My blog is a living document.
At times I return to previously published posts and there have been software updates in the interim, and/or my familiarity with using multiple tools has grown.
I preserve the contents of the original post, they reflect where I began and the evolution of my approach to learning software navigation with specific design goals in mind.
At times some small additions are made to the body of the old post, at others, dated post scrips point to later, perhaps easier or quicker methods to achieve the same goals.
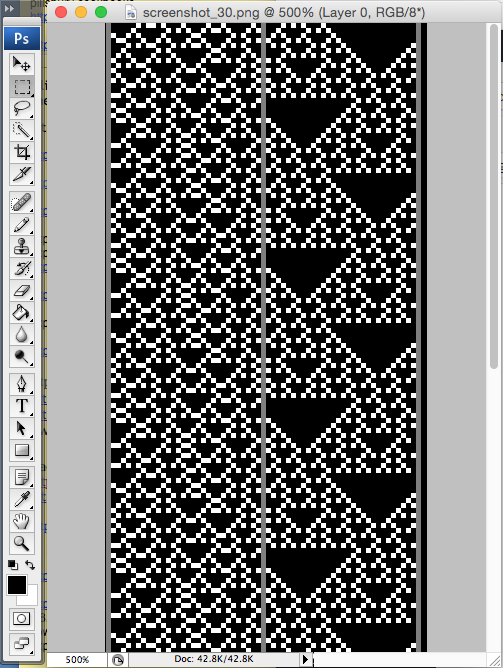
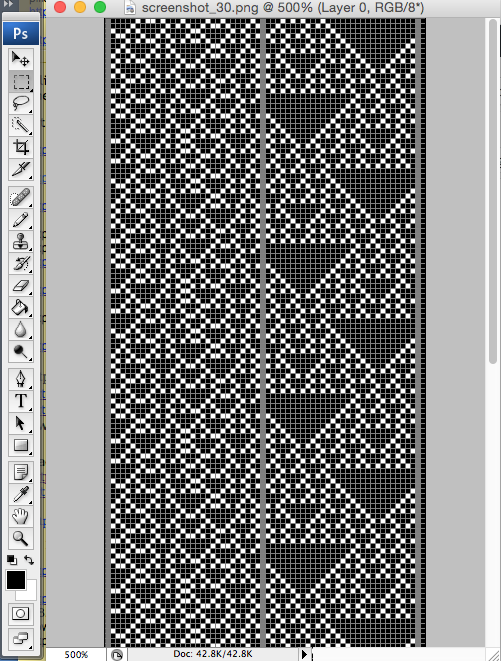
There is a Russian website with a treasure trove of machine knitting patterns, some for 12 stitch models, and extensive collections for 24 stitch models including for fair isle, lace, and single motifs.
There are pull-down options to show the full repeats charted for Silver Reed (default), Brother, and Toyota brands. The numbering system on the right of the cards will be shifted to the appropriate starting line, but the images themselves do not seem to adjust the placement of the punched holes when that is necessary for correct knitting when switching to other knitting machine brands.
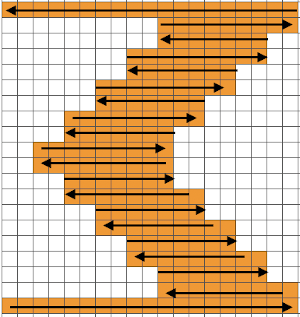
The collections begin with the longest repeats. One such repeat
 I had never had an interest in owning DAK, though never say never, I did purchase the program when my knitting software was switched to a Windows PC. From the promotional material and forums, it would appear their Graphics Studio offers an interesting range of design possibilities in converting such files.
I had never had an interest in owning DAK, though never say never, I did purchase the program when my knitting software was switched to a Windows PC. From the promotional material and forums, it would appear their Graphics Studio offers an interesting range of design possibilities in converting such files.
My experiences with the program have been chronicled in related posts.
Those of us who are Mac and Gimp users need not be left out, the conversions are achievable with the investment of a bit of time and patience.
The charts as presented often cannot be successfully converted to the indexed mode and scaled in Gimp to produce readable patterns.
One long solution is to combine the use of a spreadsheet table, in my case created in Mac Numbers, with Gimp design options.
Prior knowledge of the basics of both programs is required.
I assume similar steps could be used with Excel.
A follow-up post on this topic: Numbers and GIMP: online punchcard patterns to electronics 2.
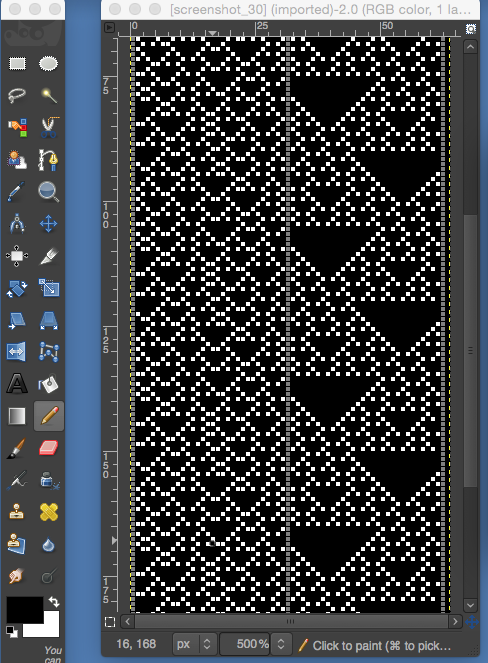
It is easier to test how-tos beginning with a source diagram which has larger, more readable dots representing the punched holes. This was found on Pinterest, dimensions for both stitches and rows are not always provided. 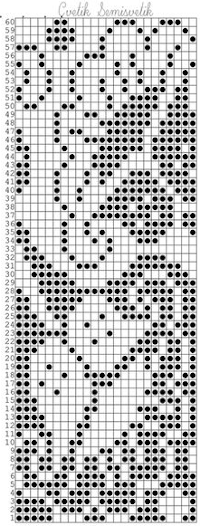 The units in many such illustrations are not square, and the goal is to end up with a PNG where each square unit represents one stitch, one row.
The units in many such illustrations are not square, and the goal is to end up with a PNG where each square unit represents one stitch, one row.
The cell size I prefer in Numbers tables has come to be 20X20 pts.
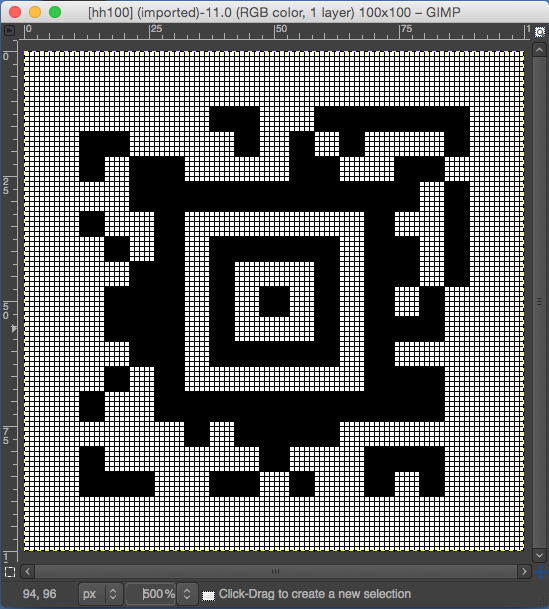
This particular design is 24 stitches wide, and 60 rows high.
To make it workable in that cell size, the repeat is opened in Gimp, cropped to its margins, scaled to 240 X 600 pixels, and the new image is exported. 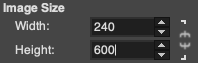 In Numbers, drag and drop the image onto a new sheet if working on a previously created Numbers document. Click on the image, and then on format/ arrange to resize it to the desired proportions,
In Numbers, drag and drop the image onto a new sheet if working on a previously created Numbers document. Click on the image, and then on format/ arrange to resize it to the desired proportions, 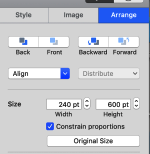 A table is then created, 24 cells wide, 60 high, each measuring 20 pt by 20 pt, with total measurements of 480 by 1200 pts.
A table is then created, 24 cells wide, 60 high, each measuring 20 pt by 20 pt, with total measurements of 480 by 1200 pts. ![]()
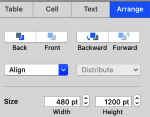 Resize the image if needed to match the table size, in this case, to 480X1200. The size may be adjusted by using the up and down marks to the right of the size option or typing in desired values in each window followed by the return key, with more accurate control than simply dragging on points at the corners of the imported original. Turning off constrain proportions allows for added tweaking of the size if needed.
Resize the image if needed to match the table size, in this case, to 480X1200. The size may be adjusted by using the up and down marks to the right of the size option or typing in desired values in each window followed by the return key, with more accurate control than simply dragging on points at the corners of the imported original. Turning off constrain proportions allows for added tweaking of the size if needed.
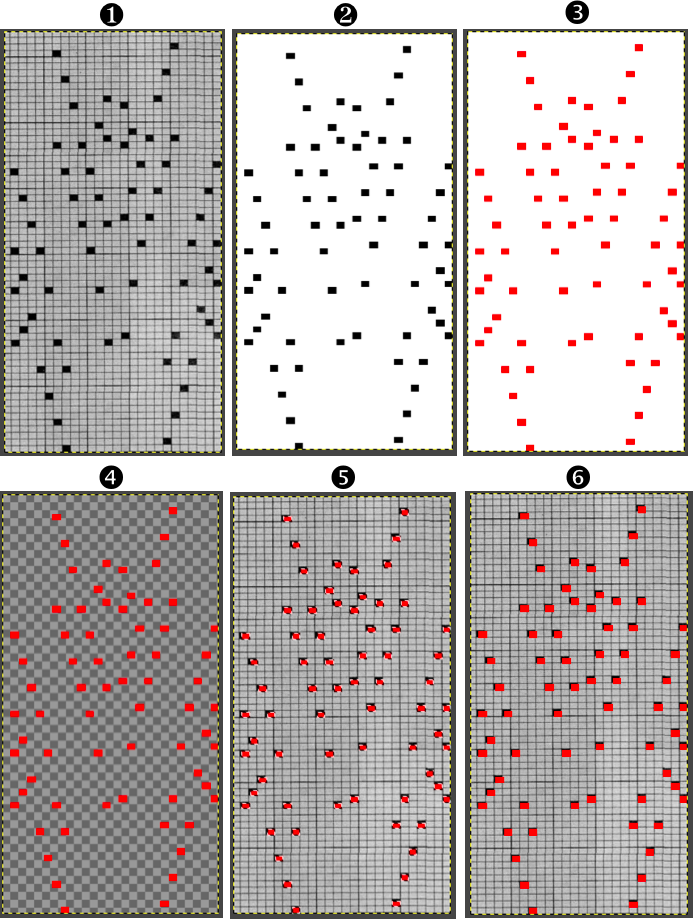
On the left is the first table image, including extra rows to check for stitch and row numbering, and to its right, is the resized punchcard pattern.  Select the whole table 24 cells by 60, by clicking on the circular symbol at the upper left,
Select the whole table 24 cells by 60, by clicking on the circular symbol at the upper left,  and alter the cell borders to a bright, contrasting color. I chose red, 3-point thickness.
and alter the cell borders to a bright, contrasting color. I chose red, 3-point thickness.  Move the table over the punchcard image or its mirror if needed.
Move the table over the punchcard image or its mirror if needed.
The arrange option may be used to place either in front or back of the other.  Dragging the table using that circle on the upper left corner will place it directly on top of the design.
Dragging the table using that circle on the upper left corner will place it directly on top of the design.
Select individual cells or cell groups by using the command key and releasing it periodically, to fill the cells with color.  The repeat in progress
The repeat in progress  Copy and paste the completed table. Make certain there is a different color cell in any white squares at the far corners of the image, in this case, upper right and upper left (yellow), remove cell borders
Copy and paste the completed table. Make certain there is a different color cell in any white squares at the far corners of the image, in this case, upper right and upper left (yellow), remove cell borders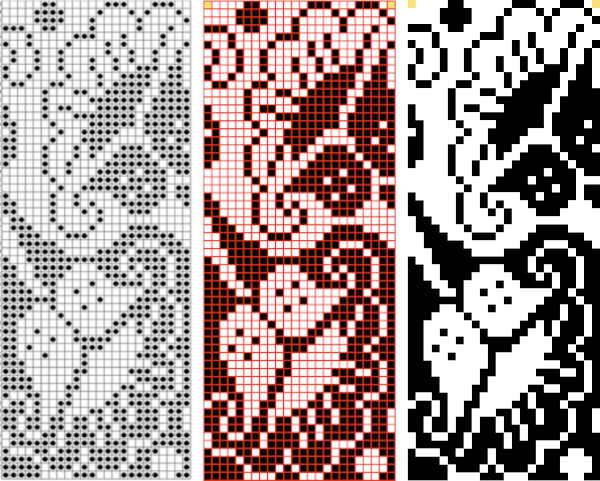  1. screengrab a larger area than the repeat
1. screengrab a larger area than the repeat
2. open the screengrabbed image in Gimp
3. choose Image, Crop to Content, to eliminate any extra surrounding cells
4. fill any contrasting color, in this case, those yellow cells, with white
5. choose image/mode/convert to indexed B/W colors
6. proceed to scale the image. In some instances, this needs to happen in 2 steps, the first scaling to make certain both values are divisible by 20, and the second to scale to the desired repeat size of 24X60
7. before saving the PNG for download, magnify the file to at least 800X, and with the grid in view, perform the first visual check. Then, using filter-map-tile, repeat the design in height and width multiple times to check its horizontal and vertical alignments and to visualize how it might appear in the intended project. 
![]() A quicker process using only Gimp version 2.10.34, 2023
A quicker process using only Gimp version 2.10.34, 2023 
![]()
 One needs to have a basic understanding of punchcard illustration markings, and often the repeat required for the use of the design in electronics may only be a very small portion of the total offered in the publication. The extra rows represent perforations that are not part of the design and may be cropped off in Gimp. The image of the repeat on the left began the FB discussion, while the one to its right illustrates the same after making the marks more visible.
One needs to have a basic understanding of punchcard illustration markings, and often the repeat required for the use of the design in electronics may only be a very small portion of the total offered in the publication. The extra rows represent perforations that are not part of the design and may be cropped off in Gimp. The image of the repeat on the left began the FB discussion, while the one to its right illustrates the same after making the marks more visible. 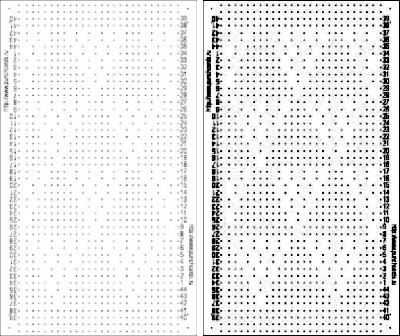 Making the marks more visible is possible by changing number values and by moving the slider immediately below the input levels
Making the marks more visible is possible by changing number values and by moving the slider immediately below the input levels 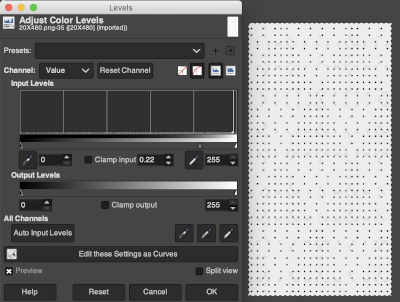 Proceed as for the first image, being mindful of an unnecessary row at the bottom. The saved image can be tweaked in size by turning off Constrain Proportions and adjusting values for width and height for proper placement under the table grid. It soon becomes evident that the card is composed of smaller repeat segments, which can be copied and pasted making for faster filling in the whole punchcard minimum row # requirement.
Proceed as for the first image, being mindful of an unnecessary row at the bottom. The saved image can be tweaked in size by turning off Constrain Proportions and adjusting values for width and height for proper placement under the table grid. It soon becomes evident that the card is composed of smaller repeat segments, which can be copied and pasted making for faster filling in the whole punchcard minimum row # requirement. 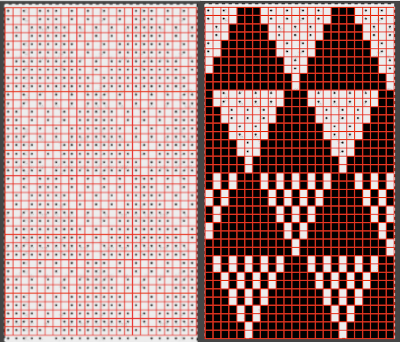 Check the repeat alignment by tiling it.
Check the repeat alignment by tiling it. 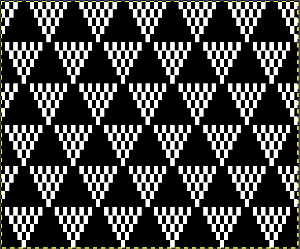 The smallest adjusted electronic repeat, 12X20 pixels.
The smallest adjusted electronic repeat, 12X20 pixels. ![]() The far longer repeats might best be managed broken up into sections. An easier, quicker solution is presented in later posts.
The far longer repeats might best be managed broken up into sections. An easier, quicker solution is presented in later posts.
This is part of #6717, shown in the process of trimming unwanted info in Gimp and after adjusting color levels to create a sharper image. 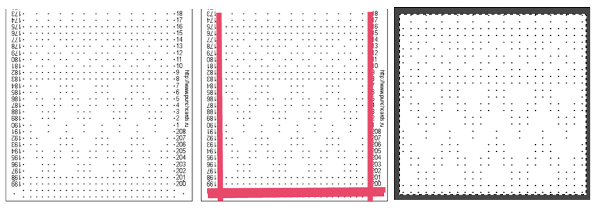 The converted, partial punchcard repeat
The converted, partial punchcard repeat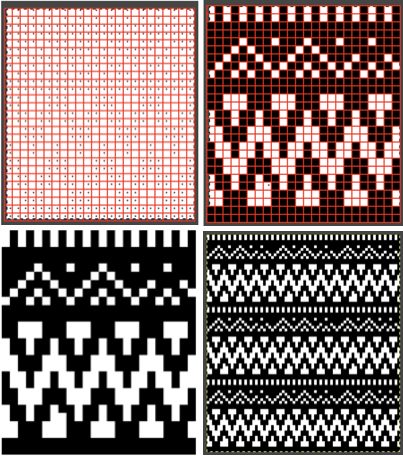  2023: ArahPaint‘s weave from grid tool makes working with the full repeat possible. The final repeat was cropped by 2 rows at the top to 24X206 to avoid a 4-row solid color line produced when the original was tiled vertically.
2023: ArahPaint‘s weave from grid tool makes working with the full repeat possible. The final repeat was cropped by 2 rows at the top to 24X206 to avoid a 4-row solid color line produced when the original was tiled vertically.

![]()
 Returning to the use of Numbers and Gimp: what of the lace punchcard repeats? There seems to be no differentiation between the different types of lace on the Russian website: thread lace, simple lace where stitches are knit and transferred in a single pass (a Silver Reed/Studio special), and lace requiring the use of 2 separate carriages, one to knit, and the other to transfer are all grouped together. In addition, the pull-down menu and changing machine brand selection,
Returning to the use of Numbers and Gimp: what of the lace punchcard repeats? There seems to be no differentiation between the different types of lace on the Russian website: thread lace, simple lace where stitches are knit and transferred in a single pass (a Silver Reed/Studio special), and lace requiring the use of 2 separate carriages, one to knit, and the other to transfer are all grouped together. In addition, the pull-down menu and changing machine brand selection,
 if used, will change the numbering on the side of the card, but not the design content
if used, will change the numbering on the side of the card, but not the design content  The conversion process intended for the final use on the Brother machine: the image on the far right shows a review of the proper placement of pairs of empty rows between lace segment sequences, highlighted in grey
The conversion process intended for the final use on the Brother machine: the image on the far right shows a review of the proper placement of pairs of empty rows between lace segment sequences, highlighted in grey 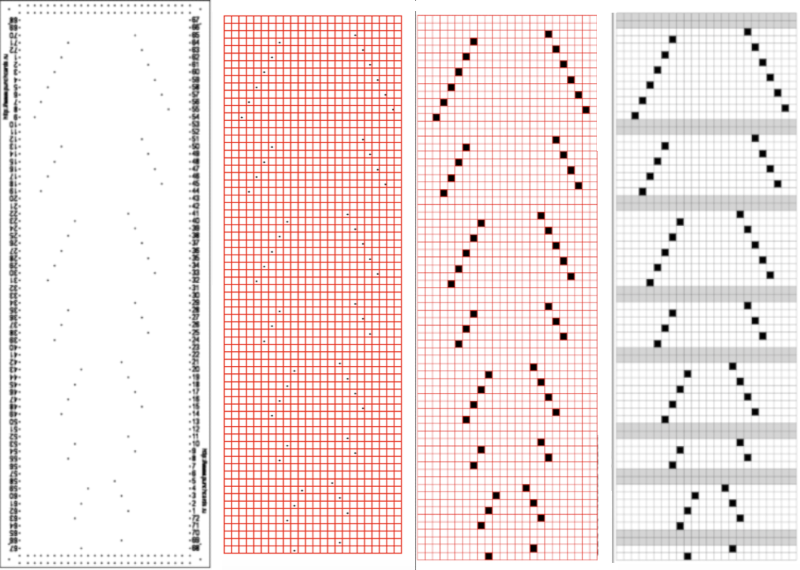 In the past I have found lace repeats, in particular, to be particularly cranky when scaled down in Gimp due to the paucity of black cells. After the above steps, I decided to try color invert, resize, and color invert again, which in this instance, produced what appears to be an accurate repeat. Of course, the final png is likely to need mirroring for use in some electronic models
In the past I have found lace repeats, in particular, to be particularly cranky when scaled down in Gimp due to the paucity of black cells. After the above steps, I decided to try color invert, resize, and color invert again, which in this instance, produced what appears to be an accurate repeat. Of course, the final png is likely to need mirroring for use in some electronic models 
![]() The process did not work for me in using Gimp alone to edit test repeats from the website directly. The white dots, in that case, disappear with scaling to the desired size.
The process did not work for me in using Gimp alone to edit test repeats from the website directly. The white dots, in that case, disappear with scaling to the desired size.
Using resize X 2 with color invert and back with a Stitchworld #150 pattern image got me closer to an editable lace repeat using Gimp alone, worth considering in the future. 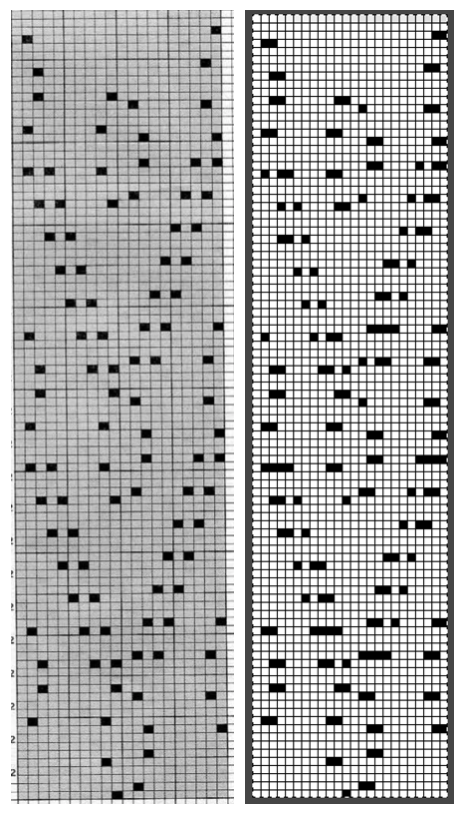 2023: a different approach:
2023: a different approach:
Left: the image from the Stitchworld book measures 26X64 cells
it is slightly tilted, the angle has been rotated for better results, and cropped to the borders of the actual design repeat
Center: the cropped image measures 442X846 pixels, it is scaled with a broken chain link first to a multiple of the original, since the output will be on a square grid, not a rectangular one, in this case, to 260X640.
Use Colors, Threshold, followed by Image, Mode, convert to BW Indexed
Right: Image, scale again with intact chain link to the final 26X64 size, export the PNG 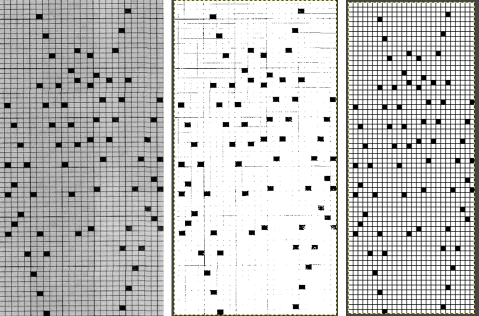
![]() With experience, one learns to trust the process.
With experience, one learns to trust the process.
A proof of concept for the final PNG matching the original is not in any way necessary but is offered here for this particular file or simply for reference.
Work in RGB mode, select and click on the rectangle tool after any steps to make changes to fix the layers.
Select edit, and undo to revert to any previous step(s).
1. open the initial cropped and rotated image, note the pixel proportions
2. in a new work window, open the final PNG, and scale it to the same pixel dimensions as 1
3. select all black pixels, and bucket fill them with red
4. use layer, transparency, white background to alpha, making it transparent
5. copy 4
6. paste 4 on 1, note that pixel placement for the final repeat matches that for the black squares on the original chart
 Adding a second color and reversing directions of shapes brings lots of yarn ends and its “price to pay”
Adding a second color and reversing directions of shapes brings lots of yarn ends and its “price to pay”

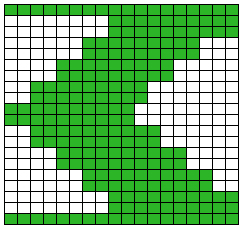
 Some handknit large scale inspiration to begin my revisit to MKing them:
Some handknit large scale inspiration to begin my revisit to MKing them: 


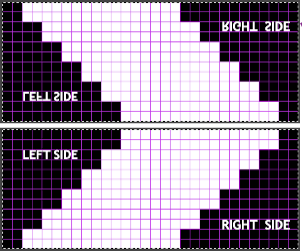
 The chart is actually rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise, could serve as inspiration for an electronic pattern.
The chart is actually rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise, could serve as inspiration for an electronic pattern. Automated holding sequences may be planned for single or multiple stitches in width, as well as for single and multiple rows in height. For the new initial test, which proved to need editing, this was my repeat
Automated holding sequences may be planned for single or multiple stitches in width, as well as for single and multiple rows in height. For the new initial test, which proved to need editing, this was my repeat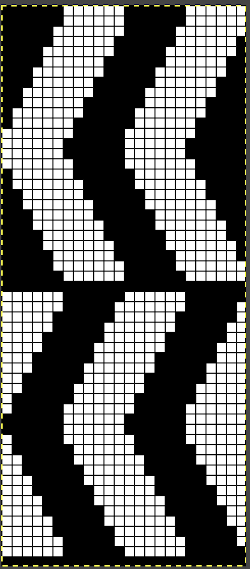 A tiny test in too thin a yarn
A tiny test in too thin a yarn  I am knitting on a 930, the image needs to be mirrored in order for it to appear in the direction I intend on the knit side. The above repeat did not work properly when knitting a whole row of shapes. With some patience, a final, edited, and mirrored repeat was developed that enabled a completed a full row of shapes using the slip setting and holding, and starting with working it from right to left. Sometimes differences are subtle, especially in designing using single-pixel units. The new repeat proved to also work for rows of shapes in the reverse direction after horizontal mirroring and restarting the pattern or design row 1. When working from right to left, the initial preselection row is from left to right, while when working from left to right, the first preselection row is from right to left. After a full row of repeats is completed, the pattern is rolled back to row 1 and mirrored. Punchcard knitters could turn the card over and start again on the proper row. I used contrast color knit rows initially in between rows of shapes to help me note transitions more clearly. The “leaf” is not pointy enough for me, but at times what was not planned may lead to a pleasing result of a different sort.
I am knitting on a 930, the image needs to be mirrored in order for it to appear in the direction I intend on the knit side. The above repeat did not work properly when knitting a whole row of shapes. With some patience, a final, edited, and mirrored repeat was developed that enabled a completed a full row of shapes using the slip setting and holding, and starting with working it from right to left. Sometimes differences are subtle, especially in designing using single-pixel units. The new repeat proved to also work for rows of shapes in the reverse direction after horizontal mirroring and restarting the pattern or design row 1. When working from right to left, the initial preselection row is from left to right, while when working from left to right, the first preselection row is from right to left. After a full row of repeats is completed, the pattern is rolled back to row 1 and mirrored. Punchcard knitters could turn the card over and start again on the proper row. I used contrast color knit rows initially in between rows of shapes to help me note transitions more clearly. The “leaf” is not pointy enough for me, but at times what was not planned may lead to a pleasing result of a different sort.
 To knit: cast on with a multiple of 12 stitches on each side of the center 24 on the needle bed
To knit: cast on with a multiple of 12 stitches on each side of the center 24 on the needle bed
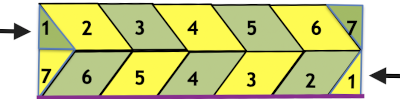
 Moving on to a wider version, using 24 stitches in width to allow for using the pattern on a punchcard: this repeats works both as-is and mirrored, the groups of stitches moved in and out of work is now half of the new design repeat = 12.
Moving on to a wider version, using 24 stitches in width to allow for using the pattern on a punchcard: this repeats works both as-is and mirrored, the groups of stitches moved in and out of work is now half of the new design repeat = 12. 
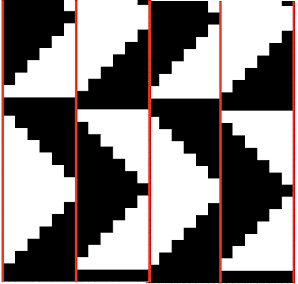 The lovely mess in the swatch happened when I stopped paying attention to everything but what was happening on the needle bed and missed the tangle of yarns in my yarn mast. There is enough knitting, however, to note that the repeat is sound and that the edges on both sides are formed by the narrowest part of the shapes in each direction. One way to solve that is by casting on and binding off along tops and bottoms of shapes as seen in the yellow and green swatch at the top of the post.
The lovely mess in the swatch happened when I stopped paying attention to everything but what was happening on the needle bed and missed the tangle of yarns in my yarn mast. There is enough knitting, however, to note that the repeat is sound and that the edges on both sides are formed by the narrowest part of the shapes in each direction. One way to solve that is by casting on and binding off along tops and bottoms of shapes as seen in the yellow and green swatch at the top of the post.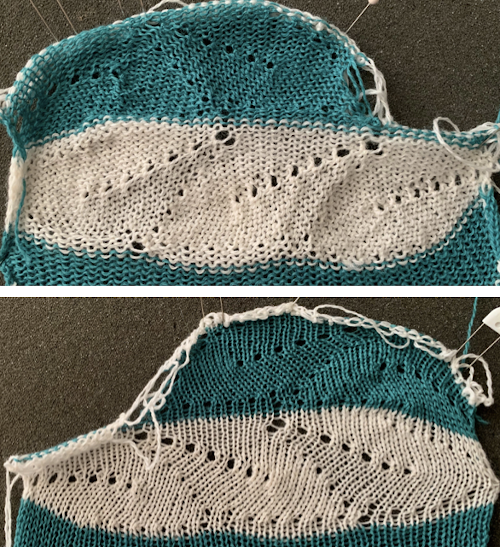  Planning things out to release those edges as seen at the top of the post
Planning things out to release those edges as seen at the top of the post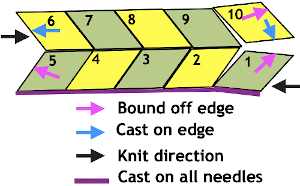

 Problems to solve: maintaining an even number of rows in-between shapes and a straight edge along both sides. The latter could happen with triangles prior to knitting full shapes at either or both ends, the first sample failed on the left side due to both triangles being knit in the same sequence;
Problems to solve: maintaining an even number of rows in-between shapes and a straight edge along both sides. The latter could happen with triangles prior to knitting full shapes at either or both ends, the first sample failed on the left side due to both triangles being knit in the same sequence; 



 Begin on waste yarn, decide on the color of the cast on, and any additional knit rows prior to beginning in the pattern. Each of the side triangles is shaped using manual holding techniques over 12 stitches. If starting on the right, the first preselection row needs to be made moving from left to right as above on the first 24 stitches. With knit carriage set to both slip in both directions and holding with COL make certain the first 24 stitches on the right in B position make a free pass to the right.
Begin on waste yarn, decide on the color of the cast on, and any additional knit rows prior to beginning in the pattern. Each of the side triangles is shaped using manual holding techniques over 12 stitches. If starting on the right, the first preselection row needs to be made moving from left to right as above on the first 24 stitches. With knit carriage set to both slip in both directions and holding with COL make certain the first 24 stitches on the right in B position make a free pass to the right.
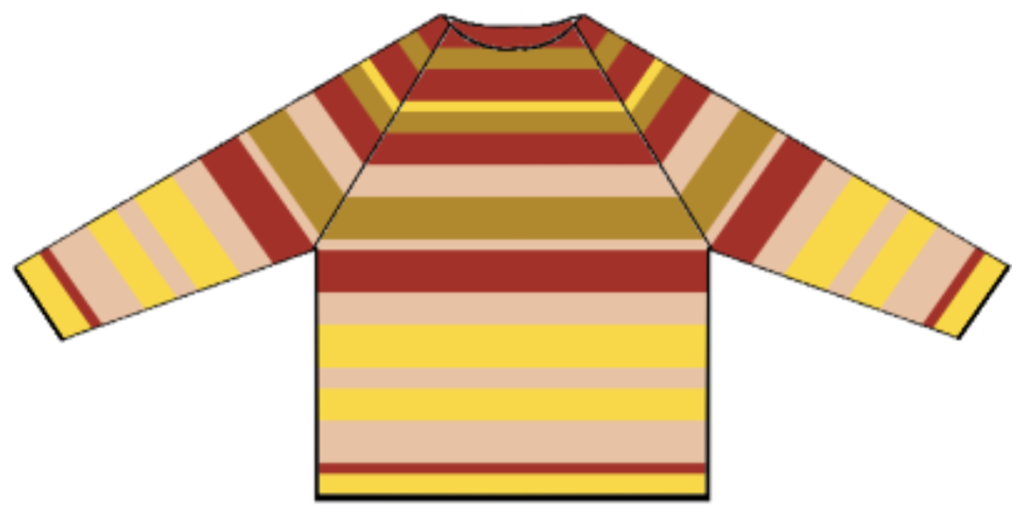
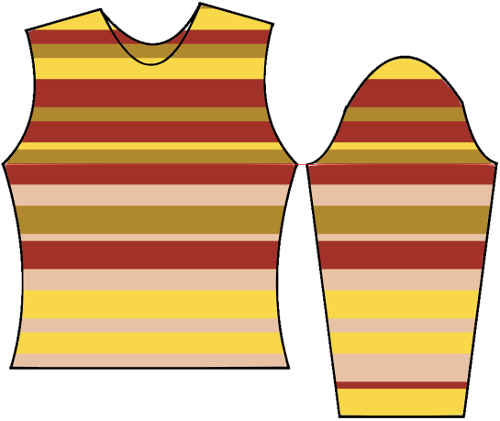
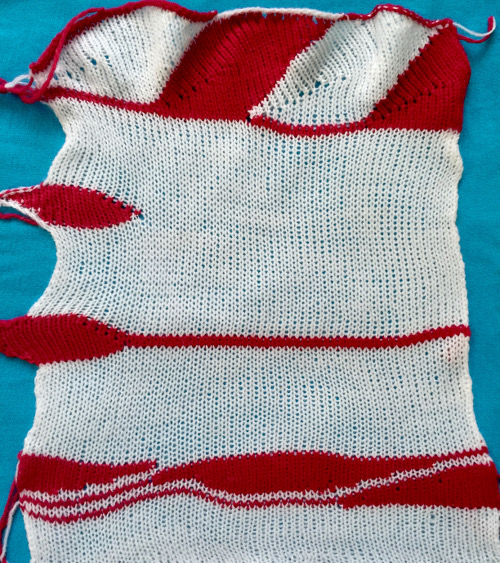
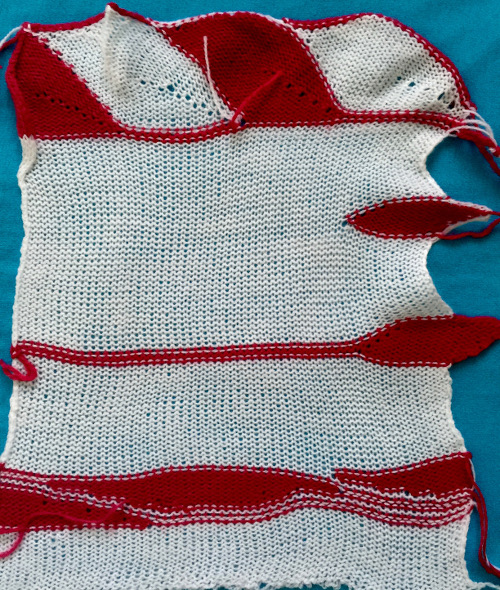








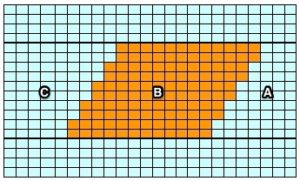
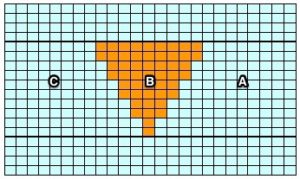
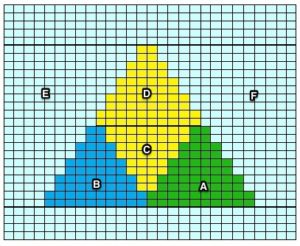
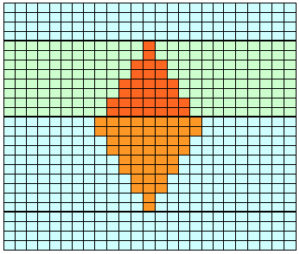
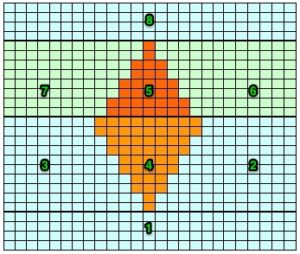





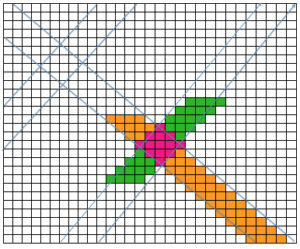
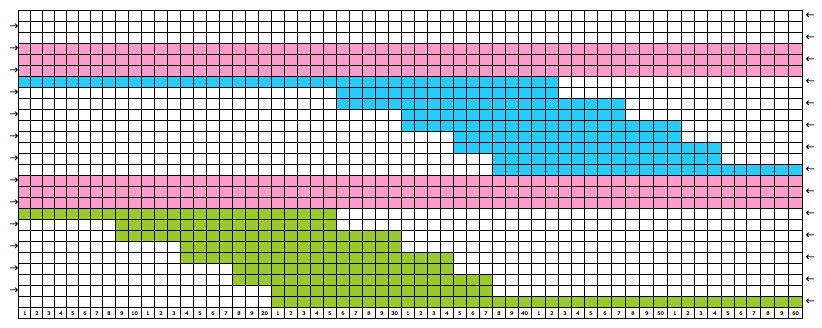
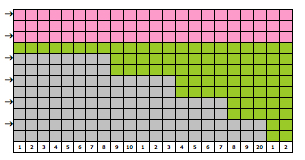
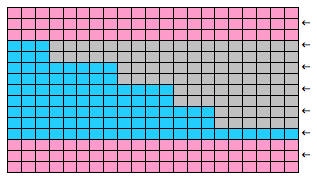


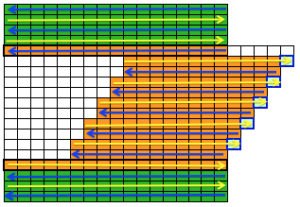
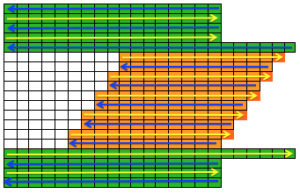
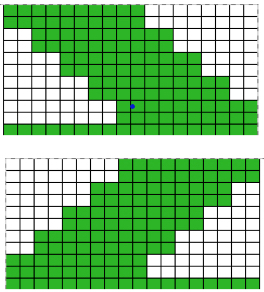
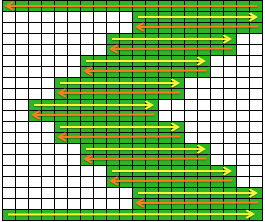
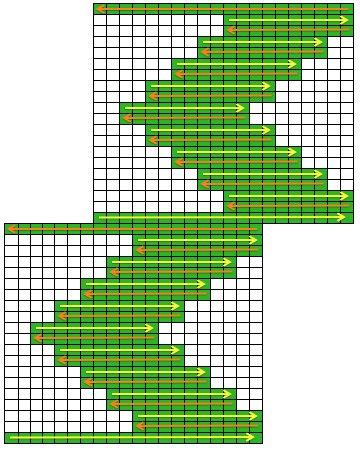

 The start of a smooth shaping sequence for those “leaf shapes” on the machine
The start of a smooth shaping sequence for those “leaf shapes” on the machine