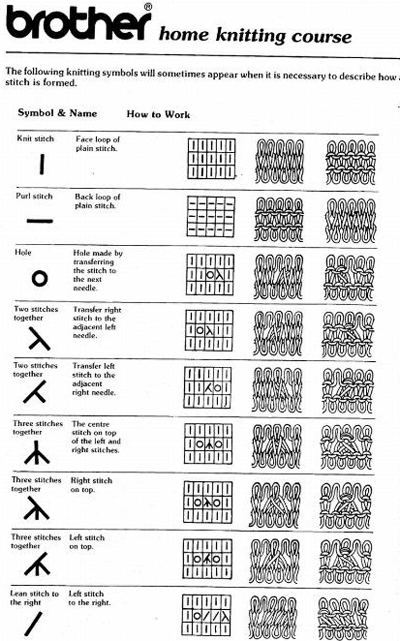
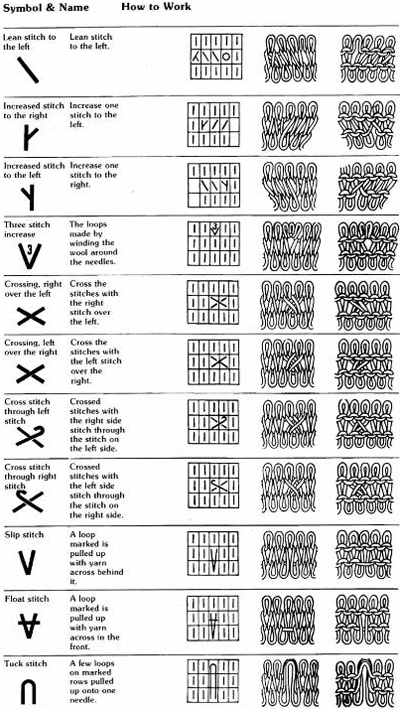
The topic of “those bubbles” has recently turned up again on Ravelry, where another forum member (Tanya /It makesyousmile) had come across a Russian video by Anna Kovin, with results that closely resembled those in the blue sweater and blankets pictured in my previous post, and poses a great solution for knitting the alternating, the same side knit and purl variants of the stitch. I knit my samples on my Passap, simply because I tend not to keep my ribber on my Brother machine. My production is on a single bed for most pieces in that gauge, and I find it easier to both see and work without the ribber on. That said, the method can work on any machine.
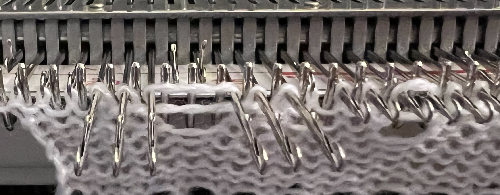
Drop stitch makes for a very loose, wide fabric, so casting on and binding off needs to accommodate that. I often will start with waste yarn, a loose first row, end the piece with a loose row. My bind-off is often around 2 gate pegs or more if needed, and rehanging the bottom and binding off, in the same manner, has top and bottom match. I did not do this in my swatch, and it is easy to see where some of the problems may be.
For swatching I chose to hang the comb with the first knit pass (open cast on trick) on the back bed (would be the main bed on Brother), using a multiple of 5 stitches, knit several rows, and then transferred in a 5/5 rib configuration, sorting out the proper tension for my yarn. I began with 5 stitches on the back bed (main bed in Japanese KM), transferred the next 5 to ribber, and repeated the process across the width of my fabric. The front bed/ ribber was set at half pitch when the pattern was about to start, with an extra needle on left. The portions of the bed that create the long stitches will essentially be knitting an every needle rib, so if point to point is used to make transfers easier, it needs to be changed back to proper pitch for the remainder of the knitting. The swatch does not address the best beginning and end of the fabric for any possible end-use
1. set up 5X5 rib, begin by leaving the first five needles on the main bed (passap back bed)
2. bring all main bed needles into work (ribber needles at this point will be 5 out of work, 5 in across bed)
3. knit 8 rows
4. drop off groups of 5 stitches on the main bed, begin with the second group of 5 from the left, moving across the bed (every needle rib section), pushing groups of needles out of work as they are emptied
5. bring all the ribber needles into work (main bed needles at this point will be 5 out of work, 5 in across bed)
6. knit 8 rows
7. now drop ribber stitches, 5 at a time, begin with first 5 on the left, and continue across the bed, pushing all the needles out of work as they are emptied
repeat the process, beginning with step 2, through 7
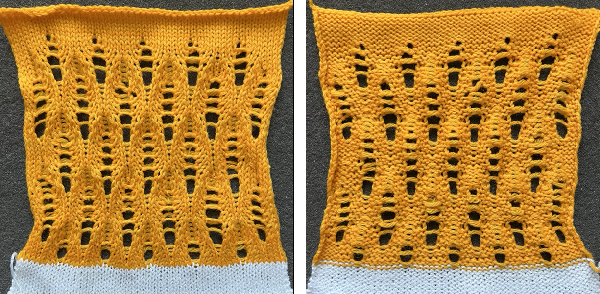
the relaxed fabric, the knit blocks alternating knit and purl

the same swatch, illustrating what happens when you press acrylic, and some of the problems to be sorted out in terms of the start and end of any piece in this type of fabric

my previous post
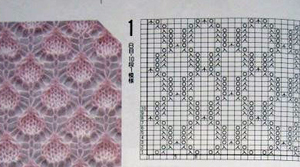
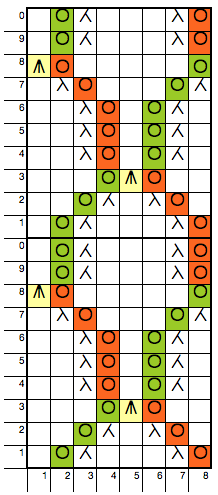
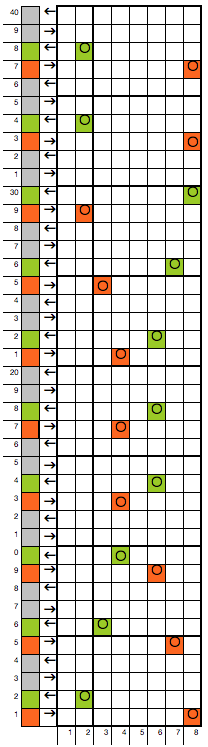
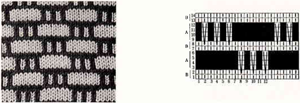
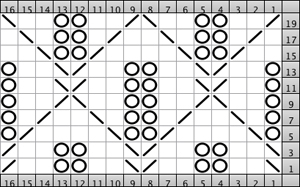
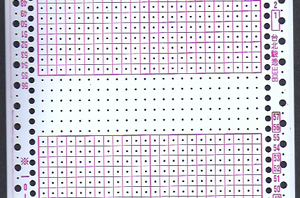
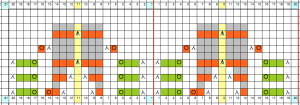
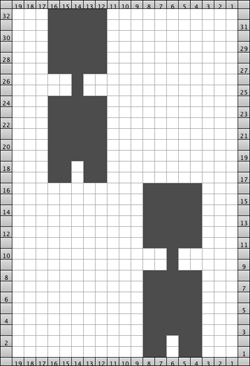
The Brother version, with aid of patterning for needle selection: this particular version of the fabric is actually created by rectangular blocks of every needle rib, with straight side edges. If one wanted recognizable shapes other than this circle illusion, then more hand manipulation would be needed. The chart below illustrates the repeats for my swatch (4 sts X 6 rs or 6 X 6 would be suitable for punchcard KMs). The solid squares represent every needle rib sections, where stitches will be dropped to create the larger ones.
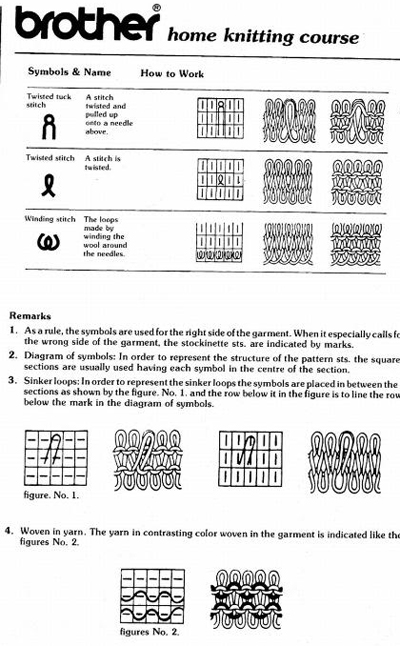
With the machine set to KC and no cam buttons in work, needles are selected, but no patterning occurs. “Air knitting” can help establish where on the needle bed the pattern repeats, and how to set up the needles and stitches to be in sync with selection as the work progresses.
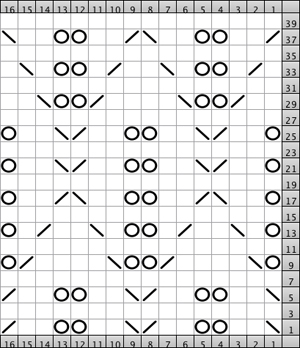
An alternative approach using this method begins with all needles on the main bed in use as opposed to ribber ones as in my Passap test. Once the sequence is understood starting points for creating full needle rib can be varied, as can selecting the first row from either side. For these swatches, I used a thinner yarn, in a bright color, which can help identify any issues in stitch formation, and I began the swatch in rib, to see the effect that might have as well.
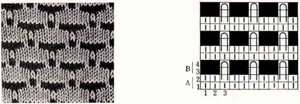
my amended repeat
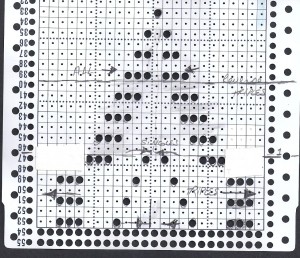
Begin by checking needle selection, set up rib as described at top of the post, beginning the first group of 5 stitches on left with selected needles, next group not selected, etc. If all the steps are repeated beginning on the same side of the KM it does not matter which block of needles are at the opposite end, allowing for width/gauge adjustment. I like to mark my needle bed with a water-soluble pen so I will be certain to have proper needles in work, not relying on memory or my sometimes “creative note keeping”.
CO ENR (every needle rib) set up with first needle on left in work on ribber, last on right on the main bed, racking at half-pitch: knit 1-row N/N, hang comb and weights, 2 rows circular (using opposite part buttons), follow with one row N/N
rack slightly to the right to make needle transfer easier, set up a multiple of 5 X 5 rib; begin with transferring first 5 on left down to ribber, pushing any empty ribber needles OOW; after the transfer, rack back to the original position so first ribber needle in work will once again be on left
bring all main bed needles into work (ribber needles at this point will be 5 in work, 5 out of work across the bed)
select your first pattern row, KC II (no end needle selection), continue to knit until needle selection changes so the second block from the left on the main bed is selected; nonselected needles on the main bed will now be dropped off, and those same emptied needles will be pushed completely out of work (the first group from left is the starting point here as well)
bring all needles into work on the ribber, knit until needle selection changes with all in main bed needles in B position, at that point I brought all remaining main bed empty needles between them out to hold/ D position in order to drop stitches on ribber between them, using the main bed as a guide, pushing any newly emptied ribber needles completely out of work as stitches were dropped (beginning with the second group of “5” from left)
as one physically looks at the stitches, there will actually be a count of six between MB needles, in my first sample, I dropped in series of 5, always beginning on the same left side.
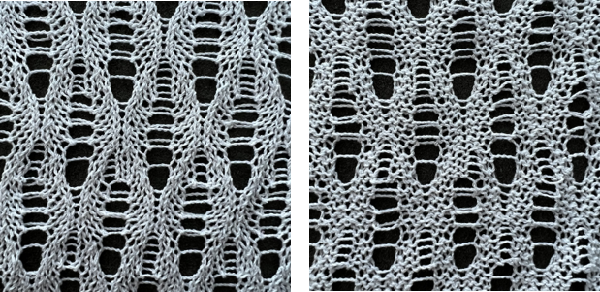
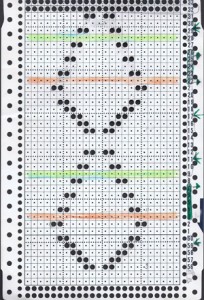
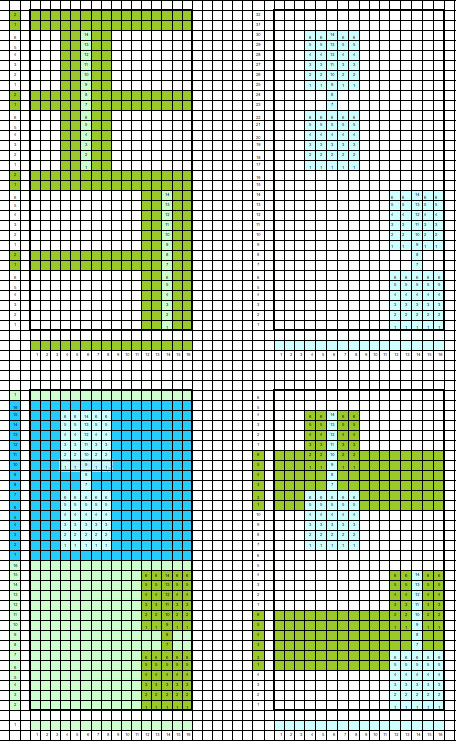
This swatch shows the resulting fabric. Of note is that one side (marked with red) is holding together along dropped stitches far better than on the right (marked in black), a desirable trait, and not as noticeable in the previous swatch knit on Passap, perhaps because of the difference in the weight of the yarn and stitch size
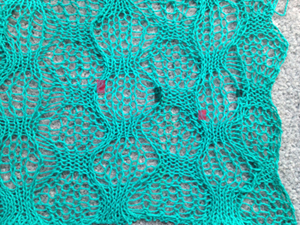
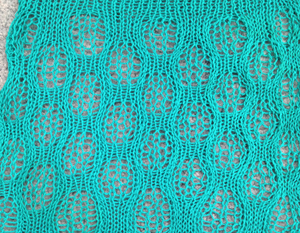
the result was much improved when only the center 4 of the 6 ribber stitches were dropped, producing a bit of a chain stitch on each side and with a better definition of dropped stitch areas; both sides of the fabric are shown below


at this point all main bed needles are in work, needle selection will once more begin on left; knit until needle selection changes, continue the sequence.
Cast on ENR rib edge has obvious width, bind off is around 2 gate pegs after transferring any remaining ribber stitches up to main bed.
The version of the stitch as worked out by Tanya Cunningham with her shared instructions for what she refers to as “bubble pops” may be found on Ravelry.
 1/21/2016: Online weaving program by Andrew Glassner ; associated blogpost
1/21/2016: Online weaving program by Andrew Glassner ; associated blogpost 

















 Assuming one uses a crochet cast on and binds off around gate pegs at the top, a chain is created at both ends, akin to that created in crochet, and one can identify a front loop, a back loop, and the whole chain. Any of the 3 may be “rehung” onto the KM, and the options are to knit a row and bind off again, or simply bind off again, for different looks that start to emulate single crochet a bit and can help stabilize edges or decorate them. It is helpful to keep notes as to the sequence used and which side is facing with each re-hanging. Audrey Palmer at one point authored the Empisal book of linked edgings ISBN 0969485905. Intended for use with the Empisal (later = Studio) linker, there are lots of interesting uses for combinations of essentially find off techniques, and some resurfaced when she published her books on knit weaving.
Assuming one uses a crochet cast on and binds off around gate pegs at the top, a chain is created at both ends, akin to that created in crochet, and one can identify a front loop, a back loop, and the whole chain. Any of the 3 may be “rehung” onto the KM, and the options are to knit a row and bind off again, or simply bind off again, for different looks that start to emulate single crochet a bit and can help stabilize edges or decorate them. It is helpful to keep notes as to the sequence used and which side is facing with each re-hanging. Audrey Palmer at one point authored the Empisal book of linked edgings ISBN 0969485905. Intended for use with the Empisal (later = Studio) linker, there are lots of interesting uses for combinations of essentially find off techniques, and some resurfaced when she published her books on knit weaving.