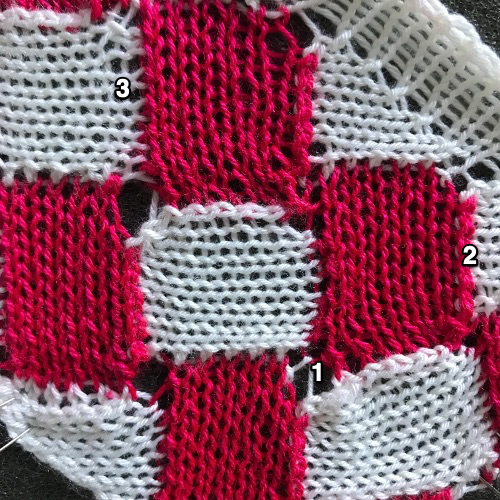
A Facebook member recently shared this photo, followed by a “wish I could make it” comment, it is from the Passap #60 pattern book.  I began a spreadsheet on my blog intending to update it over time that may be useful when traveling between Brother and Passap
I began a spreadsheet on my blog intending to update it over time that may be useful when traveling between Brother and Passap
The style in the photo is that of a generously sized dropped shoulder sweater. I will not share pattern instructions but will try to interpret some of the possibilities for knitting it as written or for achieving similar textures on the Brother machines To start with, you will note the recommended test swatch size is 100 stitches by 100 rows. When gauge matters as in dbj or heavily textured knits, this is a necessity. In turn, math calculations also become easier in metric. If using the knitleader I have sometimes reduced the swatch size to 80 stitches by 80 rows. Even for scarves where calculations may matter less when transitioning from smaller gauge swatches to larger stitch counts there can be surprises. What knits on 60 stitches may refuse to do so on larger stitch counts, requiring tension and gauge adjustments. Although Passap promoted that it knits easily with no weights, I always cast on with ribber cast on comb, and then, if needed, the addition of weights may be easily made.
To start with, you will note the recommended test swatch size is 100 stitches by 100 rows. When gauge matters as in dbj or heavily textured knits, this is a necessity. In turn, math calculations also become easier in metric. If using the knitleader I have sometimes reduced the swatch size to 80 stitches by 80 rows. Even for scarves where calculations may matter less when transitioning from smaller gauge swatches to larger stitch counts there can be surprises. What knits on 60 stitches may refuse to do so on larger stitch counts, requiring tension and gauge adjustments. Although Passap promoted that it knits easily with no weights, I always cast on with ribber cast on comb, and then, if needed, the addition of weights may be easily made.
Strippers, which push down on the knit from the lock as it moves from side to side, have no equivalent in Brother, where weight is an absolute necessity when working ribbed fabrics. Stripper handles come in varied colors: orange is for double bed work, black is for single bed work, blue is for very heavy fabrics. A suggested rule of thumb is that if you are knitting on both back and front bed in a stitch pattern where several needles in work are opposite needles out of work use black strippers ( 3×3 rib or cables and Aran work would be examples). Sometimes spacing between the 2 beds will make black strippers harder to use, other times 2 different types may be used concurrently for best results.
As the size of the piece changes ie. in shaped sleeves, any weight must be adjusted proportionately to keep the gauge constant in order to avoid sizing surprises.
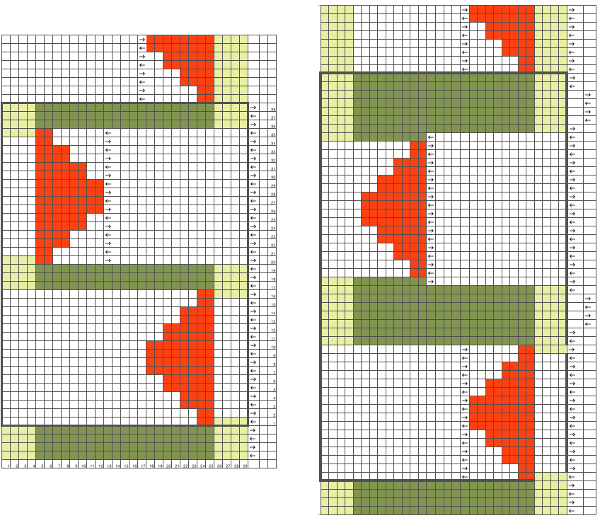
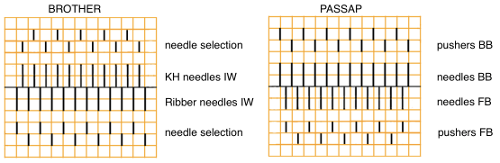
The Passap is a true double bed. The image on the left is of the Passap locks and on the right, of a stripper. The position of the beds is reversed to the Japanese, the knit bed is in front, the “ribber” in back. 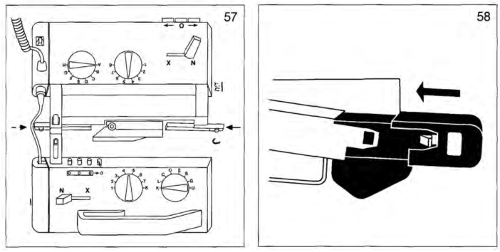 The locks (carriages) pr select pushers, they, in turn, select needles akin to Brother pre-selection. That is the reason why the Passap needle set up diagrams include more information bits than those for Japanese machines.
The locks (carriages) pr select pushers, they, in turn, select needles akin to Brother pre-selection. That is the reason why the Passap needle set up diagrams include more information bits than those for Japanese machines.  Additional details for any of the above are only provided in publications if they are necessary to create the particular stitch type. That said, one is free to add a knitting bed or alter lock settings simply based on the goal for the piece and an understanding of what black and white squares “do” in a pattern download. Looking at the Passap back lock, one can see the larger variety of the equivalent of cam button settings in Brother. The Passap buttons also referred to as arrow keys at its very rear make altering and automating patterns on the back bed easier and possible in a far wider assortment on any number of needles. The Brother lili setting, the equivalent of the #1 punchcard, must have an even number of needles in use on the ribber.
Additional details for any of the above are only provided in publications if they are necessary to create the particular stitch type. That said, one is free to add a knitting bed or alter lock settings simply based on the goal for the piece and an understanding of what black and white squares “do” in a pattern download. Looking at the Passap back lock, one can see the larger variety of the equivalent of cam button settings in Brother. The Passap buttons also referred to as arrow keys at its very rear make altering and automating patterns on the back bed easier and possible in a far wider assortment on any number of needles. The Brother lili setting, the equivalent of the #1 punchcard, must have an even number of needles in use on the ribber.
The arrow keys on the back lock reverse the Passap position of the pushers. Pushers that are down are brought up, pushers that are up are brought down. Arrows reverse when knitting in the direction of the arrow (think Brother preselection row), but cause needles to perform that function that same row. The O button releases any arrows, therefore pushers remain in the same position. N will knit disregarding arrow selection on the back bed. One arrow key reverses the pattern every 2 rows, 2 arrow keys do so every row.
Slip setting with pushers on Passap E6000 back lock is also BX, on the front lock it is LX. That differs from diagrams in the model and pattern books and magazines, which generally refer to Duomatic (Passap punchcard) settings. The assumption in the directions for the E6 is that the built-in techniques will provide you with LED prompts for any of the lock settings matching them to the right of schematics for the DUO, rather than that you would attempt to knit the pattern in some other way or on a different KM brand.
Scrolling down the pattern: Pintuck Pattern A: Deco card 77, E 6000 # 1130, technique 251
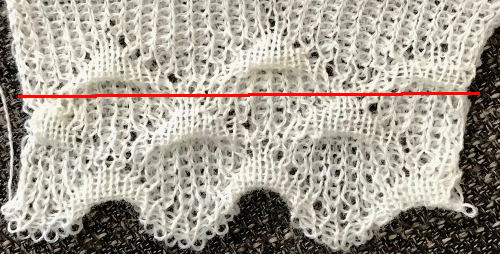
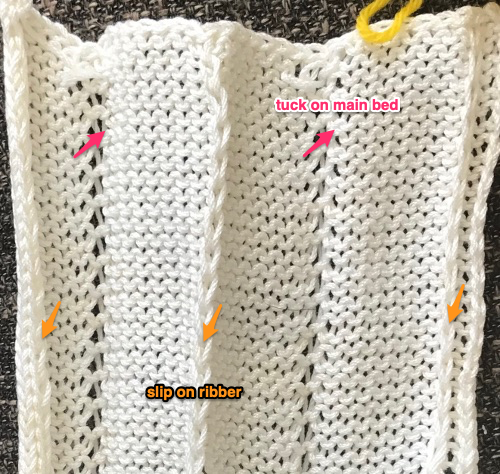
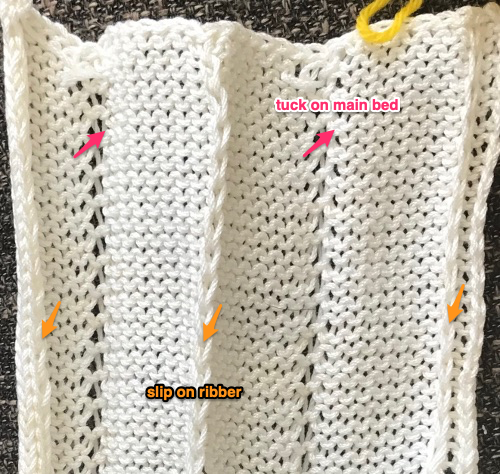
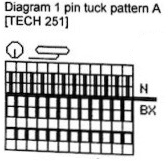 No pushers are illustrated. Back bed (N) knits every row. The front bed is set to slip in both directions (BX on Duo, LX on E6), pushers will be selected in the pattern by the console. When using Tech 251 two rows are knitting on the front bed forming pintucks where there are black squares in the stitch pattern. Brother probably would reach its limit with the original 1130, might be able to handle a thin yarn in a repeat slightly wider and taller. The Passap repeat becomes twice the length but is unaltered in its width. My swatch has an extra repeat before switching to normal knit, the red line highlights where the trim would have ended. The blistered pockets will appear as knit textured shapes on the purl side. The knit side will show a pattern of elongated stitches created when those needles are slipped. The red line in the photo shows the approximate ending for the repeat used in the trim in the magazine, I was on a roll and kept on knitting.
No pushers are illustrated. Back bed (N) knits every row. The front bed is set to slip in both directions (BX on Duo, LX on E6), pushers will be selected in the pattern by the console. When using Tech 251 two rows are knitting on the front bed forming pintucks where there are black squares in the stitch pattern. Brother probably would reach its limit with the original 1130, might be able to handle a thin yarn in a repeat slightly wider and taller. The Passap repeat becomes twice the length but is unaltered in its width. My swatch has an extra repeat before switching to normal knit, the red line highlights where the trim would have ended. The blistered pockets will appear as knit textured shapes on the purl side. The knit side will show a pattern of elongated stitches created when those needles are slipped. The red line in the photo shows the approximate ending for the repeat used in the trim in the magazine, I was on a roll and kept on knitting.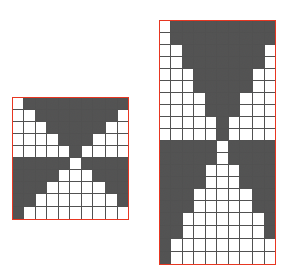
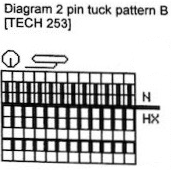
Pintuck pattern B: Deco repeat is 20 stitches wide (Duo cards are 40 stitches wide)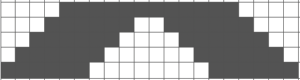 The directions at the time the model books were written for knitting with the console were designed to have the knitter work with built-in patterns and then to use the alter possibilities to manipulate them to achieve the same result as the punched holes might in the final repeat in the Duo. The Passap console had a card reader that operated with sheets that were in turn inserted into a sleeve and were drawn on with “special” pens. C6, proprietary early software that operated with a dongle, came a bit later. There was a large factory built-in pattern library, and the manufacturer, Madag, supplied free files for the Duo pattern books in formats that could be used with the program for “easy” download. The 910 had variation buttons and instructions for combining multiple patterns using the factory-supplied mylar sheets. The intent was to allow the knitter to maximize the use of both. I honestly have avoided altering patterns that way intentionally most of my knitting career, finding I simply prefer programming black and white squares for the function intended, which for me is easier to visualize and reduces errors. The trend explains the E6000 instructions in the magazine, but in fact, the 20 stitch repeat as drawn can be downloaded and entered as-is, bypassing the alter loop manipulations. Technique 253: a pintuck is formed where there are white squares. For each row of squares, one row is knitted on the front bed. Pushers will knit for one row, rest for 1 row. 1124 is the console built-in pattern used in my test swatch and below it, its mirrored image
The directions at the time the model books were written for knitting with the console were designed to have the knitter work with built-in patterns and then to use the alter possibilities to manipulate them to achieve the same result as the punched holes might in the final repeat in the Duo. The Passap console had a card reader that operated with sheets that were in turn inserted into a sleeve and were drawn on with “special” pens. C6, proprietary early software that operated with a dongle, came a bit later. There was a large factory built-in pattern library, and the manufacturer, Madag, supplied free files for the Duo pattern books in formats that could be used with the program for “easy” download. The 910 had variation buttons and instructions for combining multiple patterns using the factory-supplied mylar sheets. The intent was to allow the knitter to maximize the use of both. I honestly have avoided altering patterns that way intentionally most of my knitting career, finding I simply prefer programming black and white squares for the function intended, which for me is easier to visualize and reduces errors. The trend explains the E6000 instructions in the magazine, but in fact, the 20 stitch repeat as drawn can be downloaded and entered as-is, bypassing the alter loop manipulations. Technique 253: a pintuck is formed where there are white squares. For each row of squares, one row is knitted on the front bed. Pushers will knit for one row, rest for 1 row. 1124 is the console built-in pattern used in my test swatch and below it, its mirrored image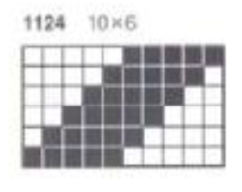
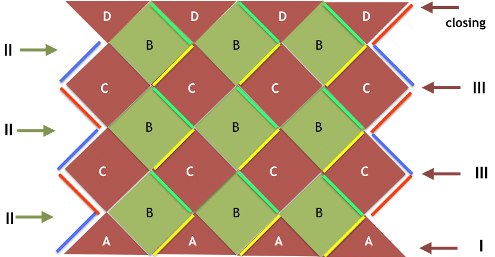
 tiled repeat to get a sense of the movement of the triangles:
tiled repeat to get a sense of the movement of the triangles: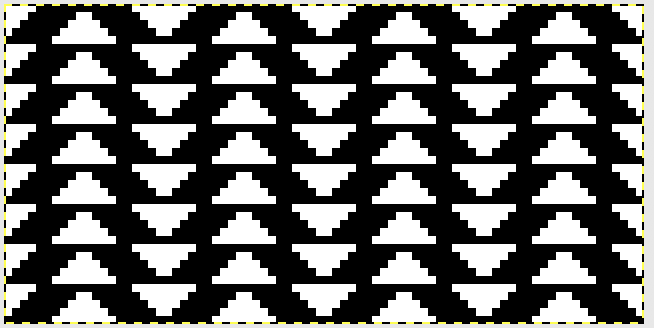 note: the direction of the chart pattern repeat for 1124 is reversed in the blisters. It appears as drawn on the knit side of the fabric, where stitches are slipped and elongated to create the pintuck texture on the purl side
note: the direction of the chart pattern repeat for 1124 is reversed in the blisters. It appears as drawn on the knit side of the fabric, where stitches are slipped and elongated to create the pintuck texture on the purl side 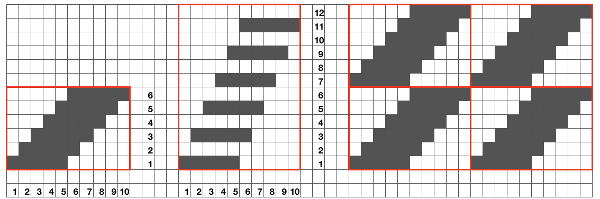


 In the Duo HX setting the front bed normally knits or slips according to the design for one row, and slips the next row. Again, the chart illustration is for the Duomatic and the lock there takes over the function performed automatically by the E6 technique. The back bed in this instance knits every row. In the E 6000 the front lock is set to LX (slip <– –>). The fabric created may be referred to as blister or pintuck (nothing to do with tuck stitch/brioche). The bubbly texture appears on the purl side. Stitches that slip on the bed with needle or pusher selection elongate, pulling extra rows together eventually, helping to form pockets that are sealed periodically by all knit rows. With pushers down, no needles selected the front (knit) bed skips/ slips associated needles. With the back bed (ribber) set to N, its stitches will knit every row.
In the Duo HX setting the front bed normally knits or slips according to the design for one row, and slips the next row. Again, the chart illustration is for the Duomatic and the lock there takes over the function performed automatically by the E6 technique. The back bed in this instance knits every row. In the E 6000 the front lock is set to LX (slip <– –>). The fabric created may be referred to as blister or pintuck (nothing to do with tuck stitch/brioche). The bubbly texture appears on the purl side. Stitches that slip on the bed with needle or pusher selection elongate, pulling extra rows together eventually, helping to form pockets that are sealed periodically by all knit rows. With pushers down, no needles selected the front (knit) bed skips/ slips associated needles. With the back bed (ribber) set to N, its stitches will knit every row.
Pusher selection is down when the front bed slips (akin to no needle preselection on Brother) This selection happens between each pattern row, as the design is advanced
This selection happens between each pattern row, as the design is advanced


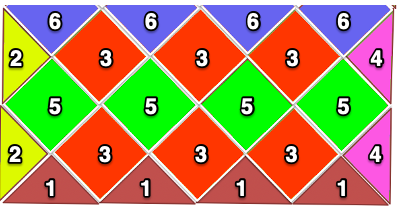
 This shows the pattern as knit on the Passap, reduced to black and white squares
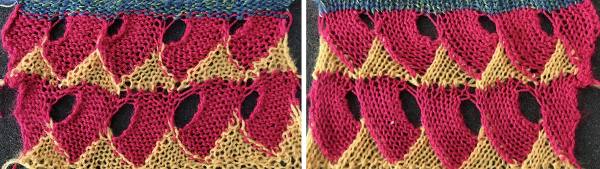
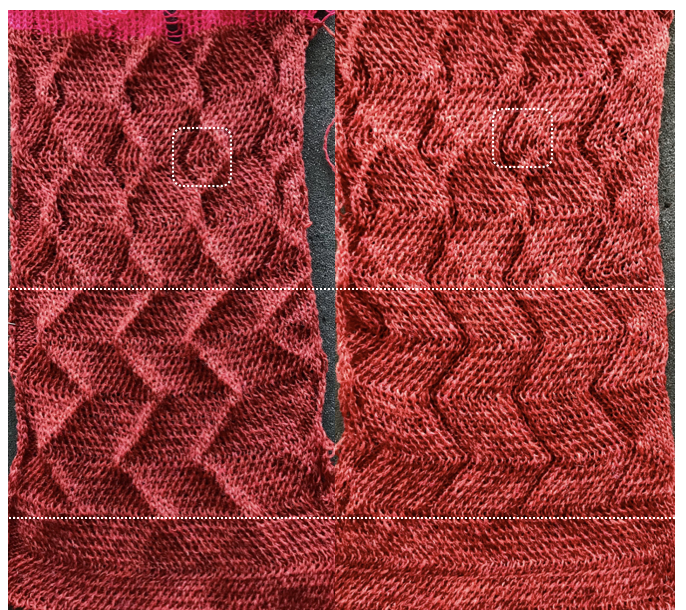
This shows the pattern as knit on the Passap, reduced to black and white squares 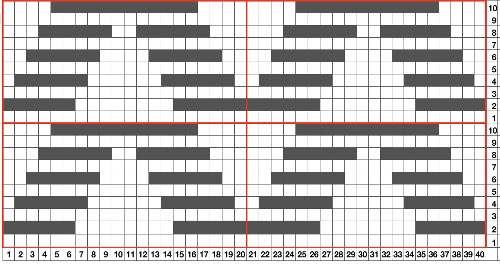 Taking a closer look at the pintucks on the sweater body
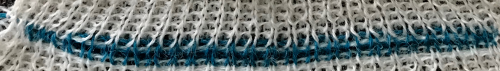
Taking a closer look at the pintucks on the sweater body  Going for the safe repeat on Brother machine: color makes a significant difference in how visible the pattern will be. Both yarns are supposedly the same weight, the white was hard to knit, and there was a needle that dropped stitches regularly. The blue yarn knit with no problem
Going for the safe repeat on Brother machine: color makes a significant difference in how visible the pattern will be. Both yarns are supposedly the same weight, the white was hard to knit, and there was a needle that dropped stitches regularly. The blue yarn knit with no problem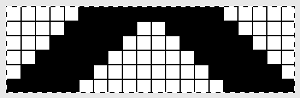
 here the repeat is rendered twice as long, and the texture becomes more visible
here the repeat is rendered twice as long, and the texture becomes more visible  a sideways view:
a sideways view: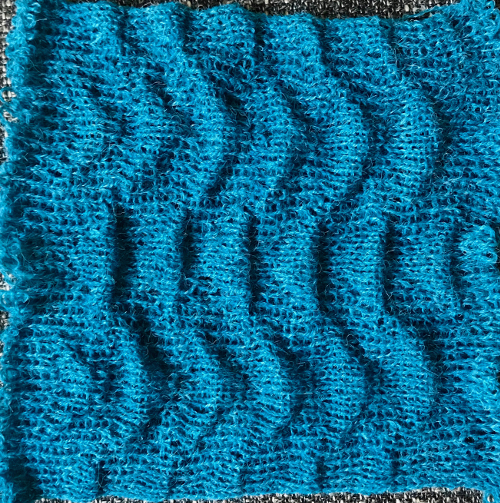  The last swatch in the series: I am now able to use Ayab once more, img2track is having issues for me with its use on the 930. My repeat, therefore, is planned for the maximum width I may wish to test knit on the 910 machines, emulating tech 253. Every other row there is no needle selection on the main bed except for the first and last needle if KCI is used. On those rows the ribber only knits, there are more rows in the blister “pockets”. I knit the sample quickly, not checking every row, and in this instance had two dropped stitches on the main bed and no breaks. Yarns with memory ie wool are the best for texture retention, acrylics such as my blue yarn would flatten permanently if pressed, resulting in a very different fabric. It takes experimentation to sort out whether the extra step is worth the effort or is problematic during lengthier knitting
The last swatch in the series: I am now able to use Ayab once more, img2track is having issues for me with its use on the 930. My repeat, therefore, is planned for the maximum width I may wish to test knit on the 910 machines, emulating tech 253. Every other row there is no needle selection on the main bed except for the first and last needle if KCI is used. On those rows the ribber only knits, there are more rows in the blister “pockets”. I knit the sample quickly, not checking every row, and in this instance had two dropped stitches on the main bed and no breaks. Yarns with memory ie wool are the best for texture retention, acrylics such as my blue yarn would flatten permanently if pressed, resulting in a very different fabric. It takes experimentation to sort out whether the extra step is worth the effort or is problematic during lengthier knitting 

In summary: Passap E6000 knitting techniques 250-255 are used to produce pintucks. When using 250, 252, 254, the pintucks are formed on the back bed on the needles that are opposite those with the pushers selected down in accordance with programmed black squares. The corresponding odd numbers 251, 253, 255, select pushers down according to programmed white squares (253 in the manual should say white, not black squares). Since the pintuck is formed on the back bed, setting it on FX (Tuck) may also be used, the pintucks then become blurred, producing a fabric that is wider. The width of the resulting knit may be significant when producing garment panels. One option in cross-brand might be to use every other needle selection on ribber, with its carriage to tuck in one direction, knit in the other, resulting in a spotted pintuck. My Passap manual is filled with scribbles, often including notes on alternate fabrics produced with the same technique numbers.
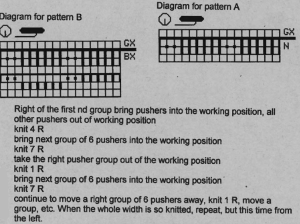
Returning to the specific sweater pattern: below the back bed is set to GX in the first 2 instances, which is akin to setting the Brother ribber to slip in both directions, no stitches are knit. There are no pushers or needles illustrated on the back bed, so the implication but not necessarily the fact is that these are single bed fabrics. How to transition between them and the double bed would need to be considered (see notes at end of the post). The pattern is an elongated one, using slip stitch and color changes every 2 rows, carrying one color at a time. Again, on the E6 front lock Duo BX is LX, the arrow key function on the front bed is replaced by the technique console instructions. The E6 front lock has no buttons or arrows.
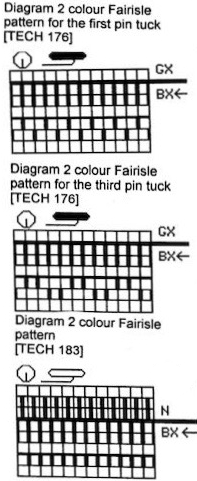 Tech 176: knits one color selection for 2 rows, then the alternate color selection for 2 rows; Pattern 1100,
Tech 176: knits one color selection for 2 rows, then the alternate color selection for 2 rows; Pattern 1100, ![]() the Brother equivalent
the Brother equivalent  in the next sample the same repeat 1100 is programmed via the console and enlarged <–> X2, which means in the number of stitches only
in the next sample the same repeat 1100 is programmed via the console and enlarged <–> X2, which means in the number of stitches only ![]() this is what will be knit, translatable to Brother, also with color change every 2 rows
this is what will be knit, translatable to Brother, also with color change every 2 rows 
Tech 183: long stitch backing, back bed knits every stitch, every row. Brother would require the separation to be made for the elongated triangle to match the Passap knit where each design row color knits twice in succession. Ribber or back bed settings could be altered to suit if preferred.
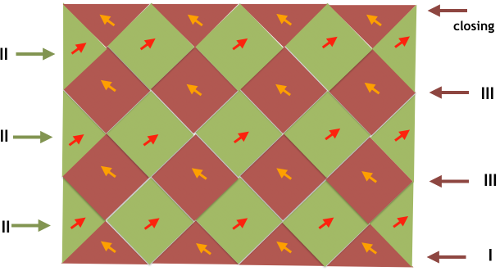
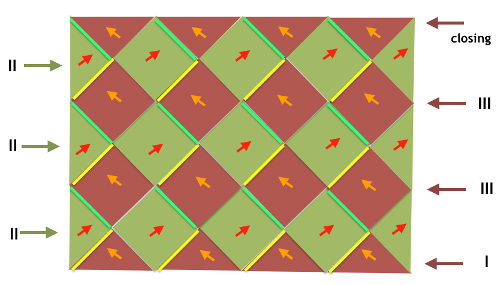
The shawl is what some may call a scarf  The above is the first illustration showing pushers on the back bed in alternate positions of rest (down) and work (up, toward the front of the machine) in groups. The pushers here at the end on either bed create the colored border on each side. The selection is opposite to the one on the end needles on the front bed. When the latter pushers are up, the back bed are down (slipping/not knitting), when they are down (not knitting the color in the yarn feeder), the back bed are up. This is an instance where to achieve the same, hand selection would need to happen on the Brother ribber on every row, or 2 sets of paired carriages, each carrying a color, could be used. Tech 181: is used for double bed fair isle with background color only on the backside. To seal the edges usually the first and last pusher on the back bed is brought into work, here 2 are used, creating a 2 stitch contrasting color border. Color is changed every 2 rows. To me this is an instance of because it is published, you may still not want to knit it. This is the first-row initial needle and pusher position on the front bed
The above is the first illustration showing pushers on the back bed in alternate positions of rest (down) and work (up, toward the front of the machine) in groups. The pushers here at the end on either bed create the colored border on each side. The selection is opposite to the one on the end needles on the front bed. When the latter pushers are up, the back bed are down (slipping/not knitting), when they are down (not knitting the color in the yarn feeder), the back bed are up. This is an instance where to achieve the same, hand selection would need to happen on the Brother ribber on every row, or 2 sets of paired carriages, each carrying a color, could be used. Tech 181: is used for double bed fair isle with background color only on the backside. To seal the edges usually the first and last pusher on the back bed is brought into work, here 2 are used, creating a 2 stitch contrasting color border. Color is changed every 2 rows. To me this is an instance of because it is published, you may still not want to knit it. This is the first-row initial needle and pusher position on the front bed  It is altered every other row (same is true on the back bed with the arrow key in use). My blue yarn is the body color, the white the border one. I only knit a very few rows, but that is enough to observe what is happening: the blue knits everywhere but on the stitches intended for the contrasting border
It is altered every other row (same is true on the back bed with the arrow key in use). My blue yarn is the body color, the white the border one. I only knit a very few rows, but that is enough to observe what is happening: the blue knits everywhere but on the stitches intended for the contrasting border  when the border stitches knit only on each side, floats are formed the width of the needle bed between border stitches for two rows
when the border stitches knit only on each side, floats are formed the width of the needle bed between border stitches for two rows 
 they are then enclosed by the next row of blue every needle rib
they are then enclosed by the next row of blue every needle rib and there is considerable bleed-through of the white on both the knit and the purl side of the fabric
and there is considerable bleed-through of the white on both the knit and the purl side of the fabric
Tech 183: produces a double bed fair isle with striper backing. It essentially knits the elongated pattern 1130.
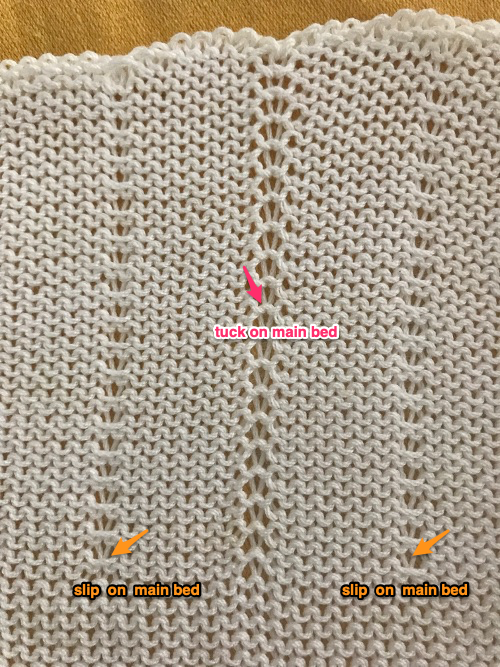
One then comes to actual knitting and putting the pieces together. Instructions are not always clear. There are several transitions in this piece. The trim at the bottom of the front, sleeves, and back is a double bed every needle rib that transitions easily from one textured pattern into the next. Its purl sides face the outside. The same is true for the back and sleeves, both are both knit from the trim on up. The front top portions are knit sideways as are the button bands, and they are in turn joined to the mixed stitch type “front border”. The “front border” is puzzling. Since the geometric pattern shows on the “knit” side, the trim by default then would have the slip stitch front bed pattern showing on the outside in order for it to transition directly to DBJ, not the pintuck. Looking closely at the photo there is a clue that that is indeed the plan in that the edge closest to the cast one has the triangles at the start facing in the opposite direction of that in the test swatch purl vs knit side.
I also see extra colored hems in addition to patterned “FI” ones. The back bed can be set to slip (GX), the patterned section knit on the front bed, then the back bed returned to knit to seal the hem. This is not indicated in the schematics or the written directions. The same can be done with added solid color changes (purple and blue in the photo), knitting several rows on the front bed, then sealing it with a return to N on the back bed. That same row can also be planned as a selection row for DBJ. I am still knitting my swatches in 2/24 acrylic, which is also not always the best to use. If I were to knit the piece, the cast on would get some work on it, as well as the tension adjustments for each fabric segment.
Pattern 1130 is also used in the same issue # 60 in the body of a man’s sweater. In using Tech 250 pintucks are formed where there are black squares in the stitch pattern, for each row of squares 2 rows are knit on the front bed, elongating the pattern X 2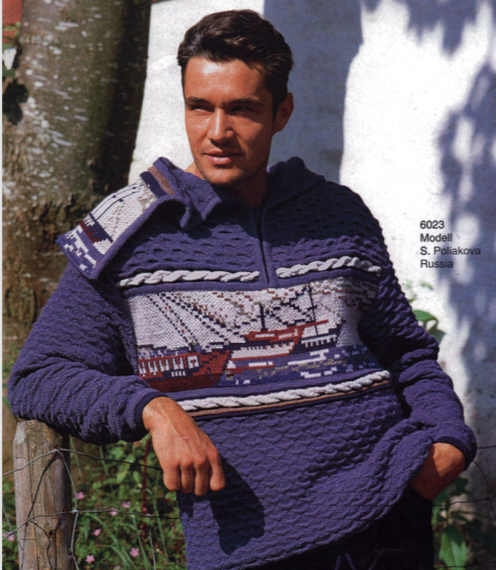
The Passap magazines generally also included a strip of heavier stock paper with samples of the yarn recommended for the particular pattern ie this one from another issue, which facilitated substitutions and provided a better sense of color than the garment photos Brother ribber and DBJ settings reviewed including for solid color backing.
Brother ribber and DBJ settings reviewed including for solid color backing.
Because of the Passap capacity for heavily textured stitches, many of their early pubs included several patterns for use with tuck or slip stitch settings. This issue is dated 1990, may be found with accompanying pattern instructions in French online,  the sweater on the right uses a pintuck pattern with appliqued pockets in a different knit structure
the sweater on the right uses a pintuck pattern with appliqued pockets in a different knit structure 
 the repeat is 20 by 20 stitches wide, E6 Tech 253 is suggested, white squares form the pintucks, the same technique used in my sample knit using console design 1124
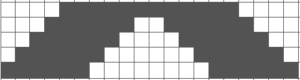
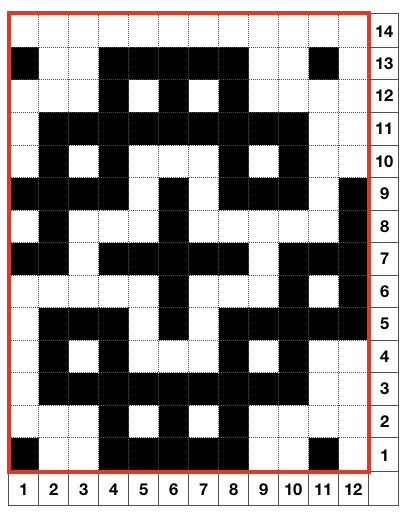
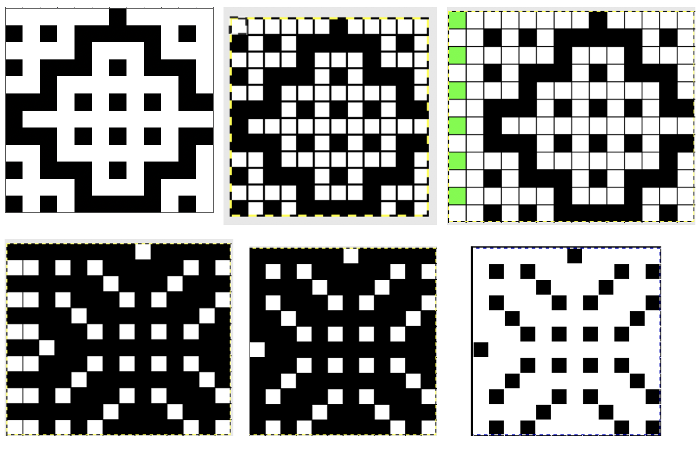
the repeat is 20 by 20 stitches wide, E6 Tech 253 is suggested, white squares form the pintucks, the same technique used in my sample knit using console design 1124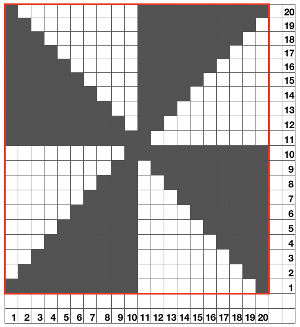 Working with simple shapes such as triangles can be an easy way to help one begin to understand how various techniques build up stitch or row counts, altering the original. Several of my DBJ posts are written using a cousin of pattern 1130 and include images of corresponding swatches executed on the Brother machine. In Brother, with rare exceptions (such as when needles are left out of work while in pattern) black squares (punched holes) knit, white squares (unpunched areas) slip. Slipped stitches are held until a black square or punched hole is reached, getting longer while the stitches on the opposite bed knit every stitch every row with that bed set to N/N. It is helpful to be using a yarn that does not break easily. Pockets are created of varying depths. As with any knitting, the color reverse option may produce an interesting variation or a “disaster” depending on the original motif. In the above chart, if knit as is, white squares would be slipped for 1-9 rows. Blisters of knit stitches will appear on the purl side. Tiling helps visualize the movement of the design in repeat.
Working with simple shapes such as triangles can be an easy way to help one begin to understand how various techniques build up stitch or row counts, altering the original. Several of my DBJ posts are written using a cousin of pattern 1130 and include images of corresponding swatches executed on the Brother machine. In Brother, with rare exceptions (such as when needles are left out of work while in pattern) black squares (punched holes) knit, white squares (unpunched areas) slip. Slipped stitches are held until a black square or punched hole is reached, getting longer while the stitches on the opposite bed knit every stitch every row with that bed set to N/N. It is helpful to be using a yarn that does not break easily. Pockets are created of varying depths. As with any knitting, the color reverse option may produce an interesting variation or a “disaster” depending on the original motif. In the above chart, if knit as is, white squares would be slipped for 1-9 rows. Blisters of knit stitches will appear on the purl side. Tiling helps visualize the movement of the design in repeat. 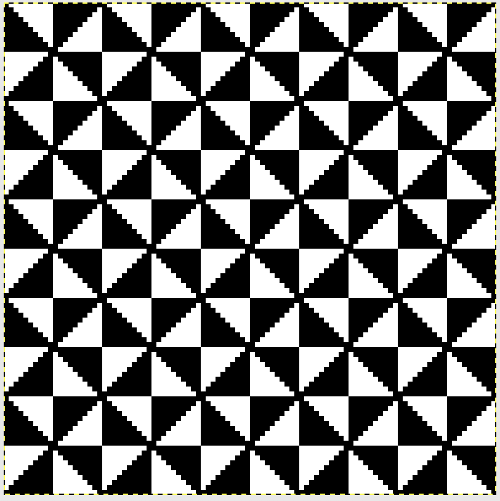
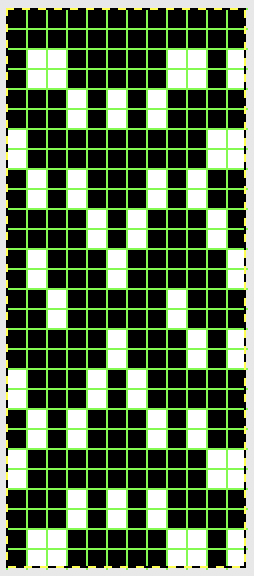
In the color reversed image the number of consecutive white squares is now increased along the center lines from 9 to 11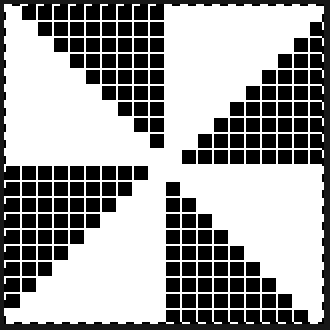 its tiled view
its tiled view 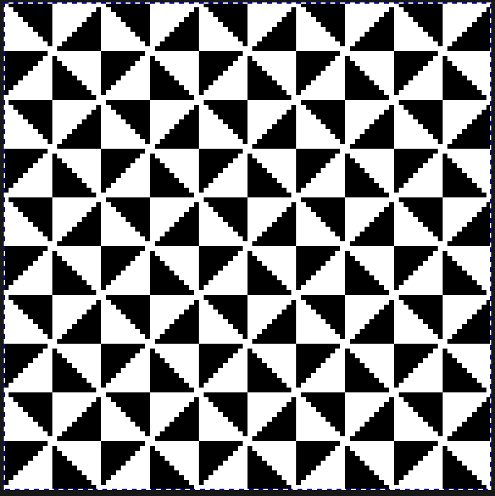 the expanded view of the original repeat emulating tech 253 now increases the height of the pattern to 40 rows from 20
the expanded view of the original repeat emulating tech 253 now increases the height of the pattern to 40 rows from 20 and its color reversed equivalent
and its color reversed equivalent 
In both expanded repeat variations of the “pinwheel” black squares create knit stitches. In double bed knitting, this seals the layers created by each bed together. The original design would create large pockets/ blisters, while in its color reverse version white areas would slip for one row, keeping the pinwheel effect, but the fabric will be predominantly sealed together. Thin yarn use is best, I used a 2/13 wool.
The original 20X20 design is shown on the knit side Left, its color reversed result on the knit side, Right.  The elongated slipped stitches are noticeable on both purl sides
The elongated slipped stitches are noticeable on both purl sides  Using the expanded 20X40 repat I did not have a slipped stitch issue such as yarn breaking, but because the pockets were so deep and so many stitches on the ribber were knitting for so many consecutive rows, the ribber stitches began to refuse to stay on their bed. I got this far: a large knit area can be seen, as well as slip stitch loops
Using the expanded 20X40 repat I did not have a slipped stitch issue such as yarn breaking, but because the pockets were so deep and so many stitches on the ribber were knitting for so many consecutive rows, the ribber stitches began to refuse to stay on their bed. I got this far: a large knit area can be seen, as well as slip stitch loops  Can the same expanded repeat be used in another way? The color reversed version results in a subtle large scale pattern that might be quite interesting in a shiny rayon or other fiber
Can the same expanded repeat be used in another way? The color reversed version results in a subtle large scale pattern that might be quite interesting in a shiny rayon or other fiber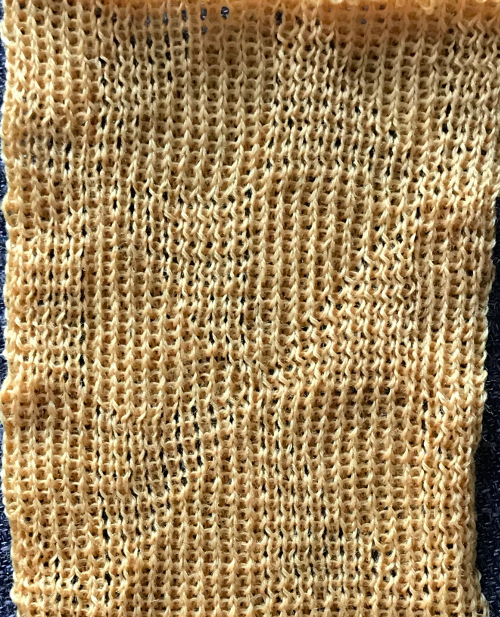  To review: Passap E6000 knitting techniques for pintucks are numbered 250-255. When using 250, 252, 254, the pint tucks are formed on the back bed on the needles that are opposite those with the pushers selected down in accordance with programmed black squares. The corresponding odd numbers 251, 253, 255, select pushers down according to programmed white squares (253 in the manual should say white, not black squares).
To review: Passap E6000 knitting techniques for pintucks are numbered 250-255. When using 250, 252, 254, the pint tucks are formed on the back bed on the needles that are opposite those with the pushers selected down in accordance with programmed black squares. The corresponding odd numbers 251, 253, 255, select pushers down according to programmed white squares (253 in the manual should say white, not black squares).
On any machine, the size of the pleat creating the ripple/ pintuck depends on the number of rows that can be knit on the all knit bed before the fabric begins to ride up and becomes difficult to retain on the needles in work. Tolerance depends on knitting machine brands as well as the type of yarn used. Bold patterns read better than smaller ones. Weights are usually helpful. The Brother Ribber techniques book (now available for free online) addresses the topic on pp. 20-22. 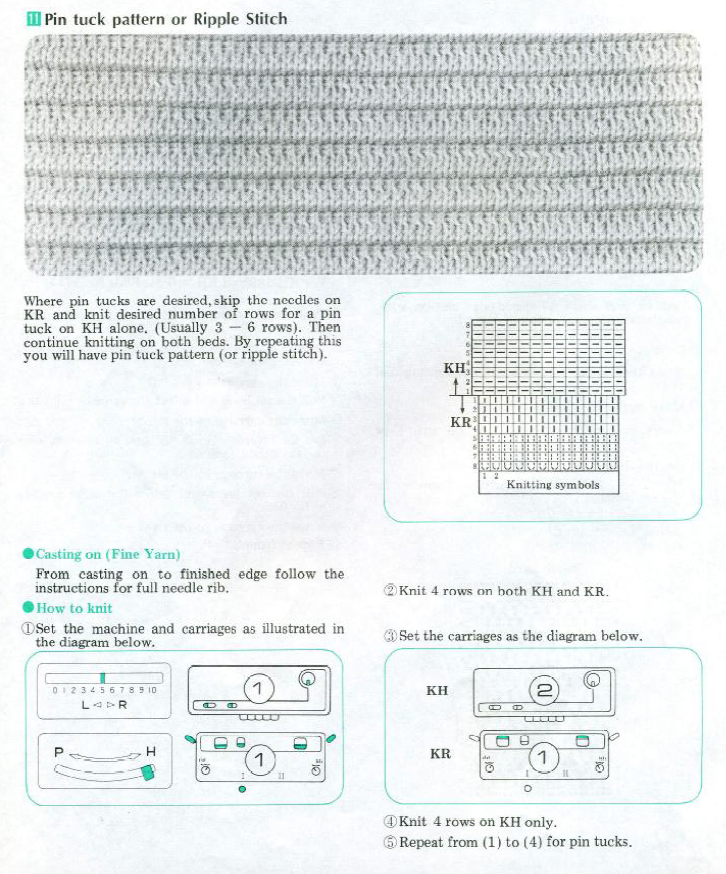
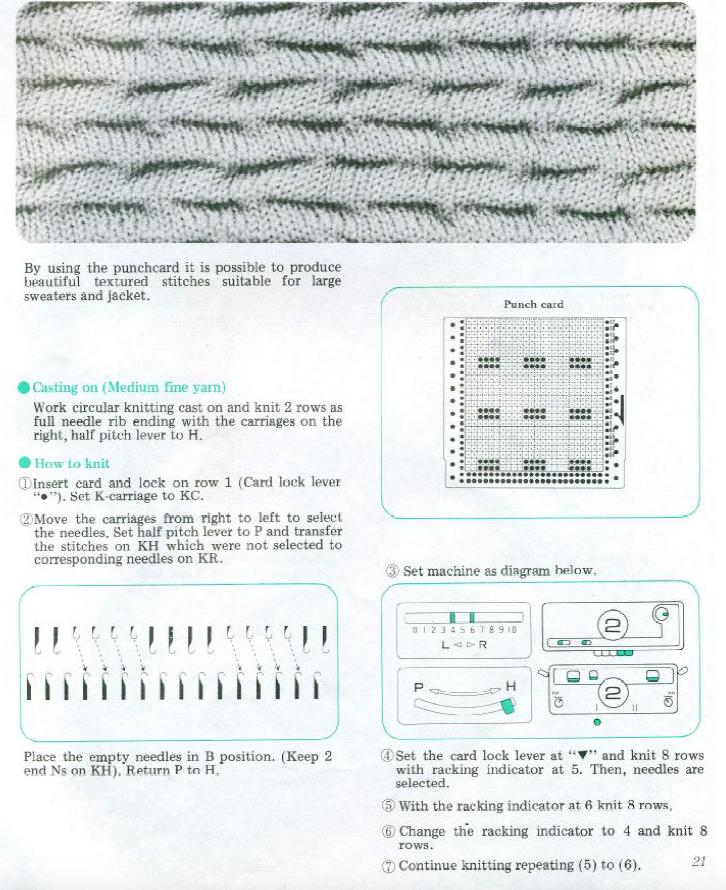
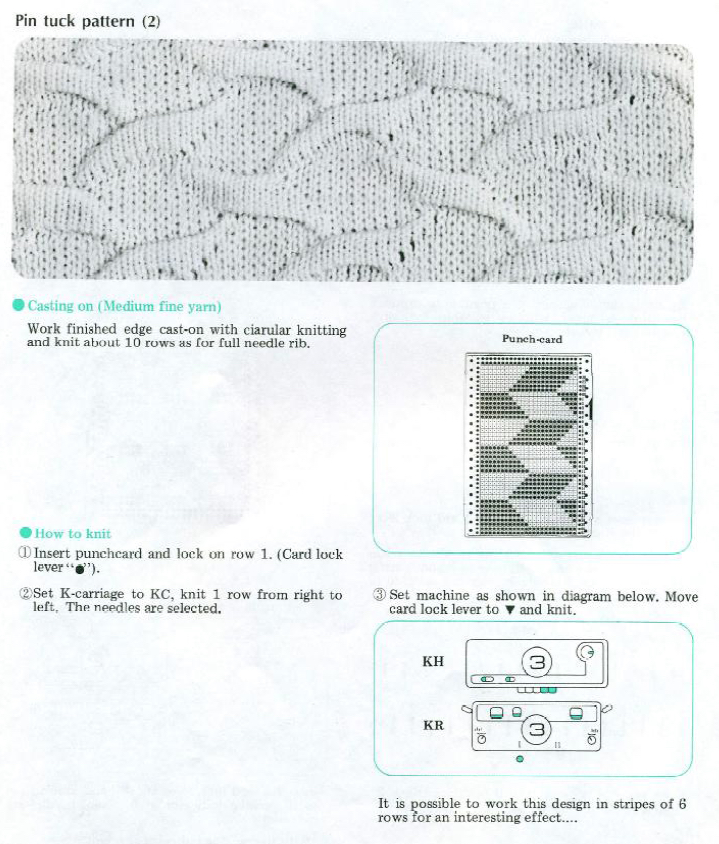 I have added a few patterns from published sources in a flickr album , most take into account any single stitch not being slipped for more than 4 rows. Doubling the length if using electronics is not recommended. These fabrics may be created in combination with needles out of work.
I have added a few patterns from published sources in a flickr album , most take into account any single stitch not being slipped for more than 4 rows. Doubling the length if using electronics is not recommended. These fabrics may be created in combination with needles out of work.

 a rearview with ends woven in
a rearview with ends woven in

 When the end of the first row that row is reached, as contrast color is added, stitches need to be cast on on the far left in order to keep the work on the bed a constant number of stitches. The usual method suggested is e wrapping, this is picking up from the row below. I found either method produced looser, longer stitches on the far edge
When the end of the first row that row is reached, as contrast color is added, stitches need to be cast on on the far left in order to keep the work on the bed a constant number of stitches. The usual method suggested is e wrapping, this is picking up from the row below. I found either method produced looser, longer stitches on the far edge 
 reaching the far right:
reaching the far right: 












 It does a good job of weighing down those straight edges along the bumps, making the stitches easier to pick up. When rehanging those stitches, uniformly hanging the loops, not the knots along the edges involved will give a smoother join. Here a paper clip is used as the “hanger”
It does a good job of weighing down those straight edges along the bumps, making the stitches easier to pick up. When rehanging those stitches, uniformly hanging the loops, not the knots along the edges involved will give a smoother join. Here a paper clip is used as the “hanger”
 Lastly, a swatch ending in all knit rows. The only remaining issue is the fact that those side triangles are formed by stitches that are looser than across the rest of the piece. This yarn is thin and a poor choice, but fine for getting the technique down and beginning to understand what happens to stitches, how one needs to move from one side to the other, and what happens along the edges of each individual shape
Lastly, a swatch ending in all knit rows. The only remaining issue is the fact that those side triangles are formed by stitches that are looser than across the rest of the piece. This yarn is thin and a poor choice, but fine for getting the technique down and beginning to understand what happens to stitches, how one needs to move from one side to the other, and what happens along the edges of each individual shape 

 to consider the number of stitches required and whether the fact that other than garter stitch knit stitches are not square,
to consider the number of stitches required and whether the fact that other than garter stitch knit stitches are not square,





 with a touch of steam and light pressing
with a touch of steam and light pressing 

 This is the isolated repeat for converting the pattern to a file suitable for download
This is the isolated repeat for converting the pattern to a file suitable for download  and its mirrored version for knitting from the opposite side
and its mirrored version for knitting from the opposite side 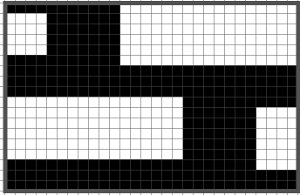 My test swatch was knit on the 930, using img2track. Because not every needle on the bed is in work throughout the knit, end needle selection must be canceled (KC II). The knit carriage after the preselection row is set to slip in both directions. Because only a few rows are knit on the red blocks in the chart, the result is subtle. The white yarn used in many of my tests happens to be a 2/24 acrylic, so on the too thin side, and likely to be well flattened if pressed.
My test swatch was knit on the 930, using img2track. Because not every needle on the bed is in work throughout the knit, end needle selection must be canceled (KC II). The knit carriage after the preselection row is set to slip in both directions. Because only a few rows are knit on the red blocks in the chart, the result is subtle. The white yarn used in many of my tests happens to be a 2/24 acrylic, so on the too thin side, and likely to be well flattened if pressed. Often, the edge stitches on the carriage side will tend to be a bit tighter than those formed away from it. The same repeat may be used to create very different fabrics. Eliminating the all knit columns on either side of the center produces a piece with “ruffles” on either side of the center as the outer edge of each shape is no longer anchored down. The principle was used in knitting “potato chip” scarves popular in both hand and machine knitting for a while. Having a repeat on one side of an all knit vertical strip creates a ruffled edging.
Often, the edge stitches on the carriage side will tend to be a bit tighter than those formed away from it. The same repeat may be used to create very different fabrics. Eliminating the all knit columns on either side of the center produces a piece with “ruffles” on either side of the center as the outer edge of each shape is no longer anchored down. The principle was used in knitting “potato chip” scarves popular in both hand and machine knitting for a while. Having a repeat on one side of an all knit vertical strip creates a ruffled edging. 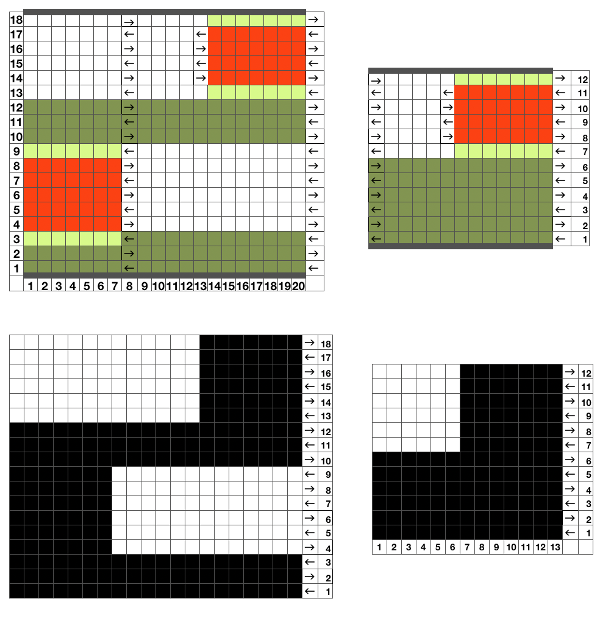
 Note the effect of the added all knit rows on the “wave” of the piece on the right.
Note the effect of the added all knit rows on the “wave” of the piece on the right. The shapes for the “bumps” may be changed, moving away from rectangular formats. Small repeats are used for the purposes of illustration here, but they, in turn, may be scaled up, rendered asymmetrical, vary in placement, and more. My design steps began with this idea
The shapes for the “bumps” may be changed, moving away from rectangular formats. Small repeats are used for the purposes of illustration here, but they, in turn, may be scaled up, rendered asymmetrical, vary in placement, and more. My design steps began with this idea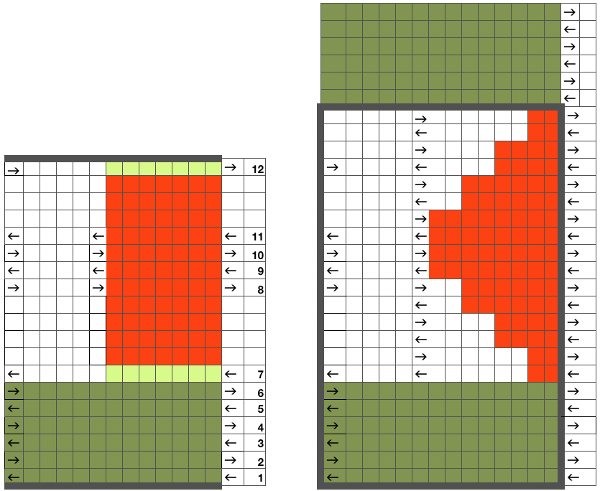 Following the goal to achieve bilateral placement along a central vertical knit strip, with vertical knit strip borders at either side, here shapes point in the same direction
Following the goal to achieve bilateral placement along a central vertical knit strip, with vertical knit strip borders at either side, here shapes point in the same direction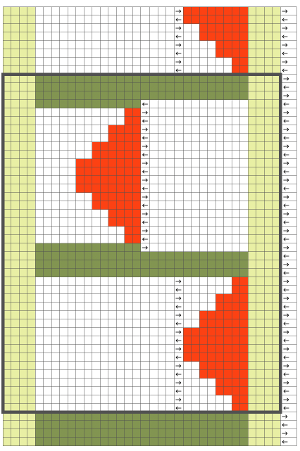
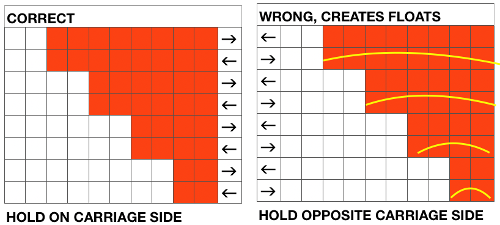
 I ran into an interesting problem for the first time. I had entered the row and stitch counts on my chart, used those counts to scale the image used for my repeat down to size for knitting, kept getting floats where there should not have been any, could not understand what the error in the repeat might be. What was happening is that because of the wrong row number used in scaling, there was an extra pixel row in the first test swatches resulting in knitting errors. The final repeat is 29 stitches wide, 38 rows high. This is the resulting swatch
I ran into an interesting problem for the first time. I had entered the row and stitch counts on my chart, used those counts to scale the image used for my repeat down to size for knitting, kept getting floats where there should not have been any, could not understand what the error in the repeat might be. What was happening is that because of the wrong row number used in scaling, there was an extra pixel row in the first test swatches resulting in knitting errors. The final repeat is 29 stitches wide, 38 rows high. This is the resulting swatch
 Once more, the repeat could be reduced down to eliminate side knit strips, or limit shapes to one side only for a one-sided ruffle. What about repeating the same slit horizontally across a row? Repeats become very long, arrows are intended again as guides in the knitting direction.
Once more, the repeat could be reduced down to eliminate side knit strips, or limit shapes to one side only for a one-sided ruffle. What about repeating the same slit horizontally across a row? Repeats become very long, arrows are intended again as guides in the knitting direction. 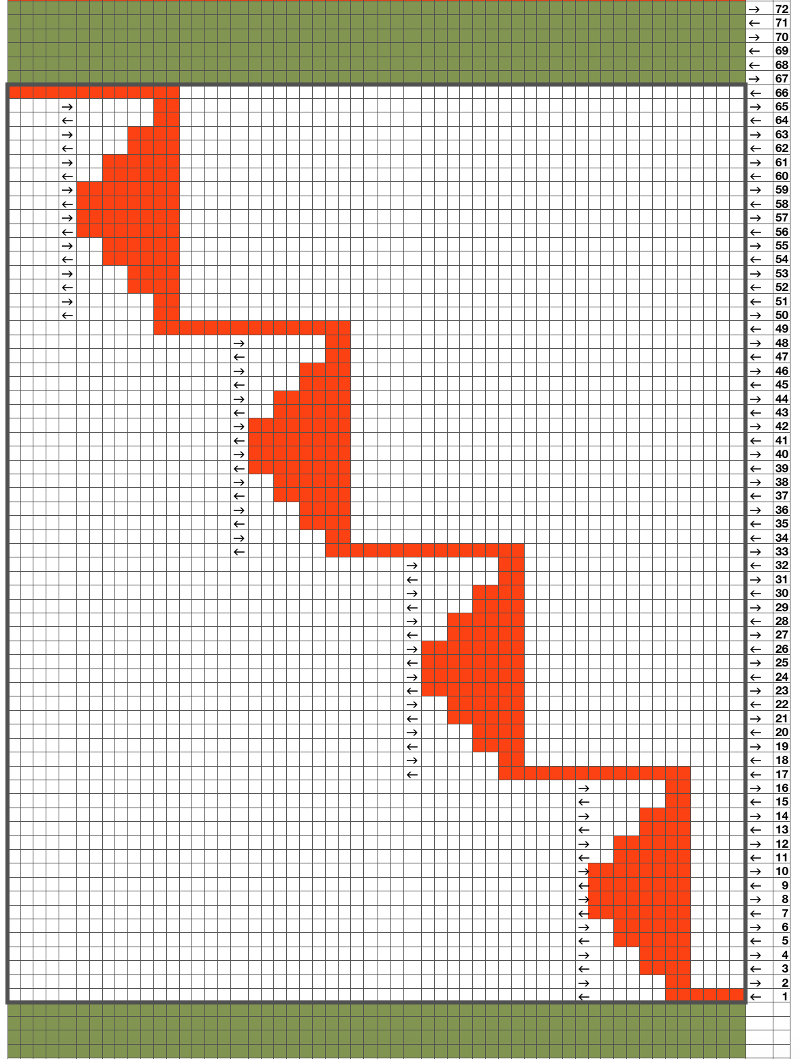 An even number of rows (green) at the end of the outlined repeat will return the carriage to begin knitting it from the right side once more. An odd number of rows added at its top will prepare for knitting the motifs beginning on the left.
An even number of rows (green) at the end of the outlined repeat will return the carriage to begin knitting it from the right side once more. An odd number of rows added at its top will prepare for knitting the motifs beginning on the left. 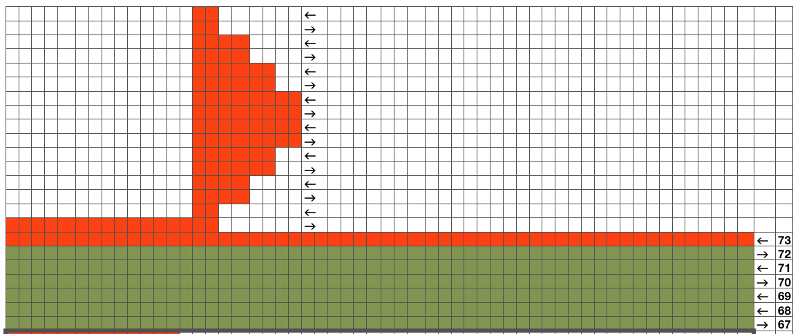
 Pushing unwanted needle groups back to the D position will make them knit rather than being held, which is another way to vary the texture distribution across any single row
Pushing unwanted needle groups back to the D position will make them knit rather than being held, which is another way to vary the texture distribution across any single row
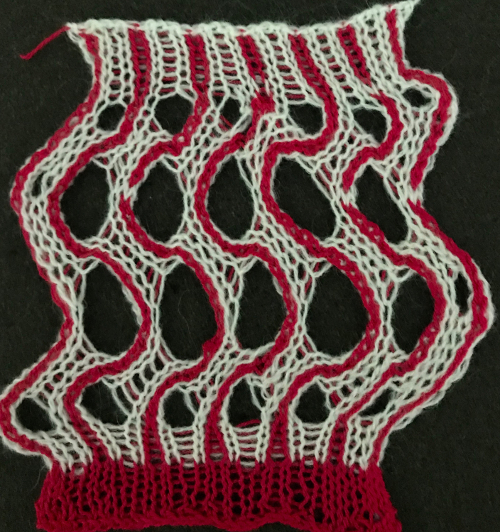
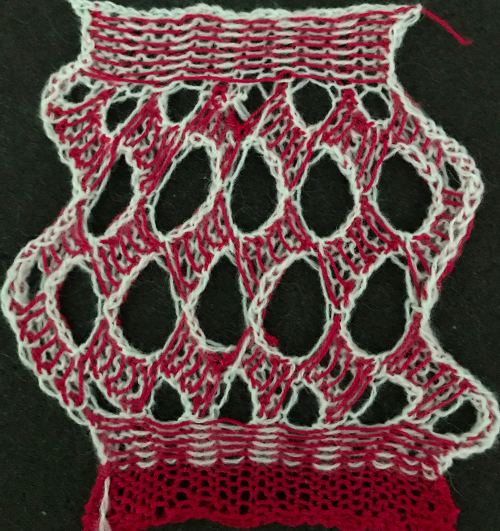




 The reverse side shows the same issue. Areas can be identified where the held stitches have been hung up to create hems. Note that as the knit grows in length, at the completion of each row of repeats there is one segment with no hem on alternating sides. A longer test swatch follows
The reverse side shows the same issue. Areas can be identified where the held stitches have been hung up to create hems. Note that as the knit grows in length, at the completion of each row of repeats there is one segment with no hem on alternating sides. A longer test swatch follows
 I created my hems on the carriage side, immediately prior to bringing the following group of stitches into work opposite it, and knitting a single row across that new group of 3 segments. The highlighted area indicates the stitches to be hung to create the hem. The eyelet on the top, right, will be smaller than the one at the opposite side of the stitches to be hung up
I created my hems on the carriage side, immediately prior to bringing the following group of stitches into work opposite it, and knitting a single row across that new group of 3 segments. The highlighted area indicates the stitches to be hung to create the hem. The eyelet on the top, right, will be smaller than the one at the opposite side of the stitches to be hung up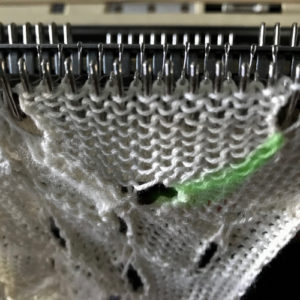







 Reversing the direction of segments
Reversing the direction of segments
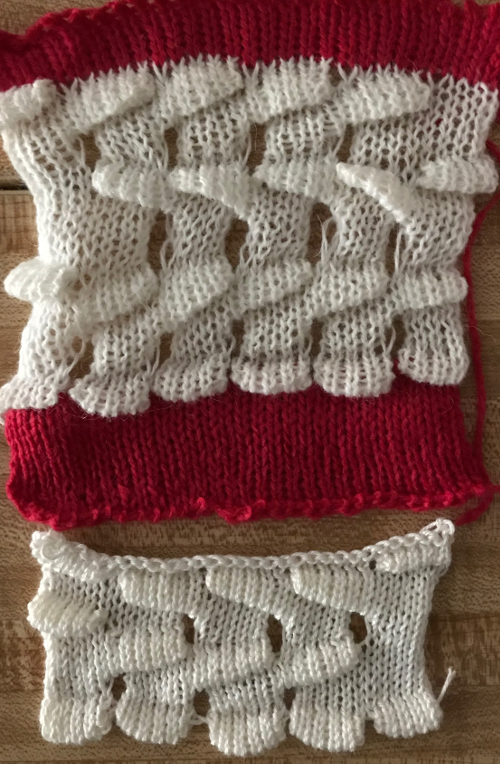






 This is one of my early graphics trying to imagine what is happening in chart form, which also references the repeat in the Passap garment, followed by plain knitting
This is one of my early graphics trying to imagine what is happening in chart form, which also references the repeat in the Passap garment, followed by plain knitting 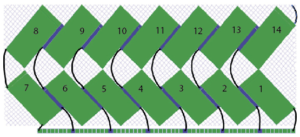

 This fabric is worked out differently, in groups of 2. After the first segment is completed, COR if the starting group 1 worked is on the right, bring group 2 into work, knit one row to left, immediately bring group one into hold, and continue across row. That “float” is created as the yarn traveling between the last stitch on the right now coming into hold and the first stitch to its left knits for many more rows gets pulled on as the piece grows.
This fabric is worked out differently, in groups of 2. After the first segment is completed, COR if the starting group 1 worked is on the right, bring group 2 into work, knit one row to left, immediately bring group one into hold, and continue across row. That “float” is created as the yarn traveling between the last stitch on the right now coming into hold and the first stitch to its left knits for many more rows gets pulled on as the piece grows. 



 Hems in knitting can be created on any number of stitches, anywhere on a garment, by definition join segments of the knit together permanently. Folds are freer. Here is an attempt at a different wisteria cousin with organized repeats. More on creating it will follow in a subsequent post now that holding techniques are back on my radar
Hems in knitting can be created on any number of stitches, anywhere on a garment, by definition join segments of the knit together permanently. Folds are freer. Here is an attempt at a different wisteria cousin with organized repeats. More on creating it will follow in a subsequent post now that holding techniques are back on my radar 



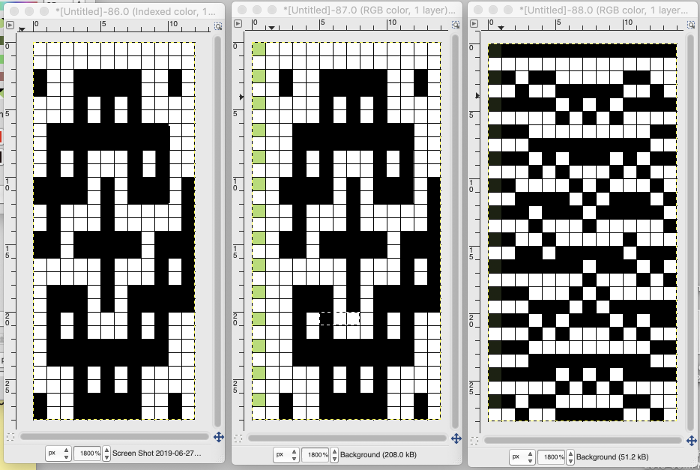
 the numbering system reflects every other row worked alternating sides of the work
the numbering system reflects every other row worked alternating sides of the work 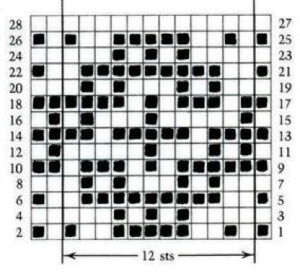 it is shown here with a superimposed table grid with its cells outlined in a thick border and positioned in front of a scaled screen grab of the original motif (arrange/ aspect ratio turned off)
it is shown here with a superimposed table grid with its cells outlined in a thick border and positioned in front of a scaled screen grab of the original motif (arrange/ aspect ratio turned off)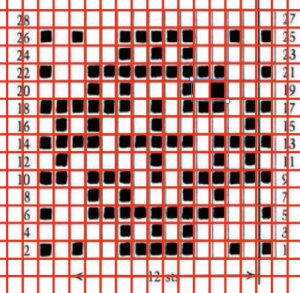
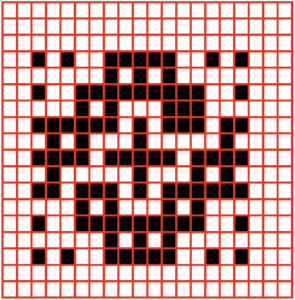 the cell borders can be edited as wished. Here borders were removed by selecting none, then, in turn, the outer border was highlighted in an easy to identify a thicker red line
the cell borders can be edited as wished. Here borders were removed by selecting none, then, in turn, the outer border was highlighted in an easy to identify a thicker red line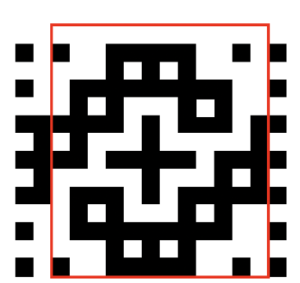

 the last image needs to be once again converted to BW mode. The 2 extra rows of pixels on left are cropped off, the image is scaled to twice as long for use with the color changer, and the original 12X14 repeat is now 12X56
the last image needs to be once again converted to BW mode. The 2 extra rows of pixels on left are cropped off, the image is scaled to twice as long for use with the color changer, and the original 12X14 repeat is now 12X56 the actual BMP
the actual BMP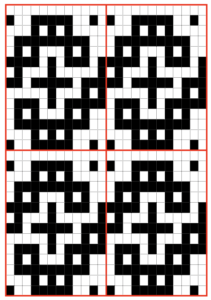
 a “pretend” longer repeat
a “pretend” longer repeat

 is compared here with the earlier
is compared here with the earlier 
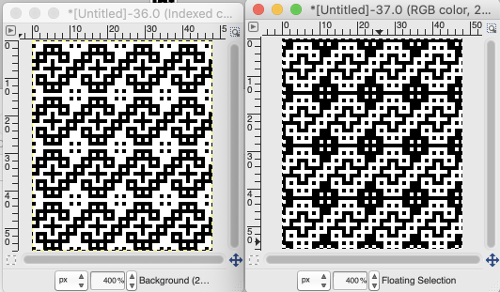
 Back to the drawing board: row height is as in the original repeat
Back to the drawing board: row height is as in the original repeat 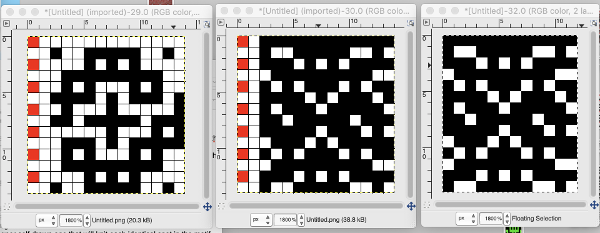 being extra careful, not necessary, the process can be inverted once more to check the repeat color separation
being extra careful, not necessary, the process can be inverted once more to check the repeat color separation 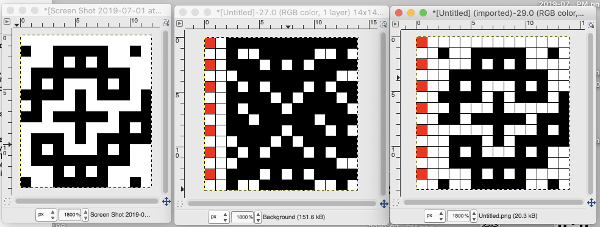
 the corresponding proof of concept swatch, with shorter floats than when the DBJ separation is used single bed
the corresponding proof of concept swatch, with shorter floats than when the DBJ separation is used single bed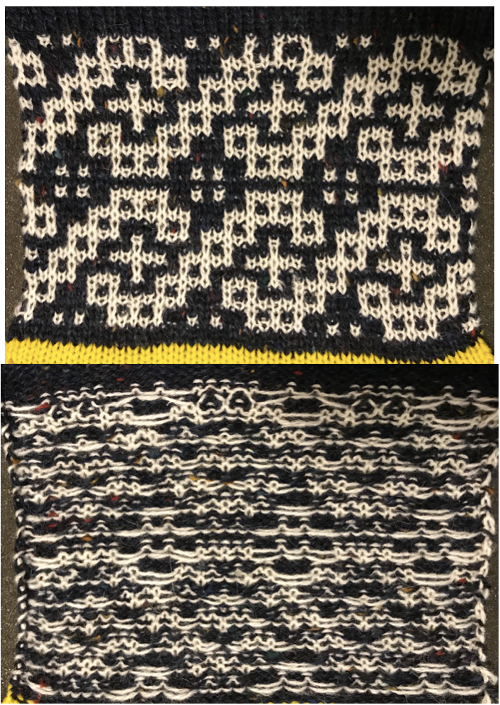 
 the repeat of the design separation on the right is intended for use in electronics with color reverse and double length
the repeat of the design separation on the right is intended for use in electronics with color reverse and double length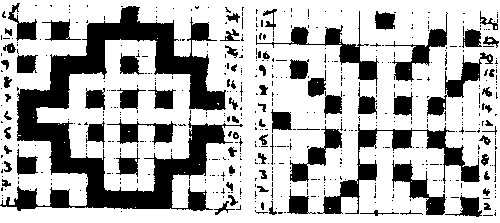
 for knitting purposes
for knitting purposes 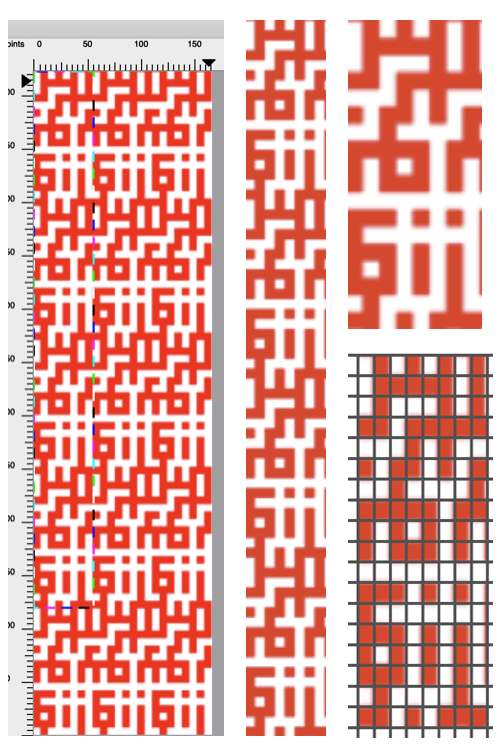
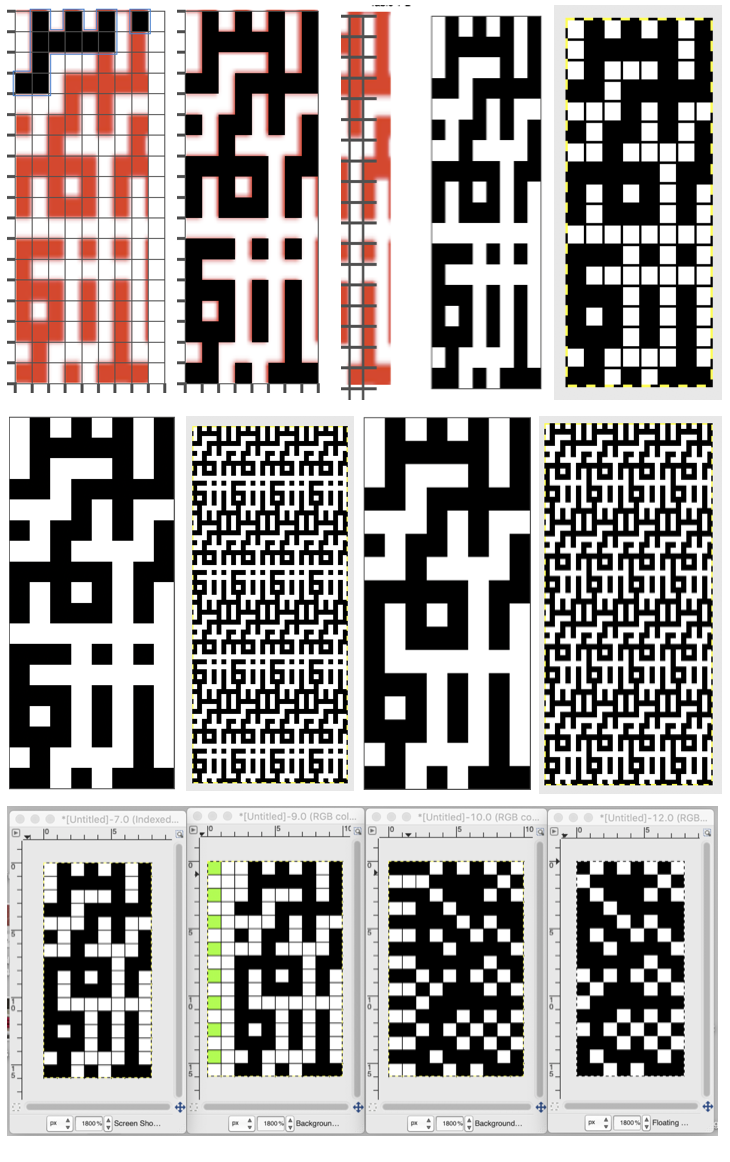 The repeat (8X16) is then doubled in length for knitting after that single all-white row was edited out (middle images). The repeat is now 8 rows wide by 32 rows in height
The repeat (8X16) is then doubled in length for knitting after that single all-white row was edited out (middle images). The repeat is now 8 rows wide by 32 rows in height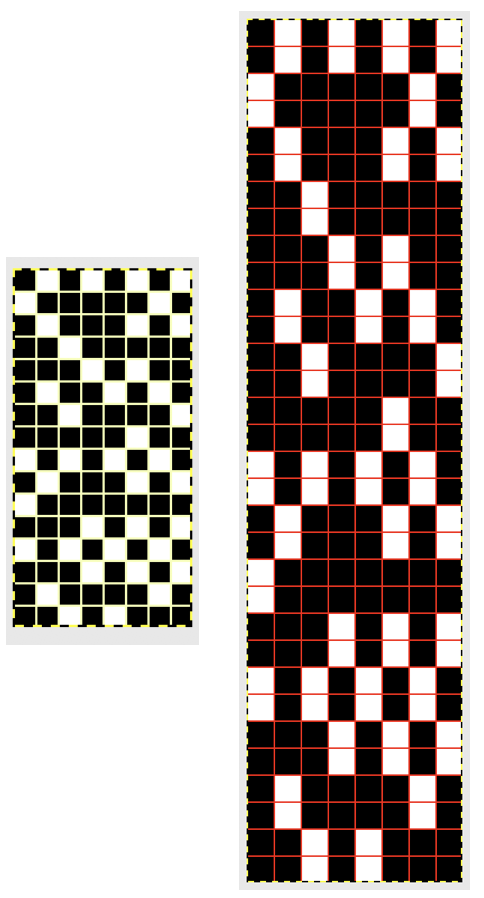 One of the yarns is chenille, the other a wool. The chenille is slightly thicker and fuzzy, so some of the yellow rows are almost hidden but the pattern is definitely there. Here the design is knit using both slip (bottom) and tuck (top) settings. Again, there is a noticeable difference in width produced by each stitch type.
One of the yarns is chenille, the other a wool. The chenille is slightly thicker and fuzzy, so some of the yellow rows are almost hidden but the pattern is definitely there. Here the design is knit using both slip (bottom) and tuck (top) settings. Again, there is a noticeable difference in width produced by each stitch type.  Observations: make certain that after the image is isolated in Numbers cell size is converted to square/ equal measurements in width and height before importing and scaling its screen grab in GIMP if not already so. It will likely load in RGB mode, convert to Indexed before scaling. Added colored squares are only possible if you return to RGB mode. After rows with colored squares are cut, return the image to indexed before saving as BMP for knitting. If any pairs of rows do not have 2 consecutive rows of cells in either color check your pattern. In DBJ the final repeat should be 4 times in numbers of rows in height to the original one, and thus divisible by four. The separation first doubles height for each row for 2 colors. Then height is doubled once more to allow for color changes every 2 rows. In Mosaics and Mazes, the color reversal happens on every other row in the original design. When that is completed, the height will be doubled for actual knitting to allow for color changes every 2 rows, with the final row count double that of the original motif. Rules for tuck knitting apply here as in any other technique. If white squares in the final chart have black ones on either side of them, the appearance is that tuck would be possible. Examining needle preselection is an easy way to assess that possibility.
Observations: make certain that after the image is isolated in Numbers cell size is converted to square/ equal measurements in width and height before importing and scaling its screen grab in GIMP if not already so. It will likely load in RGB mode, convert to Indexed before scaling. Added colored squares are only possible if you return to RGB mode. After rows with colored squares are cut, return the image to indexed before saving as BMP for knitting. If any pairs of rows do not have 2 consecutive rows of cells in either color check your pattern. In DBJ the final repeat should be 4 times in numbers of rows in height to the original one, and thus divisible by four. The separation first doubles height for each row for 2 colors. Then height is doubled once more to allow for color changes every 2 rows. In Mosaics and Mazes, the color reversal happens on every other row in the original design. When that is completed, the height will be doubled for actual knitting to allow for color changes every 2 rows, with the final row count double that of the original motif. Rules for tuck knitting apply here as in any other technique. If white squares in the final chart have black ones on either side of them, the appearance is that tuck would be possible. Examining needle preselection is an easy way to assess that possibility.
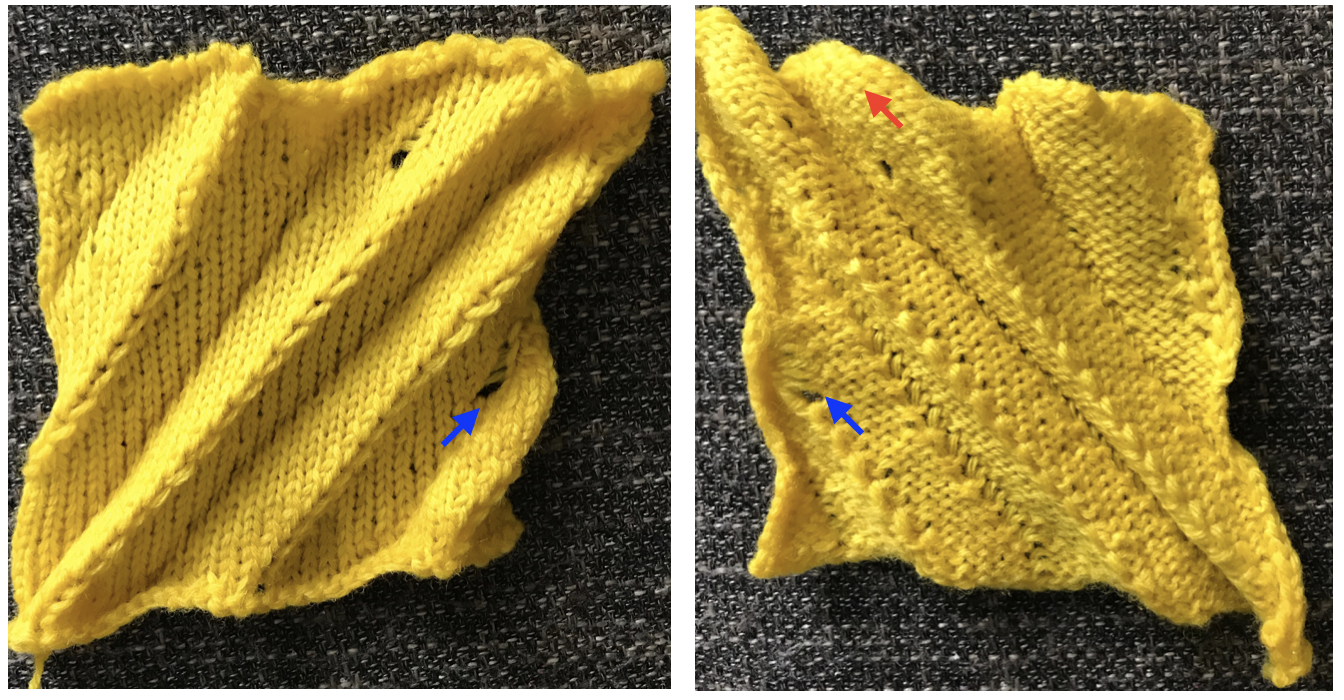 The fabric had an interesting twist and roll if tugged in opposite diagonal directions when first off the machine.
The fabric had an interesting twist and roll if tugged in opposite diagonal directions when first off the machine.  This is the working repeat, suitable for a punchcard machine. On the far left it is shown for use with electronics and color reverse, with the green grid highlighting black squares indicating holes that would need to be punched in a card, and lastly, as a tiled repeat looking for any errors in repeat sequences.
This is the working repeat, suitable for a punchcard machine. On the far left it is shown for use with electronics and color reverse, with the green grid highlighting black squares indicating holes that would need to be punched in a card, and lastly, as a tiled repeat looking for any errors in repeat sequences. 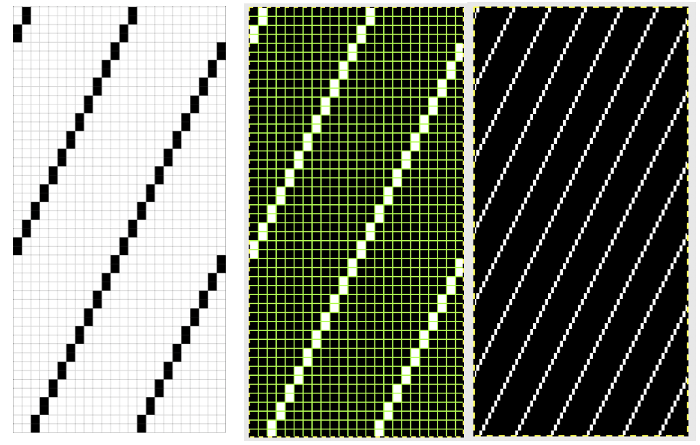

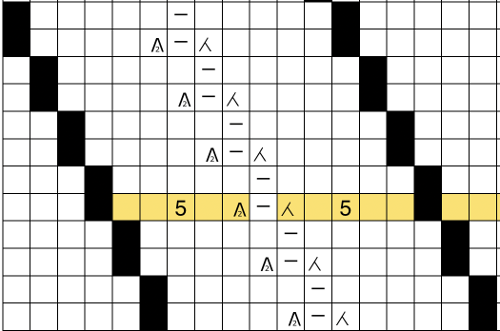
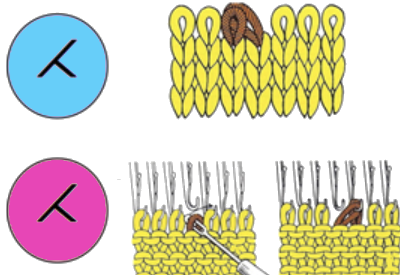
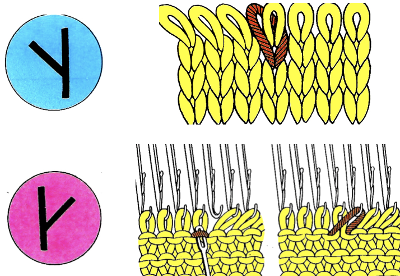 This shows my swatch in progress. ? indicates operator error, in evidence if needle count on each side of the future tuck stitch or ladder space is checked
This shows my swatch in progress. ? indicates operator error, in evidence if needle count on each side of the future tuck stitch or ladder space is checked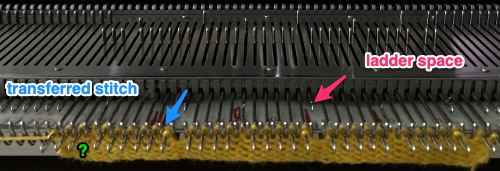 picking up loops from the row below to keep ladder width constant
picking up loops from the row below to keep ladder width constant 
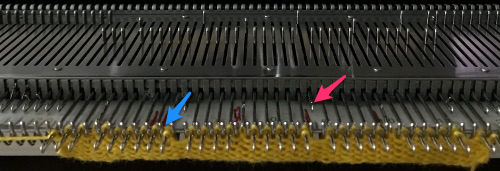 Check that stitches have knit off properly
Check that stitches have knit off properly  Needles with transfers or moved stitches may be brought out to hold position (E in Brother machines) for easier knitting. If this is done, be sure not to disturb needle selection or lack of it in location for next pair of tucked rows.
Needles with transfers or moved stitches may be brought out to hold position (E in Brother machines) for easier knitting. If this is done, be sure not to disturb needle selection or lack of it in location for next pair of tucked rows.

 Setting up a working repeat with blue representing tuck, purple slip (or vice versa). The distance between the vertical column, in this case, is fixed and seven stitches in width for a center folding repeat width of 16, color reverse is required
Setting up a working repeat with blue representing tuck, purple slip (or vice versa). The distance between the vertical column, in this case, is fixed and seven stitches in width for a center folding repeat width of 16, color reverse is required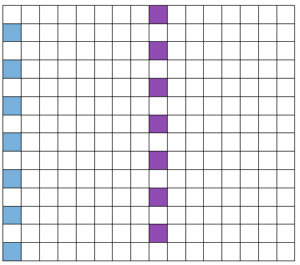
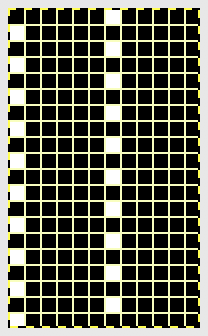

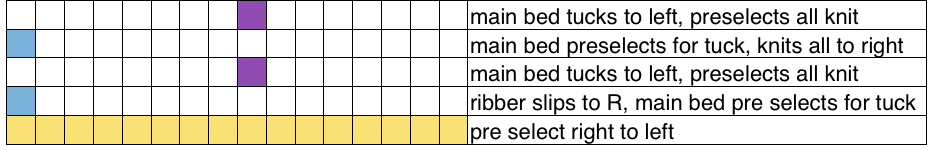
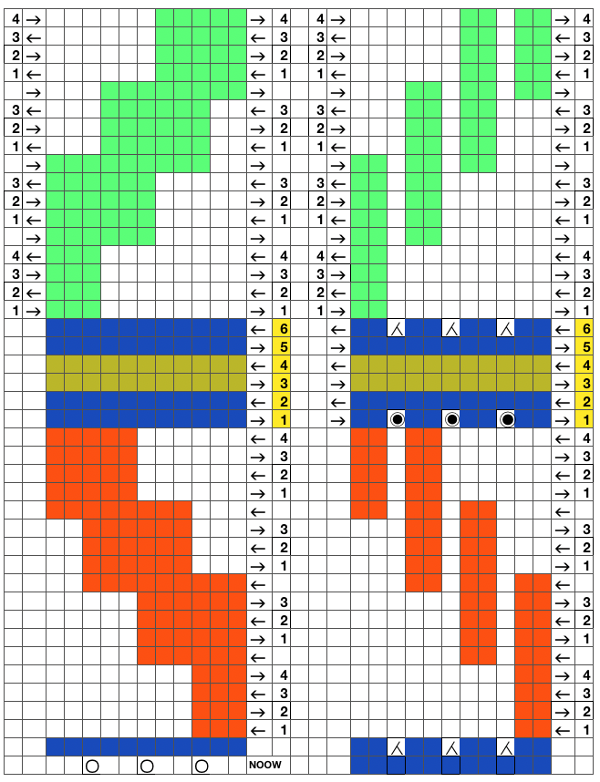
 Set up the cast-on as preferred. I used plain knitting, weighted it, and began my pattern work from the right-hand side of the machine. COL my preselection row was made from right to left. White squares in the chart with black ground and green grid become non selected needles on the main bed. Transfer nonselected stitches down to the ribber. Set the ribber to slip to the right, those stitches just transferred will slip moving to the right, knit on the return pass to the left. The knit carriage is set to knit until that first row is completed
Set up the cast-on as preferred. I used plain knitting, weighted it, and began my pattern work from the right-hand side of the machine. COL my preselection row was made from right to left. White squares in the chart with black ground and green grid become non selected needles on the main bed. Transfer nonselected stitches down to the ribber. Set the ribber to slip to the right, those stitches just transferred will slip moving to the right, knit on the return pass to the left. The knit carriage is set to knit until that first row is completed COR the ribber will knit on the next pass to the left. Set the knit carriage to tuck while the ribber is knitting
COR the ribber will knit on the next pass to the left. Set the knit carriage to tuck while the ribber is knitting Continue in pattern to the desired length. Fabric narrows considerably, so several panels may be required for items ie. skirts. The repeat on the knitting bed should also be adjusted to allow for as close to invisible seaming as possible. The stitches on either side of the single needle in work on the ribber may be inclined to drop off. I was unable to use tuck on those same needles for any significant length for that reason. It pays to visually check for stitches knitting off properly to avoid this
Continue in pattern to the desired length. Fabric narrows considerably, so several panels may be required for items ie. skirts. The repeat on the knitting bed should also be adjusted to allow for as close to invisible seaming as possible. The stitches on either side of the single needle in work on the ribber may be inclined to drop off. I was unable to use tuck on those same needles for any significant length for that reason. It pays to visually check for stitches knitting off properly to avoid this  The start of vertical pleats, with the slip stitches folding to the purl side, the tucked stitches folding to the knit side on the machine, just after binding off.
The start of vertical pleats, with the slip stitches folding to the purl side, the tucked stitches folding to the knit side on the machine, just after binding off. 

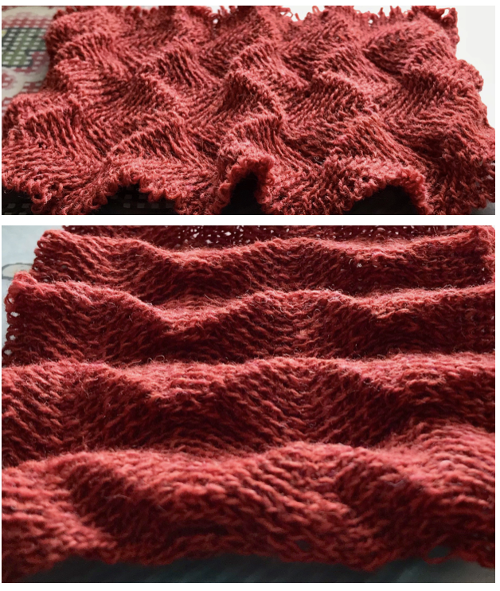
 Different fibers can produce varying results in fold and drape. Setting either bed function for the wrong direction will produce an all-knit fabric (top of the red swatch).
Different fibers can produce varying results in fold and drape. Setting either bed function for the wrong direction will produce an all-knit fabric (top of the red swatch). 
 This starts to address incorporating hand techniques and manual ones from the diagonal swatch and the one with vertical folds while also developing a design repeat to aid with planning or actions to be taken. It will be altered in future experiments
This starts to address incorporating hand techniques and manual ones from the diagonal swatch and the one with vertical folds while also developing a design repeat to aid with planning or actions to be taken. It will be altered in future experiments 
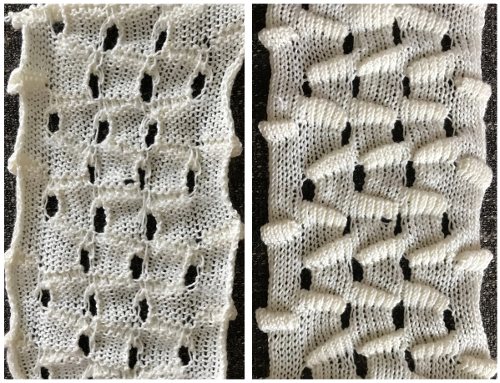
 This swatch is knit in wool, trying to sort out what does what and by how much. I am starting to get a bubble, but not a dramatic folding effect. The bottom folds more than the top. The filled eyelet technique has a hand-tooled tuck column on the reverse side. The top is automated using tuck stitch.
This swatch is knit in wool, trying to sort out what does what and by how much. I am starting to get a bubble, but not a dramatic folding effect. The bottom folds more than the top. The filled eyelet technique has a hand-tooled tuck column on the reverse side. The top is automated using tuck stitch.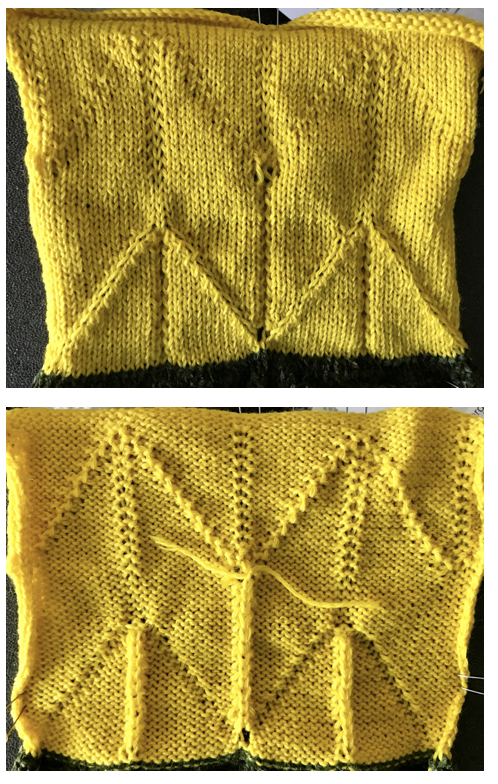  A different repeat: the bottom with carriage set to knit with needle selection as a cue to hand transfers, the top set to tuck automatically. Transition rows need to be considered further and altered where the twain meet.
A different repeat: the bottom with carriage set to knit with needle selection as a cue to hand transfers, the top set to tuck automatically. Transition rows need to be considered further and altered where the twain meet. 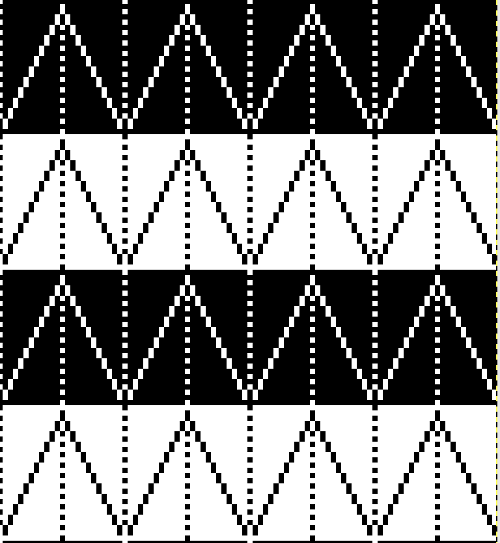 Returning to simpler creases and folds: a first experiment in racking double bed with NOOW. The setup and racking positions were not pre-planned. I knit 4 rows without racking at unplanned intervals as well; they produce a noticeable change in texture. The fabric is reversible, I actually rephotographed it adding a marker to make certain I had not shot the same side twice. The needle set up:
Returning to simpler creases and folds: a first experiment in racking double bed with NOOW. The setup and racking positions were not pre-planned. I knit 4 rows without racking at unplanned intervals as well; they produce a noticeable change in texture. The fabric is reversible, I actually rephotographed it adding a marker to make certain I had not shot the same side twice. The needle set up:  the resulting swatch presented sideways for the sake of space:
the resulting swatch presented sideways for the sake of space: 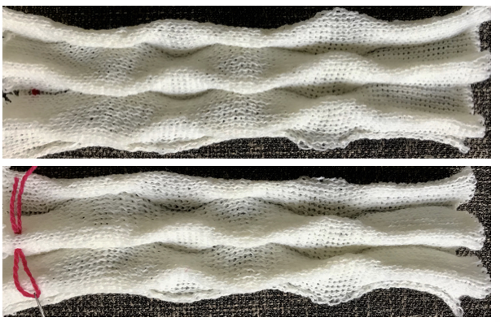 working with single needles out of work rather than two, with even spacing between them on each bed
working with single needles out of work rather than two, with even spacing between them on each bed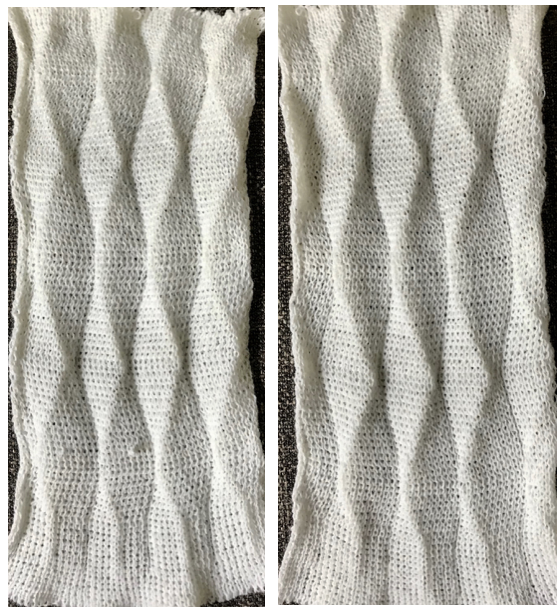 both swatches flattened to note differences between needle arrangement folds
both swatches flattened to note differences between needle arrangement folds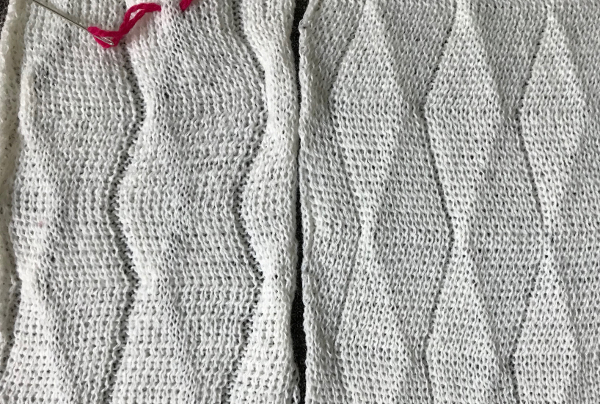  getting more organized, with a planned repeat: the needle set up
getting more organized, with a planned repeat: the needle set up Here the arrangement here is with 2 needles out of work, racking every 2 rows in the same sequence. The resulting fabric has clear “spring” and foldsRR
Here the arrangement here is with 2 needles out of work, racking every 2 rows in the same sequence. The resulting fabric has clear “spring” and foldsRR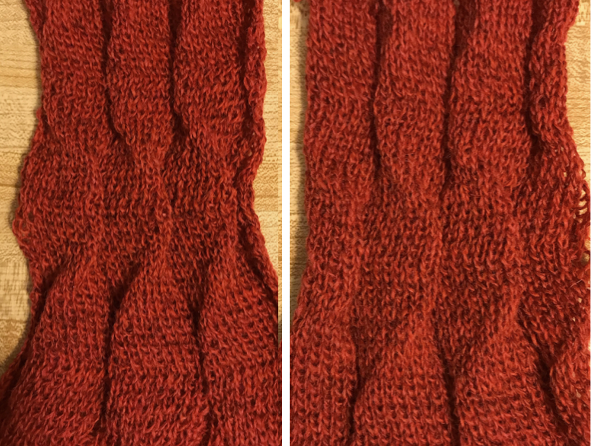 Returning to the previous needle set up, now racking every row from position 5 to 0, knit 1 more row with no racking; rack to position 10, knit one more row with no racking, reverse direction, end knitting on position # 5
Returning to the previous needle set up, now racking every row from position 5 to 0, knit 1 more row with no racking; rack to position 10, knit one more row with no racking, reverse direction, end knitting on position # 5
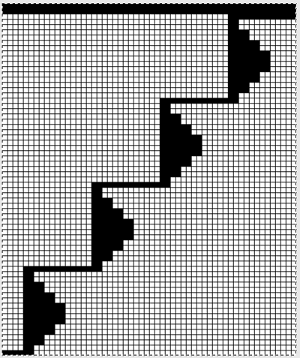
 This last in the series is a personal favorite. I found racking from the center to 10, to 0, and back easy to track. One moves in the opposite direction when not allowed to go any further in the continuing direction by the machine. Single needles out of work appear to be enough to create the folds.
This last in the series is a personal favorite. I found racking from the center to 10, to 0, and back easy to track. One moves in the opposite direction when not allowed to go any further in the continuing direction by the machine. Single needles out of work appear to be enough to create the folds.
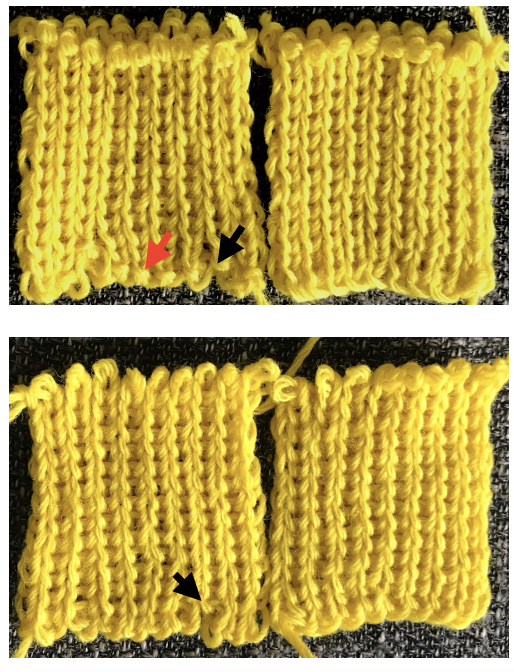
 Racking starting position on 7:
Racking starting position on 7: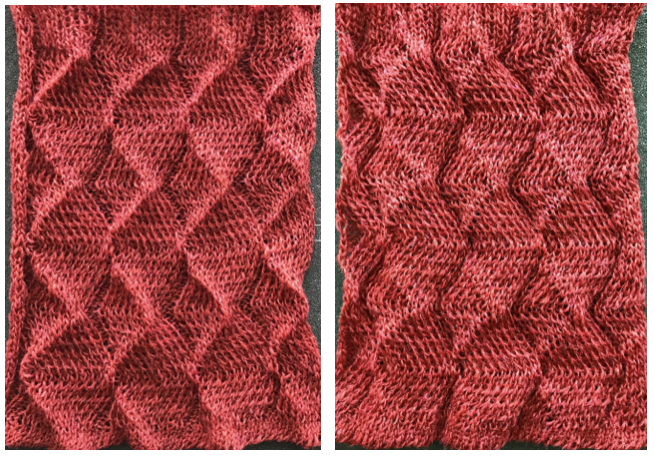 Consider playing with racking positions within the total number of needles in work on the main bed. For other possible needle arrangements and more on pleats created with needles in/out of work on both beds please see
Consider playing with racking positions within the total number of needles in work on the main bed. For other possible needle arrangements and more on pleats created with needles in/out of work on both beds please see  I like to chart out my repeats and plans for executing fabrics, along with ideas for possibly varying them in ways other than suggested, this was my beginning
I like to chart out my repeats and plans for executing fabrics, along with ideas for possibly varying them in ways other than suggested, this was my beginning 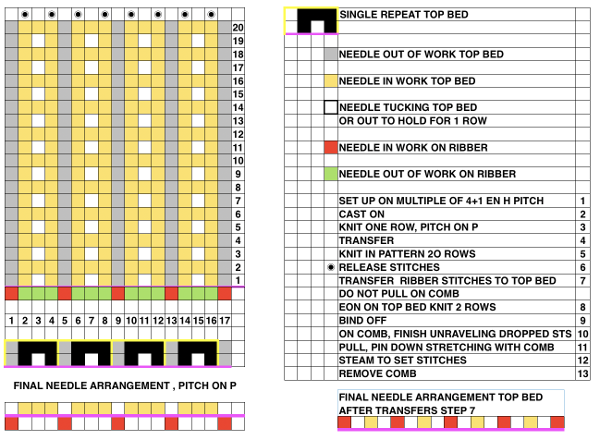

 knit one more row to return to the opposite side
knit one more row to return to the opposite side 





 I knit 3 rows rather than 2, to return to right side for bind off
I knit 3 rows rather than 2, to return to right side for bind off  here is the swatch, still on comb for “setting stitches”
here is the swatch, still on comb for “setting stitches”




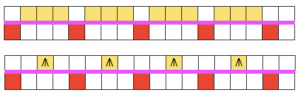


 when the 20 rows are completed the carriages will once again be on the right, all stitches will have been knit on the previous row
when the 20 rows are completed the carriages will once again be on the right, all stitches will have been knit on the previous row  transfer all ribber stitches to top bed, knit 2 rows, bind off. None of my swatches were blocked other than by some tugging, particularly along the bottom edge. The spacing between stitches is narrower because ladders created by single needles left out of work are formed by yarn lengths that are shorter than those that happen when stitches are knit and then in turn dropped. The height of the swatch is also affected, and the half fisherman texture in the wool swatch, in particular, is more evident.
transfer all ribber stitches to top bed, knit 2 rows, bind off. None of my swatches were blocked other than by some tugging, particularly along the bottom edge. The spacing between stitches is narrower because ladders created by single needles left out of work are formed by yarn lengths that are shorter than those that happen when stitches are knit and then in turn dropped. The height of the swatch is also affected, and the half fisherman texture in the wool swatch, in particular, is more evident.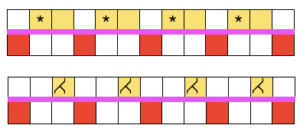 When the work is removed from the machine, stretch cast on outwards, then give each “scallop” a really good pull downwards. Steam lightly over the scallops to set them. Variations of the double bed trims may be worked on the single bed as well.
When the work is removed from the machine, stretch cast on outwards, then give each “scallop” a really good pull downwards. Steam lightly over the scallops to set them. Variations of the double bed trims may be worked on the single bed as well. 2. knit second zigzag row to right
2. knit second zigzag row to right




 In theory, it is possible to knit lace transfers in Brother by dropping the ribber bed enough for the lace carriage to move across the beds while clearing the gate pegs. This remains on my “try someday” list. To my mind, hand transferring remains the best way to deal with lace/ ribber stitches combined.
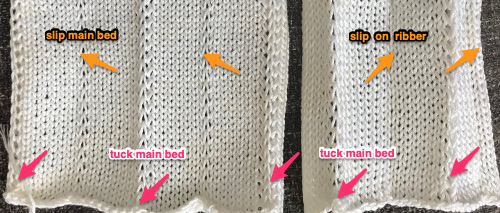
In theory, it is possible to knit lace transfers in Brother by dropping the ribber bed enough for the lace carriage to move across the beds while clearing the gate pegs. This remains on my “try someday” list. To my mind, hand transferring remains the best way to deal with lace/ ribber stitches combined.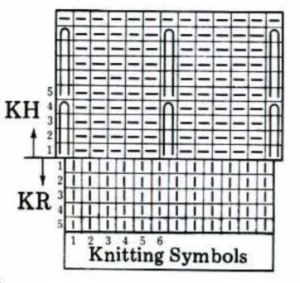 For a punchcard machine, the repeat must be a factor of 24 in width ie. 6 or 8, or 12 stitches wide. Electronic knitters can draw a single repeat, either the one on the left also using color reverse or the one on the right. Punchcard knitters need to punch the grey squares on the right across the card and repeat it in height. An extra all-knit row needs to be added at the top of each series of 4 rows tucked for the loops to be knit off automatically by the machine. Step 4 in the techniques book, resetting the main bed to N to knit a row after every 4 rows in a holding pattern is missing in their illustration above.
For a punchcard machine, the repeat must be a factor of 24 in width ie. 6 or 8, or 12 stitches wide. Electronic knitters can draw a single repeat, either the one on the left also using color reverse or the one on the right. Punchcard knitters need to punch the grey squares on the right across the card and repeat it in height. An extra all-knit row needs to be added at the top of each series of 4 rows tucked for the loops to be knit off automatically by the machine. Step 4 in the techniques book, resetting the main bed to N to knit a row after every 4 rows in a holding pattern is missing in their illustration above.  The punchcard repeat: punch each grey square to match the illustration
The punchcard repeat: punch each grey square to match the illustration 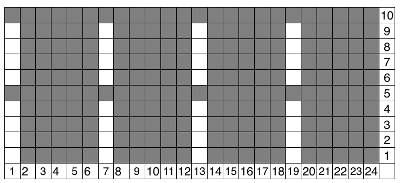 A few to try, shown in repeat X2, as BW gridded .bmps, and with the color reversed for knitting. All but one are 12 stitches in width, suitable for punchcard machines as well
A few to try, shown in repeat X2, as BW gridded .bmps, and with the color reversed for knitting. All but one are 12 stitches in width, suitable for punchcard machines as well 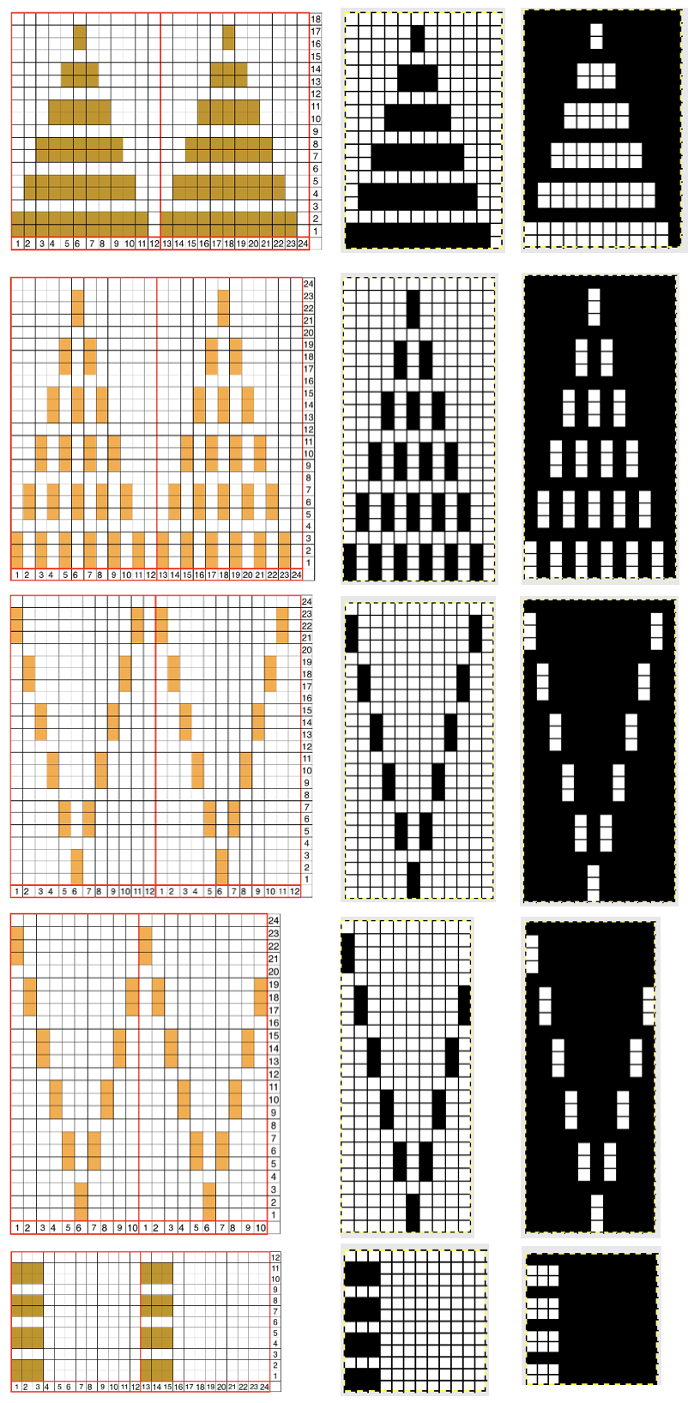 Too much black? want to count those black squares more easily? pick your preferred grid color, it will disappear when the image is saved
Too much black? want to count those black squares more easily? pick your preferred grid color, it will disappear when the image is saved 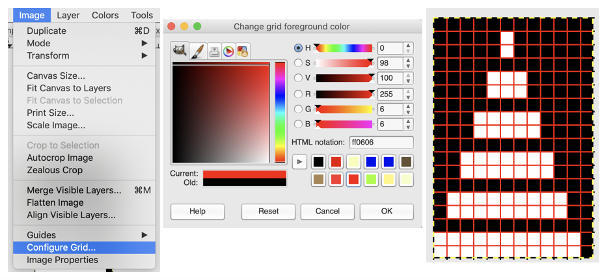 A screen grab from my iMac shows the original charts and the resulting single repeat .bmps after working in GIMP, ready for download with color reverse option and use on the electronic machines. Ayab knitters, in addition, would need to program the repeat in width to match the number of needles planned for use in the piece
A screen grab from my iMac shows the original charts and the resulting single repeat .bmps after working in GIMP, ready for download with color reverse option and use on the electronic machines. Ayab knitters, in addition, would need to program the repeat in width to match the number of needles planned for use in the piece


 Working it on Brother becomes a bit fiddly. Whether working on a punchcard or electronic KM, it is possible to introduce patterning on either or both beds as seen below. I preferred the look obtained with the racked cast on at the start. Setting up the Brother machine: program the repeat, half pitch for every needle rib, air knit to place the pattern on the bed so that the first needle on the left (or right if you prefer) is preselected forward and will produce a knit stitch on the first row knit. The yarn used is a 2/24 acrylic
Working it on Brother becomes a bit fiddly. Whether working on a punchcard or electronic KM, it is possible to introduce patterning on either or both beds as seen below. I preferred the look obtained with the racked cast on at the start. Setting up the Brother machine: program the repeat, half pitch for every needle rib, air knit to place the pattern on the bed so that the first needle on the left (or right if you prefer) is preselected forward and will produce a knit stitch on the first row knit. The yarn used is a 2/24 acrylic 
 now another needle on the ribber is brought in to work on the far left, it will tuck with lili selection when moving from left to right
now another needle on the ribber is brought in to work on the far left, it will tuck with lili selection when moving from left to right  remember the ribber rule with lili buttons: an even number of needles must be in work, this shows the start and end of selection on the ribber on alternate needle tape markings, as required
remember the ribber rule with lili buttons: an even number of needles must be in work, this shows the start and end of selection on the ribber on alternate needle tape markings, as required 



 Both pieces compared for width and rippling
Both pieces compared for width and rippling

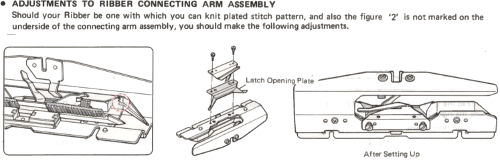

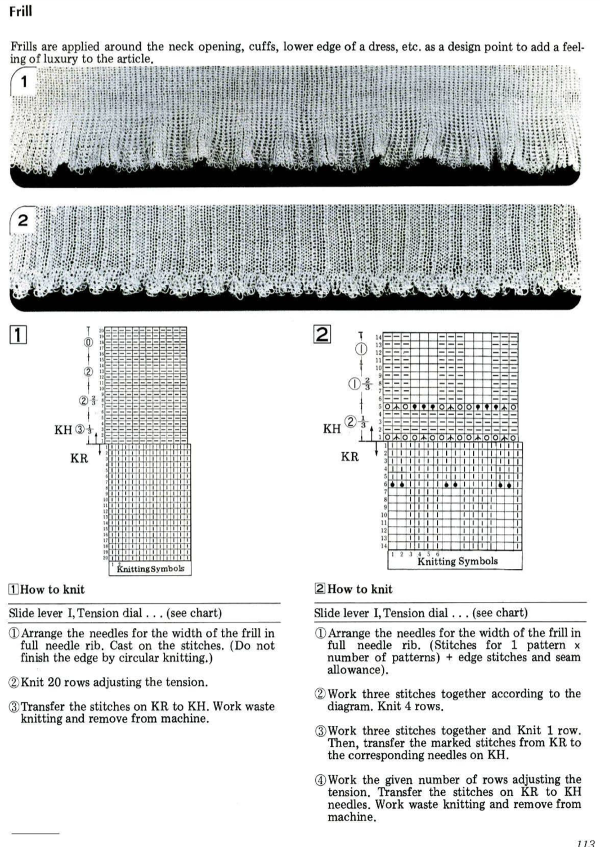
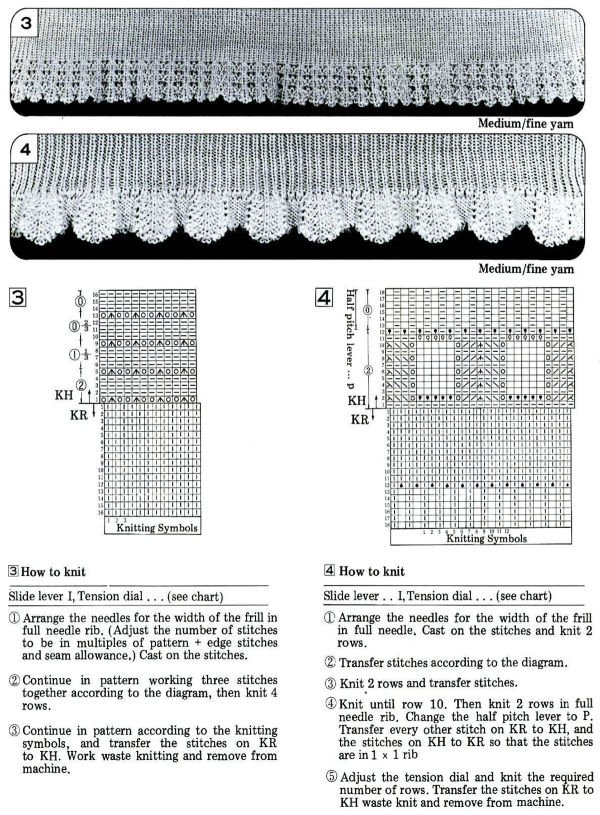
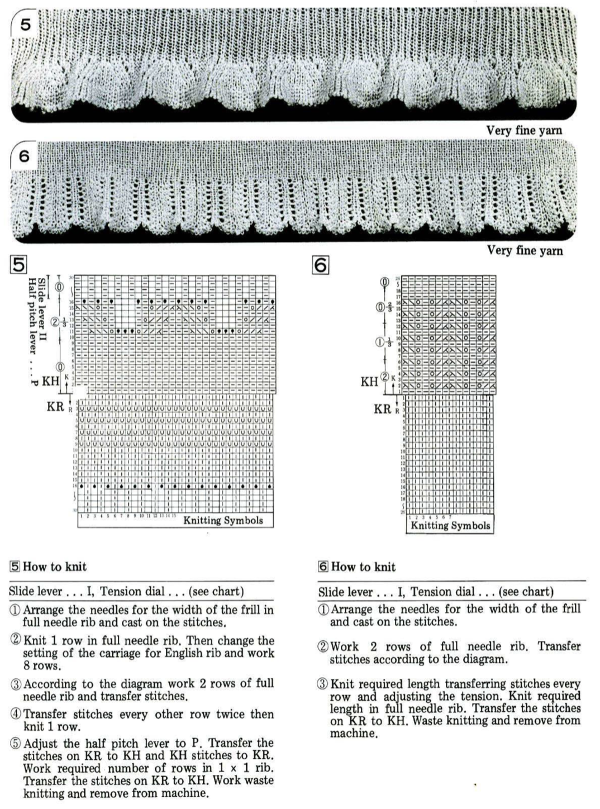 An intro to scallops: p.120
An intro to scallops: p.120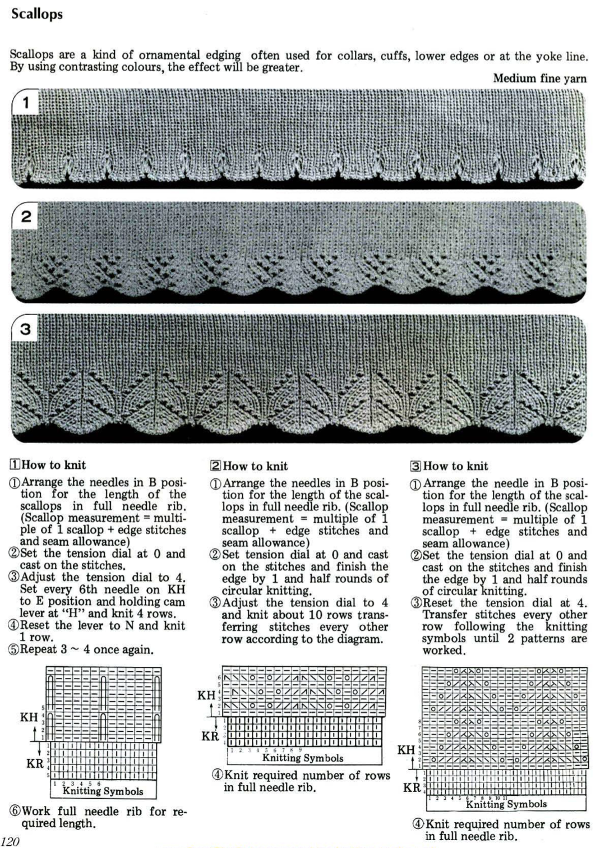

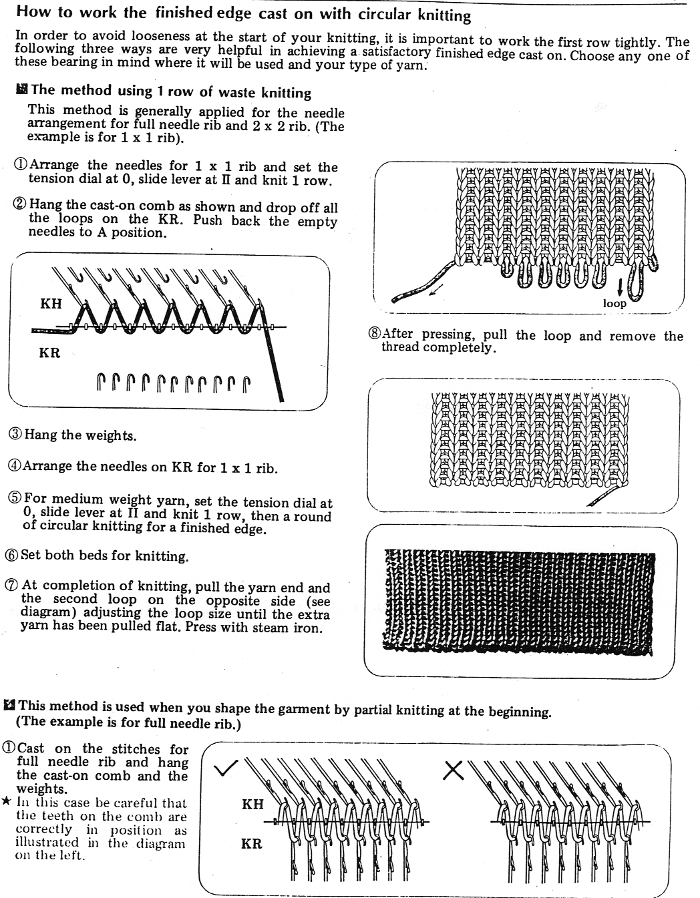
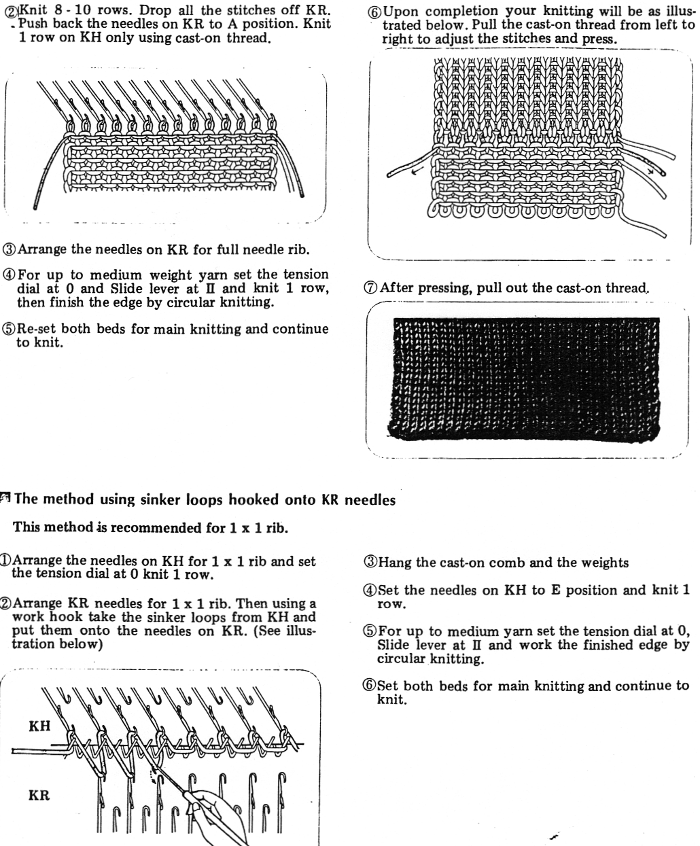
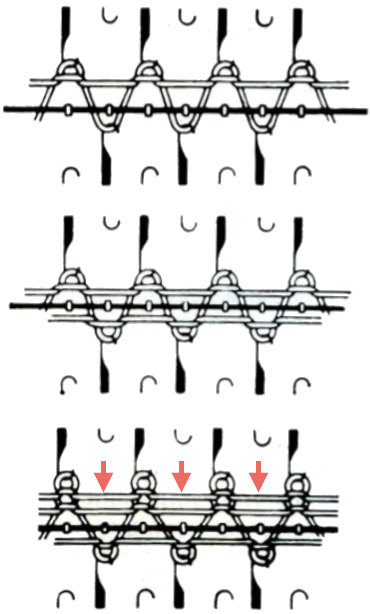
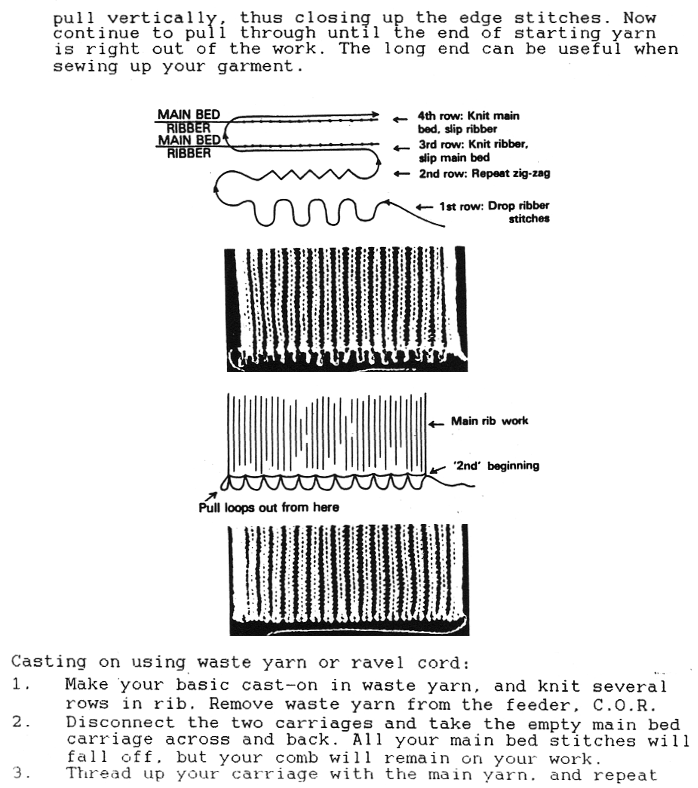
 before the next pass, make certain there are no needles in work on the ribber, they will pick unwanted loops, also, give a tug at the yarn on the carriage side as you begin to knit the next row in order to avoid loops as seen on the right below. Knit to the opposite side.
before the next pass, make certain there are no needles in work on the ribber, they will pick unwanted loops, also, give a tug at the yarn on the carriage side as you begin to knit the next row in order to avoid loops as seen on the right below. Knit to the opposite side. 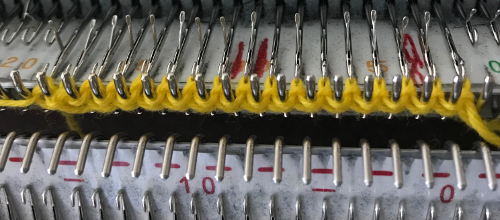 Transfer stitches in the desired needle setup. With waste yarn, ravel cord, and weights prior to its start this cast-on may be used for wider flat ribs ie 2X2, 3X3, etc. Here the comb is in place, ready for 1X1 rib
Transfer stitches in the desired needle setup. With waste yarn, ravel cord, and weights prior to its start this cast-on may be used for wider flat ribs ie 2X2, 3X3, etc. Here the comb is in place, ready for 1X1 rib 

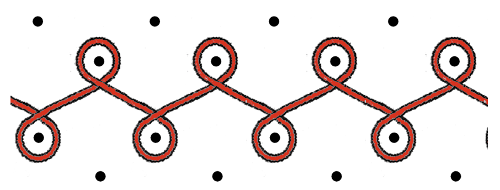
 working from the right to the left side
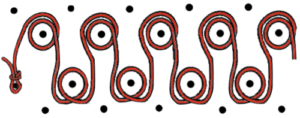
working from the right to the left side 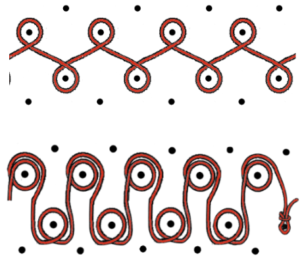
 which is knit carefully to the opposite side
which is knit carefully to the opposite side the comb is then hung. Make certain its teeth are placed properly across the row holding stitches down. Here they are not on the right, resulting in the issue marked with black arrows at the bottom of the corresponding swatch
the comb is then hung. Make certain its teeth are placed properly across the row holding stitches down. Here they are not on the right, resulting in the issue marked with black arrows at the bottom of the corresponding swatch 
 If working in fine yarns, 2 tubular rows may be needed after the wrapped cast-on.
If working in fine yarns, 2 tubular rows may be needed after the wrapped cast-on.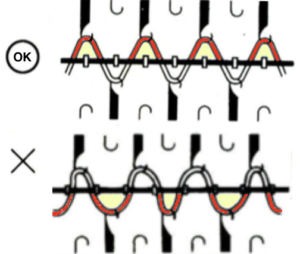


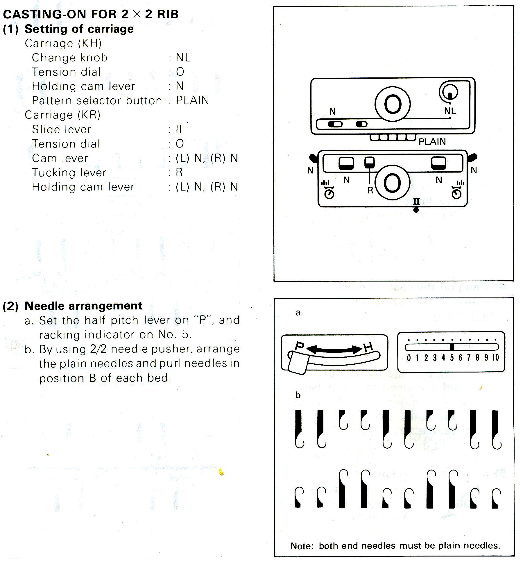
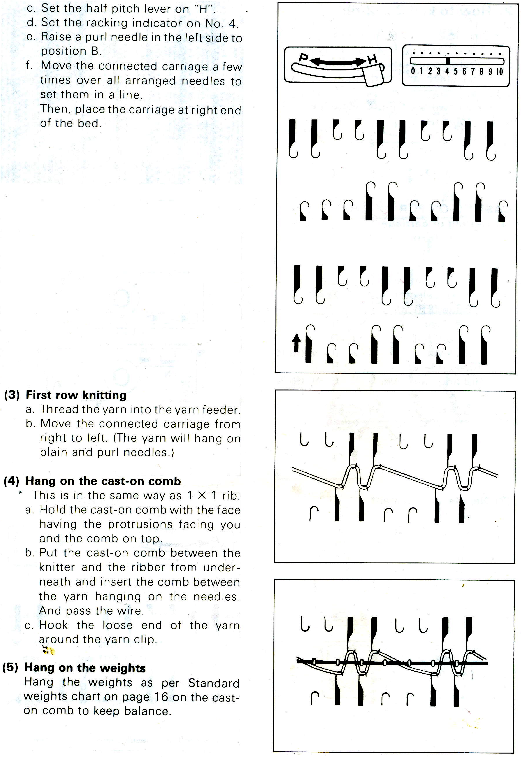
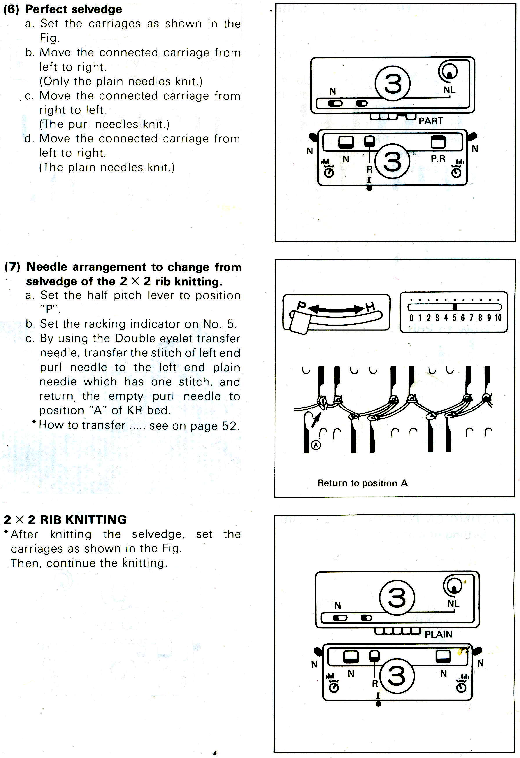
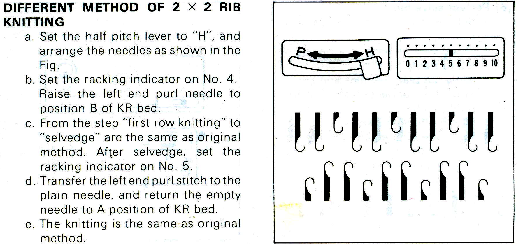
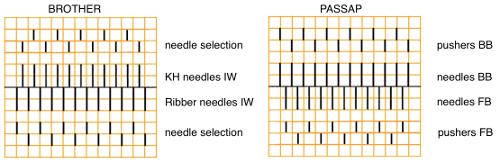 Decorative cast-ons and beginnings
Decorative cast-ons and beginnings