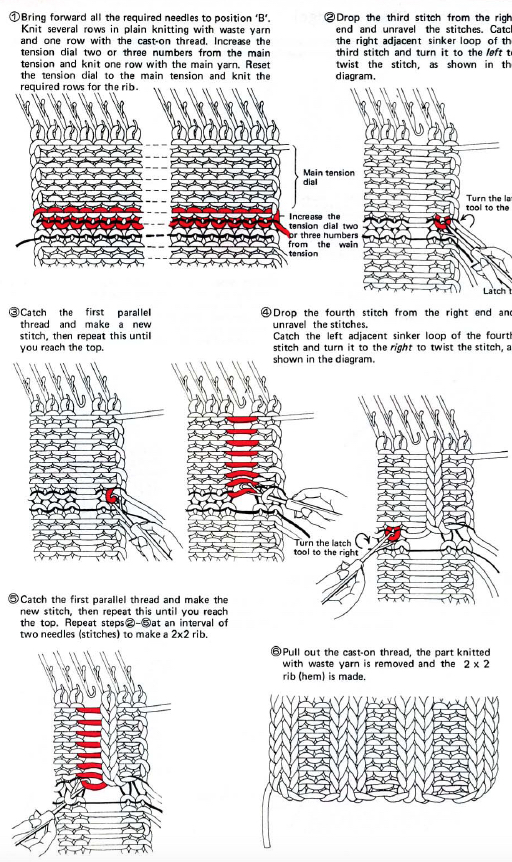
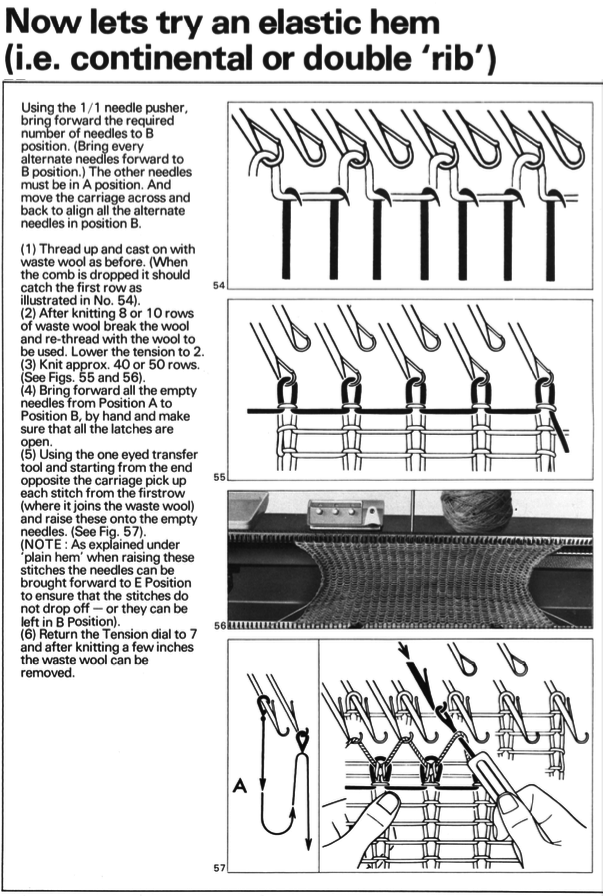
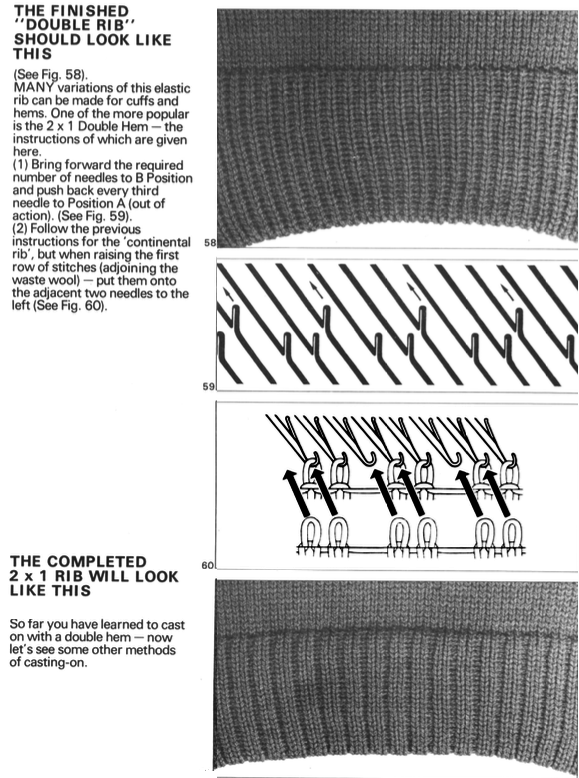
 This version is from an ancient Brother manual, always test techniques on swatches using the yarns intended for the final piece
This version is from an ancient Brother manual, always test techniques on swatches using the yarns intended for the final piece 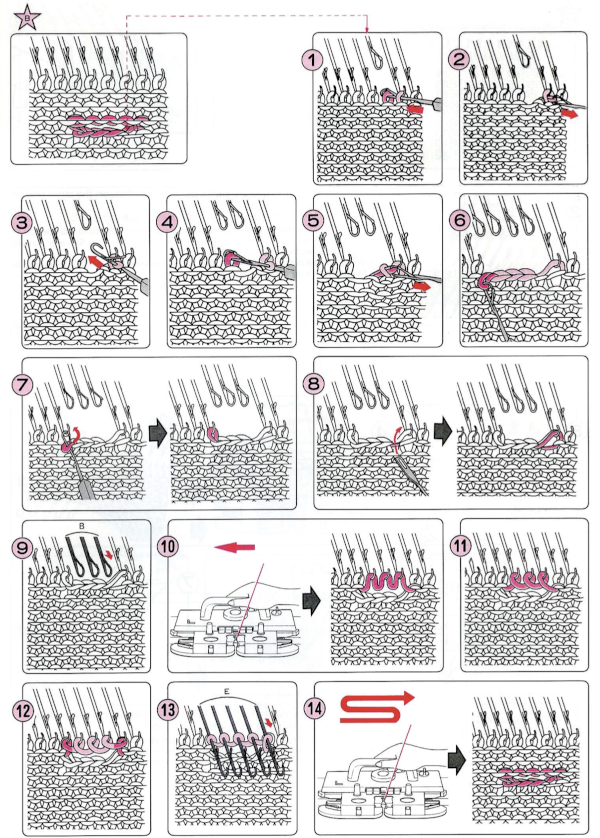
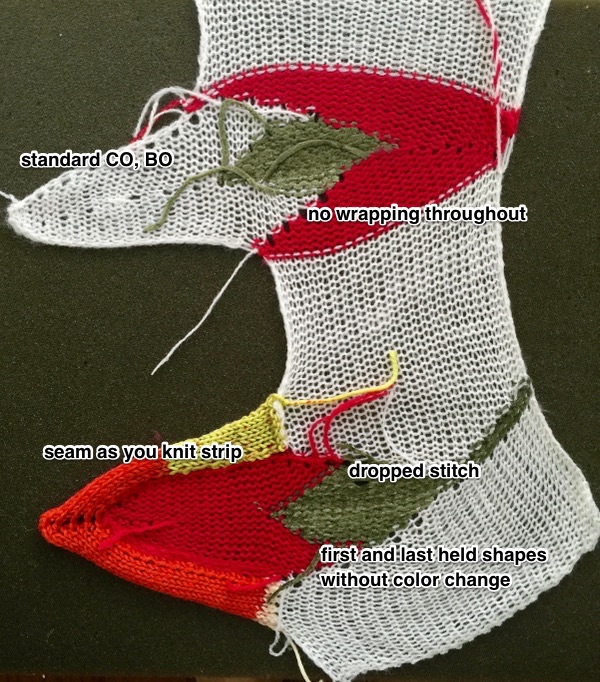
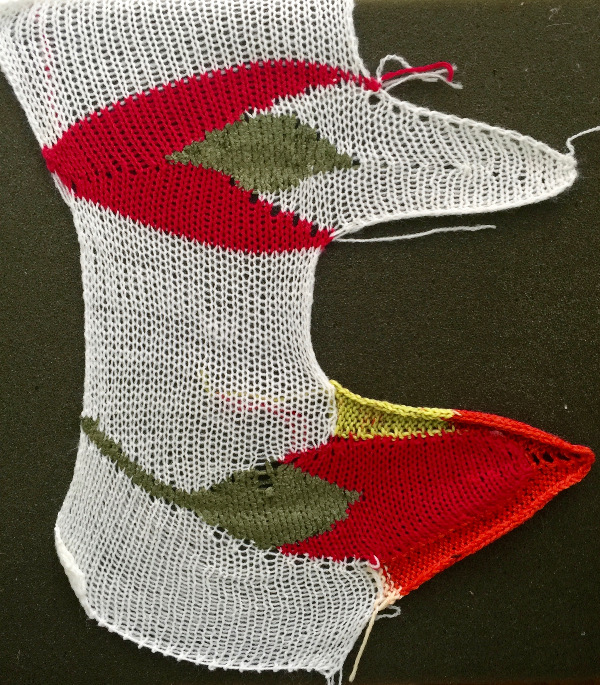


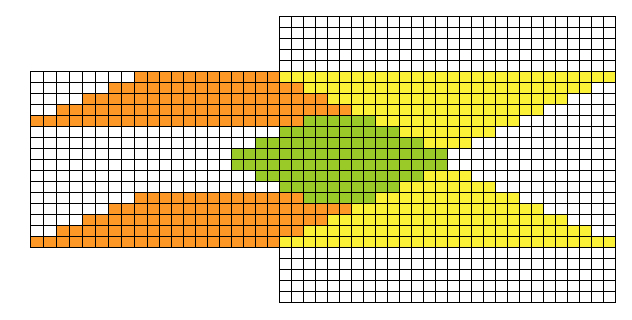
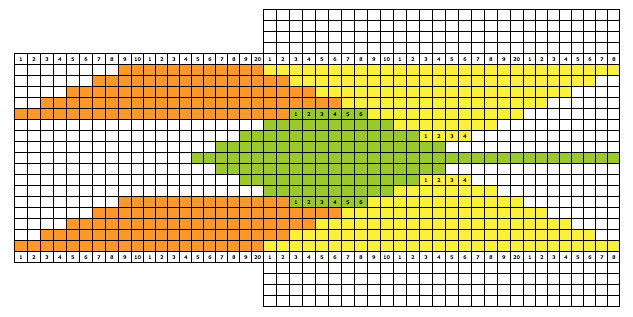


 if beginning with COL, simply flip the image horizontally
if beginning with COL, simply flip the image horizontally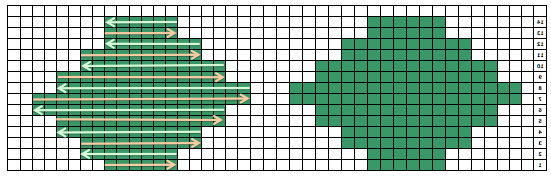
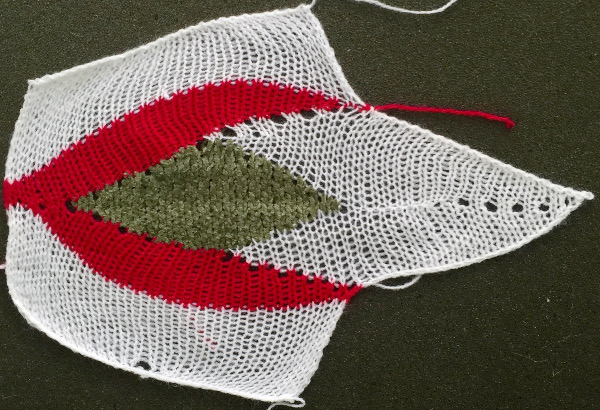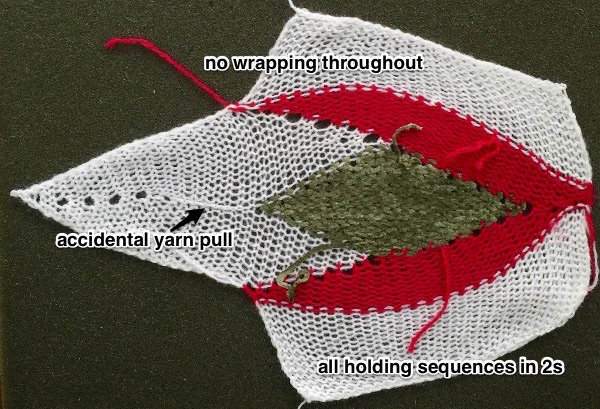
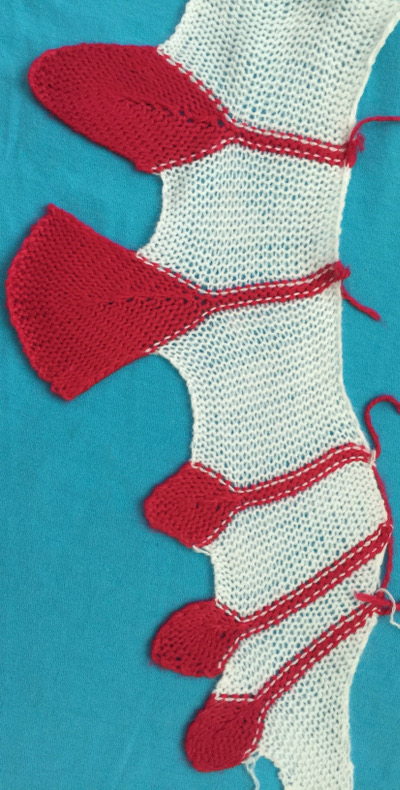
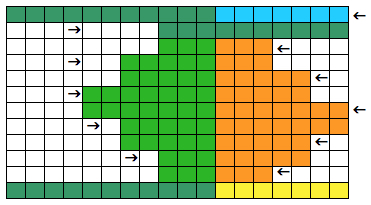
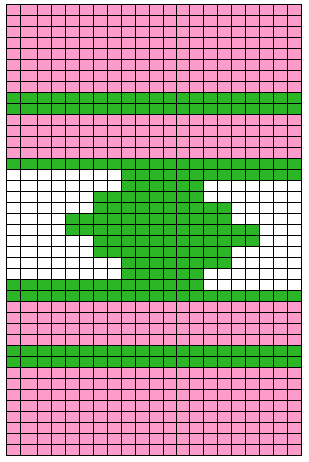
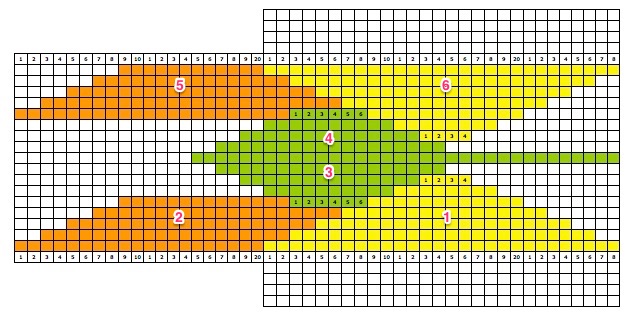
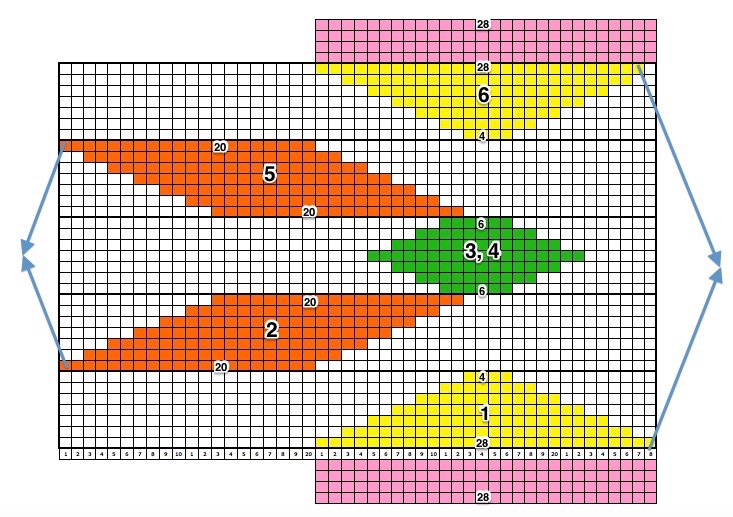
 The yarns used were “throw away acrylics” in white and red. The green is a rayon chenille, which required a looser tension, resulting in the other colors looser than I would want in a piece of the final fabric.
The yarns used were “throw away acrylics” in white and red. The green is a rayon chenille, which required a looser tension, resulting in the other colors looser than I would want in a piece of the final fabric.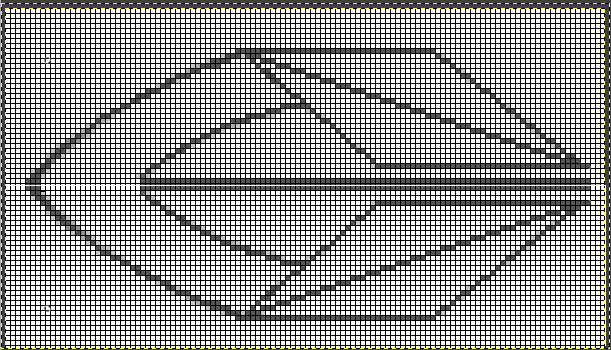
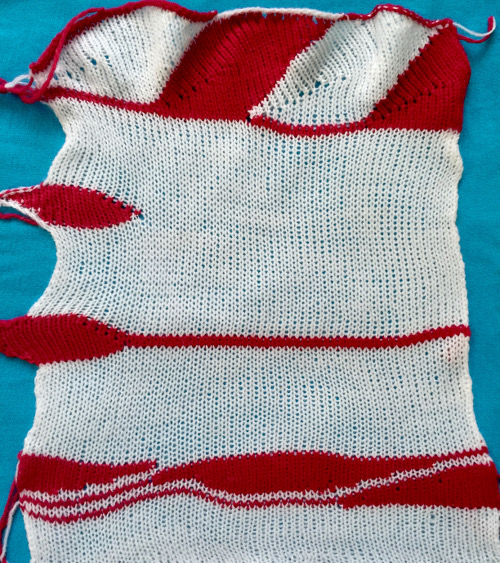
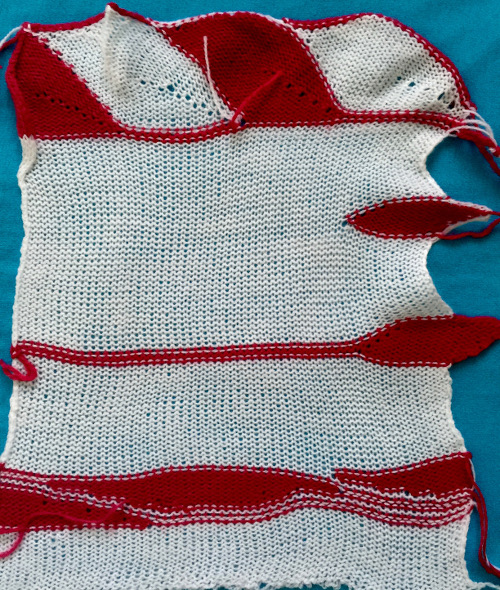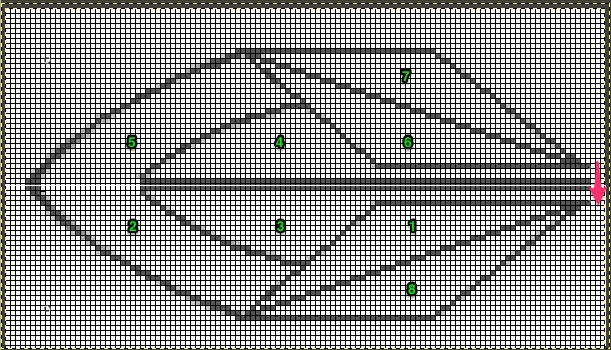
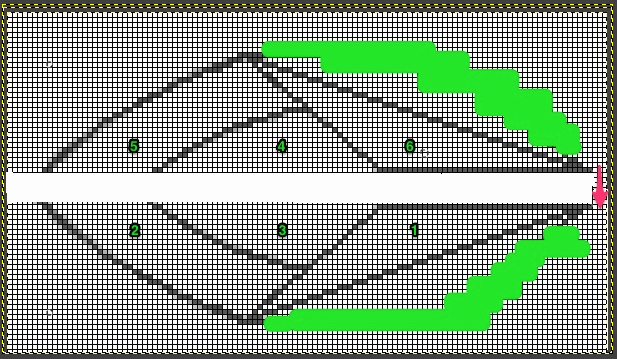
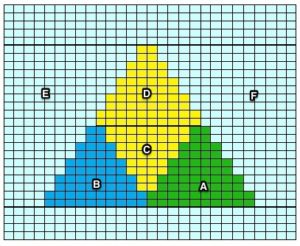
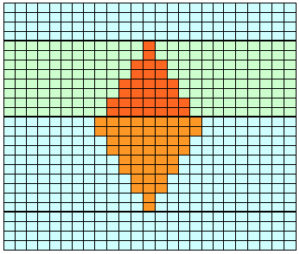
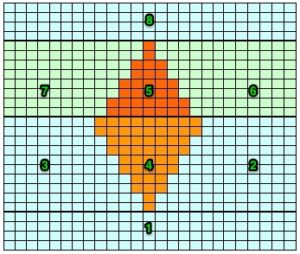





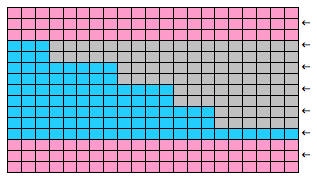


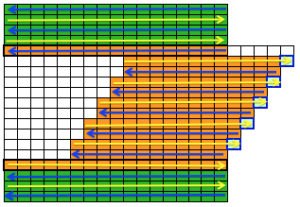
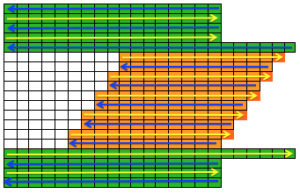
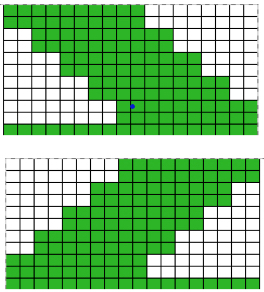
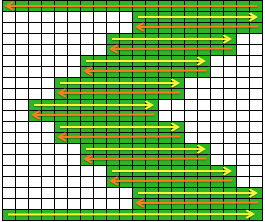
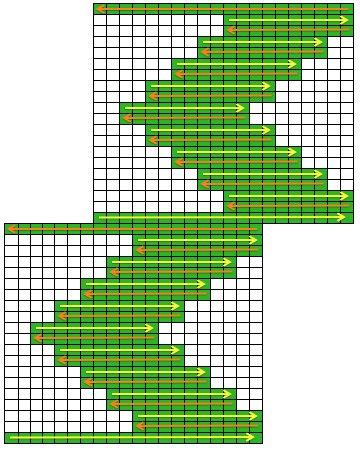

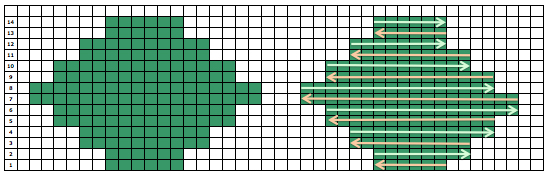
 The start of a smooth shaping sequence for those “leaf shapes” on the machine
The start of a smooth shaping sequence for those “leaf shapes” on the machine