The latest Gimp update
2023: Threshold in version 2.10.34 is now disabled by default. To activate it or to add other tools ie curves to the tool menu, go to Gimp, Settings, and select Toolbox.
In the Tools Configuration Window, 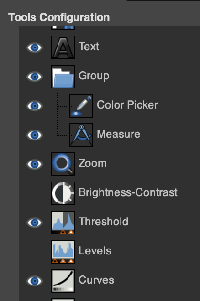 active tools have a common icon to their left, new ones may be selected and added, I chose Threshold and Curves. After clicking OK, a restart is not necessary, the new tools will appear immediately for use in the toolbox.
active tools have a common icon to their left, new ones may be selected and added, I chose Threshold and Curves. After clicking OK, a restart is not necessary, the new tools will appear immediately for use in the toolbox.  The curves tool enables editing for changing the color, brightness, contrast, or transparency of the active layer or a selection. While the Levels tool allows one to work on Shadows and Highlights, the Curves tool allows one to work in any range. It works on RGB images.
The curves tool enables editing for changing the color, brightness, contrast, or transparency of the active layer or a selection. While the Levels tool allows one to work on Shadows and Highlights, the Curves tool allows one to work in any range. It works on RGB images.
2022:The program now allows for setting pencil pixel sizes to odd and even numbers accurately, eliminating the need to save brushes for sizes missing in previous versions  See color exchange notes using the new Fuzzy select tool as opposed to using Color Exchange
See color exchange notes using the new Fuzzy select tool as opposed to using Color Exchange
Notes in post Numbers and GIMP: online punchcard patterns to electronics 2 contain information on printing punchcard designs to scale for tracing and marking cards prior to punching holes.  2021: Prior to attempting color separations of any sort, it is useful to have some understanding of how black and white pixels or punched holes relate to knit/ tuck/ slip setting stitch formation and their effect in both single and double bed techniques.
2021: Prior to attempting color separations of any sort, it is useful to have some understanding of how black and white pixels or punched holes relate to knit/ tuck/ slip setting stitch formation and their effect in both single and double bed techniques.
A recent post explored the use of layers for color separations in Gimp. It is a reliable, quick way to execute them, especially on large images. As is often found, the same results may be reached in a variety of ways.
Coupling the use of the shift key with rectangle selection and working in high magnification offers additional options in Gimp.
While working on any gridded and magnified design motif use the rectangle tool to select the rows that will be altered, make the first selection, and after doing so press and hold the shift key, continue to select specific areas, and then choose color invert in this first instance and the action will be applied to all selected areas. If working on parts of the image at a time repeat the steps until the whole image has been processed. Release the shift key when done. The image is set by clicking anywhere in the window outside of it.
In the past, I have used red pixels in an extra column beside the repeat to mark rows that need to be altered. The column is cropped prior to saving the final png for download to the km. The step is not a necessary one.
This is an illustration from another post, where color inversion was planned in the repeat selections, each of which is surrounded by dotted lines that will disappear after they are set. 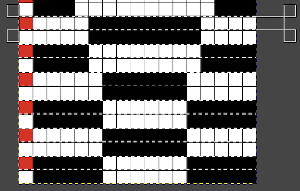 The red cells will change color as well after inversion, making it easier to track the placement of completed choices
The red cells will change color as well after inversion, making it easier to track the placement of completed choices  A result from using the method on a large image may be found in the post on fantasy fair-isle.
A result from using the method on a large image may be found in the post on fantasy fair-isle.
In the above, they are on what may be thought of as even-numbered rows of the design. If the plan is to use Cut to eliminate those same rows, the red cells need to be shifted down to “odd-numbered” rows. From a repeat in development for a drop stitch lace design 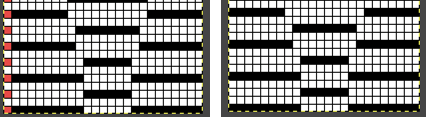 Working through the process with an easily recognized small shape, the often-used small triangle. Scaling in Gimp can become erratic while working on several files. Check that the interpolation is set to none if there appear to be odd scaling issues in the new image. When scaling in one direction only is intended, the chain link must be broken. At each step save the resulting png to make it available for further use ie additional scaling in height and width.
Working through the process with an easily recognized small shape, the often-used small triangle. Scaling in Gimp can become erratic while working on several files. Check that the interpolation is set to none if there appear to be odd scaling issues in the new image. When scaling in one direction only is intended, the chain link must be broken. At each step save the resulting png to make it available for further use ie additional scaling in height and width. 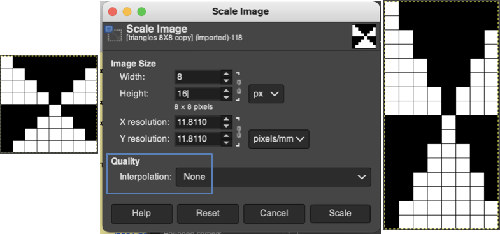
 The results with the selection of even rows simply shift the result up a row
The results with the selection of even rows simply shift the result up a row  Test in your version of the program to see whether releasing the shift key prior to making edits changes them. Either way, being consistent in the choice makes for less confusing results. Experimentation takes a matter of seconds.
Test in your version of the program to see whether releasing the shift key prior to making edits changes them. Either way, being consistent in the choice makes for less confusing results. Experimentation takes a matter of seconds.
Depending on your need the saved PNG may also be color reversed or scaled to double-length
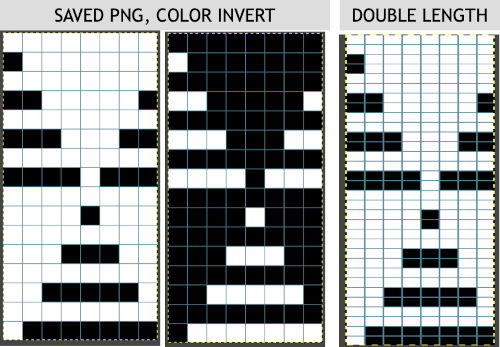 using the rectangle tool, either odd or even rows may be chosen, remaining consistent for the height of the repeat in a scale to suit the end fabric goal. Here the original file is lengthened X2
using the rectangle tool, either odd or even rows may be chosen, remaining consistent for the height of the repeat in a scale to suit the end fabric goal. Here the original file is lengthened X2
 working with the original file lengthened x4. The selections can happen on every row or every other, whether singly or in pairs. Note the difference between making the first selection on the first pair of rows or the second.
working with the original file lengthened x4. The selections can happen on every row or every other, whether singly or in pairs. Note the difference between making the first selection on the first pair of rows or the second. 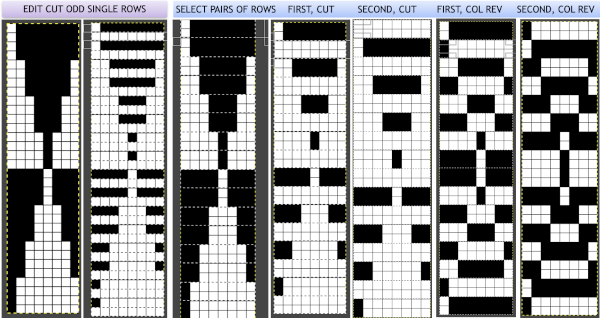 2021: Gimp update for Mac
2021: Gimp update for Mac
Supported OS: macOS 10.9 Mavericks or over, to run 2.10.24 in my new iMac, M1, OS12, needed the installation of Rosetta.  Rosetta 2 is an emulator designed to bridge the transition between Intel and Apple processors. In short, it translates apps built for Intel so they will run on Apple Silicon, more info
Rosetta 2 is an emulator designed to bridge the transition between Intel and Apple processors. In short, it translates apps built for Intel so they will run on Apple Silicon, more info
The previous post on this topic: 2019/10/07/gimp-update-for-mac/
I have been spending more time exploring version 10.22 and am becoming more familiar with new features and design options. There are slight variations in behaviors depending on the Mac OS version. Windows updates happen more frequently. GIMP 2.10.24 for Mac OS is now available.
Gimp has a wide range of paint tools 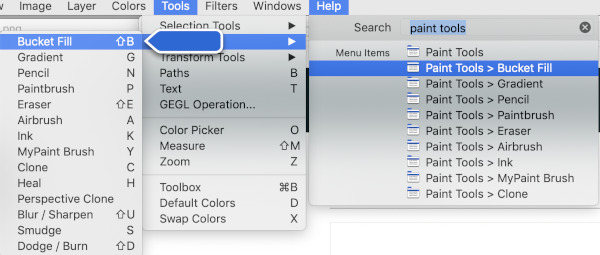 The most commonly used in creating repeats for knit designs are Pencil, Paintbrush, and Bucket Fill.
The most commonly used in creating repeats for knit designs are Pencil, Paintbrush, and Bucket Fill.
The Pencil tool is used to draw freehand lines with a hard edge. The main difference between it and the Paintbrush is that although both use the same type of brush, the pencil tool will not produce fuzzy edges.
Present experiments are placed in alphabetical order. Topics:
Brushes and patterns
Canvas resize, offset
Colors exchange
Colors threshold see grid options
Grid options, Guides, Color separations
Symmetry Painting
BRUSHES AND PATTERNS
There are many very good videos on using multiple versions of GIMP on Youtube. Most focus on working with very large images in huge numbers of colors, and brushes or patterns in the tutorials are often larger than the maximum stitch count on our home knitting machines capable of electronic download and with needle counts of 180-200. In addition, punchcard machines have a 24-pixel width repeat constraint. The content of such published material and tutorials can be overwhelming, but isolated techniques for the required binary bit-mapped knit scale are easy to sort out.
Many knitters designing small repeats use very simple programs and enter pixels singly or copy and paste in small groups. Some simple, quick functions in Gimp can simplify and speed up progress considerably. Punchcard knitters may use the same techniques to set up their 24 x X custom length repeats and tile the results to visualize how they line up when knitted in multiples.
Some content paraphrased from the online Gimp manual: in GIMP, a pattern is a small image used to fill areas by placing copies side by side. You can use them with the bucket fill tool. They vary in size and are used for filling regions by tiling, that is, by placing copies of the pattern side by side like ceramic tiles. A pattern is said to be tileable if copies of it can be adjoined left-edge-to-right-edge and top-edge-to-bottom-edge without creating obvious seams, such patterns are used in standard knitting repeats. The same effect may be obtained by using the Filter, Map, Tile option on the drawn image.
With the bucket fill tool, you can choose to fill a region with a pattern instead of a solid color. To make a pattern available, place it in one of the folders in GIMP’s pattern search path which includes two folders, the system patterns folder, which you should not use or alter, and the patterns folder inside your personal GIMP directory. The .gbr (“gimp brush”) format is used for ordinary and color brushes.
Photoshop ABR brushes are also easily imported for use.
Pressing the refresh button causes GIMP to rescan the folders in your pattern search path, adding any newly discovered patterns to the list. This button is useful if you add new patterns to a folder, and want to make them available without having to restart GIMP.
GIMP includes a set of 10 “paint tools”, which, except for the ink tool, use the same set of brushes. The brush pixmaps represent the marks that are made by single “touches” of the brush, which is desirable in working with knit scale bitmaps. Brushes can be selected by clicking on an icon in the brushes dialogue, the current brush is then shown in the Brush/Pattern/Gradient area of the Toolbox. Clicking on the brush symbol there is another way of activating the Brushes dialog.
When you use the Copy or Cut command on an image or a selection of it, a copy appears as a new brush in the upper left corner of the “Brushes” dialog. This brush will persist until you use the Copy command again. It disappears when you close GIMP.
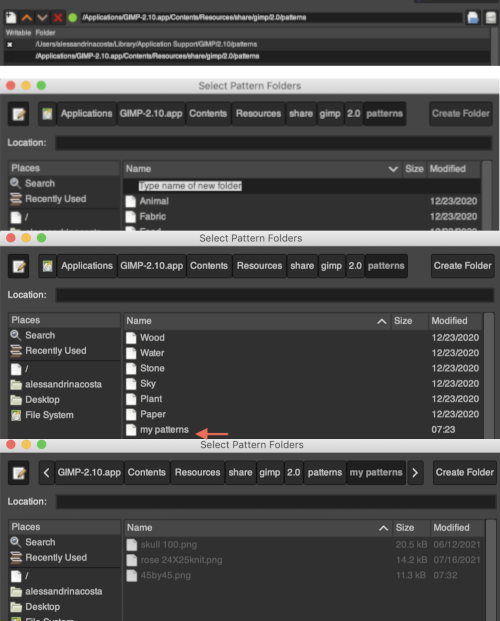
Building a personal brush pattern library on Mac: open software preferences  locate folders on the bottom left and click on the plus sign aside folders icon at the bottom left, it will change to a minus sign, and folders become visible
locate folders on the bottom left and click on the plus sign aside folders icon at the bottom left, it will change to a minus sign, and folders become visible  select brushes, two options will appear. If a proper choice is made for the addition of pattern files, a green button will appear
select brushes, two options will appear. If a proper choice is made for the addition of pattern files, a green button will appear  single click on the filing cabinet icon on the right,
single click on the filing cabinet icon on the right,  a familiar Mac finder window will appear
a familiar Mac finder window will appear  double click on the patterns folder, and its own window will appear,
double click on the patterns folder, and its own window will appear, 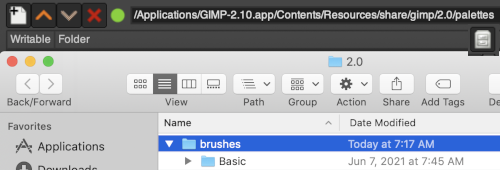 right-click in the window below the last entry, a smaller window appears, choose the add new folder option. It will appear as “untitled”
right-click in the window below the last entry, a smaller window appears, choose the add new folder option. It will appear as “untitled”  and will be added to the existing folders, rename it “my brushes” or any other choice,
and will be added to the existing folders, rename it “my brushes” or any other choice,  and the new folder will be added within the brushes one
and the new folder will be added within the brushes one  Its place in the brushes list will be determined by its initial letter, the contents are in alphabetical order.
Its place in the brushes list will be determined by its initial letter, the contents are in alphabetical order. 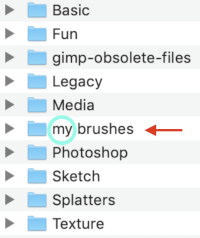 For future use, any saved brush may be dragged and dropped into the named personal pattern folder icon, or into the folder after it has been expanded or opened in its own window. My opened brush folder
For future use, any saved brush may be dragged and dropped into the named personal pattern folder icon, or into the folder after it has been expanded or opened in its own window. My opened brush folder 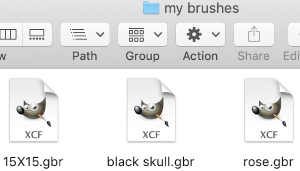 After brushes are added, the refresh button below the brush dockable dialogue may bring them up without having to restart the program.
After brushes are added, the refresh button below the brush dockable dialogue may bring them up without having to restart the program. After saving these 3 images as .gbr files and placing them in the appropriate folder
After saving these 3 images as .gbr files and placing them in the appropriate folder 
 they appear as available for use
they appear as available for use  To install .abr files on Mac:
To install .abr files on Mac:
create a new Photoshop folder within the Gimp Brushes one
Download the chosen files, drag and drop the images or folder from the downloads folder into the chosen Gimp one, they will be available after a Gimp restart
The free files I tested were very large in size, did not scale down to use for knitting cleanly, and even though they appeared to be BW they opened as RGBs making the conversion to BW indexed quite dithered. They are composed of assorted leaves and snowflakes.  When exporting self-drawn brushes, the option is offered for adding spacing surrounding the shape, here a 10% addition was chosen
When exporting self-drawn brushes, the option is offered for adding spacing surrounding the shape, here a 10% addition was chosen 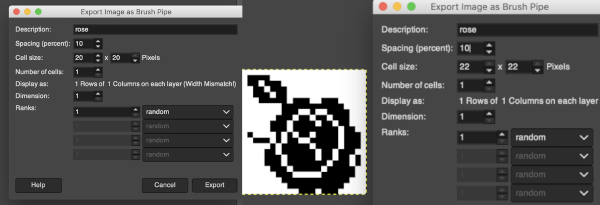 Patterns may be saved in a similar way. Since GIMP 2.2 you can use .png, .jpg, .bmp, .gif, or .tiff files as patterns.
Patterns may be saved in a similar way. Since GIMP 2.2 you can use .png, .jpg, .bmp, .gif, or .tiff files as patterns.
Saving patterns from large to tiny may be achieved using the same method as in saving brushes.  To save personal patterns, instead of choosing the file cabinet icon in preferences, one may choose the folder icon, following a similar series of steps to those above, including verifying the contents of the newly created folder
To save personal patterns, instead of choosing the file cabinet icon in preferences, one may choose the folder icon, following a similar series of steps to those above, including verifying the contents of the newly created folder 
 Use Windows, Dockable Dialogues, choose Pattern. The patterns will show on the right of the Gimp window and are viewable once you click on the fill window below the tools on the left as well.
Use Windows, Dockable Dialogues, choose Pattern. The patterns will show on the right of the Gimp window and are viewable once you click on the fill window below the tools on the left as well.
Open the image to be filled
Click on the paint bucket tool, and select the Pattern fill type.  Click on the paint bucket, then on the pattern you wish to use on right, hover over the canvas with the paint tool, click on it and the image will fill in the chosen pattern.
Click on the paint bucket, then on the pattern you wish to use on right, hover over the canvas with the paint tool, click on it and the image will fill in the chosen pattern.
Or click on the pattern icon, scroll through to the desired pattern, click on it, then on the paint bucket tool, hover over the canvas with the paint tool, and click on it to fill. 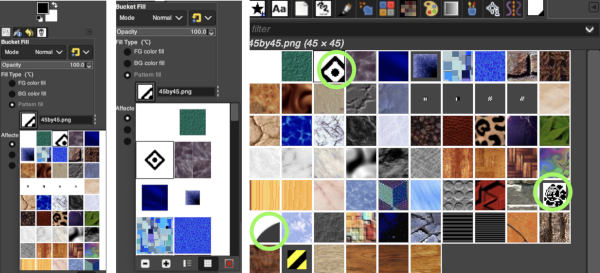 The + or _ option scales the size of the pattern view, it is handy when tiny or very large repeats are chosen. The canvas for the pattern fill needs to be large enough to accommodate the pattern in repeat.
The + or _ option scales the size of the pattern view, it is handy when tiny or very large repeats are chosen. The canvas for the pattern fill needs to be large enough to accommodate the pattern in repeat.
If the fill fails, check to see that the bucket fill mode was not somehow changed from normal to one of the many other options  Here the skull is used to fill a 400X400 canvas, an even multiple of its size
Here the skull is used to fill a 400X400 canvas, an even multiple of its size 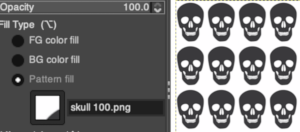 If the canvas is not in a full multiple of the whole pattern, part of the repeat is cropped
If the canvas is not in a full multiple of the whole pattern, part of the repeat is cropped  Using the same rose image tiled using the Filter, Map, Tile menu produces similar results when full multiples of the image pixels are not chosen, ie. here the tiling is on an 80-pixel wide canvas as opposed to a full multiple of 25 ie 100
Using the same rose image tiled using the Filter, Map, Tile menu produces similar results when full multiples of the image pixels are not chosen, ie. here the tiling is on an 80-pixel wide canvas as opposed to a full multiple of 25 ie 100  Designing tiny repeats:
Designing tiny repeats:
Begin with the image in black-and-white indexed mode.
To draw my repeats, I used 1800X magnification, with grid view, exported the files as png, and dragged them into my own Gimp patterns folder.
If the goal is full punchcard repeat illustrations, then by default the width of the image to be filled needs to be 24 pixels wide, and a minimum of 36 rows high. If working as a tuck stitch, punched squares are black pixels, and unpunched squares the white, creating the tucked loops. Using the bucket tool to fill the image is accomplished with a simple, very quick stroke  The rectangle tool may be used to isolate a segment of the first repeat and the area may then be filled with a different pattern.
The rectangle tool may be used to isolate a segment of the first repeat and the area may then be filled with a different pattern. 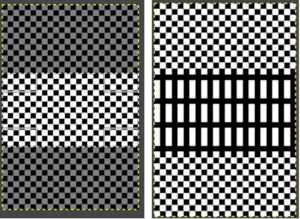 Brushes may be resized as needed, and pasted on the previously filled image, and guides are helpful in their placement.
Brushes may be resized as needed, and pasted on the previously filled image, and guides are helpful in their placement.  added info on pattern fill in Gimp 4, pattern fill, dithered portraits, and more
added info on pattern fill in Gimp 4, pattern fill, dithered portraits, and more
Canvas resize, offset: working with a 20X20 black and white pixel star  Extra grid rows or columns may be added in a variety of ways to an existing motif including using these menu options
Extra grid rows or columns may be added in a variety of ways to an existing motif including using these menu options  These images illustrate only some of the possibilities. The chain link is used broken
These images illustrate only some of the possibilities. The chain link is used broken with the exception of when placing the star centered onto the new canvas or when moving it for manual placement onto it. Use Layers choices: resize all visible layers, fill with white. With the new canvas width equal to that of the image, the 10 desired new rows may be added to either the top or the bottom of the file respectively by entering that number in the space for the offset X or Y values, and the resulting new files are shown gridded on the bottom right.
with the exception of when placing the star centered onto the new canvas or when moving it for manual placement onto it. Use Layers choices: resize all visible layers, fill with white. With the new canvas width equal to that of the image, the 10 desired new rows may be added to either the top or the bottom of the file respectively by entering that number in the space for the offset X or Y values, and the resulting new files are shown gridded on the bottom right. 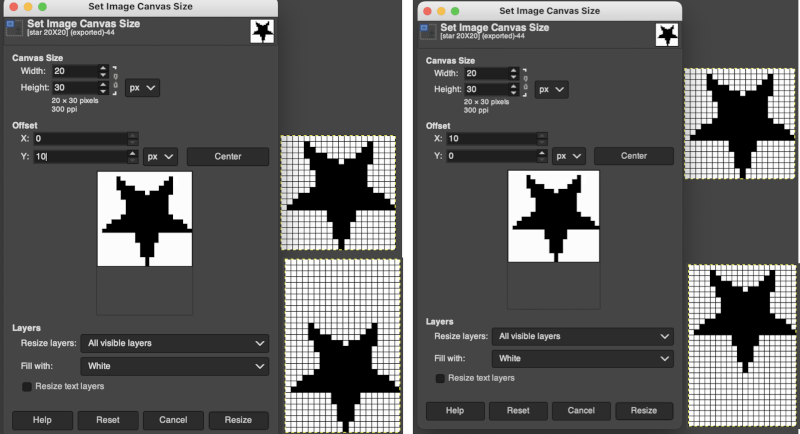 When choosing the center offset with the chain link intact, the X and Y values will be changed from 0 to 10 in this case by the program based on the new canvas size. To add cells only on the left, the chain link is broken again, and the X offset value is set accordingly.
When choosing the center offset with the chain link intact, the X and Y values will be changed from 0 to 10 in this case by the program based on the new canvas size. To add cells only on the left, the chain link is broken again, and the X offset value is set accordingly. 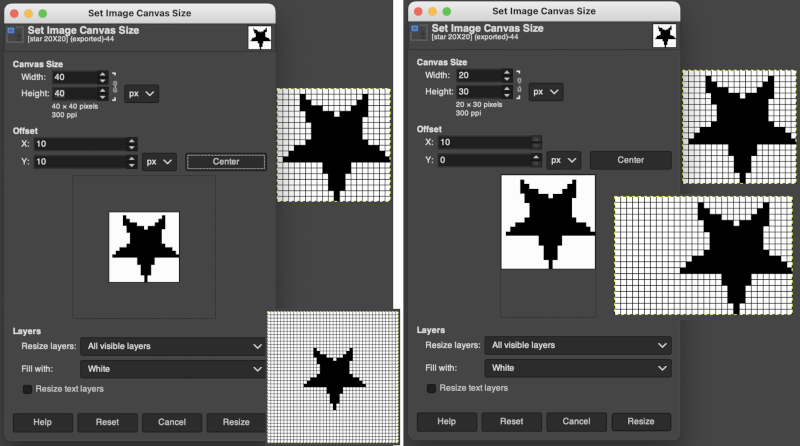 Adding 10 cells to the right, 0 offset selection
Adding 10 cells to the right, 0 offset selection 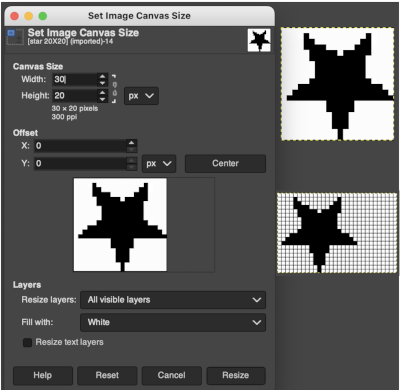 It is possible to guide the placement of the motif onto the new canvas in any position. There will not be any visible grid as a guide, so a bit of math planning ahead for the new canvas size will fine-tune the possible placement. Again, the chain link is broken. Choose the center option but before selecting resize, click on the image, drag it to its new location, then select resize. The grid can then in turn be made visible.
It is possible to guide the placement of the motif onto the new canvas in any position. There will not be any visible grid as a guide, so a bit of math planning ahead for the new canvas size will fine-tune the possible placement. Again, the chain link is broken. Choose the center option but before selecting resize, click on the image, drag it to its new location, then select resize. The grid can then in turn be made visible.
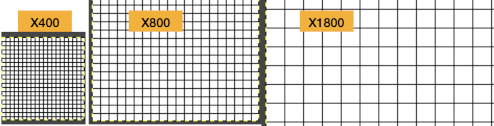
Any of these steps may be undone, adjusted, and repeated as needed. 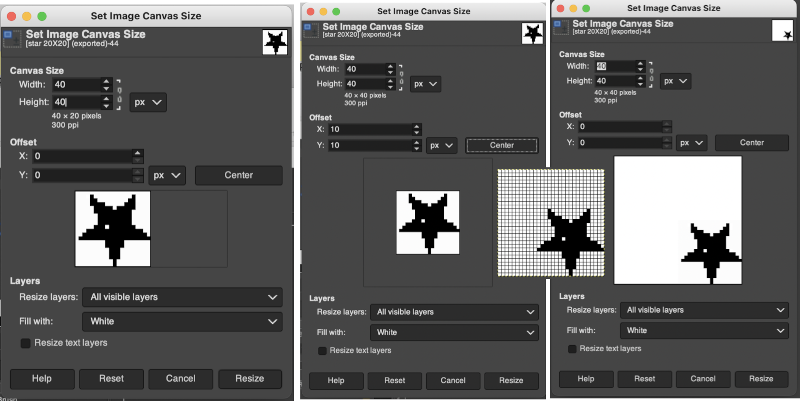 Grids and Guides: my view was magnified X 2800, and the canvas measured 24 X 36 pixels.
Grids and Guides: my view was magnified X 2800, and the canvas measured 24 X 36 pixels.
Magnification may be set using the pull-down below the image window, where any number listed may be chosen or typed in and set by hitting the return key, or by choosing the zoom tool. Click only on the image, and the zoom is applied to the whole image. If the pointer is used, click and drag the mouse pointer to create a zoom rectangle. The biggest dimension of the rectangle will correspond to the size of the image window. You can get to the Zoom Tool from the Image menu through , or by clicking the magnifying glass in the toolbox 
 Anyone needing an adjustable grid superimposed on an existing image may use the Configure Grid command to set the properties of the grid and display it over the image while working on it.
Anyone needing an adjustable grid superimposed on an existing image may use the Configure Grid command to set the properties of the grid and display it over the image while working on it.
One can choose the color of the gridlines, and the spacing and offsets from the origin of the image, independently for the horizontal and vertical grid lines. The configure grid dialogue:  The five different grid styles:
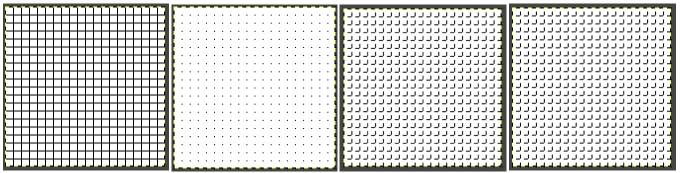
The five different grid styles: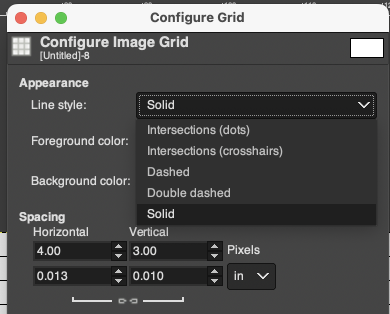 Intersections, dots: the least visible, a simple dot at each intersection of the grid lines.
Intersections, dots: the least visible, a simple dot at each intersection of the grid lines.  Intersections, crosshairs: a plus-shaped crosshair at each intersection of the grid lines
Intersections, crosshairs: a plus-shaped crosshair at each intersection of the grid lines  Dashed: dashed lines in the foreground color of the grid
Dashed: dashed lines in the foreground color of the grid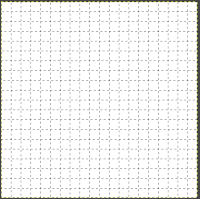 Double dashed: dashed lines, where the foreground and background colors of the grid alternate, look the same as above when the image is in BW indexed mode. It is also hard to discern the separate colors in RGB mode because the dashes are so small and so close together,
Double dashed: dashed lines, where the foreground and background colors of the grid alternate, look the same as above when the image is in BW indexed mode. It is also hard to discern the separate colors in RGB mode because the dashes are so small and so close together, 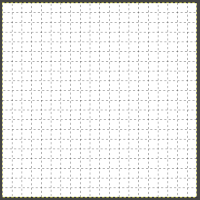 Solid: shows solid grid lines in the foreground color of the grid
Solid: shows solid grid lines in the foreground color of the grid  Foreground and Background colors: in RGB Mode, click on the foreground color to select a new color for the grid, click OK
Foreground and Background colors: in RGB Mode, click on the foreground color to select a new color for the grid, click OK 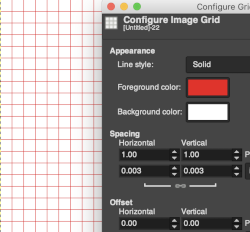
 Spacing: for use illustrations see GRIDS: OPTIONS
Spacing: for use illustrations see GRIDS: OPTIONS
Width and height: select the cell size of the grid and the unit of measurement
Offset: moves the origin of the first cell, by the fault the grid begins at the coordinate origin, 0,0
The command enables and disables Snap to Grid. When snap to grid is enabled, and a selection is moved or placed, the grid points pull on it when it approaches making accurate placement easier. If the magnification is high enough, the placement of your pencil or brush will be outlined in a dotted line. Here the snap to the area for a 3-pixel pencil is shown highlighting its possible placement location. 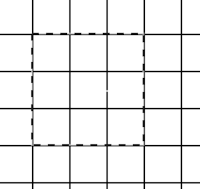 This command is found in the image menubar through , .
This command is found in the image menubar through , .
The question has been asked in forums again as to how to place knit designs other than on a square grid. If retaining the aspect ratio matters, any image used for download can be scaled in height or width after it is drawn, or even after download depending on the software used.
If the intent is to illustrate the design on a knit-stitch rectangular grid, one may choose to configure the grid for any single image, or for permanent use.
For a permanent change, the default size may be set by changing user preferences, as seen here for a 1X1 pixel grid. 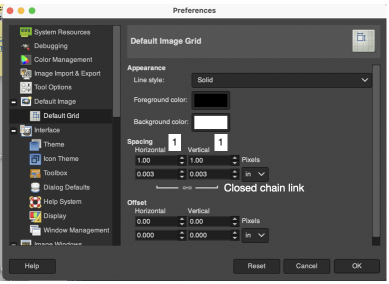 To change results on any single work file use Image, and Configure Grid values to the desired ones.
To change results on any single work file use Image, and Configure Grid values to the desired ones. 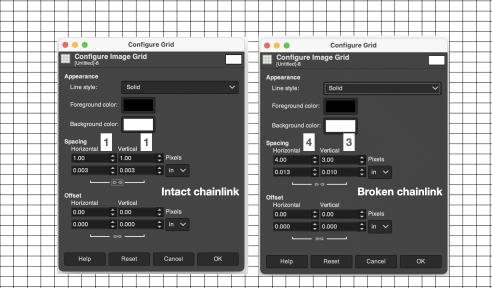 Configuration options for line styles include solid, as shown above.
Configuration options for line styles include solid, as shown above.
GUIDES: to configure guides, you can go to Image>Guides>New Guide by Percent, or simply click on one of the rulers in the image window and pull out a guide while holding the mouse Left Button pressed. The guide is then displayed as a blue, dashed line, which follows the pointer. As soon as you create a guide, the “Move” tool is activated and the mouse pointer changes to the Move icon. Releasing the mouse will place it. 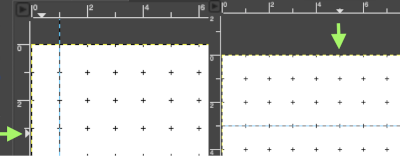 As soon as a guide is created, the “Move” tool is activated and the mouse pointer changes to the Move icon.
As soon as a guide is created, the “Move” tool is activated and the mouse pointer changes to the Move icon.
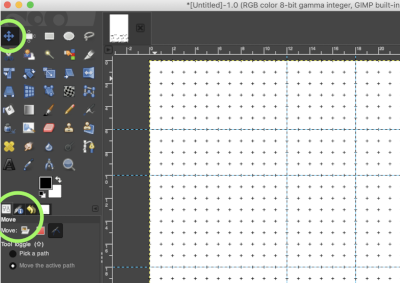 You can create as many guides as you like, positioned wherever you like. If the grid is set to a 1X1 square pixel default with a line border, at any point the Image, Configure, Grid option may be used to change the ground view
You can create as many guides as you like, positioned wherever you like. If the grid is set to a 1X1 square pixel default with a line border, at any point the Image, Configure, Grid option may be used to change the ground view 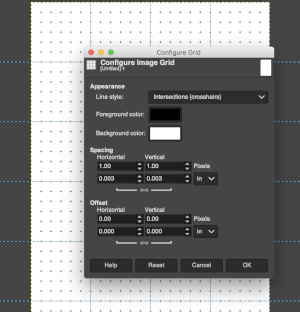 To move a guide, activate the Move tool in the Toolbox, then click on the guide (it will turn red), and drag it to a new location. Click and drag the intersection of two guides to move them together.
To move a guide, activate the Move tool in the Toolbox, then click on the guide (it will turn red), and drag it to a new location. Click and drag the intersection of two guides to move them together. 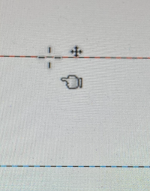 Create as many guides as needed, positioned appropriately for the design. To delete a guide, simply drag it outside the image.
Create as many guides as needed, positioned appropriately for the design. To delete a guide, simply drag it outside the image.
Holding down the Shift key moves everything but a guide, using the guides as an effective alignment aid.
As with the grid, you can cause the pointer to snap to nearby guides, by toggling View, Snap to Guides in the image menu. If you have a number of guides and they are making it difficult for you to judge the image properly, you can hide them by toggling View Show Guides.
You can remove all the guides using the Image, Guides, and Remove all Guides command.
Working on punchcard repeats whether in designing for cards or creating a BMP or PNG for electronic download using a published repeat, guides may be set to outline 6X6 blocks as seen in factory-issued Brother punchcards, or to create custom templates. For example, lace designs have few pixels. Horizontal guides may be added or moved at intervals between repeat segments, making certain the two knit rows are left blank as one continues entering the proper pixels. The vertical guides help in orienting and locating the pixels in design blocks to match the source. 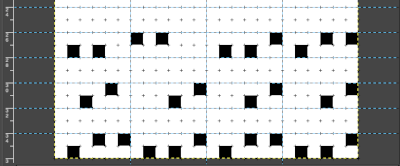 With guides in place, pattern fill may be used, adding shapes using the tools, or brushes to place motifs.
With guides in place, pattern fill may be used, adding shapes using the tools, or brushes to place motifs. 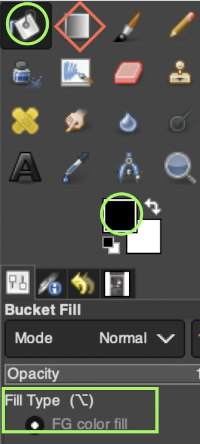 A sample of a knit repeat using the rectangle tool and the paint bucket tool combination to create filled rectangles placed in relationship to guides, creating a tuck pattern with interspersed plain knit rectangular shapes
A sample of a knit repeat using the rectangle tool and the paint bucket tool combination to create filled rectangles placed in relationship to guides, creating a tuck pattern with interspersed plain knit rectangular shapes 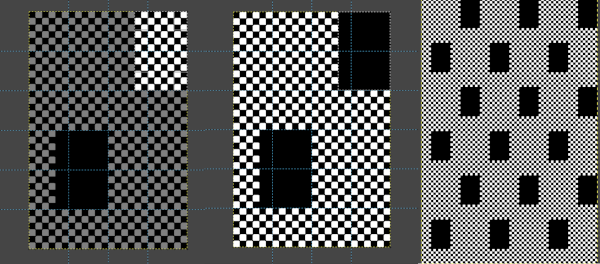 Built-in or custom brushes may be superimposed on a bucket-filled ground. Create an image in the desired width and height, here 24 X 24, and magnify at least X 800 for a grid view.
Built-in or custom brushes may be superimposed on a bucket-filled ground. Create an image in the desired width and height, here 24 X 24, and magnify at least X 800 for a grid view.
Fill with a pattern.
Place the chosen brush on the patterned ground, adjust the size and placement of the brush until satisfied, and save the image.
Consider the end-use for the pattern. For example, the designs below left would be suitable for tuck stitch, the same designs would need to be color reversed if the plan is to use them to knit thread lace. 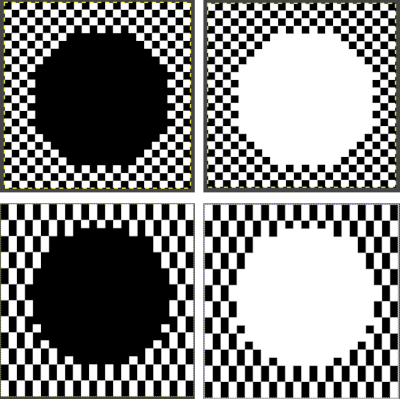 Both the original and the new image should be set to BW-indexed mode. Developing a brick version of the repeat is easy and quick. With the original image open, create a new image with the same width but twice its height, 24X48.
Both the original and the new image should be set to BW-indexed mode. Developing a brick version of the repeat is easy and quick. With the original image open, create a new image with the same width but twice its height, 24X48.
Set the magnification for both images to the same number, adjusting the number of both if needed so the longer canvas is in full view.
Configure the grid as preferred on the new image, and make it visible. Snap to grid is useful, but may not be necessary when working on such a scale.
Copy the full starting image and paste it onto the bottom of the new one.
Guides may be put in place to adjust for the pattern shift in the top half of the new image. A single, center guide, in this case, was sufficient.
If the full image copy is still available, align and paste it again, its left side to the right of the center guide, and anchor it.
Paste its right side to the left of the center guide and anchor that in place also. Undo and repeat steps if needed.
Check the alignment of the full repeat by map tiling, if satisfied, export it as PNG or BMP for future download. 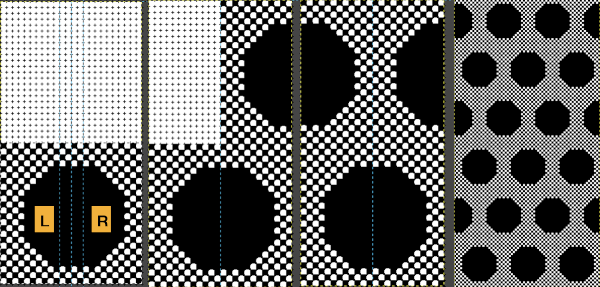 COLOR EXCHANGE 2022 Gimp update offers a selective way to exchange colors using the fuzzy-select or select-by-color tool. The bucket-fill color works differently in some ways from previous Gimp versions.
COLOR EXCHANGE 2022 Gimp update offers a selective way to exchange colors using the fuzzy-select or select-by-color tool. The bucket-fill color works differently in some ways from previous Gimp versions.  Fuzzy-select will change any contained segment of an image in RGB Mode. Make the selection of the area to be changed, it will become surrounded by a dotted line. Choose bucket fill, change the foreground color to the new one, and click on the outlined area, to the new color. Click on the rectangle tool and then anywhere in the work window to set the image and save it.
Fuzzy-select will change any contained segment of an image in RGB Mode. Make the selection of the area to be changed, it will become surrounded by a dotted line. Choose bucket fill, change the foreground color to the new one, and click on the outlined area, to the new color. Click on the rectangle tool and then anywhere in the work window to set the image and save it. 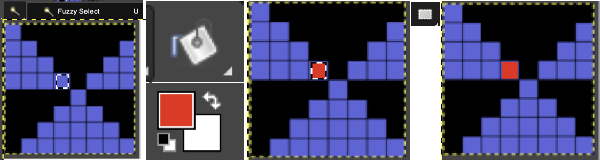 Multiple color exchanges in the same image.
Multiple color exchanges in the same image.  Edit, and undo can be used to trace steps backward at any point.
Edit, and undo can be used to trace steps backward at any point.
Using select by color will select all areas containing that color, making global edits, 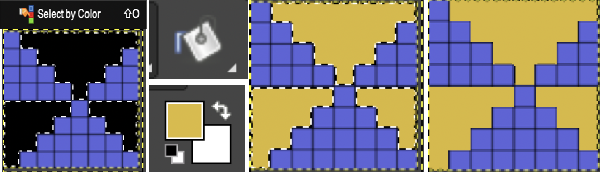 the process may be repeated within bordered segments, retaining their outlines.
the process may be repeated within bordered segments, retaining their outlines.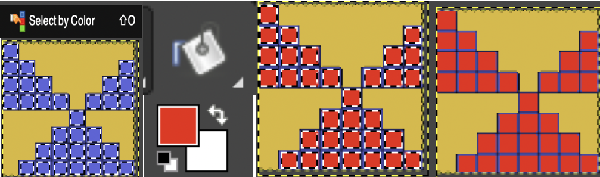 2023 version 2.10.34 use the shift key to fill by color, and the simple bucket fill tool once more to fill in any single, outlined areas
2023 version 2.10.34 use the shift key to fill by color, and the simple bucket fill tool once more to fill in any single, outlined areas
To change color in a solid background, as an alternative to using bucket fill, simply click on the associated icon, drag the desired foreground shade onto the ground, and release the mouse  COLORS EXCHANGE older version
COLORS EXCHANGE older version
Color exchanges to test designs in different colorways may be made easily and quickly using the program. To test the concept begin with a simple repeat already tested for tiling originally saved in indexed black and white colors
 This icon shows the default foreground and background colors
This icon shows the default foreground and background colors  Black is the foreground color, and white is the background.
Black is the foreground color, and white is the background.
Using such small images I often work with 800X magnification. Open the image, choose sizing, scaling, or magnification if necessary, convert to RGB mode then from the Colors menu choose Map, Color Exchange. 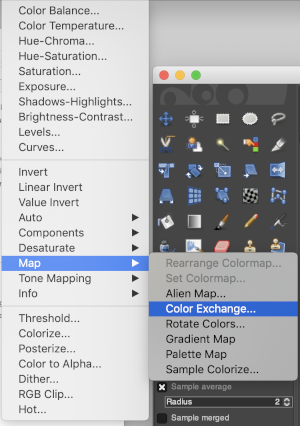 The color exchange window will appear. Here the white “from color” is left undisturbed. Select the dropper next to the “to color”, then click on the image on the color you wish to change, a palette window will appear. Make your choice, the color exchange window will now have substituted the chosen color for black, click OK, and white design areas are now changed to the chosen blue globally.
The color exchange window will appear. Here the white “from color” is left undisturbed. Select the dropper next to the “to color”, then click on the image on the color you wish to change, a palette window will appear. Make your choice, the color exchange window will now have substituted the chosen color for black, click OK, and white design areas are now changed to the chosen blue globally. 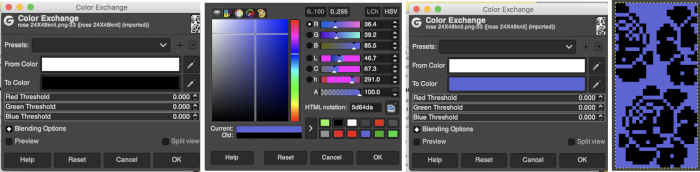 The process may then be repeated with the second color if desired. The color exchange window will show white as the default “from color”. Click on the white bar, choose black from the palette window or use the dropper to select black from the image. The from color will then appear as black. Repeat selection with the dropper from the right of the “to color” bar on any black pixels in the image, choose the color from the palette window to replace it, and the color exchange window will display the new “to color”. Click OK, and job done.
The process may then be repeated with the second color if desired. The color exchange window will show white as the default “from color”. Click on the white bar, choose black from the palette window or use the dropper to select black from the image. The from color will then appear as black. Repeat selection with the dropper from the right of the “to color” bar on any black pixels in the image, choose the color from the palette window to replace it, and the color exchange window will display the new “to color”. Click OK, and job done. 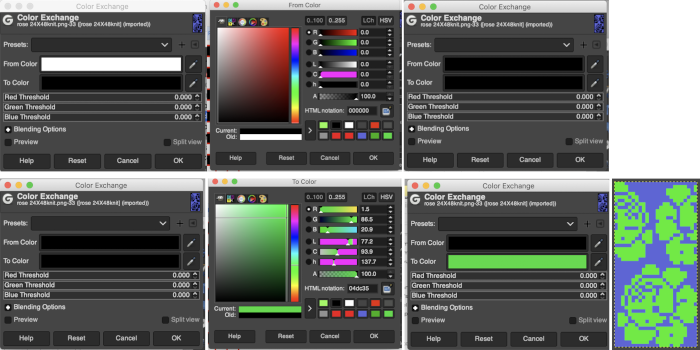 The process may be repeated multiple times on the same design or used on large-scale ones, giving one some idea as to whether or not to really commit to the estimated colors.
The process may be repeated multiple times on the same design or used on large-scale ones, giving one some idea as to whether or not to really commit to the estimated colors. 
 I recently had reason to review old PC files from my Passap knitting days and came across several cut files that when converted to png format appeared in colors rather than black and white, leading me to experiment with color exchange again. The image for the first experiment is part of a crib blanket by Cheryl Giles
I recently had reason to review old PC files from my Passap knitting days and came across several cut files that when converted to png format appeared in colors rather than black and white, leading me to experiment with color exchange again. The image for the first experiment is part of a crib blanket by Cheryl Giles The process: do not alter the original image ie. by resizing, which seems to change the color mapping responses
The process: do not alter the original image ie. by resizing, which seems to change the color mapping responses
load the image in RGB mode
working with the foreground color, click once on the white,  use the color picker to choose a color, in this case, orange, a palette window will appear,
use the color picker to choose a color, in this case, orange, a palette window will appear,  click OK, and the background color will change accordingly,
click OK, and the background color will change accordingly,  double click on the now orange background to call up its palette window, keep that window open, go to colors filter, map, color exchange
double click on the now orange background to call up its palette window, keep that window open, go to colors filter, map, color exchange
double click on the from color, the white, in the exchange window
match its values to the saved palette window working from the top down, you may find some of the remaining numbers self-correct
in the original image orange, is now exchanged for black 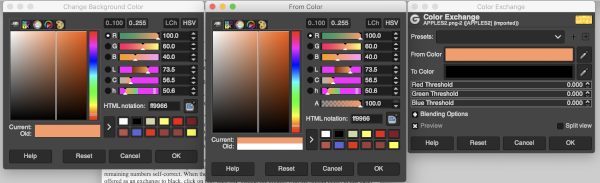
 continue, repeating the process with the alternate color, in this case, yellow. At that point, the in-process image will appear as solid black. Click on the black in the exchange window to color twice, choose white from the palette selection, click OK, and the conversion is complete.
continue, repeating the process with the alternate color, in this case, yellow. At that point, the in-process image will appear as solid black. Click on the black in the exchange window to color twice, choose white from the palette selection, click OK, and the conversion is complete. 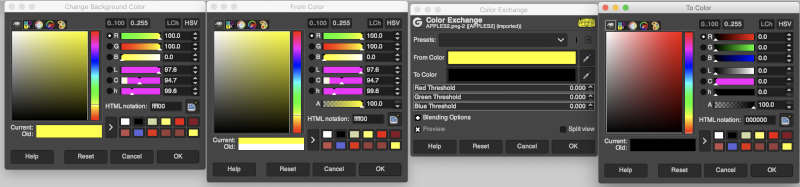
 It is possible to colorize images originally drawn in black and white. The color exchange options will remain fixed throughout the process. The image may be worked on continuously and exported when color exchanges are completed, or saved and imported again after each step. The color exchange here happens consistently on the chosen background color, changing that quickly becomes familiar and easy. There are times that the repeat being processed will turn black onscreen, trust in the process and continue.
It is possible to colorize images originally drawn in black and white. The color exchange options will remain fixed throughout the process. The image may be worked on continuously and exported when color exchanges are completed, or saved and imported again after each step. The color exchange here happens consistently on the chosen background color, changing that quickly becomes familiar and easy. There are times that the repeat being processed will turn black onscreen, trust in the process and continue.
The default color exchange window using color options in the default palette.  The steps for changing the background to red: the image will turn black as you work, click on the TO color selection to pick a color from the default palette to replace the white, in this case, the red,
The steps for changing the background to red: the image will turn black as you work, click on the TO color selection to pick a color from the default palette to replace the white, in this case, the red, 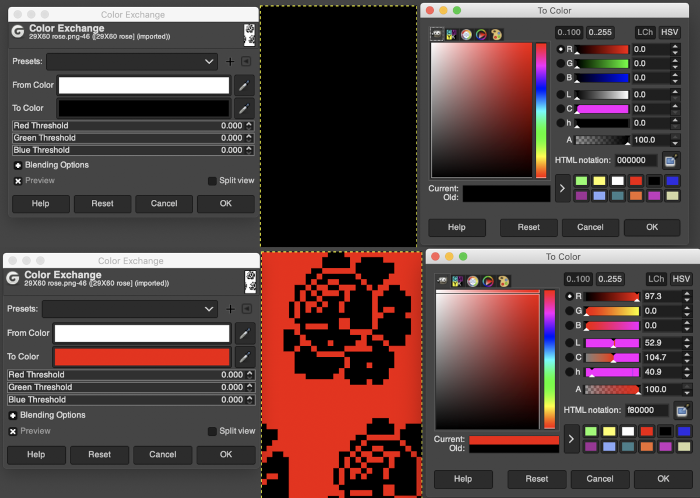 you can click OK, but do not close this last window if you want to continue, the color change will be lost
you can click OK, but do not close this last window if you want to continue, the color change will be lost 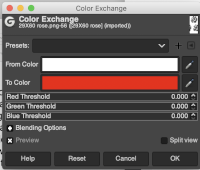 Changing the black to white in summary
Changing the black to white in summary 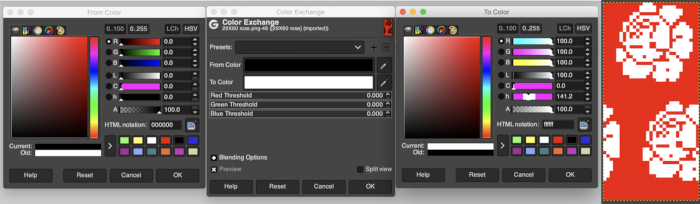 Export the image. The transitions:
Export the image. The transitions:  Developing custom palettes in order to visualize different colorways while using the same repeat:
Developing custom palettes in order to visualize different colorways while using the same repeat:
load the image, right-click on the paintbrush icon, and choose palette editor, 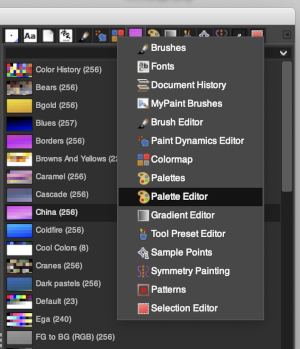 this window will open with selections for possible palette choices
this window will open with selections for possible palette choices  click on your choice, then click on the palette icon, and your color choices will appear, click on the white, to create a new background color.
click on your choice, then click on the palette icon, and your color choices will appear, click on the white, to create a new background color.  It will change it to the chosen value in this window when you click on that.
It will change it to the chosen value in this window when you click on that. 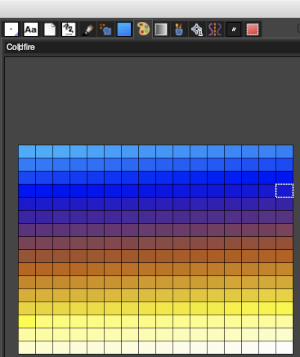 The new color choices appear in the palette in the future unless a choice is made using resetting it to the original. Two selections may be made for new colors at the same time, but the map, color exchange option will continue to work on the background color only. These were my choices for added colors.
The new color choices appear in the palette in the future unless a choice is made using resetting it to the original. Two selections may be made for new colors at the same time, but the map, color exchange option will continue to work on the background color only. These were my choices for added colors. 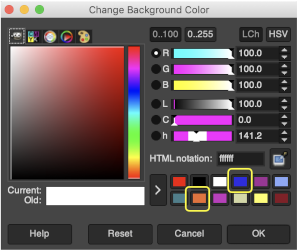 Continuing to work with color changes, changing the white in the BW repeat to blue
Continuing to work with color changes, changing the white in the BW repeat to blue the black to orange
the black to orange 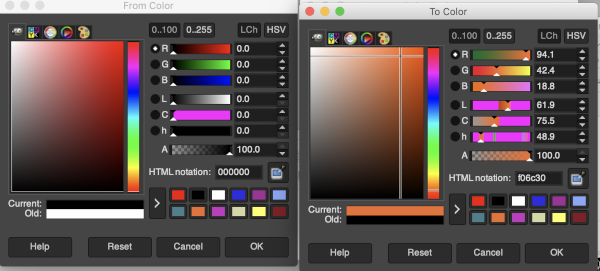
 My success with series of other images in using color exchange has been spotty. Online forums reveal this is a recurrent issue with no clear solutions. Suggestions include stipulating that the cause may be the version of Mac OS in use. Color reductions using ArahPaint achieve consistent results easily and quickly. There are advantages to hybrid conversions.
My success with series of other images in using color exchange has been spotty. Online forums reveal this is a recurrent issue with no clear solutions. Suggestions include stipulating that the cause may be the version of Mac OS in use. Color reductions using ArahPaint achieve consistent results easily and quickly. There are advantages to hybrid conversions.
COLORS THRESHOLD: see GRIDS OPTIONS
GRIDS: OPTIONS
Punchcard users may use this method to visualize which holes to punch, though this particular repeat would need to be reduced in stitch count in order to be usable. Similar charts may be adapted and used for other textile techniques such as cross-stitch or even filet crochet.
Grids help with the precise placement of pixels when designing using pixels to represent stitches and rows. The grid is not visible until it is activated via the View, Show Grid option in the Image menu. To create a custom grid, the Image, Configure Grid from the Image menu brings up a dialogue that allows you to do so. causes the pointer to “warp” perfectly to any grid line located within a certain distance. In most instances, when drawing repeats a 1X1 pixel grid works well on a canvas magnified enough for it to be visible when filling in cells, I recommend a starting magnification of X800.
Anyone needing an adjustable grid superimposed on an existing colored image may now adjust the grid size to suit while viewing the resulting changes. The beginning image and grid size both need to be large enough for the grid to be visible. Use the show grid, and Configure Grid commands  The intact chain link fixes the width and height aspect ratio of grid cells
The intact chain link fixes the width and height aspect ratio of grid cells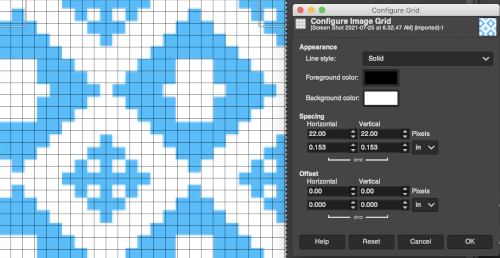 Considering the possible smallest repeat, breaking the chain link, and changing values progressively while viewing the results brings one closer to matching units
Considering the possible smallest repeat, breaking the chain link, and changing values progressively while viewing the results brings one closer to matching units 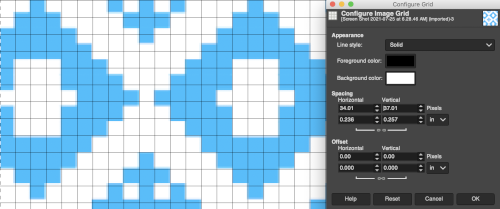 The image itself may be scaled concurrently to tweak grid border alignments. The final grid size below is 18X18, the image size is shown after scaling from a width of 277 pixels (with a broken link at that time) to a final 270 pixels in width
The image itself may be scaled concurrently to tweak grid border alignments. The final grid size below is 18X18, the image size is shown after scaling from a width of 277 pixels (with a broken link at that time) to a final 270 pixels in width 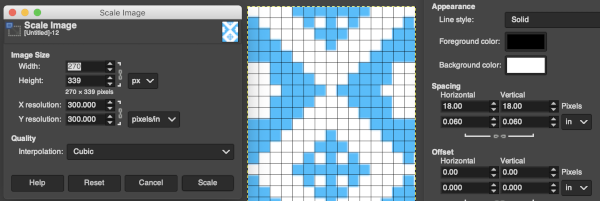 The screengrab of the above center, with a superimposed new grid; note the image, in this case, was also offset for better placement, a 3-pixel pencil was used to isolate the border of the possible smallest repeat
The screengrab of the above center, with a superimposed new grid; note the image, in this case, was also offset for better placement, a 3-pixel pencil was used to isolate the border of the possible smallest repeat 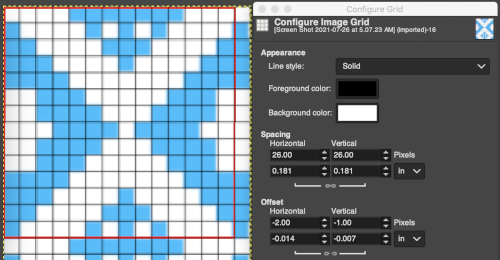 Using Filter, Map, Tile to check alignments
Using Filter, Map, Tile to check alignments 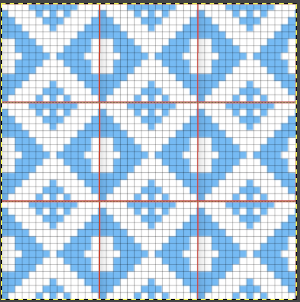 The repeat reduced to 12 stitches, suitable for punchcard, and tiled to check alignments.
The repeat reduced to 12 stitches, suitable for punchcard, and tiled to check alignments. 
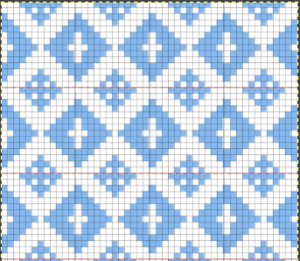 Translating the colored image to BW indexed may take several steps and some clean-up if only Gimp is used to process it. With the colored large-scale isolated repeat, the image is opened in Gimp. The Threshold tool transforms the current layer or the selection into a black-and-white image, where white pixels represent the pixels of the image whose Value is in the threshold range, and black pixels represent pixels with Value out of the threshold range. It may be activated from the pull-down colors menu or from the toolbox.
Translating the colored image to BW indexed may take several steps and some clean-up if only Gimp is used to process it. With the colored large-scale isolated repeat, the image is opened in Gimp. The Threshold tool transforms the current layer or the selection into a black-and-white image, where white pixels represent the pixels of the image whose Value is in the threshold range, and black pixels represent pixels with Value out of the threshold range. It may be activated from the pull-down colors menu or from the toolbox.  The color image will temporarily disappear, adjust levels.
The color image will temporarily disappear, adjust levels. 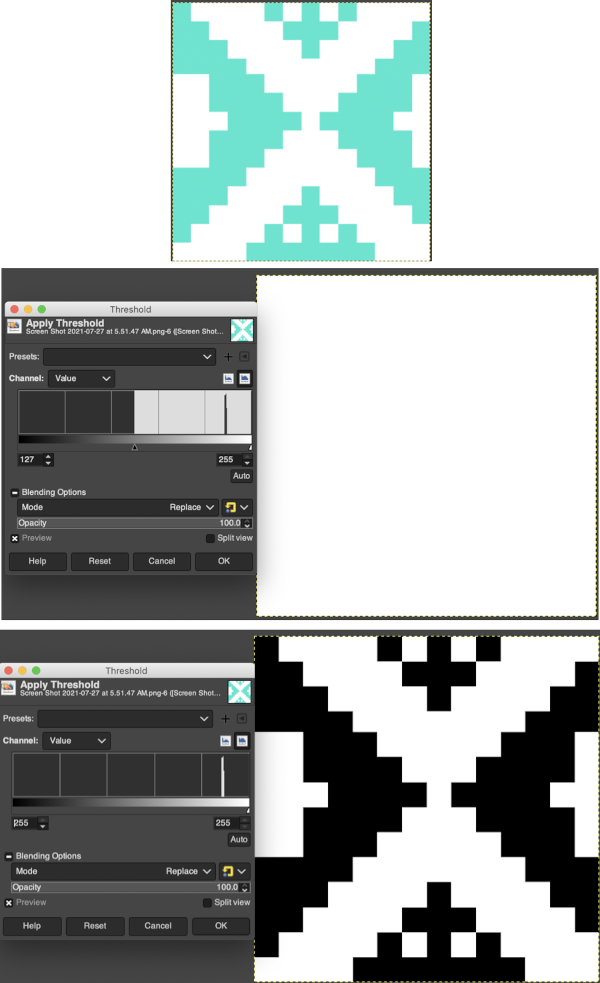 Scaling to repeat size: check the image size, making certain the present dimensions match a multiple of the final repeat count for stitches and rows. If adjustments are required, breaking the chain link allows for each count to be adjusted independently from the other. In the final scaling, use the closed chain link, adjust numbers, magnify the repeat, checking it with a superimposed grid for any missing or out-of-place cells. Check the alignment, then save the single repeat, which in this case is 14X14, ready for download
Scaling to repeat size: check the image size, making certain the present dimensions match a multiple of the final repeat count for stitches and rows. If adjustments are required, breaking the chain link allows for each count to be adjusted independently from the other. In the final scaling, use the closed chain link, adjust numbers, magnify the repeat, checking it with a superimposed grid for any missing or out-of-place cells. Check the alignment, then save the single repeat, which in this case is 14X14, ready for download 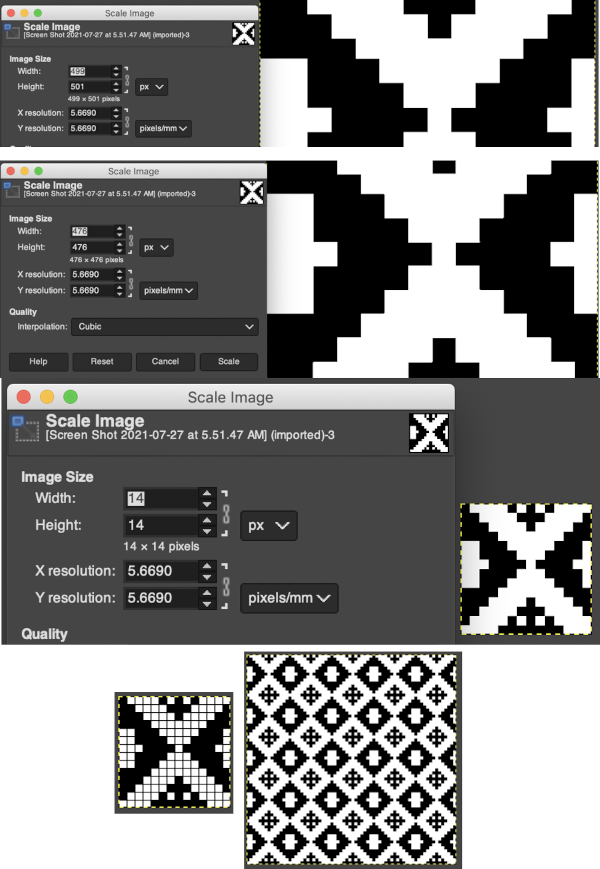
 Color separations: there are occasions where very small repeats need to be scaled in height only for color separations. I have found such scaling to be inaccurate using the option, such as here, both of the small, single repeat, and in scaling its tiled version. The triangle motif was used in many of my early posts on color separations for DBJ and its backing options.
Color separations: there are occasions where very small repeats need to be scaled in height only for color separations. I have found such scaling to be inaccurate using the option, such as here, both of the small, single repeat, and in scaling its tiled version. The triangle motif was used in many of my early posts on color separations for DBJ and its backing options. 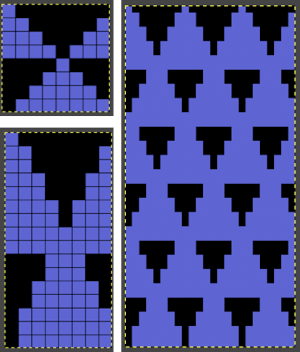 On a long enough canvas, the grid may be adjusted to 1 pixel by four in height. With that number of cells filled in with black in this case, if the 1X4 unit is captured with the rectangle tool, it will appear in the brush menu and will be available for use with the pencil tool for drawing with single strokes until one quits the program unless the unit is saved for future use as described via preferences
On a long enough canvas, the grid may be adjusted to 1 pixel by four in height. With that number of cells filled in with black in this case, if the 1X4 unit is captured with the rectangle tool, it will appear in the brush menu and will be available for use with the pencil tool for drawing with single strokes until one quits the program unless the unit is saved for future use as described via preferences  Using RGB mode, the two-color redrawn image is redrawn, A. The grid may be adjusted to 1X 1 again, B. Using magnification, I often use X1800, and pairs of rows may be selected for either color invert or value invert color options. The first will add a third color, seen in the chart bottom, the second will yield a 2 color image, seen in the chart top, B. I have had no success with using keyboard commands for the action using my OS, find it easier visually to deal with the three colors than with the 2, especially in longer repeats. C: the extra color pixels in the rows with black pixels are filled with white. D: the third color pixel rows are filled with black. D the final repeat may be color indexed to BW and saved for download.
Using RGB mode, the two-color redrawn image is redrawn, A. The grid may be adjusted to 1X 1 again, B. Using magnification, I often use X1800, and pairs of rows may be selected for either color invert or value invert color options. The first will add a third color, seen in the chart bottom, the second will yield a 2 color image, seen in the chart top, B. I have had no success with using keyboard commands for the action using my OS, find it easier visually to deal with the three colors than with the 2, especially in longer repeats. C: the extra color pixels in the rows with black pixels are filled with white. D: the third color pixel rows are filled with black. D the final repeat may be color indexed to BW and saved for download. 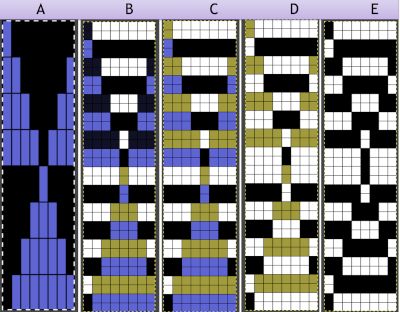 The appearance of the final repeat when color is reversed
The appearance of the final repeat when color is reversed 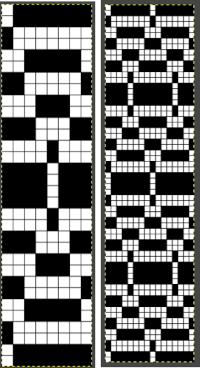 Another comparison of the 2 options for altering every other pair of rows in the specific color separation for a mosaic repeat. There is less filling in of cells with a different color, but in large files especially, I feel the result would become far more visually confusing to track.
Another comparison of the 2 options for altering every other pair of rows in the specific color separation for a mosaic repeat. There is less filling in of cells with a different color, but in large files especially, I feel the result would become far more visually confusing to track. 
 For more details on the specific mosaic, see 2021/01/27/mosaics-and-mazes-charting-meet-numbers-gimp-3/
For more details on the specific mosaic, see 2021/01/27/mosaics-and-mazes-charting-meet-numbers-gimp-3/
SYMMETRY PAINTING
Information summary from the online manual on working with symmetry:
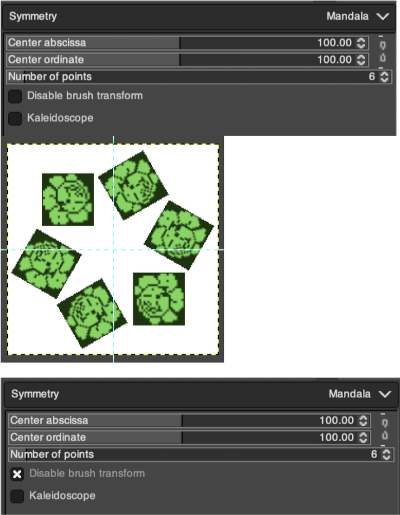
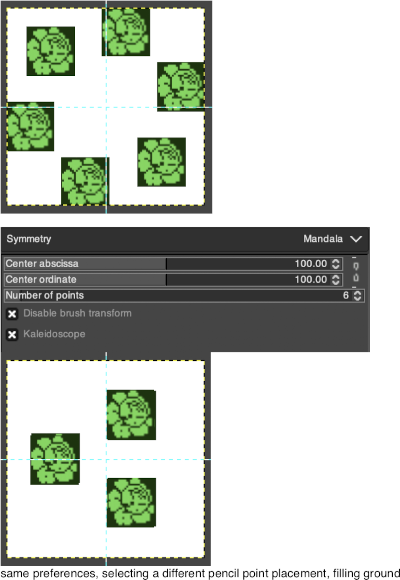
you can access this dialog from the image Menu bar through Windows-Dockable- Dialogs-Symmetry Painting, its icon appears below at the top right 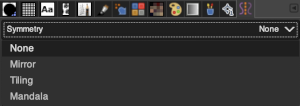 A drop-down list offers four options. As soon as you check a type of symmetry, axes appear as dotted green lines in the image window and you can start painting with the brush you have chosen.
A drop-down list offers four options. As soon as you check a type of symmetry, axes appear as dotted green lines in the image window and you can start painting with the brush you have chosen.
The default position for the symmetry axis is the middle of the image window. You can place the axis where you want using the Horizontal axis position and Vertical axis position.
Disable brush transform: when you transform the drawing, the brush itself will end up transformed as well. For instance, in a mirror transform, not only will your drawing on the right of the canvas be mirrored on the left, but the brush itself is obviously “flipped” on the left. If for some reason, you want the drawn lines to be mirrored (or other transformation) but not the brush outline itself, you can check this box.
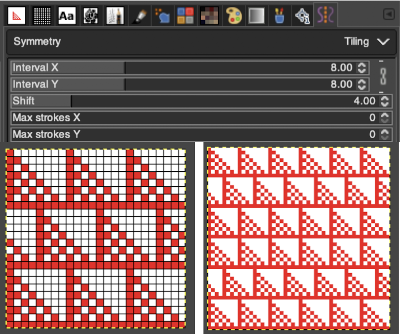
“Tiling” is a translational symmetry, which can be finite (with a maximum of strokes) or infinite. In the latter case, it is the perfect tool to create patterns or seamless tiles, at painting time. This mode covers the image with strokes.
Interval X Interval Y: these are the intervals on the X and Y axis, in pixels, between stroke centers.
Shift: this is the shift between lines on the X-axis, in pixels.
Max strokes X, Max strokes Y: these are the maximal number of brush strokes on the X and Y-axis. The default is 0, which means no limit, according to the image size.
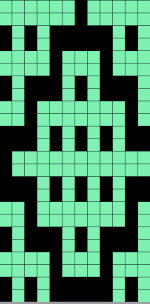
Using a large image, and testing a few iterations helps one understand the process. The pepper brush is provided in the program and is used in the tutorial on the Gimp site. Most such tutorials are intended for working on far larger and higher resolution images, while knitting is binary and at the opposite end of the spectrum in scale and required image size. The original brush is 220 pixels in size, and the maximum number of needles per pixel on standard machines programmable at one time is 200. For exploration, any of the built-in brushes may be used, I began by scaling the pepper to 50 pixels, then moved on to a self-drawn, equal size flower motif. When choosing canvas file size, consider a multiple of the brush size. Drawing repeats uses the pencil tool. 
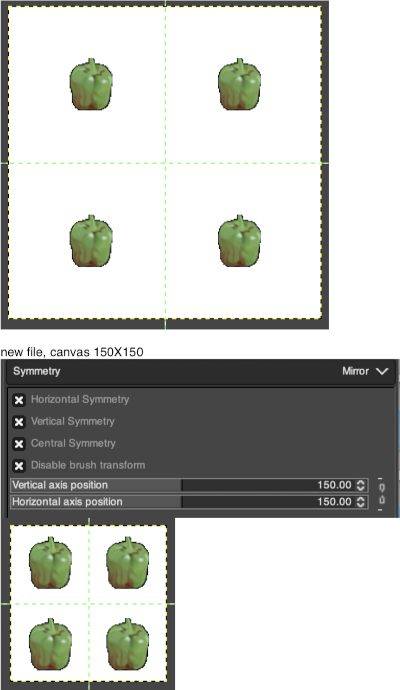
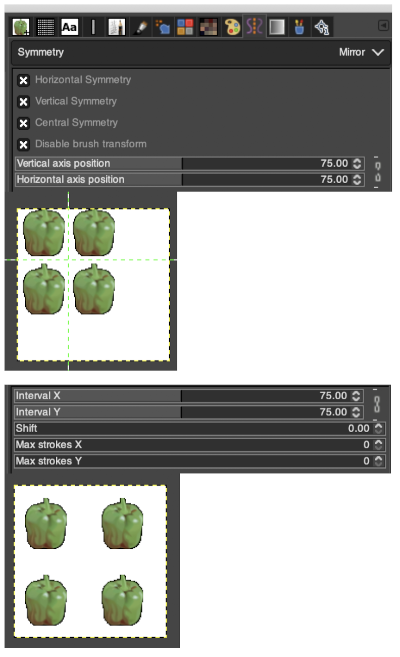
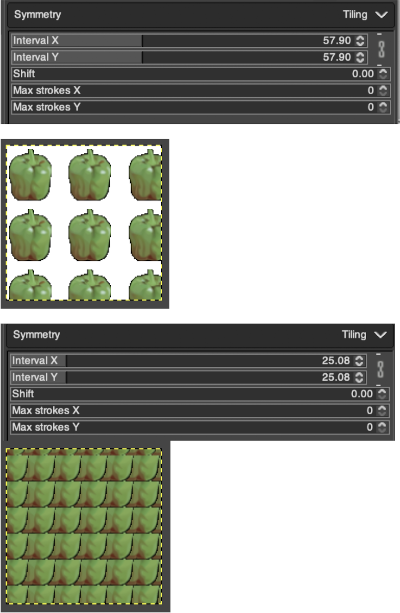
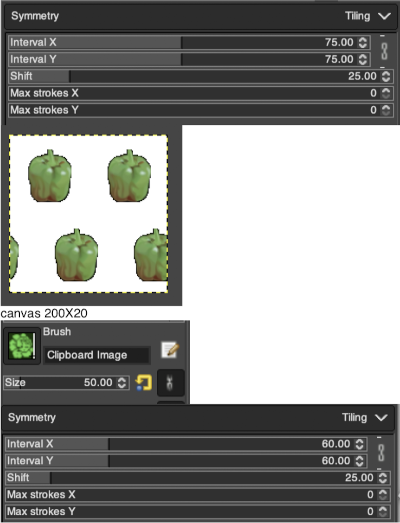

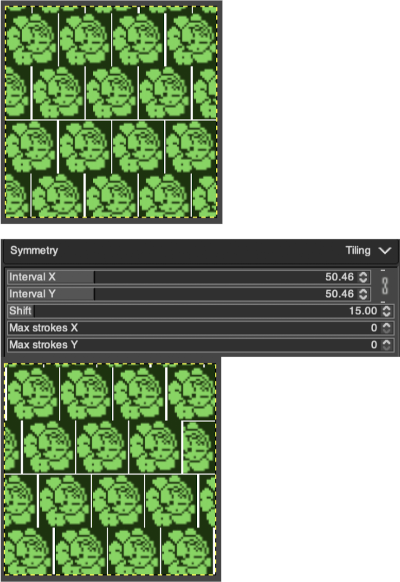
 Working with potential knit repeats the scale is reduced further. Magnification is useful for the evaluation of repeats. The smallest repeat segments for use on electronic machines may be isolated. The filter, map, and tile option easily verify how the repeats line up overall. Cropping a 24-stitch width and tiling that also visualizes the suitability of the repeat for use on punchcards with the 24-stitch limitation. Grid view helps identify any need for “clean up”.
Working with potential knit repeats the scale is reduced further. Magnification is useful for the evaluation of repeats. The smallest repeat segments for use on electronic machines may be isolated. The filter, map, and tile option easily verify how the repeats line up overall. Cropping a 24-stitch width and tiling that also visualizes the suitability of the repeat for use on punchcards with the 24-stitch limitation. Grid view helps identify any need for “clean up”.
This rose is 24 stitches wide by 25 rows in height  Open the chosen file in Gimp. Create a new file in a canvas size considering a multiple of the original.
Open the chosen file in Gimp. Create a new file in a canvas size considering a multiple of the original.
When the Copy or Cut command is used on an image or a selection of it, a copy appears as a new brush in the upper left corner of the “Brushes” dialog. This brush will persist until you use the Copy command again. It disappears when GIMP is closed.
With the single repeat opened in Gimp, magnified several times, click on the image and use the copy command. The image will appear in the symmetry dialogue. The position may vary depending on whether the program has been closed and relaunched between episodes of testing the process.  Create a new file, large enough to accommodate a multiple of the original number of pixels, add pixels for spacing between or above and below designs, set the magnification to the same number as that of the clipboard image, left-click on the brush icon, choose the image saved in the clipboard
Create a new file, large enough to accommodate a multiple of the original number of pixels, add pixels for spacing between or above and below designs, set the magnification to the same number as that of the clipboard image, left-click on the brush icon, choose the image saved in the clipboard  and a type of symmetry and accompanying settings, click on pencil tool, the motif will appear as on the above right, paste the image on the new canvas, undo and repeat setting adjustments until satisfied with the distribution of motifs.
and a type of symmetry and accompanying settings, click on pencil tool, the motif will appear as on the above right, paste the image on the new canvas, undo and repeat setting adjustments until satisfied with the distribution of motifs.
Some ways of varying repeat positions working with motifs in networks were illustrated in the post 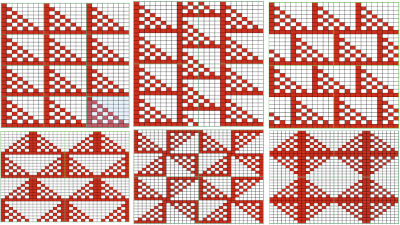 To develop a brick repeat I began with a canvas twice that of the original rose,
To develop a brick repeat I began with a canvas twice that of the original rose,  48X50 pixels, isolated the smallest repeat, used the filter map tile option to test its all over alignment
48X50 pixels, isolated the smallest repeat, used the filter map tile option to test its all over alignment 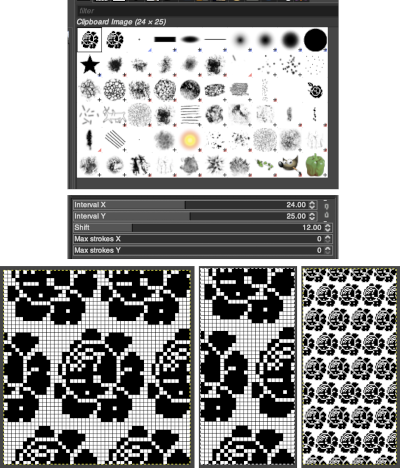 The 24X50 repeat:
The 24X50 repeat:  To decrease crowding, using the original image, the new canvas is now 40X60, with the shift decreased from 12 to 8 pixels. The result did not tile properly when mapped, using magnification 800X with a viewed grid the final repeat, 29X60 was isolated
To decrease crowding, using the original image, the new canvas is now 40X60, with the shift decreased from 12 to 8 pixels. The result did not tile properly when mapped, using magnification 800X with a viewed grid the final repeat, 29X60 was isolated 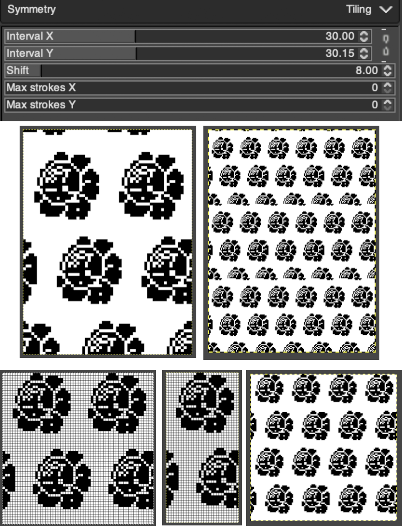 Being more deliberate with the math leads to a full, successful repeat
Being more deliberate with the math leads to a full, successful repeat 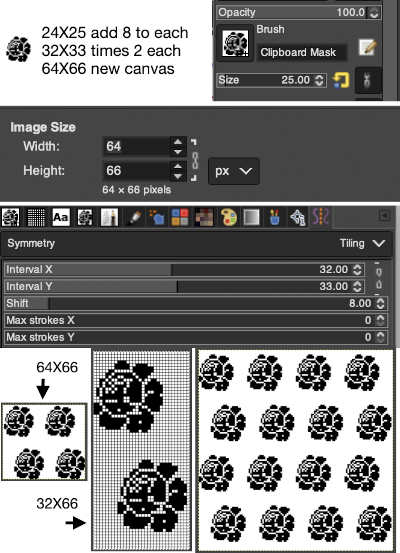
Working on the gridded image, drawing straight lines to isolate color change areas in chosen colors followed by flood filling, one may begin to visualize changing the ground color behind the motif repeats  Using that small triangular 8X8 repeat
Using that small triangular 8X8 repeat
 open in Gimp, or draw any small shape if designed by hand, remove the grid. Before using it as a brush, reduce mode to 2 colors, magnify X800. Open a new file. I found the latter needed to be increasingly small as well for the repeats to be placed accurately. After tiling using symmetry, filter, map, tile from the filter menu to check for multiple repeat alignment.
open in Gimp, or draw any small shape if designed by hand, remove the grid. Before using it as a brush, reduce mode to 2 colors, magnify X800. Open a new file. I found the latter needed to be increasingly small as well for the repeats to be placed accurately. After tiling using symmetry, filter, map, tile from the filter menu to check for multiple repeat alignment. 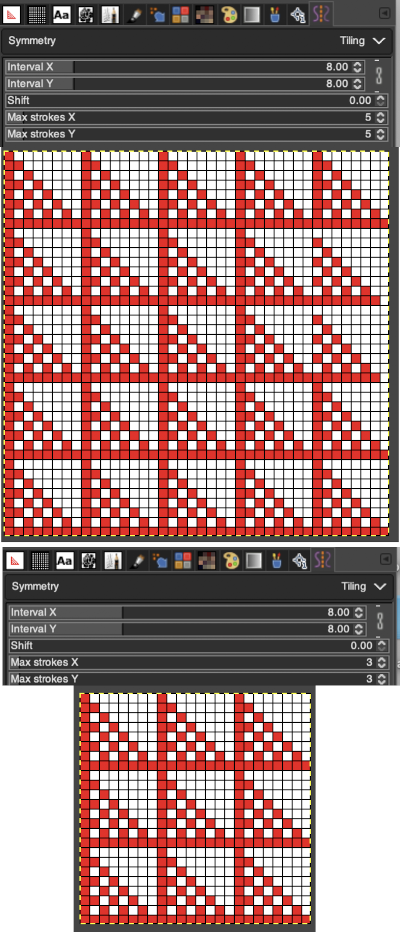
 Again, preemptive math will yield images that avoid further processing. It is up to the user to recognize any problems, the repeat here needs to and can be isolated correctly from the file on the left, it is actually only 16 rows high. Here the adjusted repeat is created on a 24X16 canvas with the same symmetry settings, and filter/mapped/tiled
Again, preemptive math will yield images that avoid further processing. It is up to the user to recognize any problems, the repeat here needs to and can be isolated correctly from the file on the left, it is actually only 16 rows high. Here the adjusted repeat is created on a 24X16 canvas with the same symmetry settings, and filter/mapped/tiled  There may be multiple ways to achieve the same result with each motif. Here the same repeat is executed two different ways
There may be multiple ways to achieve the same result with each motif. Here the same repeat is executed two different ways 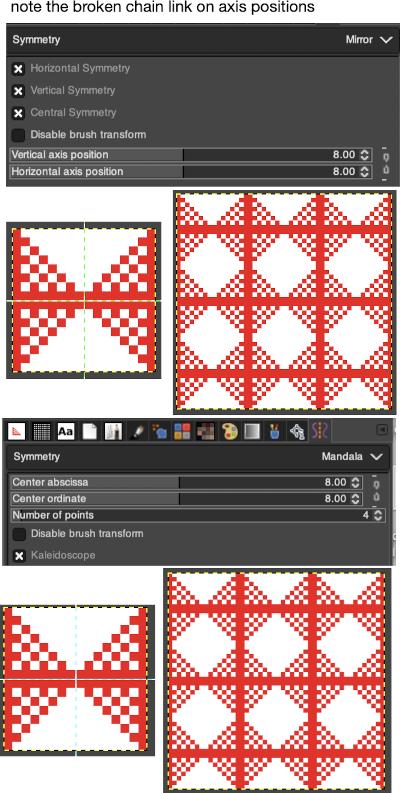 The above repeat was cropped and adjusted to 16 stitch width and 8 row height, the file saved, and the process repeated
The above repeat was cropped and adjusted to 16 stitch width and 8 row height, the file saved, and the process repeated  Using symmetry once more, remember to adjust the pencil size.
Using symmetry once more, remember to adjust the pencil size.  For the pinwheel shape
For the pinwheel shape 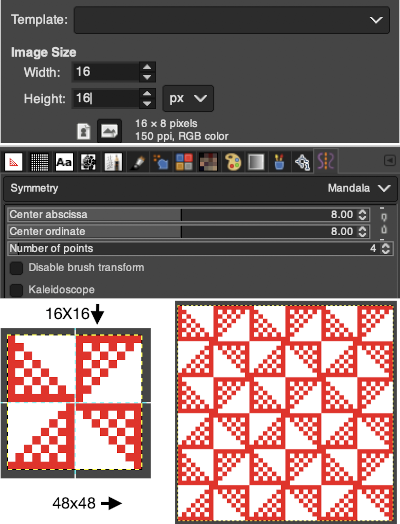 I was unable to use color exchange successfully on the above images, but with the saved 2 colors indexed red and white repeat both img2track and ayab appeared to load the repeat successfully.
I was unable to use color exchange successfully on the above images, but with the saved 2 colors indexed red and white repeat both img2track and ayab appeared to load the repeat successfully. 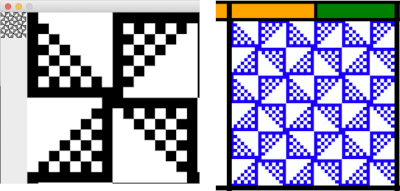 The map color exchange was successful using the steps described at the top of the post when beginning with the repeat drawn in a black and white version.
The map color exchange was successful using the steps described at the top of the post when beginning with the repeat drawn in a black and white version. 
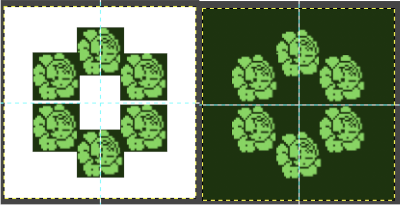
A different approach, experimenting with built-in brushes: symmetry preferences remain constant, the brush size is reduced. The results are best if the canvas is created in black and white indexed mode to start with, and shapes reduce with varying degrees of success. The numbers reflect brush sizes in each dot pattern. 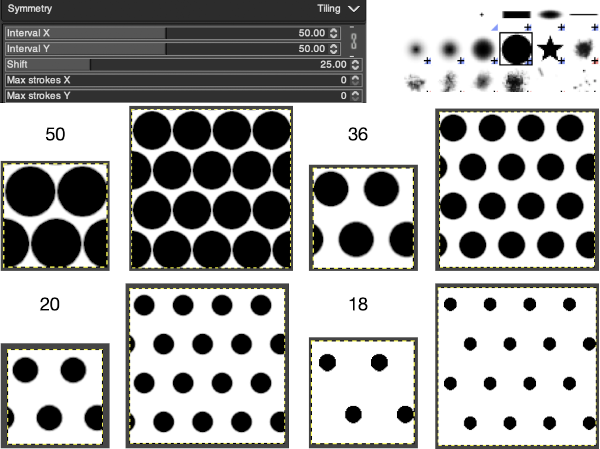 Different types of symmetry may be applied to the same image
Different types of symmetry may be applied to the same image 
For afghans or wall art, if one is attracted to large shapes, drawing in mandala symmetry on large canvas size is as gratifying and immediate as when using a spirograph, the results happen in seconds, these were drawn using 32 points. Steps may easily be undone along the way as one attempts to make the images more complex. 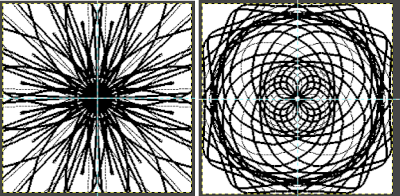
 click on Legacy to switch mode selections.
click on Legacy to switch mode selections.  In December 2022 I began to experiment with layer transparency please see the post Gimp Update for Mac 3.
In December 2022 I began to experiment with layer transparency please see the post Gimp Update for Mac 3. 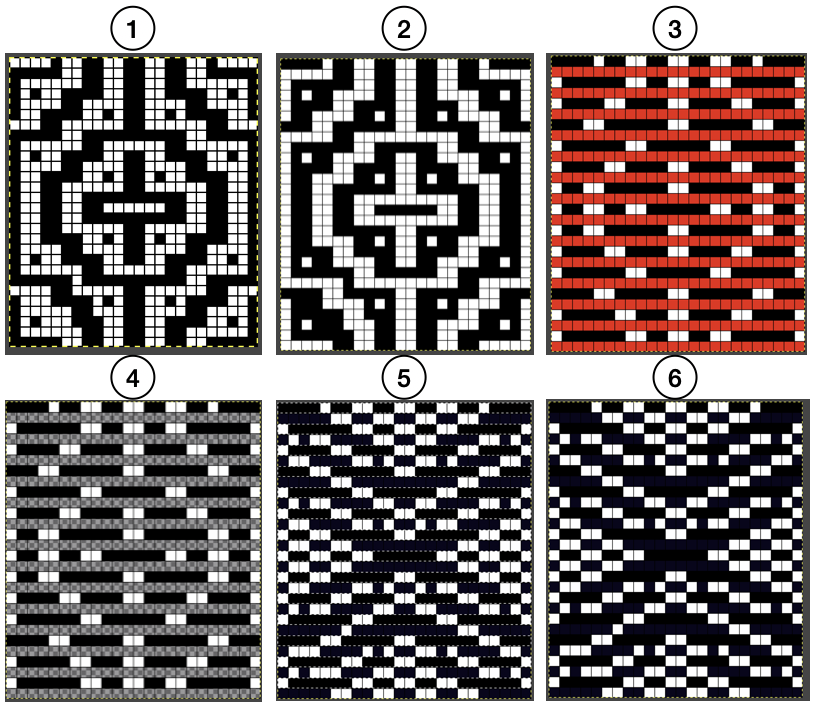 Over the years I have developed personal methods for creating color separations for many types of knit fabrics, born from lots of experimentation when published resources were absent or extremely limited.
Over the years I have developed personal methods for creating color separations for many types of knit fabrics, born from lots of experimentation when published resources were absent or extremely limited. will display layer options in my Mac on the bottom right side of the screen
will display layer options in my Mac on the bottom right side of the screen  A simple geometric shape
A simple geometric shape ![]() is scaled in Gimp to twice its height, check that Quality Interpolation is set to None. I have sometimes had issues with scaling in Gimp, particularly when working with small repeats. The cause appears to have been that the Quality, Interpolation, needs to be set to None and may randomly change while working through several steps in processing any image or after a program restart. Arahpaint scaling is still an excellent option for knitters who have it available.
is scaled in Gimp to twice its height, check that Quality Interpolation is set to None. I have sometimes had issues with scaling in Gimp, particularly when working with small repeats. The cause appears to have been that the Quality, Interpolation, needs to be set to None and may randomly change while working through several steps in processing any image or after a program restart. Arahpaint scaling is still an excellent option for knitters who have it available.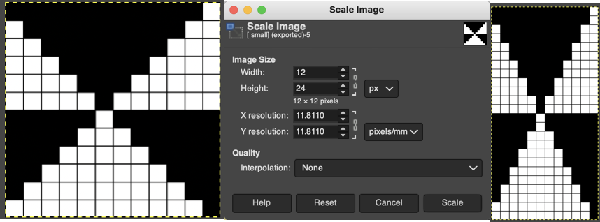 the white ground of the resulting image is rendered transparent by using Color to Alpha
the white ground of the resulting image is rendered transparent by using Color to Alpha  and will constitute the first layer for the separation process
and will constitute the first layer for the separation process 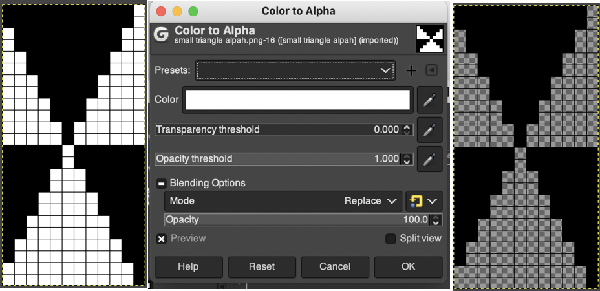 Select New Layer from the Layers menu (see chart), choosing the background or foreground color to have a white screen. It will share properties with the alpha repeat such as pixel count, magnification, and the grid view if used.
Select New Layer from the Layers menu (see chart), choosing the background or foreground color to have a white screen. It will share properties with the alpha repeat such as pixel count, magnification, and the grid view if used. Copy the selection, and it will be saved to the clipboard and remain available for filling with the pattern unless the program is quit. It may also be saved as a pattern for future use.
Copy the selection, and it will be saved to the clipboard and remain available for filling with the pattern unless the program is quit. It may also be saved as a pattern for future use.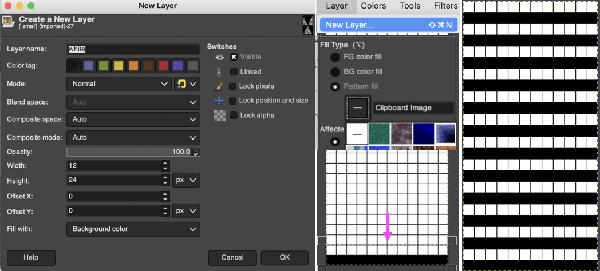 In the layers dialogue, use the mouse to drag and drop the alpha image icon for the triangle layer onto the newly created one. The selected icon will appear surrounded by a border when chosen, a new icon will appear during the step.
In the layers dialogue, use the mouse to drag and drop the alpha image icon for the triangle layer onto the newly created one. The selected icon will appear surrounded by a border when chosen, a new icon will appear during the step.  Both layers measure the same pixel dimensions, no placement adjustments are necessary. The mode, highlighted here is changed in a later step.
Both layers measure the same pixel dimensions, no placement adjustments are necessary. The mode, highlighted here is changed in a later step. 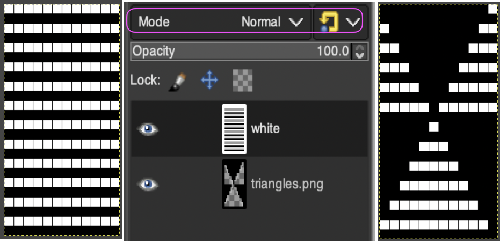 Color invert the new image
Color invert the new image 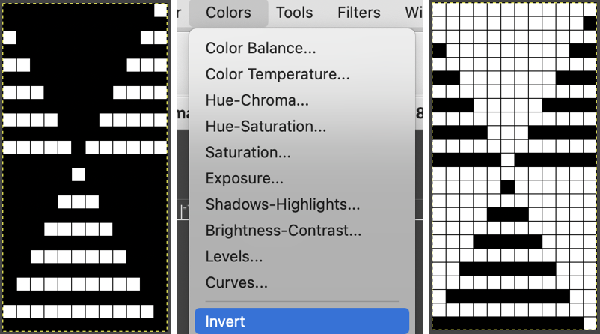 Click on the downward pointer to the right of Normal and select Difference. The result is a repeat that may then be saved and used doubled in height to knit DBJ in a variety of settings.
Click on the downward pointer to the right of Normal and select Difference. The result is a repeat that may then be saved and used doubled in height to knit DBJ in a variety of settings.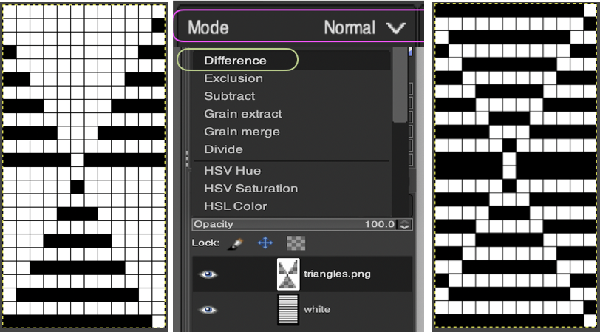 Elongation after download can be avoided by working with the same initial image scaled in height X4 and following the same process, saving and using the repeat on the far right.
Elongation after download can be avoided by working with the same initial image scaled in height X4 and following the same process, saving and using the repeat on the far right. 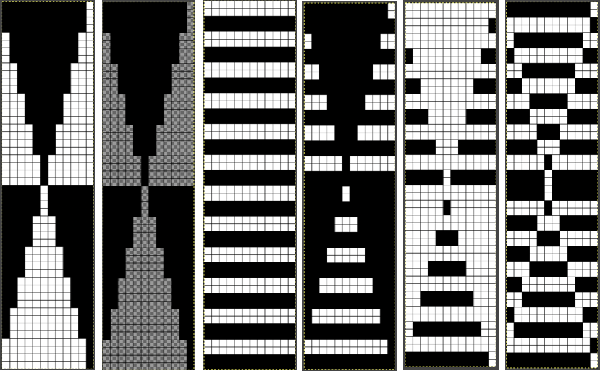 The same separation was achieved using other methods in the post on fantasy fair isle.
The same separation was achieved using other methods in the post on fantasy fair isle. Are punchcard knitters left out? In the post on the color separation used for the KRC equivalent separation for a punchcard two results were presented, the full card
Are punchcard knitters left out? In the post on the color separation used for the KRC equivalent separation for a punchcard two results were presented, the full card 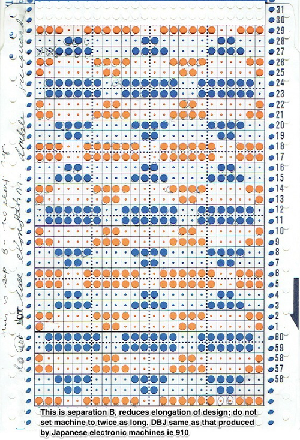 and the starting design shown with the color reversed repeat of the above.
and the starting design shown with the color reversed repeat of the above. 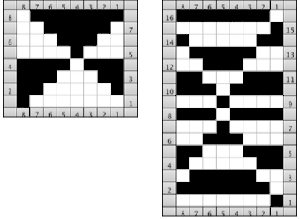 The process begins with obtaining the double-length separation
The process begins with obtaining the double-length separation ![]()
 after saving the last file on the right as PNG
after saving the last file on the right as PNG ![]() discard any files still open. Open the saved png and process it the same way, changing the ground
discard any files still open. Open the saved png and process it the same way, changing the ground  Save the last file as png. Punchcard knitters would need to tile the fileX4 in width and height X2 but the final repeat appears different than that in the punchcard post, the proof of success or failure is in the knitting. If the swatch is knit on electronic models, the first preselection row is made from left to right, as it would be if using the built-in color separation. The main bed for this fabric after the preselection row is set to slip in both directions, the ribber, using an even number of needles, is also set to slip in both directions with lili buttons. The 8X32 png
Save the last file as png. Punchcard knitters would need to tile the fileX4 in width and height X2 but the final repeat appears different than that in the punchcard post, the proof of success or failure is in the knitting. If the swatch is knit on electronic models, the first preselection row is made from left to right, as it would be if using the built-in color separation. The main bed for this fabric after the preselection row is set to slip in both directions, the ribber, using an even number of needles, is also set to slip in both directions with lili buttons. The 8X32 png ![]() The result from repeating it twice indicates the separation indeed works.
The result from repeating it twice indicates the separation indeed works.  When a color separation is downloaded it is used as one would a fair isle. If the motif is representational and direction on the knit side matters, any repeats may have to be mirrored horizontally if they are automatically reversed by either your software prior to download or your machine model after it.
When a color separation is downloaded it is used as one would a fair isle. If the motif is representational and direction on the knit side matters, any repeats may have to be mirrored horizontally if they are automatically reversed by either your software prior to download or your machine model after it.![]()

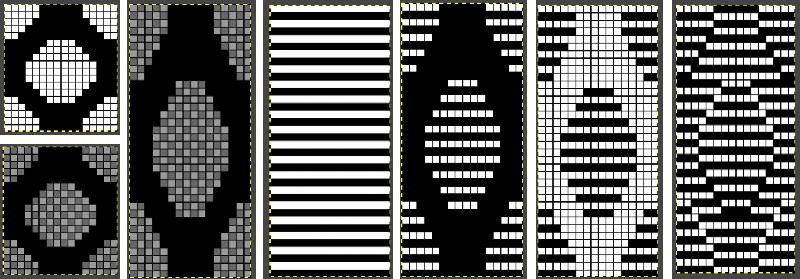
 The 16X72 double-length PNG
The 16X72 double-length PNG ![]() A quicker matching result:
A quicker matching result: Tiling to visualize alternative repeats, beginning with the 24X72 pixel file
Tiling to visualize alternative repeats, beginning with the 24X72 pixel file![]()
 The file for the image in the center, modified to 24X144 pixels file for the image on the right, modified to 48X144 pixels
The file for the image in the center, modified to 24X144 pixels file for the image on the right, modified to 48X144 pixels ![]() Removing the color on every other row for use in specialty fabrics ie drop stitch lace using a modified stitch dropping tool with a now edited 24 stitch repeat, suitable for punchcard models:
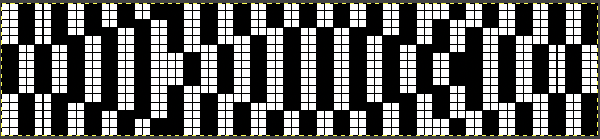
Removing the color on every other row for use in specialty fabrics ie drop stitch lace using a modified stitch dropping tool with a now edited 24 stitch repeat, suitable for punchcard models:  The image is processed as for the previous separation, the final png is exported. Open the saved in Gimp.
The image is processed as for the previous separation, the final png is exported. Open the saved in Gimp. Using the rectangle tool, select a single blue row, after the selection, press and hold down the shift key and repeat selections of multiple rows in the same color. Each selection will be bordered by a dotted line.
Using the rectangle tool, select a single blue row, after the selection, press and hold down the shift key and repeat selections of multiple rows in the same color. Each selection will be bordered by a dotted line.  Release the shift key. Click on the rectangle select tool and then again in the work window outside the image to set it. The dotted lines will disappear. The same action is repeated if working on segments of the full file at a time.
Release the shift key. Click on the rectangle select tool and then again in the work window outside the image to set it. The dotted lines will disappear. The same action is repeated if working on segments of the full file at a time.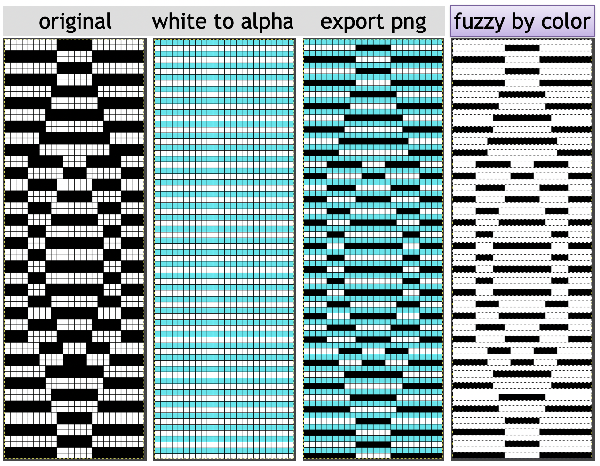 The 24X72 new png
The 24X72 new png ![]() MOSAICS: For proof of concept, I intend to use separations for fabrics accompanied by knit samples in previous posts, beginning with a mosaic one, achieved in the post. The images shown are for the final repeat as separated there are shown at the top of this new image. Below comparisons are made between the original download file and its companion elongated repeat alongside the same developed using Layers
MOSAICS: For proof of concept, I intend to use separations for fabrics accompanied by knit samples in previous posts, beginning with a mosaic one, achieved in the post. The images shown are for the final repeat as separated there are shown at the top of this new image. Below comparisons are made between the original download file and its companion elongated repeat alongside the same developed using Layers Both results require scaling X2 before knitting, whether by button setting changes in the repeat after download or in Gimp before.
Both results require scaling X2 before knitting, whether by button setting changes in the repeat after download or in Gimp before. ![]() After reaching the step where the layer mode is changed to Difference (or Exclusion), stop and save the png, using color reverse at this point will revert to previous a previous layers view
After reaching the step where the layer mode is changed to Difference (or Exclusion), stop and save the png, using color reverse at this point will revert to previous a previous layers view 
![]() open the saved png in Gimp, use color reverse, then scale the result doubling its height, save the png for download and knitting without changes in any machine settings.
open the saved png in Gimp, use color reverse, then scale the result doubling its height, save the png for download and knitting without changes in any machine settings. 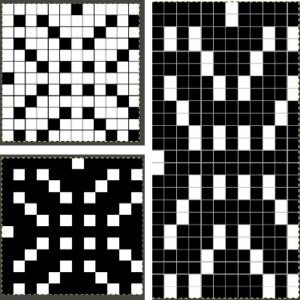
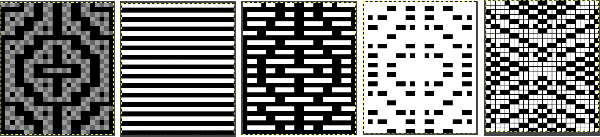
![]() Testing another image separated in a previous post: the original charted image is now rendered in black and white
Testing another image separated in a previous post: the original charted image is now rendered in black and white 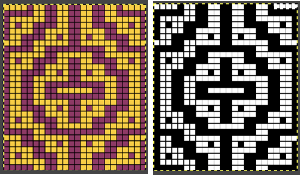 the repeat as a PNG
the repeat as a PNG ![]() tile check
tile check  The process in Layers
The process in Layers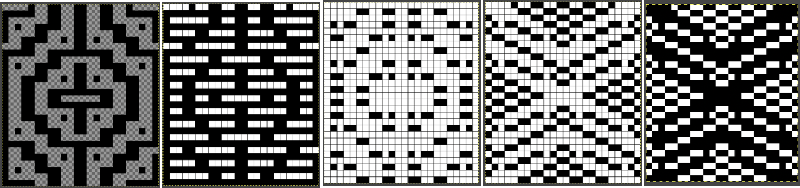 The very last file on the right is saved as a PNG. In turn, it is opened again in Gimp, scaled to twice its height
The very last file on the right is saved as a PNG. In turn, it is opened again in Gimp, scaled to twice its height ![]() The non-elongated repeat matches that in the punchcard, which was knit with the machine set to double length
The non-elongated repeat matches that in the punchcard, which was knit with the machine set to double length  Exclusion is the alternative Layer mode which when following the same process yields identical results.
Exclusion is the alternative Layer mode which when following the same process yields identical results. 
 A block slip stitch design from the post requires color inversion and doubling the length.
A block slip stitch design from the post requires color inversion and doubling the length.  A: design motif
A: design motif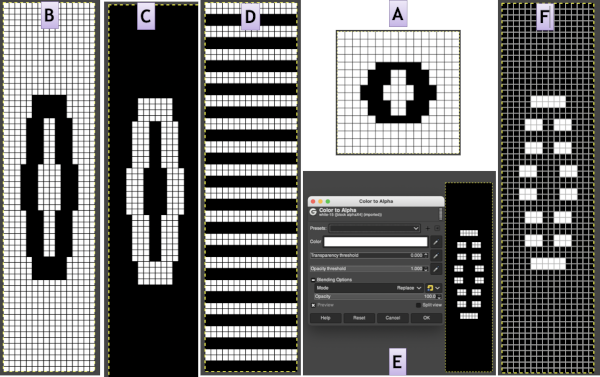








 The results with the selection of even rows simply shift the result up a row
The results with the selection of even rows simply shift the result up a row  Test in your version of the program to see whether releasing the shift key prior to making edits changes them. Either way, being consistent in the choice makes for less confusing results. Experimentation takes a matter of seconds.
Test in your version of the program to see whether releasing the shift key prior to making edits changes them. Either way, being consistent in the choice makes for less confusing results. Experimentation takes a matter of seconds. using the rectangle tool, either odd or even rows may be chosen, remaining consistent for the height of the repeat in a scale to suit the end fabric goal. Here the original file is lengthened X2
using the rectangle tool, either odd or even rows may be chosen, remaining consistent for the height of the repeat in a scale to suit the end fabric goal. Here the original file is lengthened X2 working with the original file lengthened x4. The selections can happen on every row or every other, whether singly or in pairs. Note the difference between making the first selection on the first pair of rows or the second.
working with the original file lengthened x4. The selections can happen on every row or every other, whether singly or in pairs. Note the difference between making the first selection on the first pair of rows or the second.  2021:
2021: 



 single click on the filing cabinet icon on the right,
single click on the filing cabinet icon on the right, 
 double click on the patterns folder, and its own window will appear,
double click on the patterns folder, and its own window will appear, 

 For future use, any saved brush may be dragged and dropped into the named personal pattern folder icon, or into the folder after it has been expanded or opened in its own window. My opened brush folder
For future use, any saved brush may be dragged and dropped into the named personal pattern folder icon, or into the folder after it has been expanded or opened in its own window. My opened brush folder 



 When exporting self-drawn brushes, the option is offered for adding spacing surrounding the shape, here a 10% addition was chosen
When exporting self-drawn brushes, the option is offered for adding spacing surrounding the shape, here a 10% addition was chosen 
 To save personal patterns, instead of choosing the file cabinet icon in preferences, one may choose the folder icon, following a similar series of steps to those above, including verifying the contents of the newly created folder
To save personal patterns, instead of choosing the file cabinet icon in preferences, one may choose the folder icon, following a similar series of steps to those above, including verifying the contents of the newly created folder 
 Use Windows, Dockable Dialogues, choose Pattern. The patterns will show on the right
Use Windows, Dockable Dialogues, choose Pattern. The patterns will show on the right Click on the paint bucket, then on the pattern you wish to use on right, hover over the canvas with the paint tool, click on it and the image will fill in the chosen pattern.
Click on the paint bucket, then on the pattern you wish to use on right, hover over the canvas with the paint tool, click on it and the image will fill in the chosen pattern.





















 Foreground and Background colors: in RGB Mode, click on the foreground color to select a new color for the grid, click OK
Foreground and Background colors: in RGB Mode, click on the foreground color to select a new color for the grid, click OK 

 This command is found in the image menubar through
This command is found in the image menubar through 






 Built-in or custom brushes may be superimposed on a bucket-filled ground. Create an image in the desired width and height, here 24 X 24, and magnify at least X 800 for a grid view.
Built-in or custom brushes may be superimposed on a bucket-filled ground. Create an image in the desired width and height, here 24 X 24, and magnify at least X 800 for a grid view.








 The color exchange window will appear. Here the white “from color” is left undisturbed. Select the dropper next to the “to color”, then click on the image on the color you wish to change, a palette window will appear. Make your choice, the color exchange window will now have substituted the chosen color for black, click OK, and white design areas are now changed to the chosen blue globally.
The color exchange window will appear. Here the white “from color” is left undisturbed. Select the dropper next to the “to color”, then click on the image on the color you wish to change, a palette window will appear. Make your choice, the color exchange window will now have substituted the chosen color for black, click OK, and white design areas are now changed to the chosen blue globally.  The process may then be repeated with the second color if desired. The color exchange window will show white as the default “from color”. Click on the white bar, choose black from the palette window or use the dropper to select black from the image. The from color will then appear as black. Repeat selection with the dropper from the right of the “to color” bar on any black pixels in the image, choose the color from the palette window to replace it, and the color exchange window will display the new “to color”. Click OK, and job done.
The process may then be repeated with the second color if desired. The color exchange window will show white as the default “from color”. Click on the white bar, choose black from the palette window or use the dropper to select black from the image. The from color will then appear as black. Repeat selection with the dropper from the right of the “to color” bar on any black pixels in the image, choose the color from the palette window to replace it, and the color exchange window will display the new “to color”. Click OK, and job done.  The process may be repeated multiple times on the same design or used on large-scale ones, giving one some idea as to whether or not to really commit to the estimated colors.
The process may be repeated multiple times on the same design or used on large-scale ones, giving one some idea as to whether or not to really commit to the estimated colors. 
 I recently had reason to review old PC files from my Passap knitting days and came across several cut files that when converted to png format appeared in colors rather than black and white, leading me to experiment with color exchange again. The image for the first experiment is part of a crib blanket by Cheryl Giles
I recently had reason to review old PC files from my Passap knitting days and came across several cut files that when converted to png format appeared in colors rather than black and white, leading me to experiment with color exchange again. The image for the first experiment is part of a crib blanket by Cheryl Giles






 It is possible to colorize images originally drawn in black and white. The color exchange options will remain fixed throughout the process. The image may be worked on continuously and exported when color exchanges are completed, or saved and imported again after each step. The color exchange here happens consistently on the chosen background color, changing that quickly becomes familiar and easy. There are times that the repeat being processed will turn black onscreen, trust in the process and continue.
It is possible to colorize images originally drawn in black and white. The color exchange options will remain fixed throughout the process. The image may be worked on continuously and exported when color exchanges are completed, or saved and imported again after each step. The color exchange here happens consistently on the chosen background color, changing that quickly becomes familiar and easy. There are times that the repeat being processed will turn black onscreen, trust in the process and continue.



 Developing custom palettes in order to visualize different colorways while using the same repeat:
Developing custom palettes in order to visualize different colorways while using the same repeat: this window will open with selections for possible palette choices
this window will open with selections for possible palette choices  click on your choice, then click on the palette icon, and your color choices will appear, click on the white, to create a new background color.
click on your choice, then click on the palette icon, and your color choices will appear, click on the white, to create a new background color. 



 My success with series of other images in using color exchange has been spotty. Online forums reveal this is a recurrent issue with no clear solutions. Suggestions include stipulating that the cause may be the version of Mac OS in use. Color reductions using
My success with series of other images in using color exchange has been spotty. Online forums reveal this is a recurrent issue with no clear solutions. Suggestions include stipulating that the cause may be the version of Mac OS in use. Color reductions using 

 The image itself may be scaled concurrently to tweak grid border alignments. The final grid size below is 18X18, the image size is shown after scaling from a width of 277 pixels (with a broken link at that time) to a final 270 pixels in width
The image itself may be scaled concurrently to tweak grid border alignments. The final grid size below is 18X18, the image size is shown after scaling from a width of 277 pixels (with a broken link at that time) to a final 270 pixels in width  The screengrab of the above center, with a superimposed new grid; note the image, in this case, was also offset for better placement, a 3-pixel pencil was used to isolate the border of the possible smallest repeat
The screengrab of the above center, with a superimposed new grid; note the image, in this case, was also offset for better placement, a 3-pixel pencil was used to isolate the border of the possible smallest repeat 


 Translating the colored image to BW indexed may take several steps and some clean-up if only Gimp is used to process it. With the colored large-scale isolated repeat, the image is opened in Gimp. The Threshold tool transforms the current layer or the selection into a black-and-white image, where white pixels represent the pixels of the image whose Value is in the threshold range, and black pixels represent pixels with Value out of the threshold range. It may be activated from the pull-down colors menu or from the toolbox.
Translating the colored image to BW indexed may take several steps and some clean-up if only Gimp is used to process it. With the colored large-scale isolated repeat, the image is opened in Gimp. The Threshold tool transforms the current layer or the selection into a black-and-white image, where white pixels represent the pixels of the image whose Value is in the threshold range, and black pixels represent pixels with Value out of the threshold range. It may be activated from the pull-down colors menu or from the toolbox. 




 The appearance of the final repeat when color is reversed
The appearance of the final repeat when color is reversed  Another comparison of the 2 options for altering every other pair of rows in the specific color separation for a mosaic repeat. There is less filling in of cells with a different color, but in large files especially, I feel the result would become far more visually confusing to track.
Another comparison of the 2 options for altering every other pair of rows in the specific color separation for a mosaic repeat. There is less filling in of cells with a different color, but in large files especially, I feel the result would become far more visually confusing to track. 












 Working with potential knit repeats the scale is reduced further. Magnification is useful for the evaluation of repeats. The smallest repeat segments for use on electronic machines may be isolated. The filter, map, and tile option easily verify how the repeats line up overall. Cropping a 24-stitch width and tiling that also visualizes the suitability of the repeat for use on punchcards with the 24-stitch limitation. Grid view helps identify any need for “clean up”.
Working with potential knit repeats the scale is reduced further. Magnification is useful for the evaluation of repeats. The smallest repeat segments for use on electronic machines may be isolated. The filter, map, and tile option easily verify how the repeats line up overall. Cropping a 24-stitch width and tiling that also visualizes the suitability of the repeat for use on punchcards with the 24-stitch limitation. Grid view helps identify any need for “clean up”. and a type of symmetry and accompanying settings, click on pencil tool, the motif will appear as on the above right, paste the image on the new canvas, undo and repeat setting adjustments until satisfied with the distribution of motifs.
and a type of symmetry and accompanying settings, click on pencil tool, the motif will appear as on the above right, paste the image on the new canvas, undo and repeat setting adjustments until satisfied with the distribution of motifs.
 The 24X50 repeat:
The 24X50 repeat:  Being more deliberate with the math leads to a full, successful repeat
Being more deliberate with the math leads to a full, successful repeat 
 Using that small triangular 8X8 repeat
Using that small triangular 8X8 repeat

 Again, preemptive math will yield images that avoid further processing. It is up to the user to recognize any problems, the repeat here needs to and can be isolated correctly from the file on the left, it is actually only 16 rows high. Here the adjusted repeat is created on a 24X16 canvas with the same symmetry settings, and filter/mapped/tiled
Again, preemptive math will yield images that avoid further processing. It is up to the user to recognize any problems, the repeat here needs to and can be isolated correctly from the file on the left, it is actually only 16 rows high. Here the adjusted repeat is created on a 24X16 canvas with the same symmetry settings, and filter/mapped/tiled 
 The above repeat was cropped and adjusted to 16 stitch width and 8 row height, the file saved, and the process repeated
The above repeat was cropped and adjusted to 16 stitch width and 8 row height, the file saved, and the process repeated  Using symmetry once more, remember to adjust the pencil size.
Using symmetry once more, remember to adjust the pencil size. 
 I was unable to use color exchange successfully on the above images, but with the saved 2 colors indexed red and white repeat both img2track and ayab appeared to load the repeat successfully.
I was unable to use color exchange successfully on the above images, but with the saved 2 colors indexed red and white repeat both img2track and ayab appeared to load the repeat successfully.  The map color exchange was successful using the steps described at the top of the post when beginning with the repeat drawn in a black and white version.
The map color exchange was successful using the steps described at the top of the post when beginning with the repeat drawn in a black and white version. 





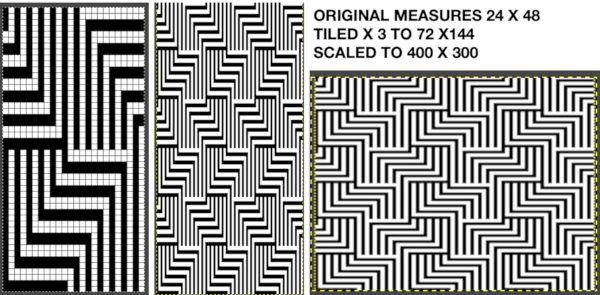 The colored versions before and after scaling, compared with the slip-stitch swatch.
The colored versions before and after scaling, compared with the slip-stitch swatch.  It is possible to produce a rectangular grid to start with on which to draw in Gimp, but the larger canvas size occupies a significantly larger space on the screen, complicating the process. For small designs, however, that may be an option to give one the sense of aspect ratio for the design in the final knit ie in representational FI. To resize the grid in uneven proportions, the chain-link below the spacing values needs to be broken
It is possible to produce a rectangular grid to start with on which to draw in Gimp, but the larger canvas size occupies a significantly larger space on the screen, complicating the process. For small designs, however, that may be an option to give one the sense of aspect ratio for the design in the final knit ie in representational FI. To resize the grid in uneven proportions, the chain-link below the spacing values needs to be broken 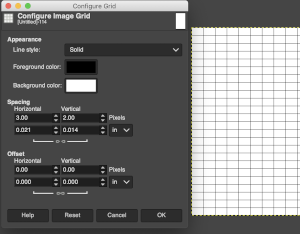 This repeat is designed for an electronic, and requires color-reverse.
This repeat is designed for an electronic, and requires color-reverse.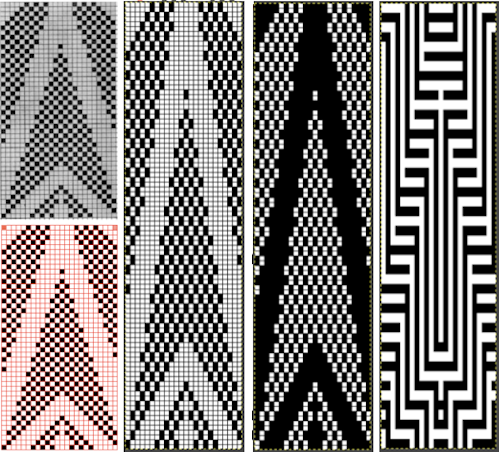 Once again, the possible change in scale is estimated. The repeat though only 24 stitches wide, is 92 rows high. On the left the repeat is shown as it appears on a square grid, to its right is the scaled 4:3 version, in a pixel count approximating the size of the swatch. It takes a bit of squinting to see the pattern more recognizable in the longer repeat in the larger tile
Once again, the possible change in scale is estimated. The repeat though only 24 stitches wide, is 92 rows high. On the left the repeat is shown as it appears on a square grid, to its right is the scaled 4:3 version, in a pixel count approximating the size of the swatch. It takes a bit of squinting to see the pattern more recognizable in the longer repeat in the larger tile 


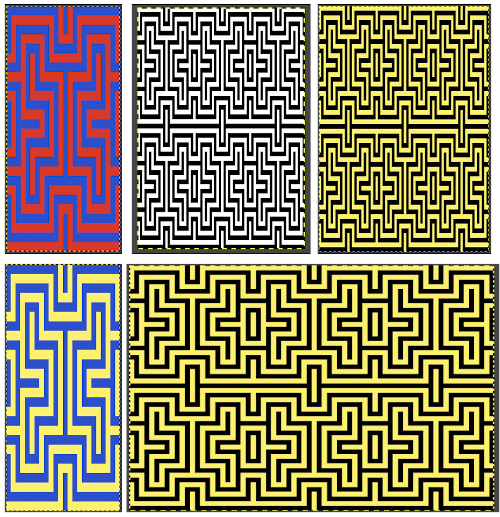
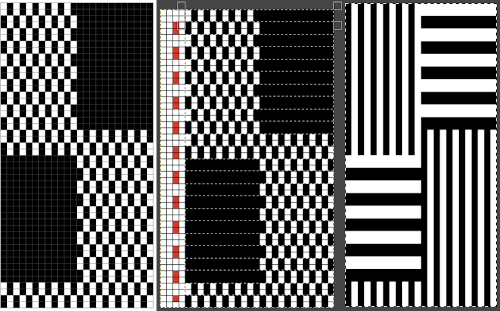
 The proof of concept swatch, knit in tuck stitch, begins to show the distortion by the stitch formations, textures vs plain knit, easily seen at the top edge. The bind-off is around 2 gate pegs in order to allow enough stretch.
The proof of concept swatch, knit in tuck stitch, begins to show the distortion by the stitch formations, textures vs plain knit, easily seen at the top edge. The bind-off is around 2 gate pegs in order to allow enough stretch.  Anyone familiar with either or both programs may find this a very quick way to visualize the scaling and moving of motifs within DIY designs and their possible outcomes prior to test knitting
Anyone familiar with either or both programs may find this a very quick way to visualize the scaling and moving of motifs within DIY designs and their possible outcomes prior to test knitting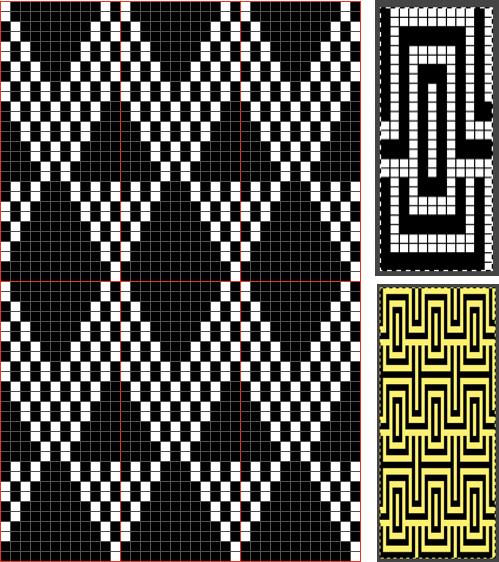

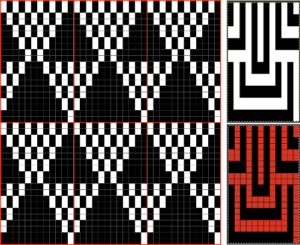

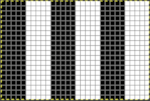
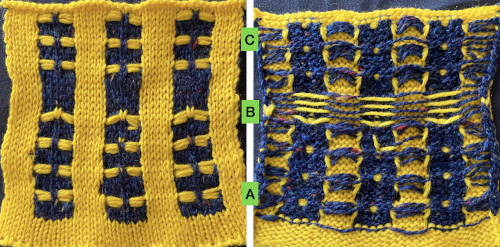 As stated, the process is easier and quicker working on non-selected groups. Above, the yellow yarn was thicker than the blue. To maintain proper color selection in the non-selected column, the center needle needs to remain in the B position, with the slipped stitch forming floats below it before the next row knits. If the needle is brought out to E, it will knit in the contrast color, forming floats in that color on the purl side, and a knit stitch in what was planned as an all-solid column on the knit. The results are seen at the top of the first sequence in the swatch. I chose to limit my number of floats to 4 to keep the process manageable, moved stitches on the left of the center needle to the front of the knit, and then followed with those to its right. One of the many things to explore in hand technique fabrics is finding a way to handle tools that may be more comfortable than others, practicing on single blocks of color first can help establish that. Below both yarns are equal in weight and thinner. The floats formed by the color in the B feeder are also hooked up on the center needle in each vertical group in that color, forming a pattern on the purl side as well.
As stated, the process is easier and quicker working on non-selected groups. Above, the yellow yarn was thicker than the blue. To maintain proper color selection in the non-selected column, the center needle needs to remain in the B position, with the slipped stitch forming floats below it before the next row knits. If the needle is brought out to E, it will knit in the contrast color, forming floats in that color on the purl side, and a knit stitch in what was planned as an all-solid column on the knit. The results are seen at the top of the first sequence in the swatch. I chose to limit my number of floats to 4 to keep the process manageable, moved stitches on the left of the center needle to the front of the knit, and then followed with those to its right. One of the many things to explore in hand technique fabrics is finding a way to handle tools that may be more comfortable than others, practicing on single blocks of color first can help establish that. Below both yarns are equal in weight and thinner. The floats formed by the color in the B feeder are also hooked up on the center needle in each vertical group in that color, forming a pattern on the purl side as well. 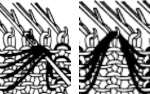 The needle position for selection for B feeder yarn also needs to be maintained. Bringing the needle out to E ensures it will knit on the next pass. In both of my tests, the slip stitch floats on the knit side lie more horizontally than the lifted-up floats on the purl.
The needle position for selection for B feeder yarn also needs to be maintained. Bringing the needle out to E ensures it will knit on the next pass. In both of my tests, the slip stitch floats on the knit side lie more horizontally than the lifted-up floats on the purl. 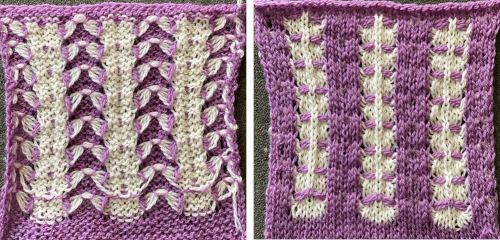
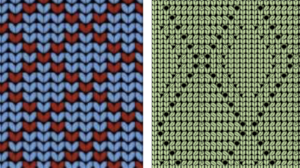

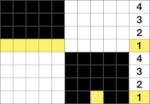 The transfers in the piece begin on row 5. Before the next row is knit in the alternate color, the slip stitch floats are reconfigured, bringing stitches 1 and 2, 4 and 5 in each group to the knit side of the fabric, leaving the center floats undisturbed.
The transfers in the piece begin on row 5. Before the next row is knit in the alternate color, the slip stitch floats are reconfigured, bringing stitches 1 and 2, 4 and 5 in each group to the knit side of the fabric, leaving the center floats undisturbed.  Bring the whole group out to the E position so they will form knit stitches with the first row of contrast as the carriage moves to the right.
Bring the whole group out to the E position so they will form knit stitches with the first row of contrast as the carriage moves to the right. 


 The extra needle selection prior to the next all knit row helps track the direction of the moves, stitches are moved three at a time, there are no cable crossings
The extra needle selection prior to the next all knit row helps track the direction of the moves, stitches are moved three at a time, there are no cable crossings


 The next step for me was to explore cable crossings on elongated stitches working double-bed. A basic pattern on any programmable machine for playing with elongated stitches on one bed while knitting every stitch on the other is to program pairs of blank rows followed by solid punched or black pixel rows. The yellow line in this chart illustrates the row on which cabling might occur.
The next step for me was to explore cable crossings on elongated stitches working double-bed. A basic pattern on any programmable machine for playing with elongated stitches on one bed while knitting every stitch on the other is to program pairs of blank rows followed by solid punched or black pixel rows. The yellow line in this chart illustrates the row on which cabling might occur.  Programming the width of the needle bed allows for only the stitches forming vertical columns in chosen locations to be put into work, allowing one to place groups that will involve crossings anywhere on the chosen pattern width. A base is knit in the ground color, which slips for 2 rows on the main bed, creating the elongated stitches that will be cabled. I had no problem with 2X2 cables,
Programming the width of the needle bed allows for only the stitches forming vertical columns in chosen locations to be put into work, allowing one to place groups that will involve crossings anywhere on the chosen pattern width. A base is knit in the ground color, which slips for 2 rows on the main bed, creating the elongated stitches that will be cabled. I had no problem with 2X2 cables, 
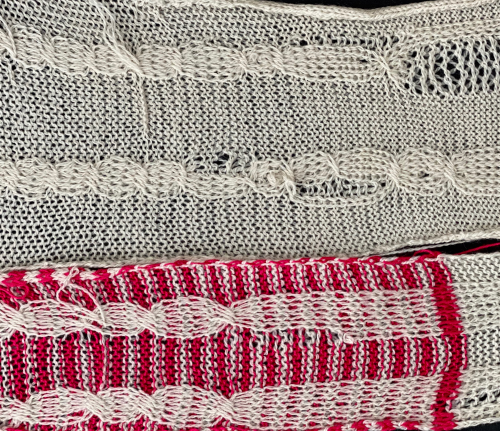 Cabling, returned to in a later post, with adjustments, making things work.
Cabling, returned to in a later post, with adjustments, making things work.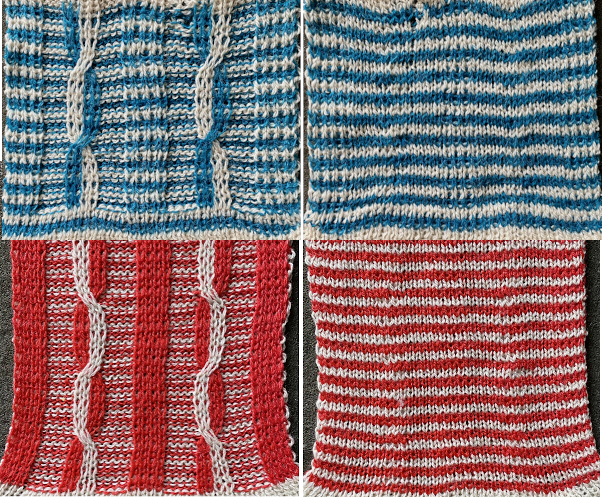 Continuing with shapes on striped grounds, this is the result of a self-drawn pattern
Continuing with shapes on striped grounds, this is the result of a self-drawn pattern  The approach is different than in the blog post on
The approach is different than in the blog post on 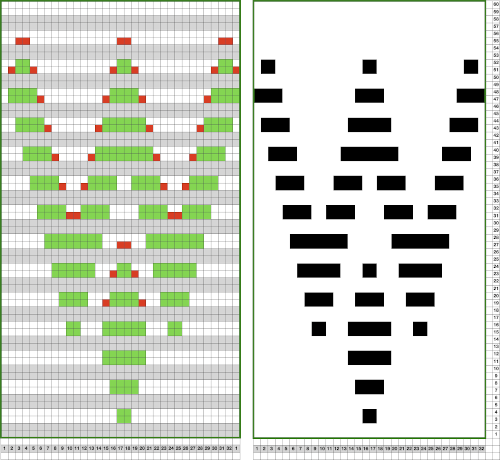

 Punchcards, in theory, may be used as given and set to double length, while for use in electronics drawing the pattern single height and using the double-length setting is also an option. Starting sides and fixing errors have always been more confusing for me when using the double-length feature, I prefer to punch holes or program pixels as I intend to knit them. The isolated reduced repeat for use in the electronic is charted, with an initial one-pixel error in 2 consecutive rows, marked with red cells. In transcribing any design, it is worth checking repeats multiple times after eyeballs and brains have had a rest. This was my start:
Punchcards, in theory, may be used as given and set to double length, while for use in electronics drawing the pattern single height and using the double-length setting is also an option. Starting sides and fixing errors have always been more confusing for me when using the double-length feature, I prefer to punch holes or program pixels as I intend to knit them. The isolated reduced repeat for use in the electronic is charted, with an initial one-pixel error in 2 consecutive rows, marked with red cells. In transcribing any design, it is worth checking repeats multiple times after eyeballs and brains have had a rest. This was my start: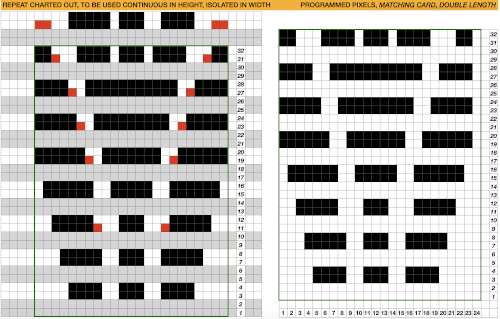 The first test is of an isolated motif. The yellow arrow points to the pixel error, the cyan to the positions where some needles in the full repeat were “accidentally” placed in A position, not B, resulting in pattern stitches not being formed.
The first test is of an isolated motif. The yellow arrow points to the pixel error, the cyan to the positions where some needles in the full repeat were “accidentally” placed in A position, not B, resulting in pattern stitches not being formed. 
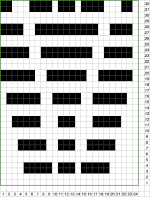

 Two other options for charting the fabric in numbers: A. draw the repeat as given
Two other options for charting the fabric in numbers: A. draw the repeat as given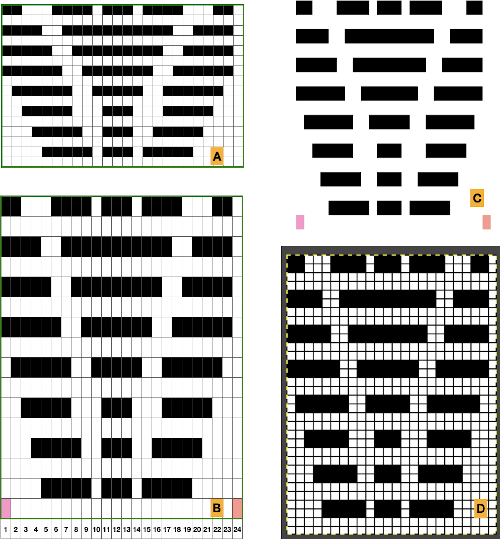 Any simple Fair Isle repeat may also be used. The numbering in the charts matches what is normally seen on the left edge of the tables
Any simple Fair Isle repeat may also be used. The numbering in the charts matches what is normally seen on the left edge of the tables


 The world of possibilities grows even further for single color shadow lace, when, examining the same design, one recognizes that the pile knit card, with the blank rows filled in in pattern, is the same as the fair isle version of the repeat, rendered double long
The world of possibilities grows even further for single color shadow lace, when, examining the same design, one recognizes that the pile knit card, with the blank rows filled in in pattern, is the same as the fair isle version of the repeat, rendered double long 


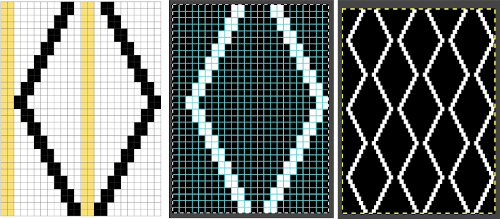

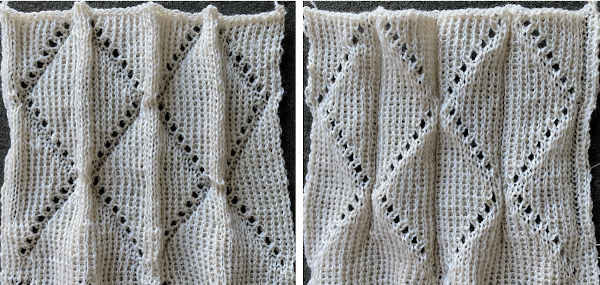

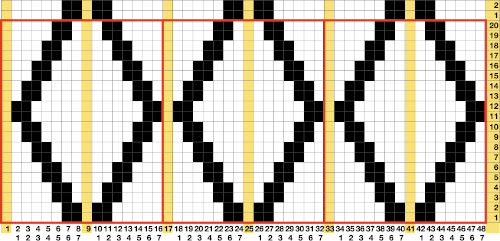 the file for multiple repeats after color reverse
the file for multiple repeats after color reverse 
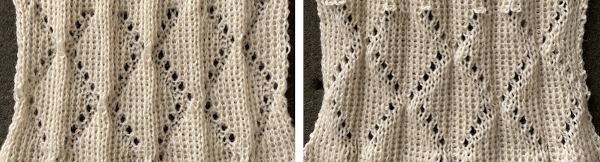

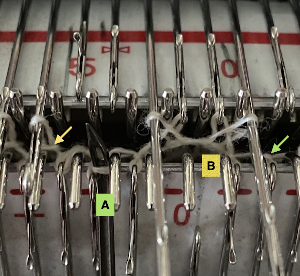
 There is an interesting scale and depth of fold comparison between this version and the first using the repeat, achieved by tightening the tension as much as possible, and possibly by reducing the size of the eyelets.
There is an interesting scale and depth of fold comparison between this version and the first using the repeat, achieved by tightening the tension as much as possible, and possibly by reducing the size of the eyelets. 
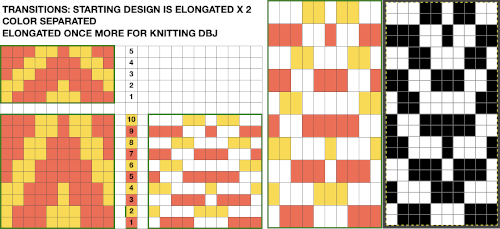
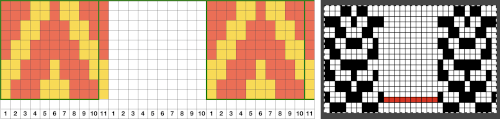 Take care if copying and pasting single columns to alter a repeat width that the whole column is indeed copied and that if using the pencil tool flood fill is not used unintentionally. The original intent was also to correct the elongated slip stitch segments on the edge of the programmed vertical designs marked in blue, but the paste with errors in red accomplished creating the same issue
Take care if copying and pasting single columns to alter a repeat width that the whole column is indeed copied and that if using the pencil tool flood fill is not used unintentionally. The original intent was also to correct the elongated slip stitch segments on the edge of the programmed vertical designs marked in blue, but the paste with errors in red accomplished creating the same issue 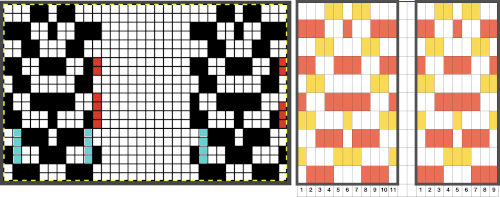
 The first segments were knit using striper backing, with the ribber knitting every stitch, every row, in both colors. When a slip stitch is used with needles out of work on the main bed, end needle selection should be canceled. In A it was not. The result is that end needles alongside the out-of-work column knit with each color in each row. In B, end needle selection was canceled, and one can now see the elongated slipped stitches that result from areas that should have been marked with the contrasting color
The first segments were knit using striper backing, with the ribber knitting every stitch, every row, in both colors. When a slip stitch is used with needles out of work on the main bed, end needle selection should be canceled. In A it was not. The result is that end needles alongside the out-of-work column knit with each color in each row. In B, end needle selection was canceled, and one can now see the elongated slipped stitches that result from areas that should have been marked with the contrasting color 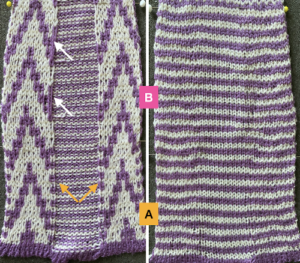 As long as the number of stitches on the ribber is even, lili buttons may be used, affecting the scale of the pattern in both height and width. In A, they were used with the ribber set to slip in both directions, in B, set to tuck in both directions. C marks the return to the N/N setting, with needle transfers to mark a possible pleat.
As long as the number of stitches on the ribber is even, lili buttons may be used, affecting the scale of the pattern in both height and width. In A, they were used with the ribber set to slip in both directions, in B, set to tuck in both directions. C marks the return to the N/N setting, with needle transfers to mark a possible pleat.  The initial pleat idea charted out for single stitch folds, stitches transferred to ribber in the R columns, to the top bed in the T columns
The initial pleat idea charted out for single stitch folds, stitches transferred to ribber in the R columns, to the top bed in the T columns 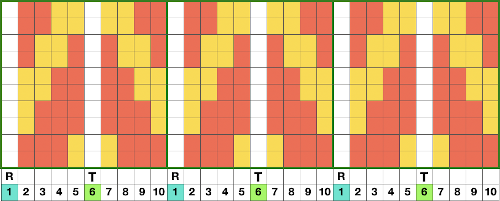 The result is a fairly soft pleat, the choice below was to retain end needle selection.
The result is a fairly soft pleat, the choice below was to retain end needle selection.  Various ribbed pleat configurations are explored in
Various ribbed pleat configurations are explored in  Paired transfers in the planning stages: because the repeat is small and has a single center pivot point, it is rendered once more, adding columns
Paired transfers in the planning stages: because the repeat is small and has a single center pivot point, it is rendered once more, adding columns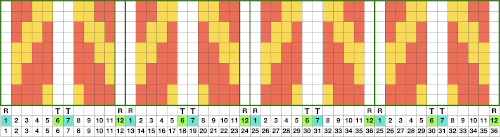
 The resulting fabric relaxed on the left, lightly steamed on the right
The resulting fabric relaxed on the left, lightly steamed on the right 
 Note: the color positions in the design have been reversed from those in the first swatch. If “floats” are noted at any time in the spaces where needles are out of work on the ribber, look for dropped stitches.
Note: the color positions in the design have been reversed from those in the first swatch. If “floats” are noted at any time in the spaces where needles are out of work on the ribber, look for dropped stitches. Needles in locations where only the backing is to be shown are transferred down to the ribber. Leaving the eyelets, they were transferred back up to the main bed when brought into work to reverse or change the shape. Addition and subtraction of stitches take place before the next pass with the alternate color. Here movement is random, to get some sense of the effect, it could be made deliberate by following a chart or color separating and automating the pattern, with its starting side on the right.
Needles in locations where only the backing is to be shown are transferred down to the ribber. Leaving the eyelets, they were transferred back up to the main bed when brought into work to reverse or change the shape. Addition and subtraction of stitches take place before the next pass with the alternate color. Here movement is random, to get some sense of the effect, it could be made deliberate by following a chart or color separating and automating the pattern, with its starting side on the right. 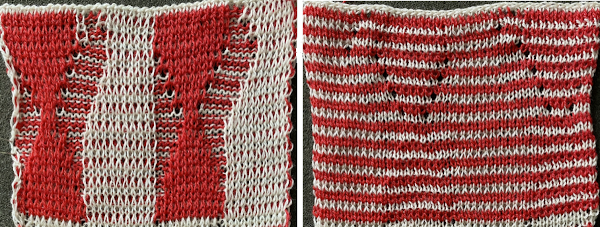
 What of having shapes appearing in each of the 2 colors on a striped ground? Eliminating some of the guesswork I used the repeat from a previous single-bed blog post on
What of having shapes appearing in each of the 2 colors on a striped ground? Eliminating some of the guesswork I used the repeat from a previous single-bed blog post on 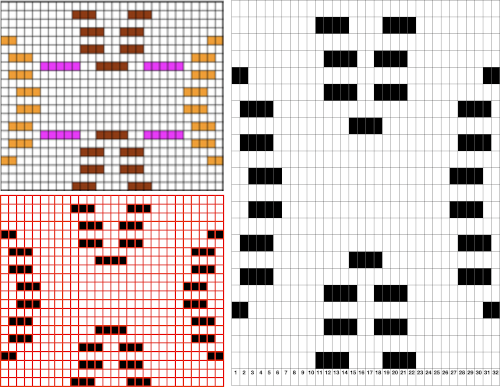
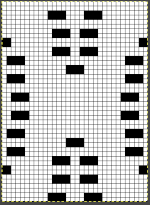 The resulting sample, the yarn is thin, might have benefited from tighter tension and more contrast.
The resulting sample, the yarn is thin, might have benefited from tighter tension and more contrast. 
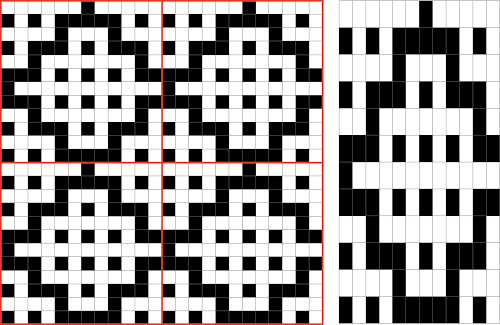
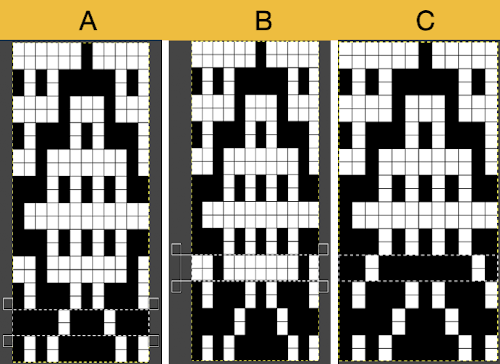

 Proof of concept: the bottom half is knit using the slip stitch setting, the top half in the tuck setting. The added texture on the tuck stitch purl side makes the fabric a more interesting, reversible one, and wider than its companion.
Proof of concept: the bottom half is knit using the slip stitch setting, the top half in the tuck setting. The added texture on the tuck stitch purl side makes the fabric a more interesting, reversible one, and wider than its companion.  For a different way of working with two-color initial images using only Gimp, see tips in
For a different way of working with two-color initial images using only Gimp, see tips in 
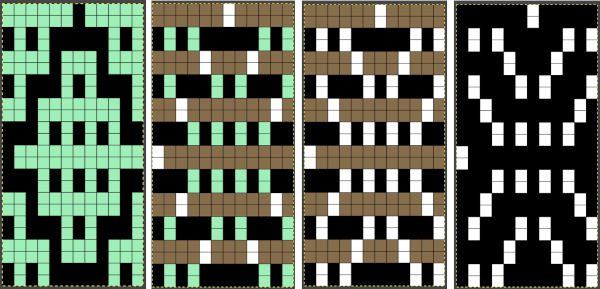

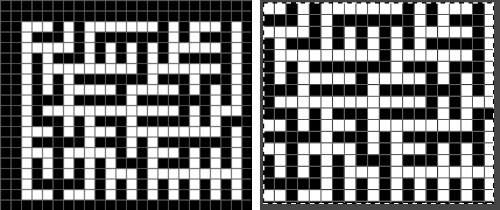
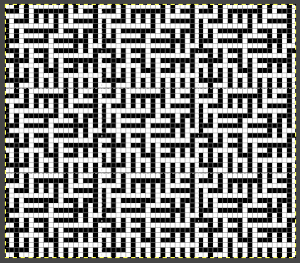 Numbers processing to ready the repeat for final gimp editing:
Numbers processing to ready the repeat for final gimp editing: 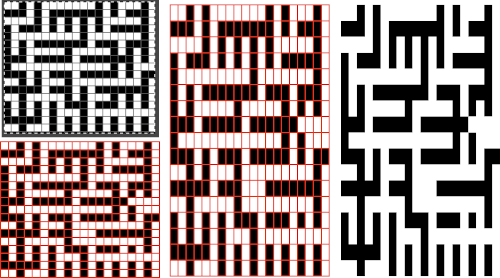

 Getting back to clearer pattern results: when using electronics, it is possible to create far wider and taller repeats for download. The technique to achieve them uses the same process. That said, there are quicker ways to attain the final repeat illustrated in the 2024 posts on using Gimp color to alpha through the Layer> Transparency option or Colors> Color to Alpha.
Getting back to clearer pattern results: when using electronics, it is possible to create far wider and taller repeats for download. The technique to achieve them uses the same process. That said, there are quicker ways to attain the final repeat illustrated in the 2024 posts on using Gimp color to alpha through the Layer> Transparency option or Colors> Color to Alpha.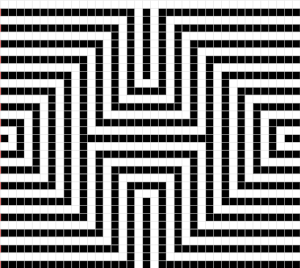
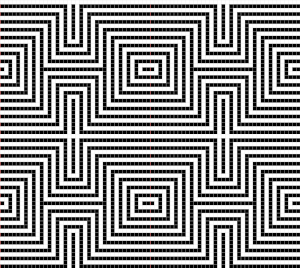
 the isolated repeat, double-length
the isolated repeat, double-length 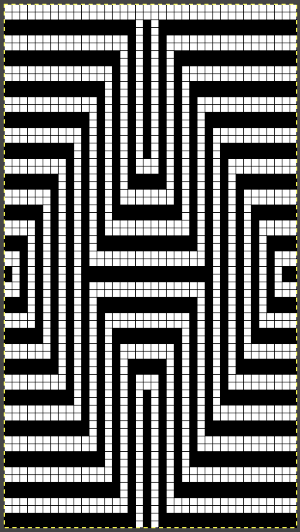 the color separation in progress
the color separation in progress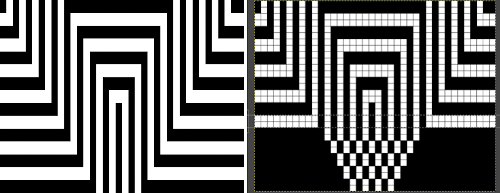 When knit, that white cell pair of rows break up the overall shapes and shifts the pattern in the top and bottom half
When knit, that white cell pair of rows break up the overall shapes and shifts the pattern in the top and bottom half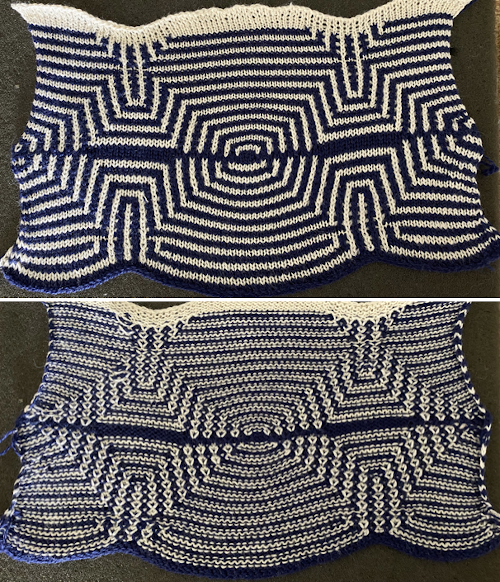 

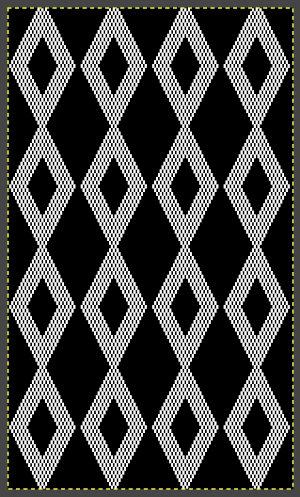 The final adjusted repeat
The final adjusted repeat 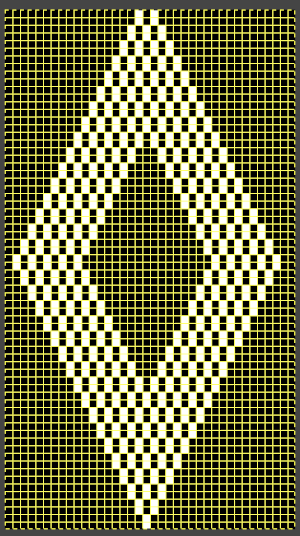
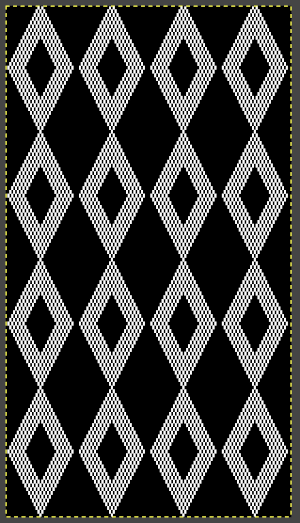 knit using the tuck stitch setting in both directions, KCI, first row left to right, leading with the dark color
knit using the tuck stitch setting in both directions, KCI, first row left to right, leading with the dark color  and here with the lighter color
and here with the lighter color  In progress, on the km
In progress, on the km  the relaxed, 3D-ish view on the reverse
the relaxed, 3D-ish view on the reverse  why projects can take longer than planned
why projects can take longer than planned  The finished, relaxed scarf with pressed edges only, retaining the conical striped forms
The finished, relaxed scarf with pressed edges only, retaining the conical striped forms The repeat knit double length, changing colors every 2 rows, becomes something quite different, with a sharp curl to the purl side
The repeat knit double length, changing colors every 2 rows, becomes something quite different, with a sharp curl to the purl side 
 with my color changer in this threading sequence throughout
with my color changer in this threading sequence throughout
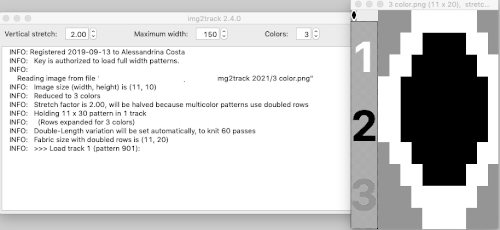 where normally each color in each design row knits twice. Because selection occurs for pairs of rows, the first preselection row is from right to left. To decrease the backing rows, the ribber is set for birdseye. I prefer to have an end needle on each end on the ribber, keeping in mind that the total number of needles in use there needs to be even. The machine provides reminders as to which color should be knitting. My samples are knit using KCI on the top bed. Because the preselection happens twice, it is easy enough to knit in pattern from left to right,
where normally each color in each design row knits twice. Because selection occurs for pairs of rows, the first preselection row is from right to left. To decrease the backing rows, the ribber is set for birdseye. I prefer to have an end needle on each end on the ribber, keeping in mind that the total number of needles in use there needs to be even. The machine provides reminders as to which color should be knitting. My samples are knit using KCI on the top bed. Because the preselection happens twice, it is easy enough to knit in pattern from left to right,  when the carriages have reached the right side, simply use a ribber comb to push all needles back to B.
when the carriages have reached the right side, simply use a ribber comb to push all needles back to B. 


 Speeding things up with color separation, beginning with the method that will have each color, each design row knitting twice. The repeat is 10 rows high, so it is expanded X6 to 10 by 60 rows. In the final result, the second row for each color in the separation is in turn erased. The red was added to make all 3 colors visible while working the separation, avoiding confusion with the white ground. The knittable result as usual is in a black and white png
Speeding things up with color separation, beginning with the method that will have each color, each design row knitting twice. The repeat is 10 rows high, so it is expanded X6 to 10 by 60 rows. In the final result, the second row for each color in the separation is in turn erased. The red was added to make all 3 colors visible while working the separation, avoiding confusion with the white ground. The knittable result as usual is in a black and white png 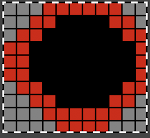
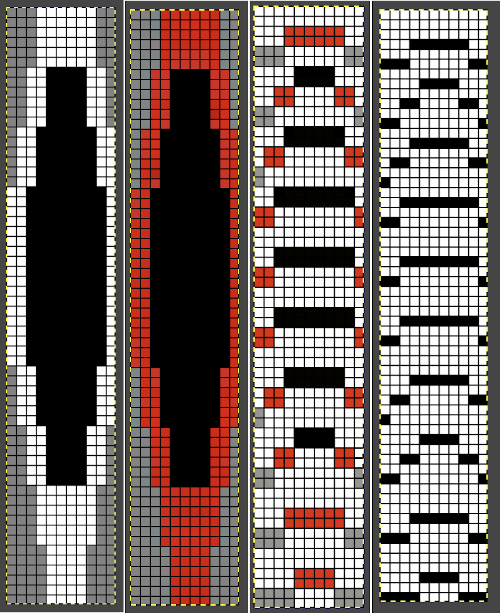

 The ribber can also be set to knit every row, resulting in elongation on the knit side, while creating an interesting striper backing
The ribber can also be set to knit every row, resulting in elongation on the knit side, while creating an interesting striper backing
 Comparing this version to the birdseye backed one for repeat height
Comparing this version to the birdseye backed one for repeat height  Comparisons: HoP, pushing back needles to B, and color separation results. In the latter, the design is likely elongated in part due to a change in the distribution of thinner yarns to larger design areas with no tension adjustments
Comparisons: HoP, pushing back needles to B, and color separation results. In the latter, the design is likely elongated in part due to a change in the distribution of thinner yarns to larger design areas with no tension adjustments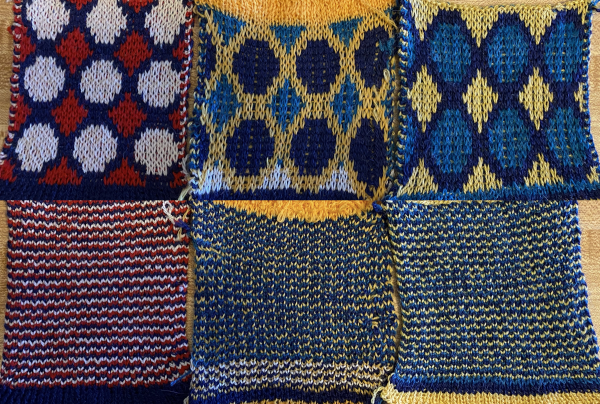 
 The Ayab lettering as opposed to numbers move from right to left. The manual states that the color separation order is: white C, grey B, black A with their sequence = C (3), B (2), A(1). If the prompts for changing colors as given are followed it provides a very valuable in tracking them, but if out of habit one knits in the usual 1,2,3 sequence, the color placement occurs in an unexpected order and may result in errors. The on-screen letter prompt corresponding to the anticipated color change sometimes occurs with the knit carriage on the right, sometimes as it approaches the changer, and the size of the font was hard for me to see since the screen was not close enough for easy visibility.
The Ayab lettering as opposed to numbers move from right to left. The manual states that the color separation order is: white C, grey B, black A with their sequence = C (3), B (2), A(1). If the prompts for changing colors as given are followed it provides a very valuable in tracking them, but if out of habit one knits in the usual 1,2,3 sequence, the color placement occurs in an unexpected order and may result in errors. The on-screen letter prompt corresponding to the anticipated color change sometimes occurs with the knit carriage on the right, sometimes as it approaches the changer, and the size of the font was hard for me to see since the screen was not close enough for easy visibility.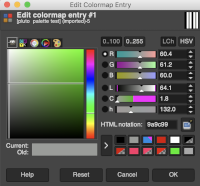 The small file makes for a quick test of proper color selection for each of the three colors used
The small file makes for a quick test of proper color selection for each of the three colors used 
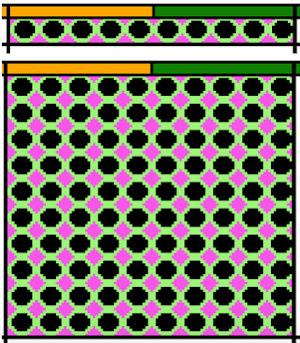 Having some idea of stitch counts for each color in the design in the first few rows can help identify proper, planned color placement errors
Having some idea of stitch counts for each color in the design in the first few rows can help identify proper, planned color placement errors 
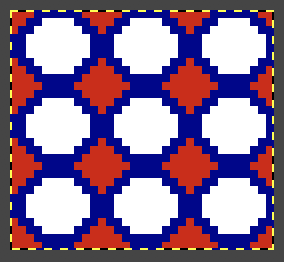 My first swatch using the heart of Pluto separation and a greyscale motif
My first swatch using the heart of Pluto separation and a greyscale motif 
 My tested color change sequence is #1, #2, #3 colors throughout, I disregarded the prompts for color changes at the bottom of the Ayab screen. Some things to ponder: in pieces that require color changes, starting with waste knitting in the same colors can help assess the best tension, whether each color will be picked up properly, and if the colors work well together. Looking at these 3 small tests, it appears that a choice should be made when casting on about using color 1 or 2 for the preselection and cast on rows. If the setting to slip is forgotten for the first move to the left, the color in the feeder will knit every stitch rather than a pattern selection. Always check settings when on the right, making certain lili buttons are set as well. This pattern does not contain 3 colors on every row. In addition to that, when working DBJ with other color separations one is likely used to seeing knit bed needle selections on every row. That is not true here, is a function of the technique, not a patterning error. On rows that have colors missing, when that color is in use, the main bed slips, the ribber works every other needle, first in one direction, then the other, adding to the row count on the purl side of the knit.
My tested color change sequence is #1, #2, #3 colors throughout, I disregarded the prompts for color changes at the bottom of the Ayab screen. Some things to ponder: in pieces that require color changes, starting with waste knitting in the same colors can help assess the best tension, whether each color will be picked up properly, and if the colors work well together. Looking at these 3 small tests, it appears that a choice should be made when casting on about using color 1 or 2 for the preselection and cast on rows. If the setting to slip is forgotten for the first move to the left, the color in the feeder will knit every stitch rather than a pattern selection. Always check settings when on the right, making certain lili buttons are set as well. This pattern does not contain 3 colors on every row. In addition to that, when working DBJ with other color separations one is likely used to seeing knit bed needle selections on every row. That is not true here, is a function of the technique, not a patterning error. On rows that have colors missing, when that color is in use, the main bed slips, the ribber works every other needle, first in one direction, then the other, adding to the row count on the purl side of the knit. 


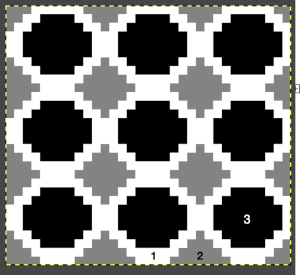
 The mess at the bottom was due to the green yarn getting caught on the needle bed and not knitting the necessary stitches on the ribber, so dropped stitches were formed
The mess at the bottom was due to the green yarn getting caught on the needle bed and not knitting the necessary stitches on the ribber, so dropped stitches were formed  The assumption is that if the C, B, A rotation and prompts are to be followed, the middle color 2 can stay in place, and the placement of 1 and 3 can be exchanged.
The assumption is that if the C, B, A rotation and prompts are to be followed, the middle color 2 can stay in place, and the placement of 1 and 3 can be exchanged.

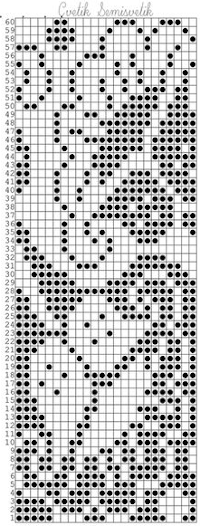 The units in many such illustrations are not square, and the goal is to end up with a PNG where each square unit represents one stitch, one row.
The units in many such illustrations are not square, and the goal is to end up with a PNG where each square unit represents one stitch, one row.
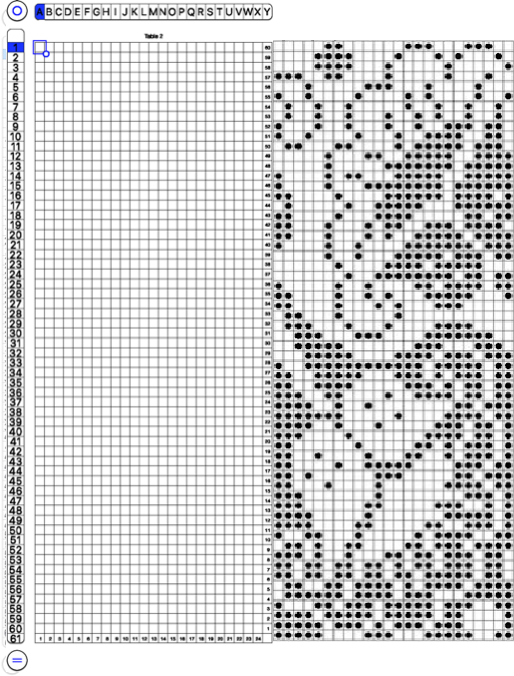
 and alter the cell borders to a bright, contrasting color. I chose red, 3-point thickness.
and alter the cell borders to a bright, contrasting color. I chose red, 3-point thickness. 
 Copy and paste the completed table. Make certain there is a different color cell in any white squares at the far corners of the image, in this case, upper right and upper left (yellow), remove cell borders
Copy and paste the completed table. Make certain there is a different color cell in any white squares at the far corners of the image, in this case, upper right and upper left (yellow), remove cell borders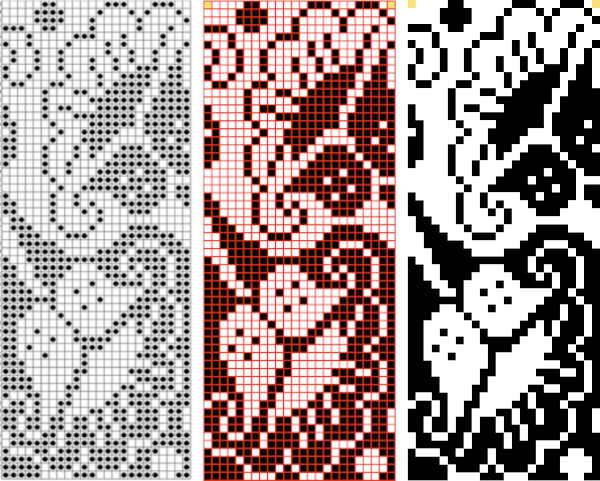 



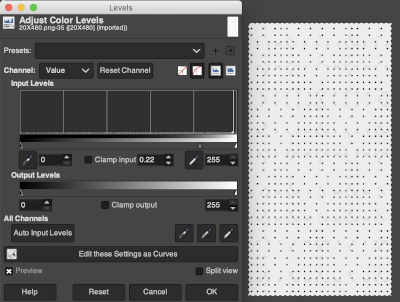 Proceed as for the first image, being mindful of an unnecessary row at the bottom. The saved image can be tweaked in size by turning off Constrain Proportions and adjusting values for width and height for proper placement under the table grid. It soon becomes evident that the card is composed of smaller repeat segments, which can be copied and pasted making for faster filling in the whole punchcard minimum row # requirement.
Proceed as for the first image, being mindful of an unnecessary row at the bottom. The saved image can be tweaked in size by turning off Constrain Proportions and adjusting values for width and height for proper placement under the table grid. It soon becomes evident that the card is composed of smaller repeat segments, which can be copied and pasted making for faster filling in the whole punchcard minimum row # requirement. 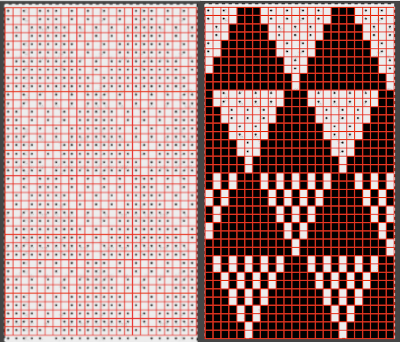 Check the repeat alignment by tiling it.
Check the repeat alignment by tiling it. 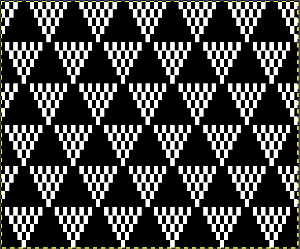 The smallest adjusted electronic repeat, 12X20 pixels.
The smallest adjusted electronic repeat, 12X20 pixels.  The converted, partial punchcard repeat
The converted, partial punchcard repeat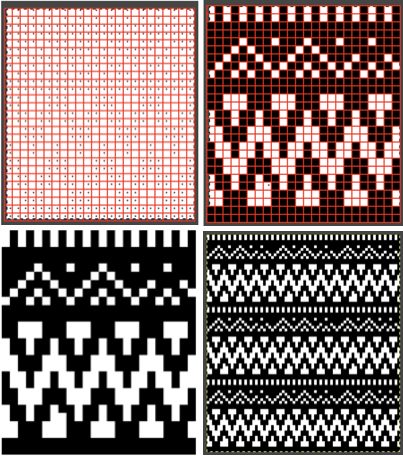  2023: ArahPaint‘s weave from grid tool makes working with the full repeat possible. The final repeat was cropped by 2 rows at the top to 24X206 to avoid a 4-row solid color line produced when the original was tiled vertically.
2023: ArahPaint‘s weave from grid tool makes working with the full repeat possible. The final repeat was cropped by 2 rows at the top to 24X206 to avoid a 4-row solid color line produced when the original was tiled vertically.

 if used, will change the numbering on the side of the card, but not the design content
if used, will change the numbering on the side of the card, but not the design content 
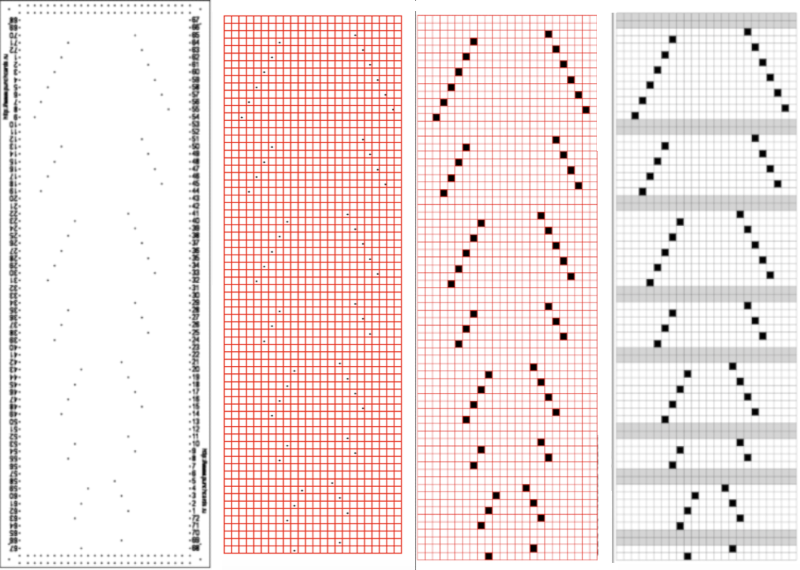 In the past I have found lace repeats, in particular, to be particularly cranky when scaled down in Gimp due to the paucity of black cells. After the above steps, I decided to try color invert, resize, and color invert again, which in this instance, produced what appears to be an accurate repeat. Of course, the final png is likely to need mirroring for use in some electronic models
In the past I have found lace repeats, in particular, to be particularly cranky when scaled down in Gimp due to the paucity of black cells. After the above steps, I decided to try color invert, resize, and color invert again, which in this instance, produced what appears to be an accurate repeat. Of course, the final png is likely to need mirroring for use in some electronic models 
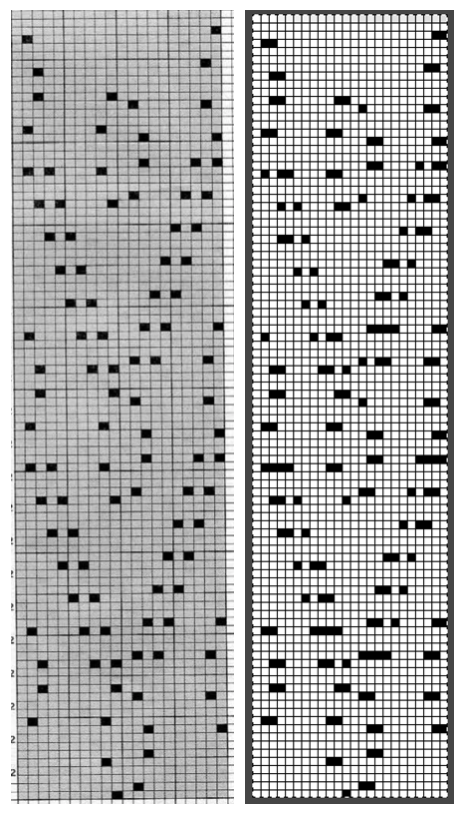 2023: a different approach:
2023: a different approach: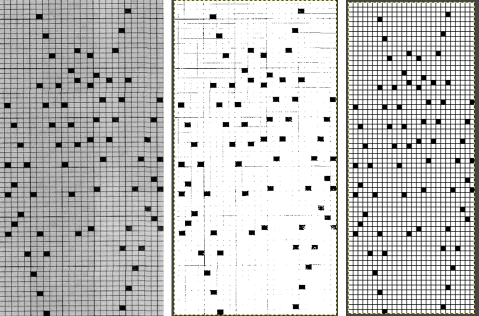
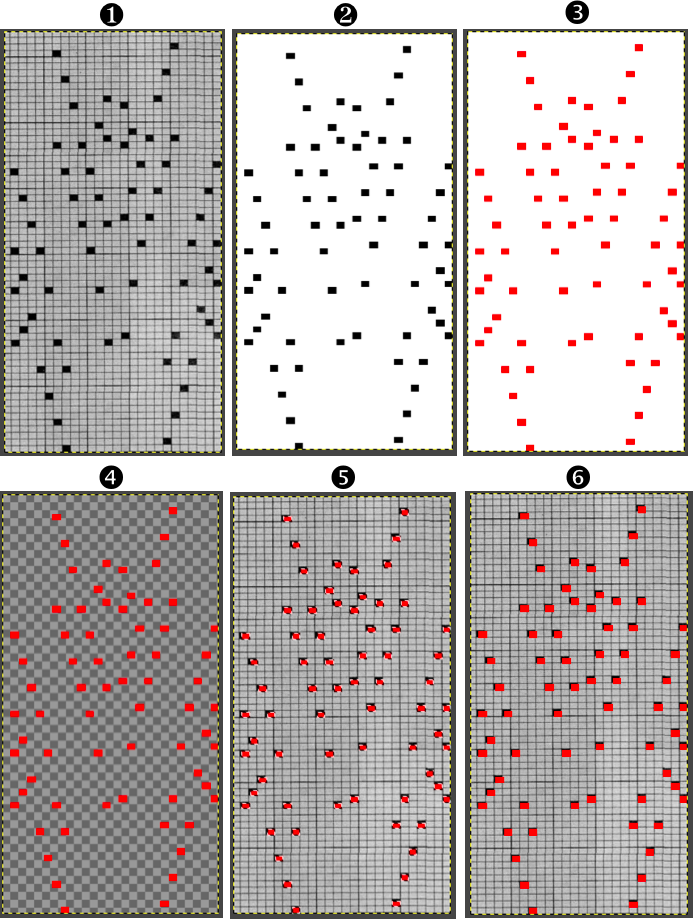


 offers 4 punchcards for use with this technique
offers 4 punchcards for use with this technique  I chose to work with #170. The lace carriage in the Toyota models operates from the right side rather than the left as in Brother. The direction of the arrows marked on the card actually indicates movements for the carriage operating from that side. That fact is taken into consideration planning a possible Brother punchcard repeat. Lace direction arrows are matched based on the punchcard image being mirrored horizontally. The card in its original version is imaged on the left, mirrored on the far right, the proposed Brother punchcard in the center
I chose to work with #170. The lace carriage in the Toyota models operates from the right side rather than the left as in Brother. The direction of the arrows marked on the card actually indicates movements for the carriage operating from that side. That fact is taken into consideration planning a possible Brother punchcard repeat. Lace direction arrows are matched based on the punchcard image being mirrored horizontally. The card in its original version is imaged on the left, mirrored on the far right, the proposed Brother punchcard in the center 
 The proposed Brother punchcard repeat is now expanded for use on the electronic machine, ready for converting to .bmp in Gimp. Numbers in the middle of the chart on the left helped keep track of repeat segments. I also used red dots initially to mark segments as I had completed in the expanded the repeat, then erased them
The proposed Brother punchcard repeat is now expanded for use on the electronic machine, ready for converting to .bmp in Gimp. Numbers in the middle of the chart on the left helped keep track of repeat segments. I also used red dots initially to mark segments as I had completed in the expanded the repeat, then erased them


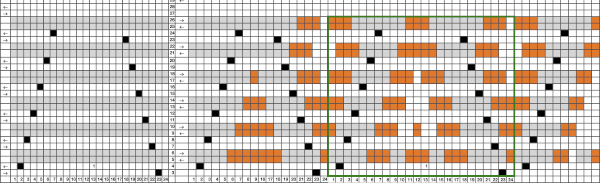 I expected something like this
I expected something like this 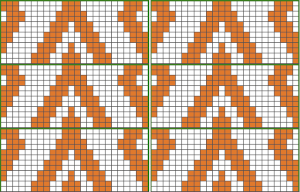
 Regrouping: the easiest place to insert eyelets is in the dominant, background-color
Regrouping: the easiest place to insert eyelets is in the dominant, background-color  The 930 .png
The 930 .png Can the exchange of the color positions in the yarn feeder create colored shapes with eyelets on the white ground? not only does it not do so in a way I liked, but my machine was having none of it as well
Can the exchange of the color positions in the yarn feeder create colored shapes with eyelets on the white ground? not only does it not do so in a way I liked, but my machine was having none of it as well 
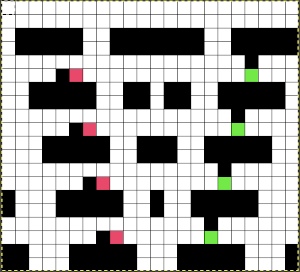

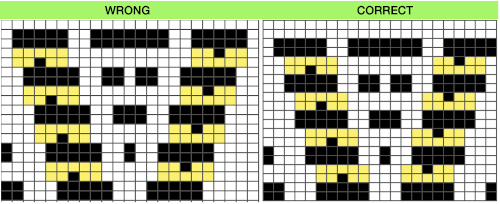 It’s good to start with a small repeat.
It’s good to start with a small repeat.
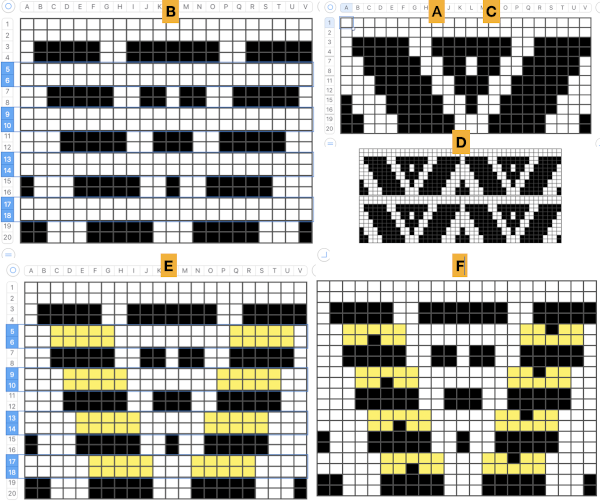 Taking it to continuous shapes and checking them in repeat: red cells represent transfers to the right, cyan ones the transfers to the left. The empty cells adjoining each of both colors represent the location of the doubled-up stitch after the transfer is made
Taking it to continuous shapes and checking them in repeat: red cells represent transfers to the right, cyan ones the transfers to the left. The empty cells adjoining each of both colors represent the location of the doubled-up stitch after the transfer is made 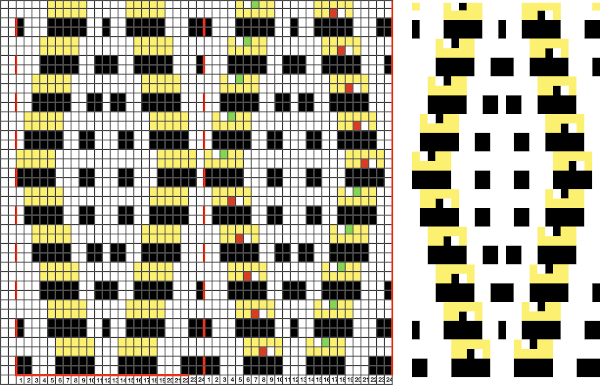
 I like to check tiling for the repats along the whole process
I like to check tiling for the repats along the whole process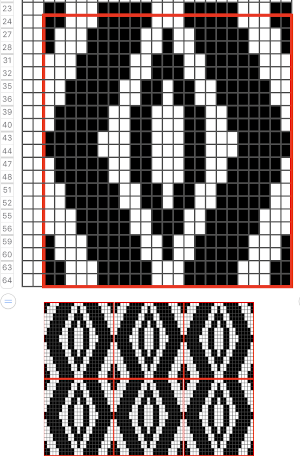 Though the repeat is 24 stitches wide, it is not suitable for use on the punchcard machines in this format, its tiled test
Though the repeat is 24 stitches wide, it is not suitable for use on the punchcard machines in this format, its tiled test
 Adding another contrast color stitch to shapes will make the number of stitches on either side of the eyelets consistent
Adding another contrast color stitch to shapes will make the number of stitches on either side of the eyelets consistent 

 and with the addition of two blank rows at the top of each segment.
and with the addition of two blank rows at the top of each segment. The possibilities are endless, with some patience, they can be manipulated to meet personal preferences and taste.
The possibilities are endless, with some patience, they can be manipulated to meet personal preferences and taste.