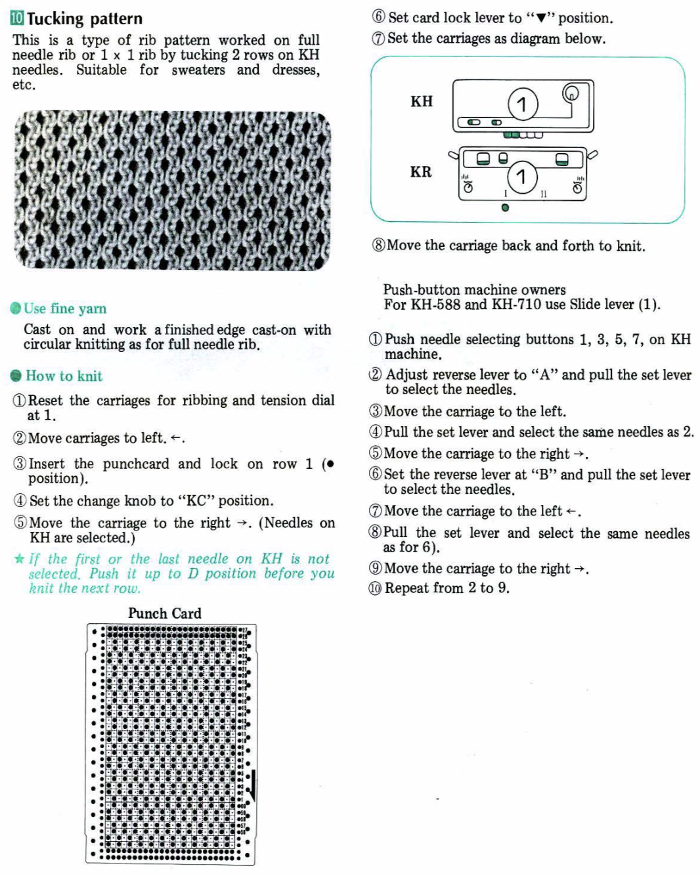
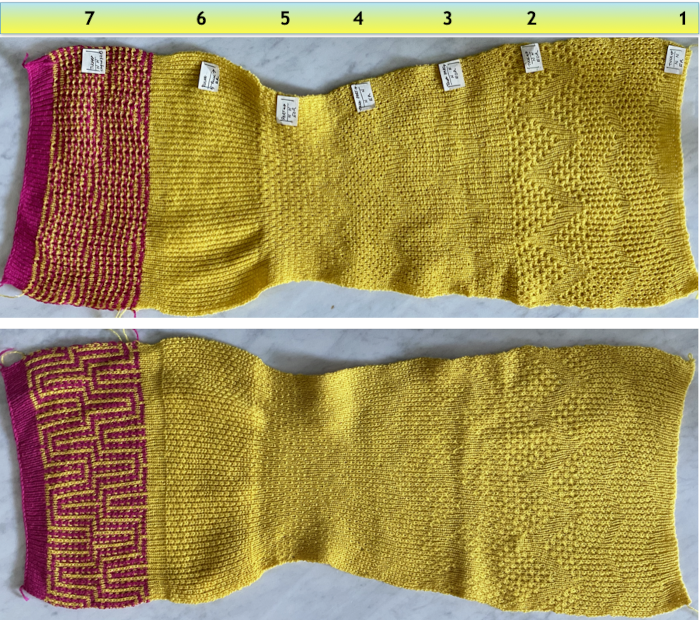
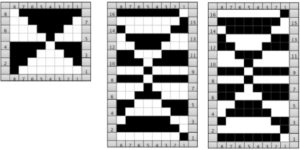
I have been asked whether this fabric discussed in the post could be produced on the Passap.  The only way to find out is to try it. The lesson already learned: use a crisp yarn that can retain memory for maximum effect. Here, the swatch is knit in a 3/14 cotton. To start with, racking was from position 0 to 6 and back. Racking every 2 rows at the bottom of the sample, every row at its top
The only way to find out is to try it. The lesson already learned: use a crisp yarn that can retain memory for maximum effect. Here, the swatch is knit in a 3/14 cotton. To start with, racking was from position 0 to 6 and back. Racking every 2 rows at the bottom of the sample, every row at its top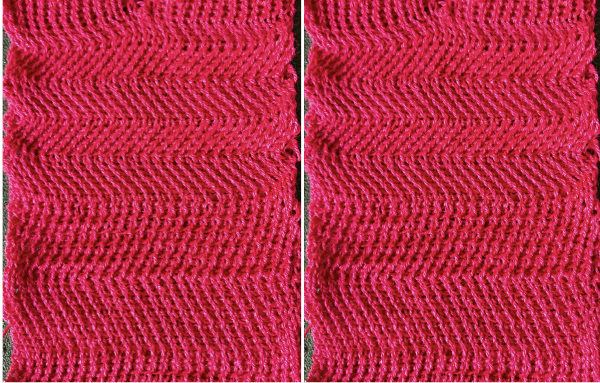 Now adding needles out of work with the expectation of folds at approximate center of each fold
Now adding needles out of work with the expectation of folds at approximate center of each fold![]() This was my set up, after planning the repeat and transferring a couple of stitches on each end to the back bed for better side edges
This was my set up, after planning the repeat and transferring a couple of stitches on each end to the back bed for better side edges  Racking started in center position 0, then swung to 3 left, to 3 right, ending on 0. I long ago got frustrated with the Passap numbering, marked the racking positions with a permanent marker from 0 on the right to 6 on the left. The knit result is a rolling fabric, though a bit less so than the Brother sample, which was able to move across more racking positions.
Racking started in center position 0, then swung to 3 left, to 3 right, ending on 0. I long ago got frustrated with the Passap numbering, marked the racking positions with a permanent marker from 0 on the right to 6 on the left. The knit result is a rolling fabric, though a bit less so than the Brother sample, which was able to move across more racking positions.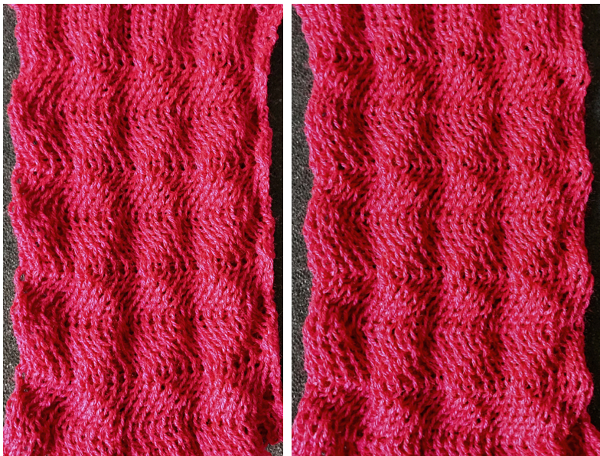  Reviewing some racking facts: several posts previously written that include information for racking designs on both brands
Reviewing some racking facts: several posts previously written that include information for racking designs on both brands
2018/07/19/more-scales-and-chevrons-in-ribbed-racked-4-fabrics/
2016/01/13/racking-2-vertical-chevrons-herringbone/
2016/02/02/vertical-racking-3-automating-half-fisherman-in-pattern-2/
2016/01/09/ribber-pitch-a-bit-on-racking-1-chevrons-horizontal-herringbone/
2018/10/14/fisherman-english-tuck-stitch-rib-1-checks-patterns-brother-passap/
2015/11/22/racked-ribber-cast-on-and-rib-configuration-tips/
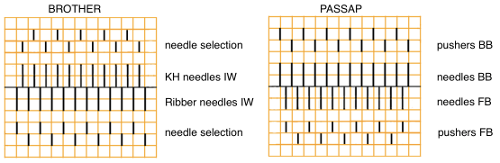
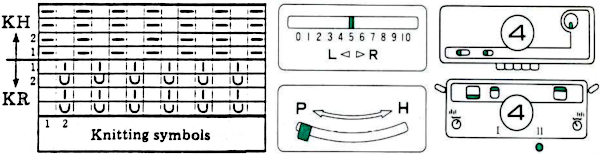
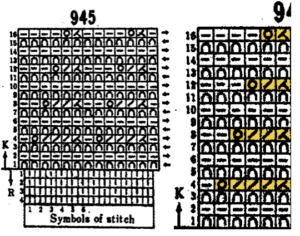
Brother racking controls: the handle, racking indicator, and pitch lever 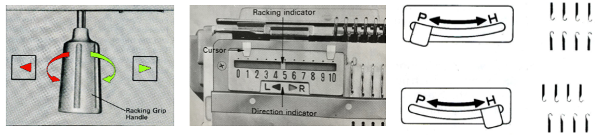 There are ample illustrations including from Brother Ribber Techniques Book in previous posts on procedural steps. Passap: racking handle is up for full pitch (point to point), down for half-pitch. It is turned one full rotation for each unit/ number change in ranking positions. Partial rotations may be suggested when some of its accessories ie their transfer carriage are used. As stated, Brother has 10 positions, Passap only 6.
There are ample illustrations including from Brother Ribber Techniques Book in previous posts on procedural steps. Passap: racking handle is up for full pitch (point to point), down for half-pitch. It is turned one full rotation for each unit/ number change in ranking positions. Partial rotations may be suggested when some of its accessories ie their transfer carriage are used. As stated, Brother has 10 positions, Passap only 6. 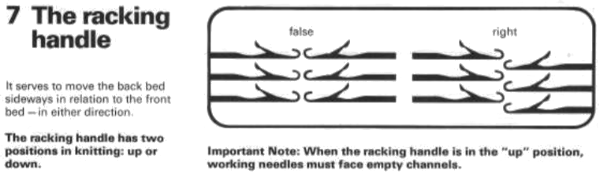
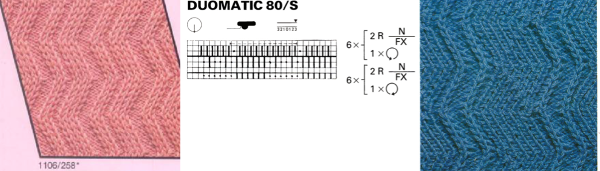
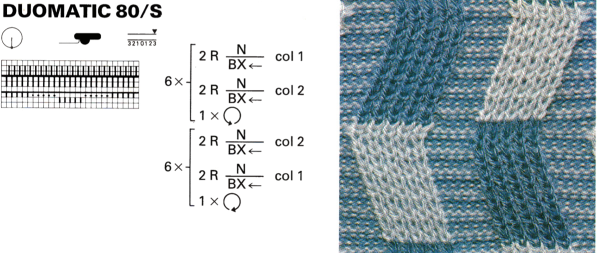
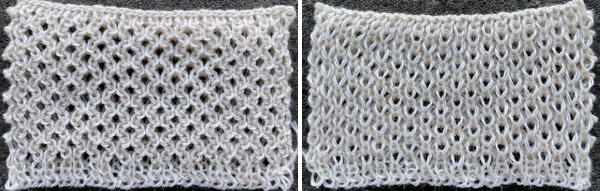
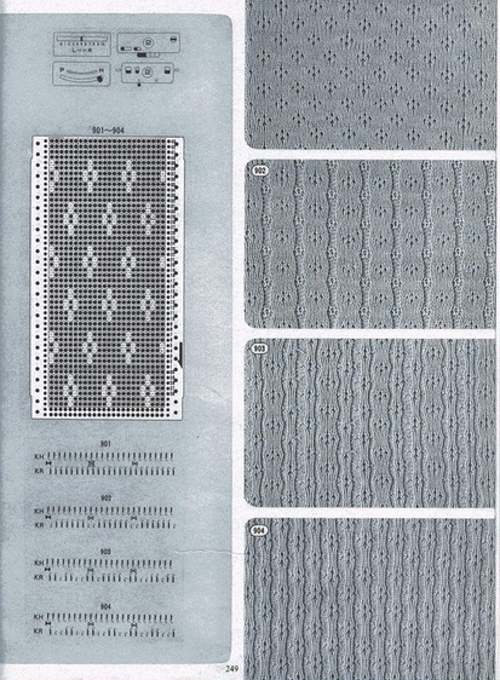
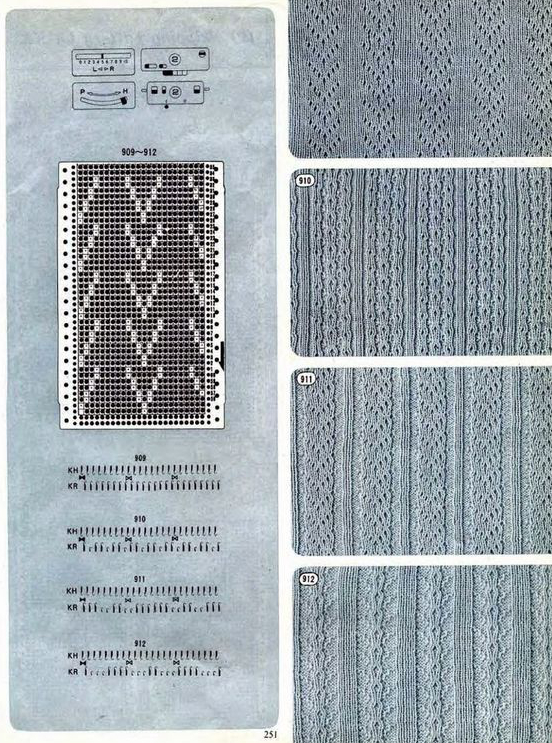
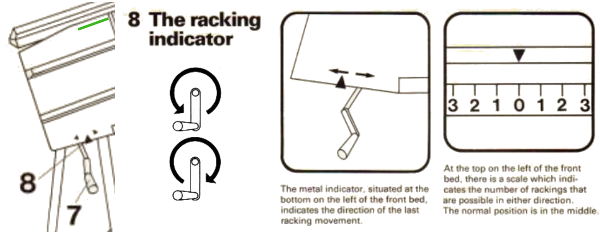 The Passap E6 manual shows racking patterns possible with console built-in designs on pp. 118, 119, 120, 121, with techniques used in racking patterns number 257-272. The console gives prompts for the direction in racking sequences. Self-programmed designs would need a separate knitting technique entered into the console as an additional “design”. This can be done with a card reader combined with a pattern download from a computer. Programs that automate the function are no longer on the market. Typically, in published patterns for either brand, if the starting point for the racking sequence is important, it will be given along with the frequency of movements such as in this design from the Duo 80 book
The Passap E6 manual shows racking patterns possible with console built-in designs on pp. 118, 119, 120, 121, with techniques used in racking patterns number 257-272. The console gives prompts for the direction in racking sequences. Self-programmed designs would need a separate knitting technique entered into the console as an additional “design”. This can be done with a card reader combined with a pattern download from a computer. Programs that automate the function are no longer on the market. Typically, in published patterns for either brand, if the starting point for the racking sequence is important, it will be given along with the frequency of movements such as in this design from the Duo 80 book Programming the front bed on Passap or main bed on Brother with tuck or slip selections begins to enter far greater common ground. Decades ago, my advanced knitting curriculum included Passap weekend workshops in addition to Brother course classroom and studio hours. I spent a lot of time exploring techniques, often, my manual includes scribbled notes. Manual guidelines for E6 patterning, beginning with advice for knitting them
Programming the front bed on Passap or main bed on Brother with tuck or slip selections begins to enter far greater common ground. Decades ago, my advanced knitting curriculum included Passap weekend workshops in addition to Brother course classroom and studio hours. I spent a lot of time exploring techniques, often, my manual includes scribbled notes. Manual guidelines for E6 patterning, beginning with advice for knitting them 


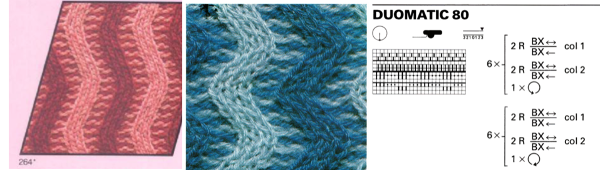
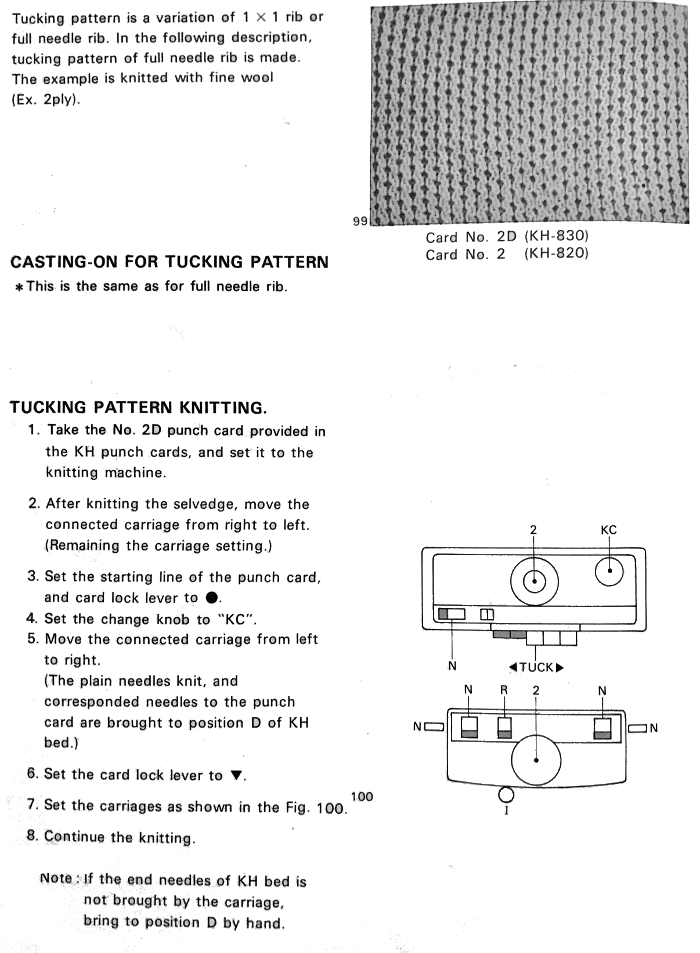
 I have to admit I cannot always decipher some of my note-taking or handwriting. The additional confusion that comes into work in cross-brand translations is the fact that some E6 techniques may only be used as programmed by the factory, others may be “combined with stitch patterns”. Getting it down to black and white squares when stitch patterns in E6 are to be translated for other KM brands is a bit more complex. It is easier done from the Duo 80 instructions when an E 6 is not available for test knitting. The Duo manual is low on swatches and pattern assortments, but a small book, available online,can inspire many textures, the Passap system’s particular strength.
I have to admit I cannot always decipher some of my note-taking or handwriting. The additional confusion that comes into work in cross-brand translations is the fact that some E6 techniques may only be used as programmed by the factory, others may be “combined with stitch patterns”. Getting it down to black and white squares when stitch patterns in E6 are to be translated for other KM brands is a bit more complex. It is easier done from the Duo 80 instructions when an E 6 is not available for test knitting. The Duo manual is low on swatches and pattern assortments, but a small book, available online,can inspire many textures, the Passap system’s particular strength.  Some Duo symbols and their meaning
Some Duo symbols and their meaning
 Many designs are based on one or both beds having needles out of work. Transferring stitches from one bed to the other can be done based on needle diagrams on the Duo 80 and punchcard machines after the cast-on row is closed. If the specific technique in the E6 offers a pusher selection after the first SX/GX row (262,264, 265, 269, 270, 282) transfer stitches with locks on the left, otherwise, transfer after the second SX/GX pass to the right (257,258,259). After the pattern is set up in E6, place all the pushers in rest position, completely out of work.
Many designs are based on one or both beds having needles out of work. Transferring stitches from one bed to the other can be done based on needle diagrams on the Duo 80 and punchcard machines after the cast-on row is closed. If the specific technique in the E6 offers a pusher selection after the first SX/GX row (262,264, 265, 269, 270, 282) transfer stitches with locks on the left, otherwise, transfer after the second SX/GX pass to the right (257,258,259). After the pattern is set up in E6, place all the pushers in rest position, completely out of work.
Pushers corresponding to needles out of work on the back bed need to be in the back rail so as not to cause mispatterning if arrow keys are used. In Japanese electronics, transfers can be made after the first KC pass, making certain the emptied needles are placed completely out of work. Set up the knit bed first so that alignment relationships are correct for out-of-work selections on both beds.
As in any ribber pattern, if the major part of the piece is being knit single bed, the tension will need to be adjusted to closer to that used in stocking stitch for the same yarn. Passap knitters have the added option of changing the strippers in use to another color.
When designing your own patterns and starting the movements on either side of the machine, it will take some sorting out as to what arrangement of needles in work is best on the Passap back bed or Brother ribber is best for side edges as one bed moves beyond the last stitch in work on the knit bed. There should be no stitches on it without stitches behind them as the racked stitches travel from each side to the other if the goal is pieces that will be seamed ie. the front and back of a sweater.
The E6 console may not always give the proper selection for needle setup for the front bed as seen in one of my swatches. There are never instructions for the back bed needle or pusher positions. Those need to be hand-selected based on diagrams after the front bed is set up and following the diagrams provided with each technique to produce the specific fabric illustrated. That can be disregarded in one’s experiments with needle arrangement and lock settings and how they relate to the movement in the racked stitches.
If one needs to stop the process at any point, it is a good idea to devise a method of keeping track of where the stop occurred and whether a racking movement has taken place yet or not. Forming personal, consistent habits is also useful, ie. I find when racking with color changes, I rack before I change the color consistently. Racking when using multiple colors often happens at the end of the color change sequence, ie, 2 colors, rack after 4 rows. A bit more attention needs to be paid when racking is for only a few positions. I tend to start mine on the far right at 0, so I can move the one or 2 steps and am stopped by the machine on my return, giving me an error margin on only one side.
A few Duo/Passap comparisons 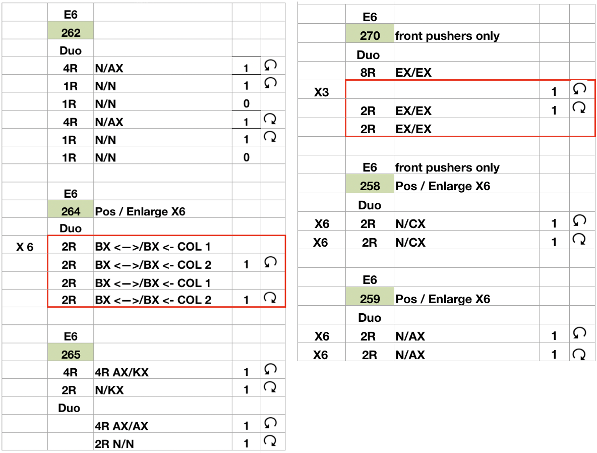
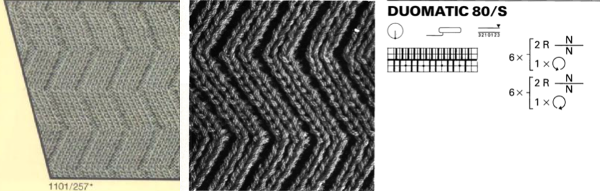
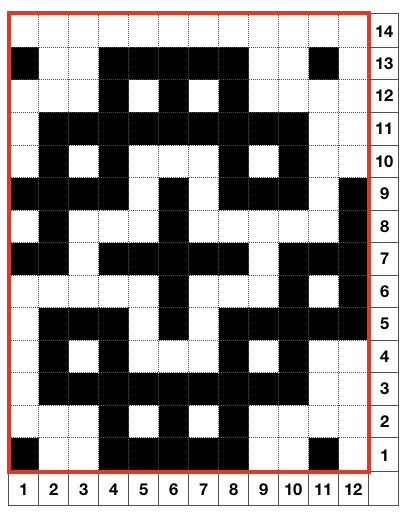
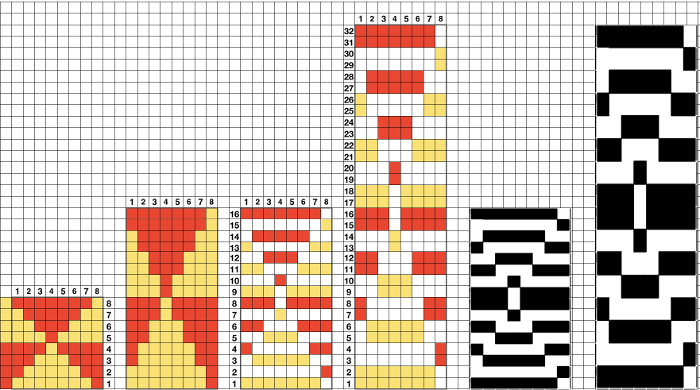
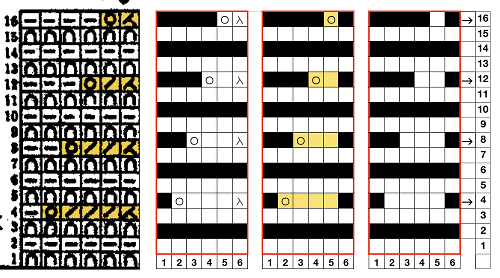
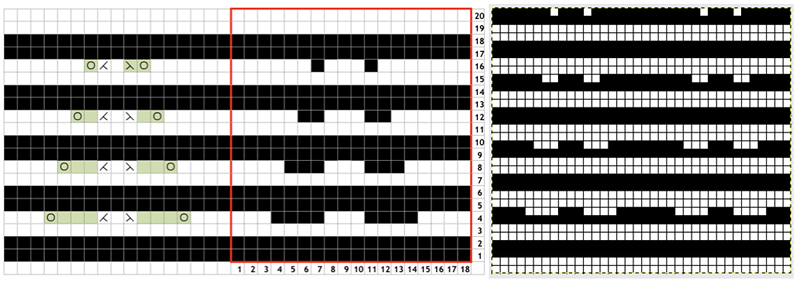
Swatches: this E6 design introduces needles out of work. The E6 swatch in color below on the far left has a slightly different needle arrangement than the DUO one to its right. Technique #257 has a * beside it, which indicates the repeat must be altered to produce the fabric. 120 is the page on which the swatch photo appears Altered designs are listed on pp. 129-131of the E6 pattern book for all stitch types. ![]()
![]() The original on the left is mirrored, the selection is fixed, the height is multiplied X 6. The lengthening does not influence the design, it tells the console how many swings in each direction are planned. The console, in turn, gives visual and sound prompts for each racking movement, in this instance, by one full turn clockwise. The prompts often start the pattern in the center 0, and begin and end with half a sequence.
The original on the left is mirrored, the selection is fixed, the height is multiplied X 6. The lengthening does not influence the design, it tells the console how many swings in each direction are planned. The console, in turn, gives visual and sound prompts for each racking movement, in this instance, by one full turn clockwise. The prompts often start the pattern in the center 0, and begin and end with half a sequence. ![]() The front bed is set to slip stitch, so black squares knit. Both beds will knit every needle/pusher in work throughout. After the first preselection row on either brand, needles and pushers in non-selected areas need to be put out of work, accomplished by transferring them to the opposite bed. The design process is the same as having a fixed row on a punchcard machine, with a single selection repeated over and over. The racking position indicator on the duo shows the start of the pattern at 0 position, Brother equivalent = 10. In the Duomatic, the carriage is set for plain knitting, and no patterning is required. The needle out-of-work selection differs from the E6 sample, but the racking sequence is the same. Brother options: fixed needle selection if the fabric is created fully as a hand technique does not require any programming. Electronics could be used with the repeat drawn X6 in height so that the racking direction is reversed after the first sequence is completed and the return to row 1 of the repeat is preselected. Machines that allow for it can have info added to memo windows, or mylar sheets may be marked to help accuracy in long pieces. Punchcard machines could punch a single row on #1 for accurate needle selection if it falls within the 24-stitch limits or hand-select them, mark racking numbers in repeat, and go on from there.
The front bed is set to slip stitch, so black squares knit. Both beds will knit every needle/pusher in work throughout. After the first preselection row on either brand, needles and pushers in non-selected areas need to be put out of work, accomplished by transferring them to the opposite bed. The design process is the same as having a fixed row on a punchcard machine, with a single selection repeated over and over. The racking position indicator on the duo shows the start of the pattern at 0 position, Brother equivalent = 10. In the Duomatic, the carriage is set for plain knitting, and no patterning is required. The needle out-of-work selection differs from the E6 sample, but the racking sequence is the same. Brother options: fixed needle selection if the fabric is created fully as a hand technique does not require any programming. Electronics could be used with the repeat drawn X6 in height so that the racking direction is reversed after the first sequence is completed and the return to row 1 of the repeat is preselected. Machines that allow for it can have info added to memo windows, or mylar sheets may be marked to help accuracy in long pieces. Punchcard machines could punch a single row on #1 for accurate needle selection if it falls within the 24-stitch limits or hand-select them, mark racking numbers in repeat, and go on from there. 
 My sample was knit in a tightly twisted cotton, and when off the machine had an interesting and unexpected fold 3Dquality
My sample was knit in a tightly twisted cotton, and when off the machine had an interesting and unexpected fold 3Dquality 

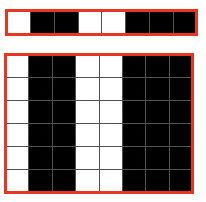 The setup is essentially the same, with white squares representing needles and pushers that need to be out of work. Tech 258 uses LX (slip) on the front bed, back bed si set to N. The duomatic pattern has a different OOW needle arrangement, the front lock is also set to tuck = FX (E6=KX), adding another layer of texture and complexity. Needles are also out of work on the back bed.
The setup is essentially the same, with white squares representing needles and pushers that need to be out of work. Tech 258 uses LX (slip) on the front bed, back bed si set to N. The duomatic pattern has a different OOW needle arrangement, the front lock is also set to tuck = FX (E6=KX), adding another layer of texture and complexity. Needles are also out of work on the back bed.
E6000 264* is used both as a pattern and a technique number uses the X6 as well for accompanying prompts. Needle/pusher selection is for 3 in work and 9 out of work for 2 rows, then reversing it for to 9 in work, 2 out of work for 2 rows, thus accommodating the alternating color change. The Duo on the front bed performs a similar selection with the BX <– arrow key, racking is every 4 rows in both. It takes 24 rows to reach the full racking position reversal. These were the pusher selections, each repeated X 2, creating the wrong fabric What is knitting in terms of black and white squares if one continues:
What is knitting in terms of black and white squares if one continues: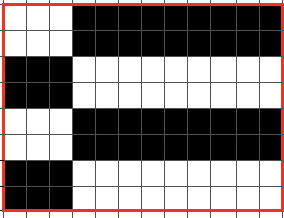
 this repeat is what is required to match the technique diagram
this repeat is what is required to match the technique diagram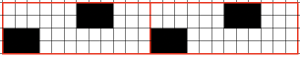 After the first row of pusher selection transfer 3 stitches on either side of the center 3 in each group of 9 to the back bed. This shows the proper selection, each is repeated twice
After the first row of pusher selection transfer 3 stitches on either side of the center 3 in each group of 9 to the back bed. This shows the proper selection, each is repeated twice I continued to knit with plain knitting on the back bed for proof of concept, every other needle selection, and slip (BX) stitch <– –> there would compress the “wave” since half as many rows would then be knit on that bed in each color. As always, forgetting to set the lock/carriage to slip will result in knit stripes as seen on the right of my sideways swatch
I continued to knit with plain knitting on the back bed for proof of concept, every other needle selection, and slip (BX) stitch <– –> there would compress the “wave” since half as many rows would then be knit on that bed in each color. As always, forgetting to set the lock/carriage to slip will result in knit stripes as seen on the right of my sideways swatch
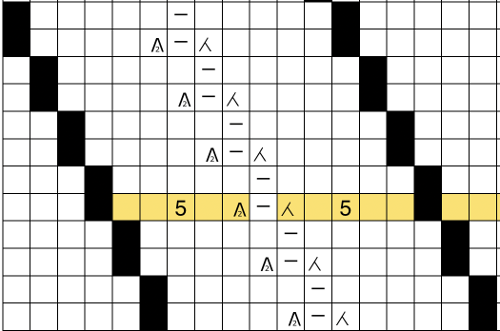
 Below the pattern alternates blocks of 5 black squares, 5 white, color changing every 2 rows and reversing racking direction after every 24 rows. The full repeat is 48 rows. If rows knit in the zig-zag are counted, they amount to 12 because each color slips it is not knitting for 2 rows. Note that to achieve the color reversal at the halfway point of the repeat the same color (2) knits for 4 rows, at the top of the repeat color 1 does the same.
Below the pattern alternates blocks of 5 black squares, 5 white, color changing every 2 rows and reversing racking direction after every 24 rows. The full repeat is 48 rows. If rows knit in the zig-zag are counted, they amount to 12 because each color slips it is not knitting for 2 rows. Note that to achieve the color reversal at the halfway point of the repeat the same color (2) knits for 4 rows, at the top of the repeat color 1 does the same.
Below tuck patterning is introduced in both beds. The front bed is knitting tuck on every other needle for 2 rows each, easy to reproduce on Brother ![]() AX<– on the back bed will knit when pushers are up for 2 rows, tuck on the same needles when they are selected down, also for 2 rows. Brother knitters could try to set the ribber carriage to tuck in one direction only, or simply set it to knit every row
AX<– on the back bed will knit when pushers are up for 2 rows, tuck on the same needles when they are selected down, also for 2 rows. Brother knitters could try to set the ribber carriage to tuck in one direction only, or simply set it to knit every row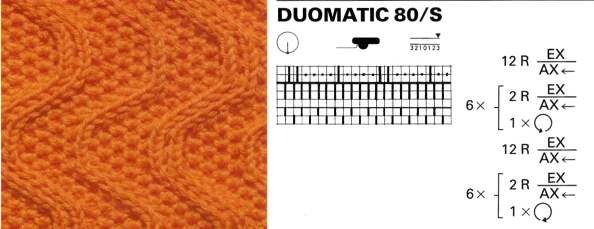
Though tech 264 states it may not be combined with a stitch pattern, I programmed built-in # 1002 X 6 in height, back bed set to slip (BX<–) every 2 rows. Racking occurs every 4. The full repeat is 48 rows. Back bed pushers should be in work so they stay inside the edge from knit stitches on the front bed. This was a quick test. The knit side is unremarkable. The mess on the left edge on the upper right of the top photo is because I began with 2 needles in work on the back bed like in the illustration above. As I racked counterclockwise, the stitches on them kept pulling away from the side edge (back bed, left). The technique continues to give racking prompts as written by the factory, none would exist for the rows with no racking in the pattern
 Back to acrylic yarn, light color for more visibility, creative yarn snag on the left midway, full swing movement is shown, each is 48 rows in height. As always, it helps to check whether the stitches are obliging by staying on the needle bed. The top half of the swatch is pictured.
Back to acrylic yarn, light color for more visibility, creative yarn snag on the left midway, full swing movement is shown, each is 48 rows in height. As always, it helps to check whether the stitches are obliging by staying on the needle bed. The top half of the swatch is pictured.
 In turn, I programmed # 1000 X 6 in height, but the pusher selection was all up for one row, one down. I left it alone, and lastly, worked with pusher selection on the back bed, BX <–. Patterning advances a fixed repeat every row or every other, determined by original hand-selected up for selection and down above rail for out of selection. The front lock is left on N (disregard front for setting it to LX). There is a world of other possibilities, while the console racking sequences can be used from built-in techniques.
In turn, I programmed # 1000 X 6 in height, but the pusher selection was all up for one row, one down. I left it alone, and lastly, worked with pusher selection on the back bed, BX <–. Patterning advances a fixed repeat every row or every other, determined by original hand-selected up for selection and down above rail for out of selection. The front lock is left on N (disregard front for setting it to LX). There is a world of other possibilities, while the console racking sequences can be used from built-in techniques.  Any ribber needle selection on Brother other than with the use of lili buttons would have to be done manually.
Any ribber needle selection on Brother other than with the use of lili buttons would have to be done manually.
The range of fabrics with programming additional patterns in tuck, slip, or combinations thereof, along with needles in and out of work on either or both beds, increases the possibilities for fabrics with texture and dimension exponentially.



 the numbering system reflects every other row worked alternating sides of the work
the numbering system reflects every other row worked alternating sides of the work 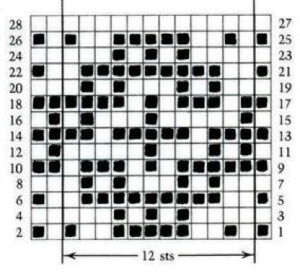 it is shown here with a superimposed table grid with its cells outlined in a thick border and positioned in front of a scaled screen grab of the original motif (arrange/ aspect ratio turned off)
it is shown here with a superimposed table grid with its cells outlined in a thick border and positioned in front of a scaled screen grab of the original motif (arrange/ aspect ratio turned off)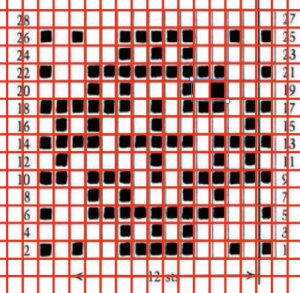
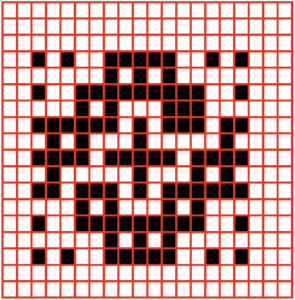 the cell borders can be edited as wished. Here borders were removed by selecting none, then, in turn, the outer border was highlighted in an easy to identify a thicker red line
the cell borders can be edited as wished. Here borders were removed by selecting none, then, in turn, the outer border was highlighted in an easy to identify a thicker red line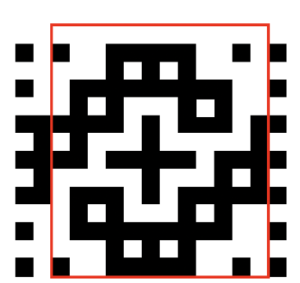

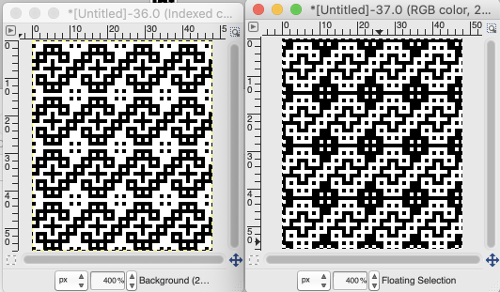
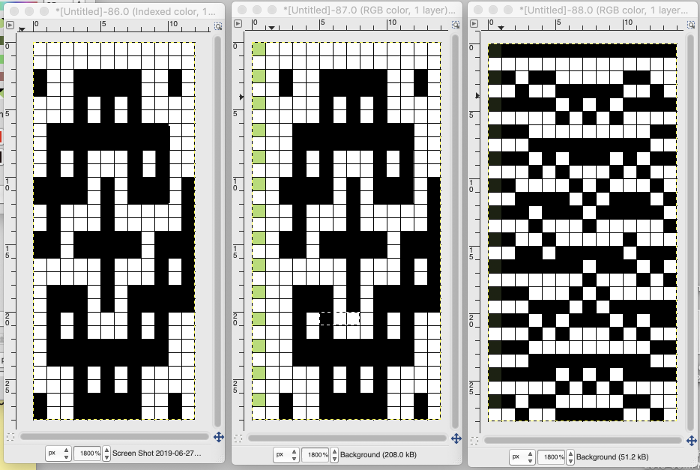 the last image needs to be once again converted to BW mode. The 2 extra rows of pixels on left are cropped off, the image is scaled to twice as long for use with the color changer, and the original 12X14 repeat is now 12X56
the last image needs to be once again converted to BW mode. The 2 extra rows of pixels on left are cropped off, the image is scaled to twice as long for use with the color changer, and the original 12X14 repeat is now 12X56 the actual BMP
the actual BMP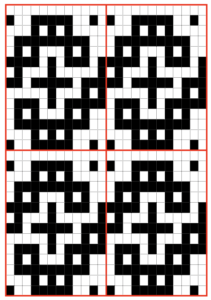
 a “pretend” longer repeat
a “pretend” longer repeat

 is compared here with the earlier
is compared here with the earlier 
 Back to the drawing board: row height is as in the original repeat
Back to the drawing board: row height is as in the original repeat  being extra careful, not necessary, the process can be inverted once more to check the repeat color separation
being extra careful, not necessary, the process can be inverted once more to check the repeat color separation 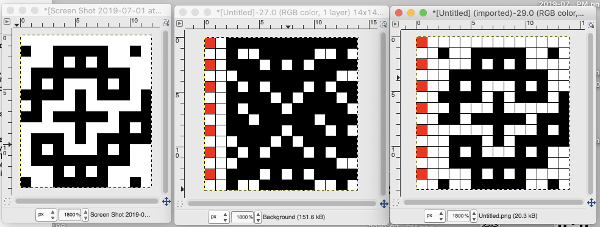
 the corresponding proof of concept swatch, with shorter floats than when the DBJ separation is used single bed
the corresponding proof of concept swatch, with shorter floats than when the DBJ separation is used single bed 
 the repeat of the design separation on the right is intended for use in electronics with color reverse and double length
the repeat of the design separation on the right is intended for use in electronics with color reverse and double length
 for knitting purposes
for knitting purposes 
 The repeat (8X16) is then doubled in length for knitting after that single all-white row was edited out (middle images). The repeat is now 8 rows wide by 32 rows in height
The repeat (8X16) is then doubled in length for knitting after that single all-white row was edited out (middle images). The repeat is now 8 rows wide by 32 rows in height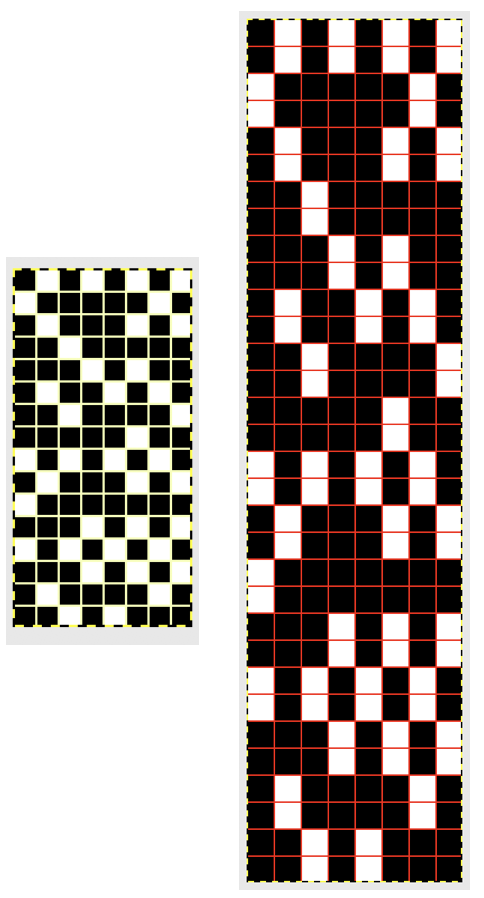 One of the yarns is chenille, the other a wool. The chenille is slightly thicker and fuzzy, so some of the yellow rows are almost hidden but the pattern is definitely there. Here the design is knit using both slip (bottom) and tuck (top) settings. Again, there is a noticeable difference in width produced by each stitch type.
One of the yarns is chenille, the other a wool. The chenille is slightly thicker and fuzzy, so some of the yellow rows are almost hidden but the pattern is definitely there. Here the design is knit using both slip (bottom) and tuck (top) settings. Again, there is a noticeable difference in width produced by each stitch type.  Observations: make certain that after the image is isolated in Numbers cell size is converted to square/ equal measurements in width and height before importing and scaling its screen grab in GIMP if not already so. It will likely load in RGB mode, convert to Indexed before scaling. Added colored squares are only possible if you return to RGB mode. After rows with colored squares are cut, return the image to indexed before saving as BMP for knitting. If any pairs of rows do not have 2 consecutive rows of cells in either color check your pattern. In DBJ the final repeat should be 4 times in numbers of rows in height to the original one, and thus divisible by four. The separation first doubles height for each row for 2 colors. Then height is doubled once more to allow for color changes every 2 rows. In Mosaics and Mazes, the color reversal happens on every other row in the original design. When that is completed, the height will be doubled for actual knitting to allow for color changes every 2 rows, with the final row count double that of the original motif. Rules for tuck knitting apply here as in any other technique. If white squares in the final chart have black ones on either side of them, the appearance is that tuck would be possible. Examining needle preselection is an easy way to assess that possibility.
Observations: make certain that after the image is isolated in Numbers cell size is converted to square/ equal measurements in width and height before importing and scaling its screen grab in GIMP if not already so. It will likely load in RGB mode, convert to Indexed before scaling. Added colored squares are only possible if you return to RGB mode. After rows with colored squares are cut, return the image to indexed before saving as BMP for knitting. If any pairs of rows do not have 2 consecutive rows of cells in either color check your pattern. In DBJ the final repeat should be 4 times in numbers of rows in height to the original one, and thus divisible by four. The separation first doubles height for each row for 2 colors. Then height is doubled once more to allow for color changes every 2 rows. In Mosaics and Mazes, the color reversal happens on every other row in the original design. When that is completed, the height will be doubled for actual knitting to allow for color changes every 2 rows, with the final row count double that of the original motif. Rules for tuck knitting apply here as in any other technique. If white squares in the final chart have black ones on either side of them, the appearance is that tuck would be possible. Examining needle preselection is an easy way to assess that possibility.
 The fabric had an interesting twist and roll if tugged in opposite diagonal directions when first off the machine.
The fabric had an interesting twist and roll if tugged in opposite diagonal directions when first off the machine.  This is the working repeat, suitable for a punchcard machine. On the far left it is shown for use with electronics and color reverse, with the green grid highlighting black squares indicating holes that would need to be punched in a card, and lastly, as a tiled repeat looking for any errors in repeat sequences.
This is the working repeat, suitable for a punchcard machine. On the far left it is shown for use with electronics and color reverse, with the green grid highlighting black squares indicating holes that would need to be punched in a card, and lastly, as a tiled repeat looking for any errors in repeat sequences. 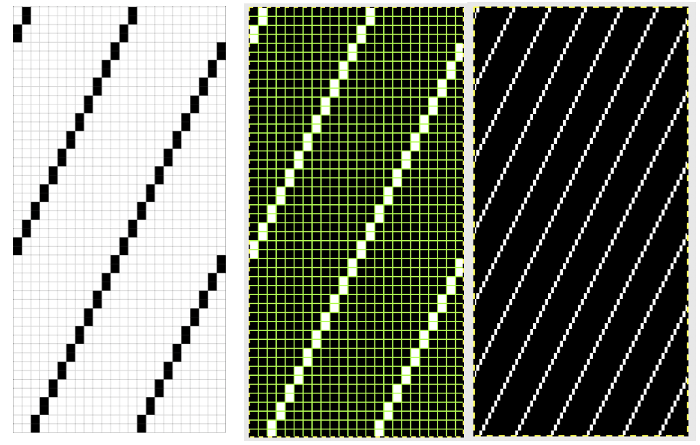

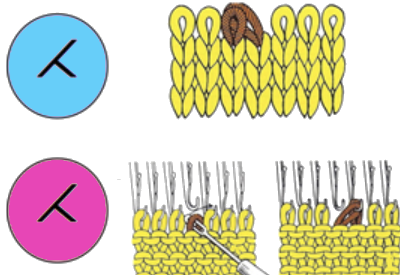
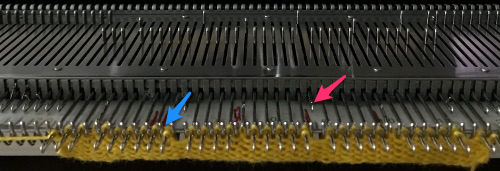
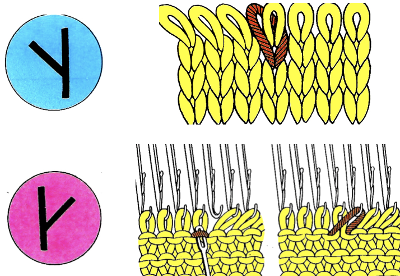 This shows my swatch in progress. ? indicates operator error, in evidence if needle count on each side of the future tuck stitch or ladder space is checked
This shows my swatch in progress. ? indicates operator error, in evidence if needle count on each side of the future tuck stitch or ladder space is checked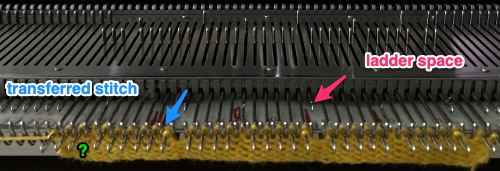 picking up loops from the row below to keep ladder width constant
picking up loops from the row below to keep ladder width constant 
 Check that stitches have knit off properly
Check that stitches have knit off properly  Needles with transfers or moved stitches may be brought out to hold position (E in Brother machines) for easier knitting. If this is done, be sure not to disturb needle selection or lack of it in location for next pair of tucked rows.
Needles with transfers or moved stitches may be brought out to hold position (E in Brother machines) for easier knitting. If this is done, be sure not to disturb needle selection or lack of it in location for next pair of tucked rows.

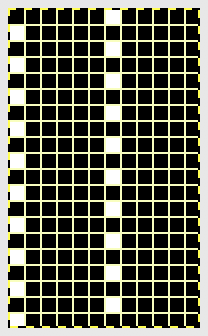
 Setting up a working repeat with blue representing tuck, purple slip (or vice versa). The distance between the vertical column, in this case, is fixed and seven stitches in width for a center folding repeat width of 16, color reverse is required
Setting up a working repeat with blue representing tuck, purple slip (or vice versa). The distance between the vertical column, in this case, is fixed and seven stitches in width for a center folding repeat width of 16, color reverse is required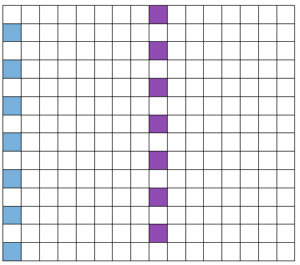
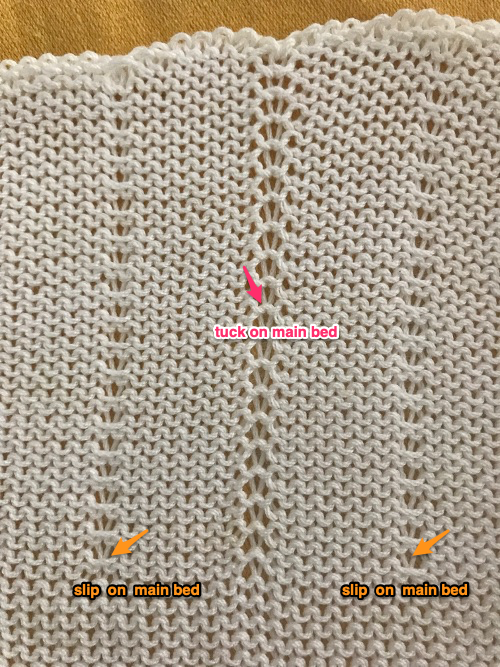
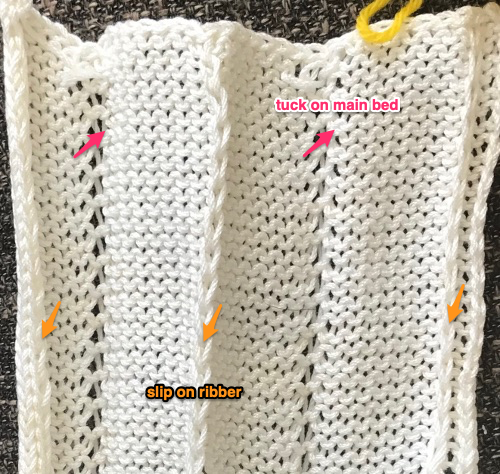

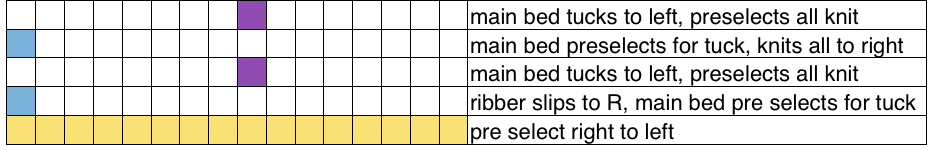
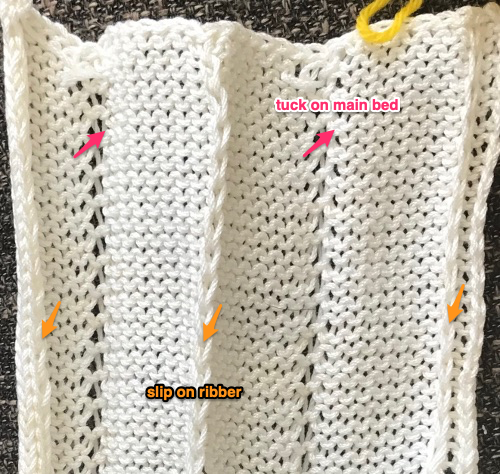
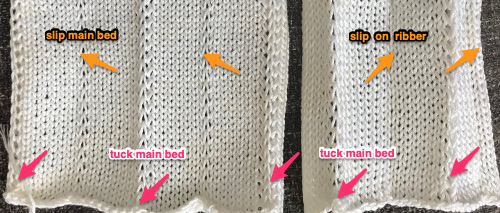
 Set up the cast-on as preferred. I used plain knitting, weighted it, and began my pattern work from the right-hand side of the machine. COL my preselection row was made from right to left. White squares in the chart with black ground and green grid become non selected needles on the main bed. Transfer nonselected stitches down to the ribber. Set the ribber to slip to the right, those stitches just transferred will slip moving to the right, knit on the return pass to the left. The knit carriage is set to knit until that first row is completed
Set up the cast-on as preferred. I used plain knitting, weighted it, and began my pattern work from the right-hand side of the machine. COL my preselection row was made from right to left. White squares in the chart with black ground and green grid become non selected needles on the main bed. Transfer nonselected stitches down to the ribber. Set the ribber to slip to the right, those stitches just transferred will slip moving to the right, knit on the return pass to the left. The knit carriage is set to knit until that first row is completed COR the ribber will knit on the next pass to the left. Set the knit carriage to tuck while the ribber is knitting
COR the ribber will knit on the next pass to the left. Set the knit carriage to tuck while the ribber is knitting Continue in pattern to the desired length. Fabric narrows considerably, so several panels may be required for items ie. skirts. The repeat on the knitting bed should also be adjusted to allow for as close to invisible seaming as possible. The stitches on either side of the single needle in work on the ribber may be inclined to drop off. I was unable to use tuck on those same needles for any significant length for that reason. It pays to visually check for stitches knitting off properly to avoid this
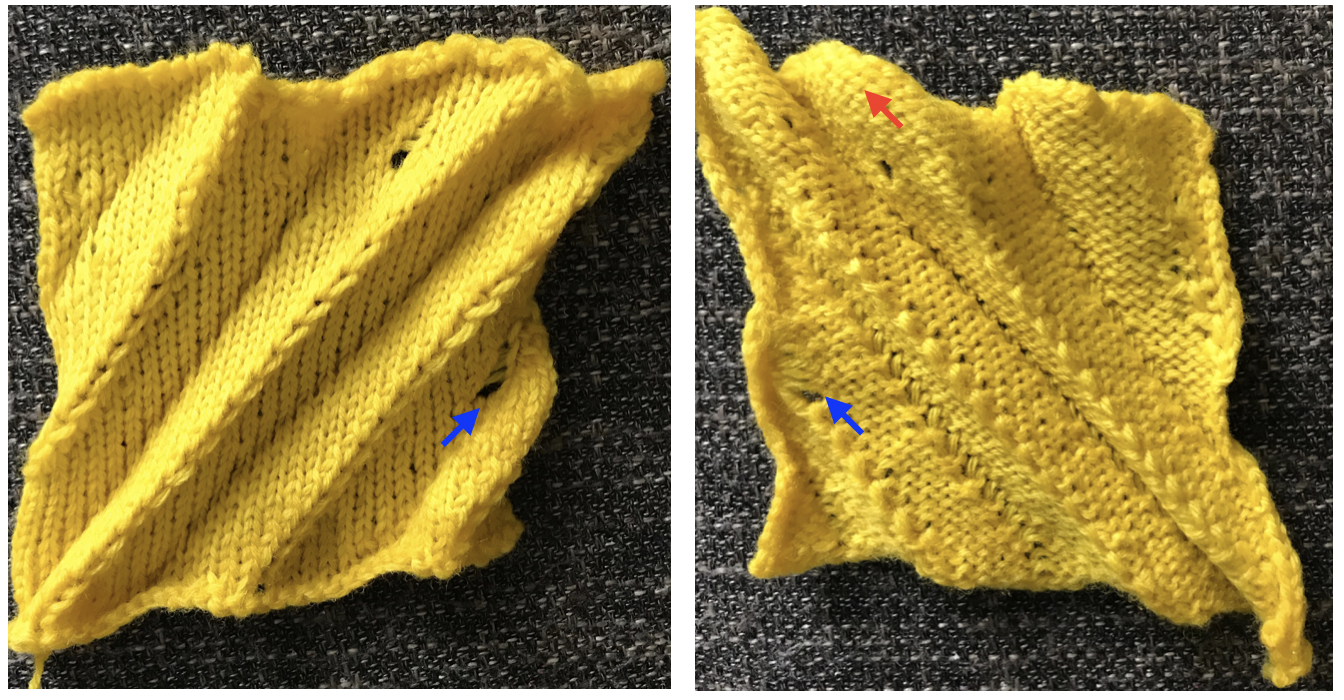
Continue in pattern to the desired length. Fabric narrows considerably, so several panels may be required for items ie. skirts. The repeat on the knitting bed should also be adjusted to allow for as close to invisible seaming as possible. The stitches on either side of the single needle in work on the ribber may be inclined to drop off. I was unable to use tuck on those same needles for any significant length for that reason. It pays to visually check for stitches knitting off properly to avoid this  The start of vertical pleats, with the slip stitches folding to the purl side, the tucked stitches folding to the knit side on the machine, just after binding off.
The start of vertical pleats, with the slip stitches folding to the purl side, the tucked stitches folding to the knit side on the machine, just after binding off. 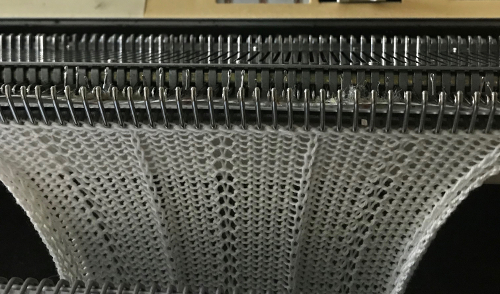

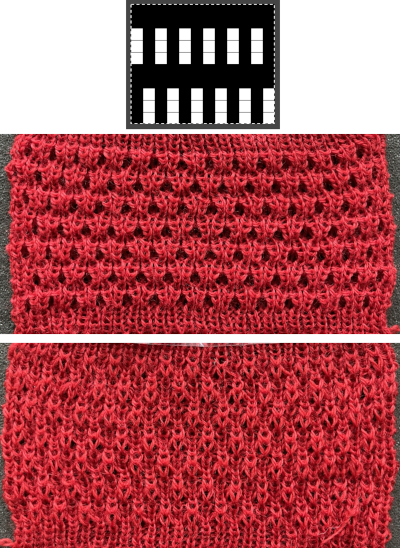
 Different fibers can produce varying results in fold and drape. Setting either bed function for the wrong direction will produce an all-knit fabric (top of the red swatch).
Different fibers can produce varying results in fold and drape. Setting either bed function for the wrong direction will produce an all-knit fabric (top of the red swatch). 
 This starts to address incorporating hand techniques and manual ones from the diagonal swatch and the one with vertical folds while also developing a design repeat to aid with planning or actions to be taken. It will be altered in future experiments
This starts to address incorporating hand techniques and manual ones from the diagonal swatch and the one with vertical folds while also developing a design repeat to aid with planning or actions to be taken. It will be altered in future experiments 
 This swatch is knit in wool, trying to sort out what does what and by how much. I am starting to get a bubble, but not a dramatic folding effect. The bottom folds more than the top. The filled eyelet technique has a hand-tooled tuck column on the reverse side. The top is automated using tuck stitch.
This swatch is knit in wool, trying to sort out what does what and by how much. I am starting to get a bubble, but not a dramatic folding effect. The bottom folds more than the top. The filled eyelet technique has a hand-tooled tuck column on the reverse side. The top is automated using tuck stitch.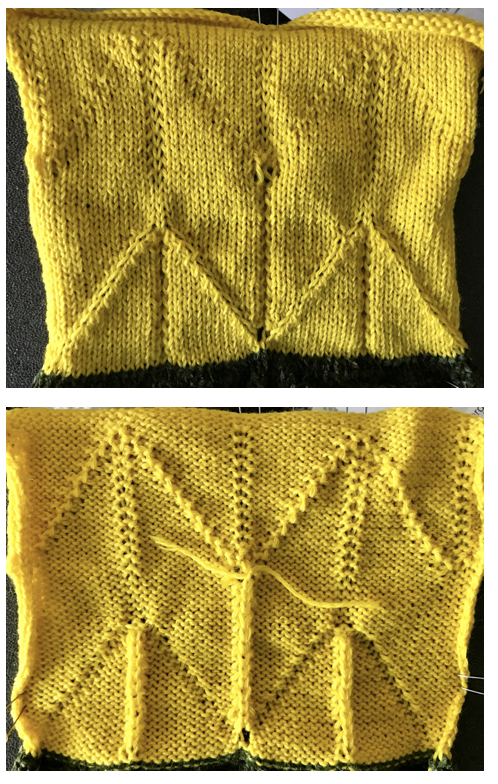  A different repeat: the bottom with carriage set to knit with needle selection as a cue to hand transfers, the top set to tuck automatically. Transition rows need to be considered further and altered where the twain meet.
A different repeat: the bottom with carriage set to knit with needle selection as a cue to hand transfers, the top set to tuck automatically. Transition rows need to be considered further and altered where the twain meet. 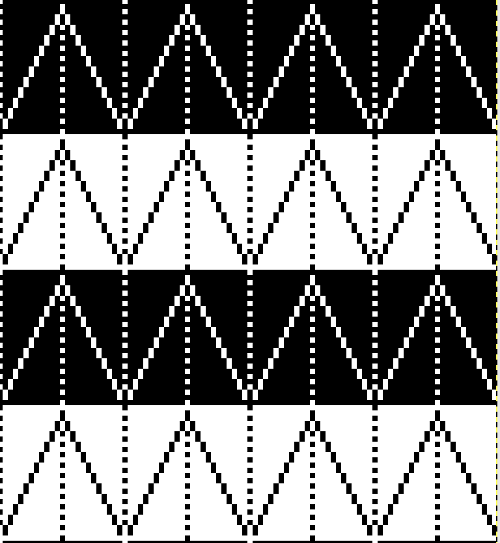 Returning to simpler creases and folds: a first experiment in racking double bed with NOOW. The setup and racking positions were not pre-planned. I knit 4 rows without racking at unplanned intervals as well; they produce a noticeable change in texture. The fabric is reversible, I actually rephotographed it adding a marker to make certain I had not shot the same side twice. The needle set up:
Returning to simpler creases and folds: a first experiment in racking double bed with NOOW. The setup and racking positions were not pre-planned. I knit 4 rows without racking at unplanned intervals as well; they produce a noticeable change in texture. The fabric is reversible, I actually rephotographed it adding a marker to make certain I had not shot the same side twice. The needle set up:  the resulting swatch presented sideways for the sake of space:
the resulting swatch presented sideways for the sake of space: 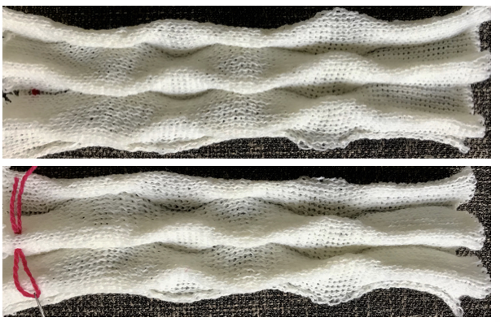 working with single needles out of work rather than two, with even spacing between them on each bed
working with single needles out of work rather than two, with even spacing between them on each bed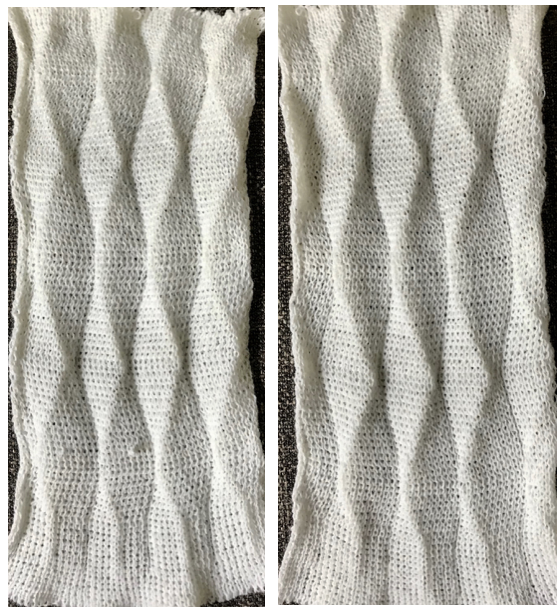 both swatches flattened to note differences between needle arrangement folds
both swatches flattened to note differences between needle arrangement folds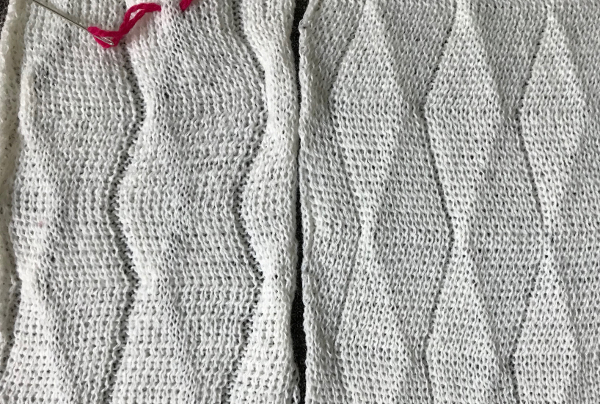  getting more organized, with a planned repeat: the needle set up
getting more organized, with a planned repeat: the needle set up Here the arrangement here is with 2 needles out of work, racking every 2 rows in the same sequence. The resulting fabric has clear “spring” and foldsRR
Here the arrangement here is with 2 needles out of work, racking every 2 rows in the same sequence. The resulting fabric has clear “spring” and foldsRR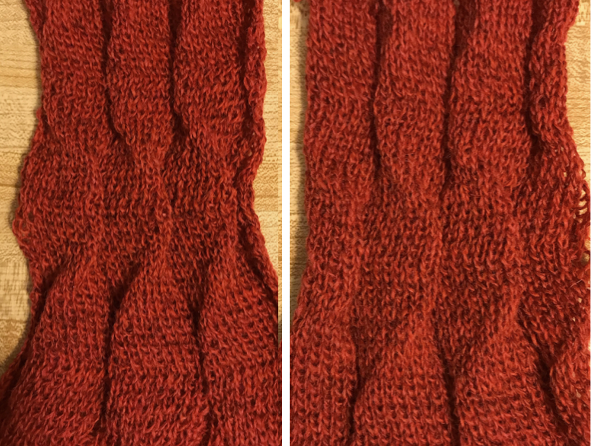 Returning to the previous needle set up, now racking every row from position 5 to 0, knit 1 more row with no racking; rack to position 10, knit one more row with no racking, reverse direction, end knitting on position # 5
Returning to the previous needle set up, now racking every row from position 5 to 0, knit 1 more row with no racking; rack to position 10, knit one more row with no racking, reverse direction, end knitting on position # 5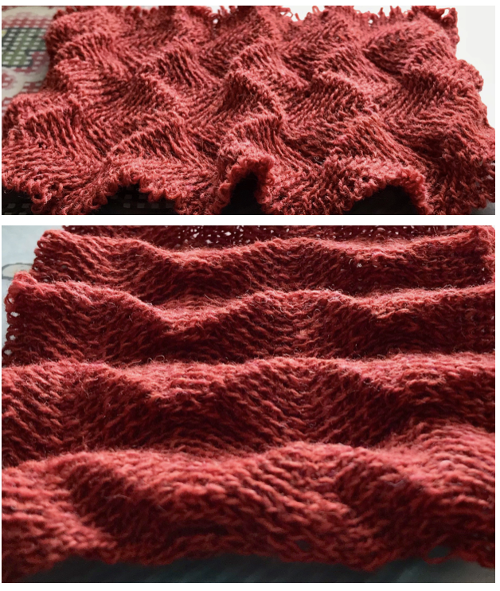 This last in the series is a personal favorite. I found racking from the center to 10, to 0, and back easy to track. One moves in the opposite direction when not allowed to go any further in the continuing direction by the machine. Single needles out of work appear to be enough to create the folds.
This last in the series is a personal favorite. I found racking from the center to 10, to 0, and back easy to track. One moves in the opposite direction when not allowed to go any further in the continuing direction by the machine. Single needles out of work appear to be enough to create the folds.
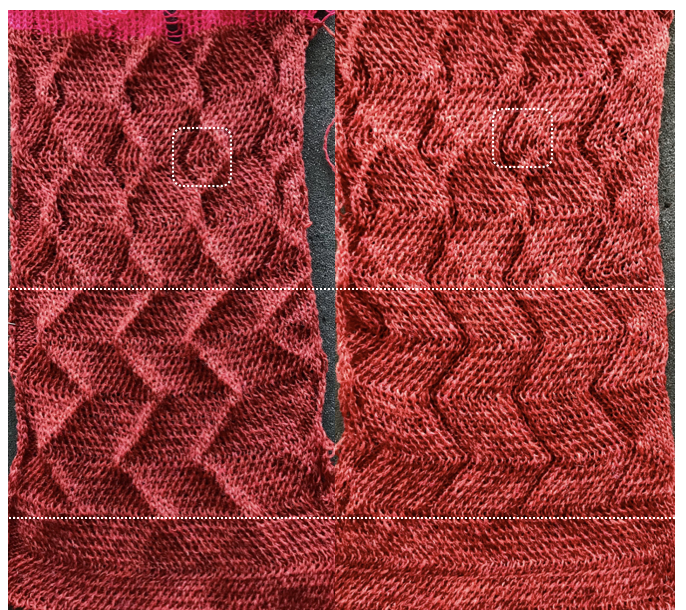 Racking starting position on 7:
Racking starting position on 7: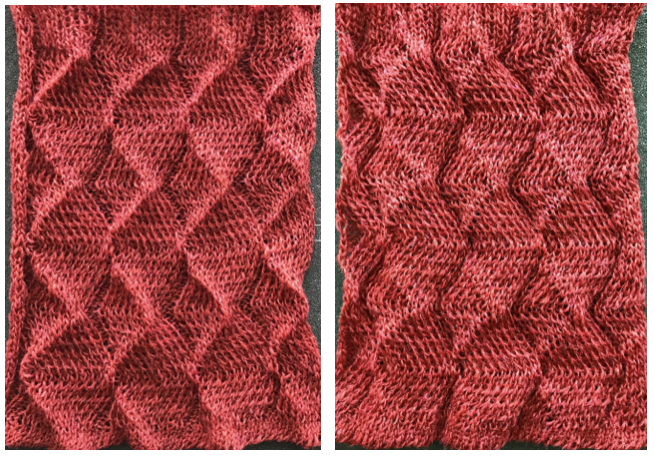 Consider playing with racking positions within the total number of needles in work on the main bed. For other possible needle arrangements and more on pleats created with needles in/out of work on both beds please see
Consider playing with racking positions within the total number of needles in work on the main bed. For other possible needle arrangements and more on pleats created with needles in/out of work on both beds please see  I like to chart out my repeats and plans for executing fabrics, along with ideas for possibly varying them in ways other than suggested, this was my beginning
I like to chart out my repeats and plans for executing fabrics, along with ideas for possibly varying them in ways other than suggested, this was my beginning 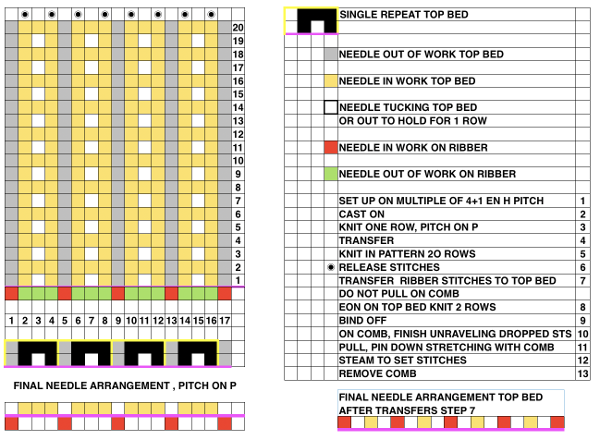

 knit one more row to return to the opposite side
knit one more row to return to the opposite side 





 I knit 3 rows rather than 2, to return to right side for bind off
I knit 3 rows rather than 2, to return to right side for bind off  here is the swatch, still on comb for “setting stitches”
here is the swatch, still on comb for “setting stitches”






 when the 20 rows are completed the carriages will once again be on the right, all stitches will have been knit on the previous row
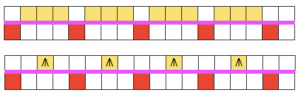
when the 20 rows are completed the carriages will once again be on the right, all stitches will have been knit on the previous row  transfer all ribber stitches to top bed, knit 2 rows, bind off. None of my swatches were blocked other than by some tugging, particularly along the bottom edge. The spacing between stitches is narrower because ladders created by single needles left out of work are formed by yarn lengths that are shorter than those that happen when stitches are knit and then in turn dropped. The height of the swatch is also affected, and the half fisherman texture in the wool swatch, in particular, is more evident.
transfer all ribber stitches to top bed, knit 2 rows, bind off. None of my swatches were blocked other than by some tugging, particularly along the bottom edge. The spacing between stitches is narrower because ladders created by single needles left out of work are formed by yarn lengths that are shorter than those that happen when stitches are knit and then in turn dropped. The height of the swatch is also affected, and the half fisherman texture in the wool swatch, in particular, is more evident.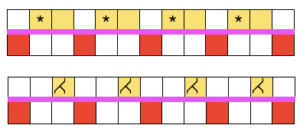 When the work is removed from the machine, stretch cast on outwards, then give each “scallop” a really good pull downwards. Steam lightly over the scallops to set them. Variations of the double bed trims may be worked on the single bed as well.
When the work is removed from the machine, stretch cast on outwards, then give each “scallop” a really good pull downwards. Steam lightly over the scallops to set them. Variations of the double bed trims may be worked on the single bed as well. 2. knit second zigzag row to right
2. knit second zigzag row to right




 In theory, it is possible to knit lace transfers in Brother by dropping the ribber bed enough for the lace carriage to move across the beds while clearing the gate pegs. This remains on my “try someday” list. To my mind, hand transferring remains the best way to deal with lace/ ribber stitches combined.
In theory, it is possible to knit lace transfers in Brother by dropping the ribber bed enough for the lace carriage to move across the beds while clearing the gate pegs. This remains on my “try someday” list. To my mind, hand transferring remains the best way to deal with lace/ ribber stitches combined. For a punchcard machine, the repeat must be a factor of 24 in width ie. 6 or 8, or 12 stitches wide. Electronic knitters can draw a single repeat, either the one on the left also using color reverse or the one on the right. Punchcard knitters need to punch the grey squares on the right across the card and repeat it in height. An extra all-knit row needs to be added at the top of each series of 4 rows tucked for the loops to be knit off automatically by the machine. Step 4 in the techniques book, resetting the main bed to N to knit a row after every 4 rows in a holding pattern is missing in their illustration above.
For a punchcard machine, the repeat must be a factor of 24 in width ie. 6 or 8, or 12 stitches wide. Electronic knitters can draw a single repeat, either the one on the left also using color reverse or the one on the right. Punchcard knitters need to punch the grey squares on the right across the card and repeat it in height. An extra all-knit row needs to be added at the top of each series of 4 rows tucked for the loops to be knit off automatically by the machine. Step 4 in the techniques book, resetting the main bed to N to knit a row after every 4 rows in a holding pattern is missing in their illustration above.  The punchcard repeat: punch each grey square to match the illustration
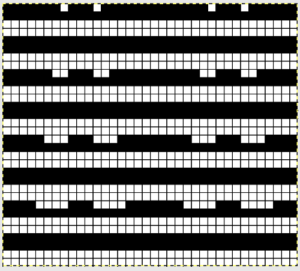
The punchcard repeat: punch each grey square to match the illustration  A few to try, shown in repeat X2, as BW gridded .bmps, and with the color reversed for knitting. All but one are 12 stitches in width, suitable for punchcard machines as well
A few to try, shown in repeat X2, as BW gridded .bmps, and with the color reversed for knitting. All but one are 12 stitches in width, suitable for punchcard machines as well 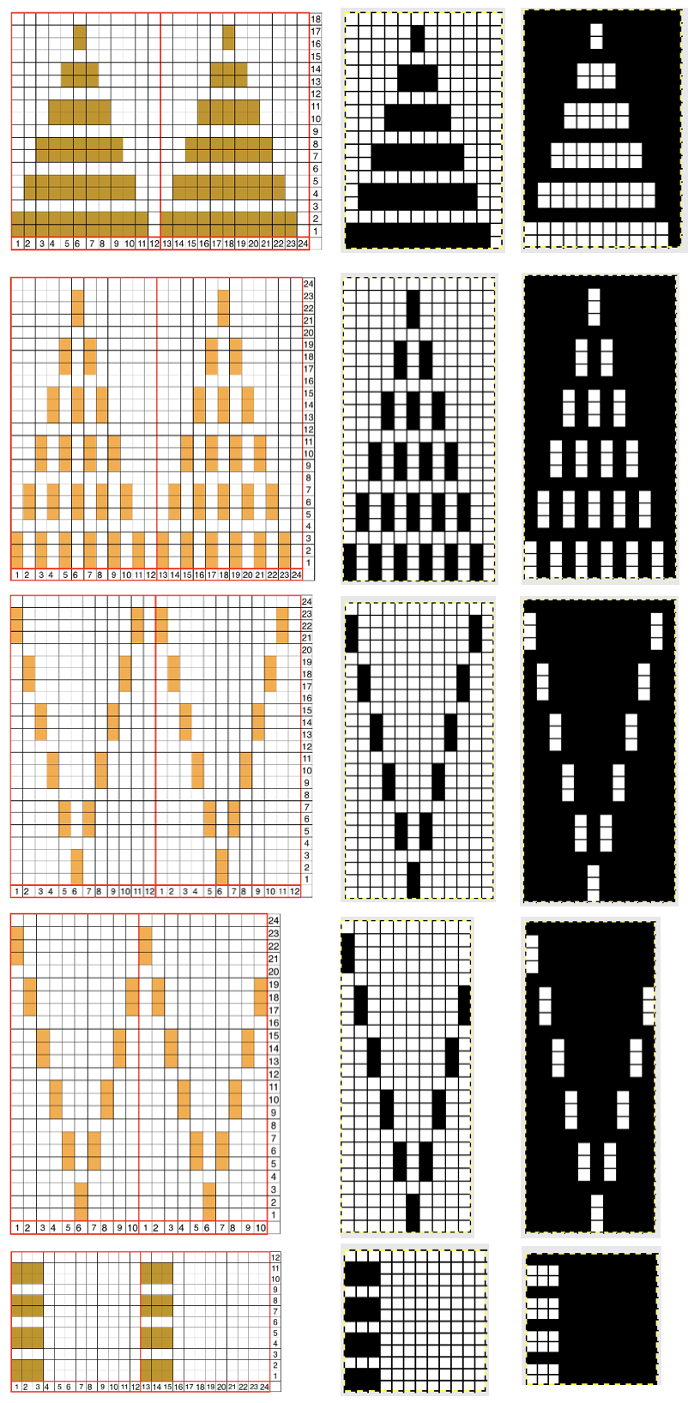 Too much black? want to count those black squares more easily? pick your preferred grid color, it will disappear when the image is saved
Too much black? want to count those black squares more easily? pick your preferred grid color, it will disappear when the image is saved 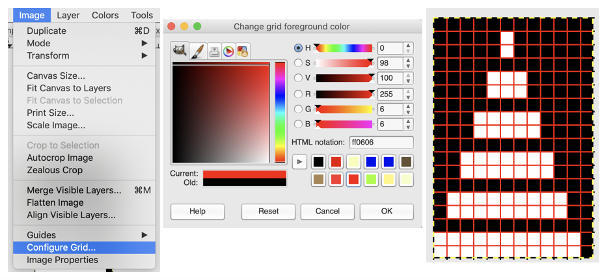 A screen grab from my iMac shows the original charts and the resulting single repeat .bmps after working in GIMP, ready for download with color reverse option and use on the electronic machines. Ayab knitters, in addition, would need to program the repeat in width to match the number of needles planned for use in the piece
A screen grab from my iMac shows the original charts and the resulting single repeat .bmps after working in GIMP, ready for download with color reverse option and use on the electronic machines. Ayab knitters, in addition, would need to program the repeat in width to match the number of needles planned for use in the piece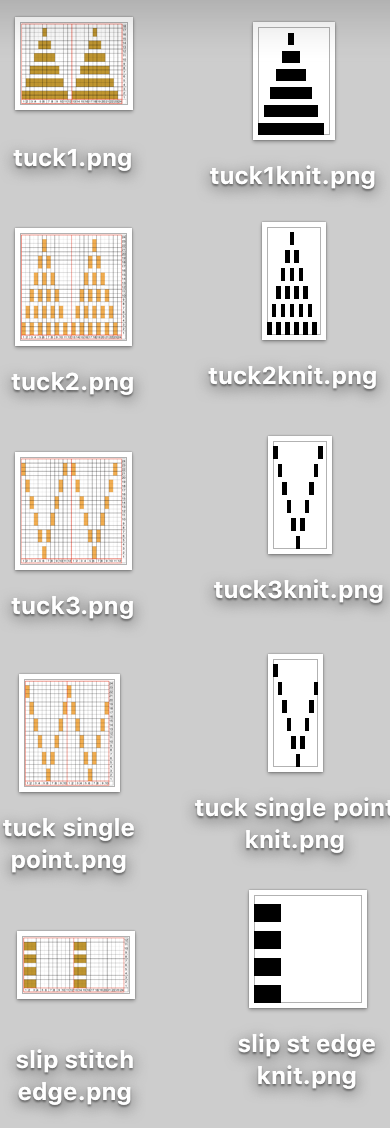


 Working it on Brother becomes a bit fiddly. Whether working on a punchcard or electronic KM, it is possible to introduce patterning on either or both beds as seen below. I preferred the look obtained with the racked cast on at the start. Setting up the Brother machine: program the repeat, half pitch for every needle rib, air knit to place the pattern on the bed so that the first needle on the left (or right if you prefer) is preselected forward and will produce a knit stitch on the first row knit. The yarn used is a 2/24 acrylic
Working it on Brother becomes a bit fiddly. Whether working on a punchcard or electronic KM, it is possible to introduce patterning on either or both beds as seen below. I preferred the look obtained with the racked cast on at the start. Setting up the Brother machine: program the repeat, half pitch for every needle rib, air knit to place the pattern on the bed so that the first needle on the left (or right if you prefer) is preselected forward and will produce a knit stitch on the first row knit. The yarn used is a 2/24 acrylic 
 now another needle on the ribber is brought in to work on the far left, it will tuck with lili selection when moving from left to right
now another needle on the ribber is brought in to work on the far left, it will tuck with lili selection when moving from left to right  remember the ribber rule with lili buttons: an even number of needles must be in work, this shows the start and end of selection on the ribber on alternate needle tape markings, as required
remember the ribber rule with lili buttons: an even number of needles must be in work, this shows the start and end of selection on the ribber on alternate needle tape markings, as required 



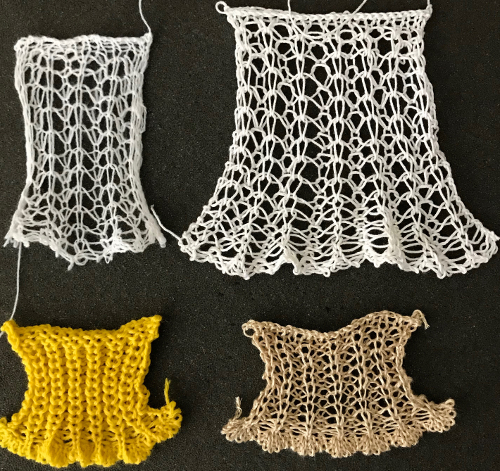
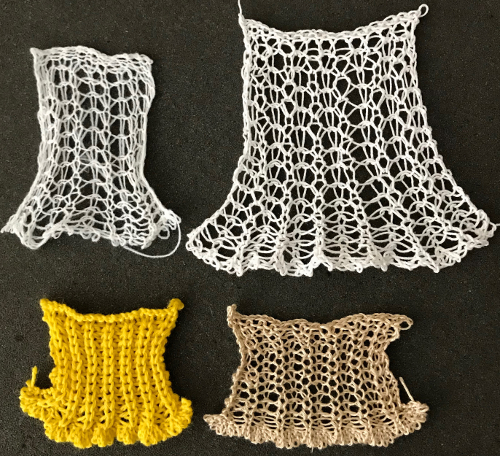
 Both pieces compared for width and rippling
Both pieces compared for width and rippling


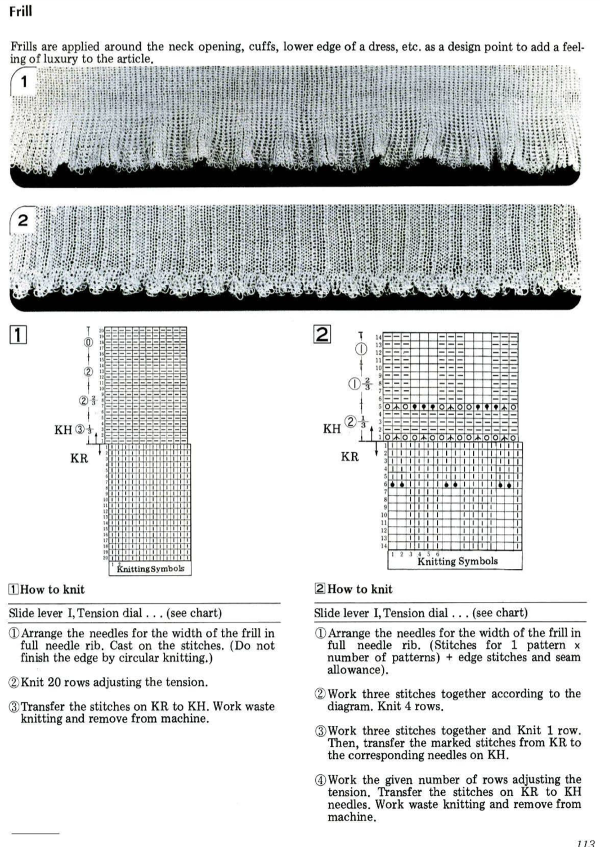
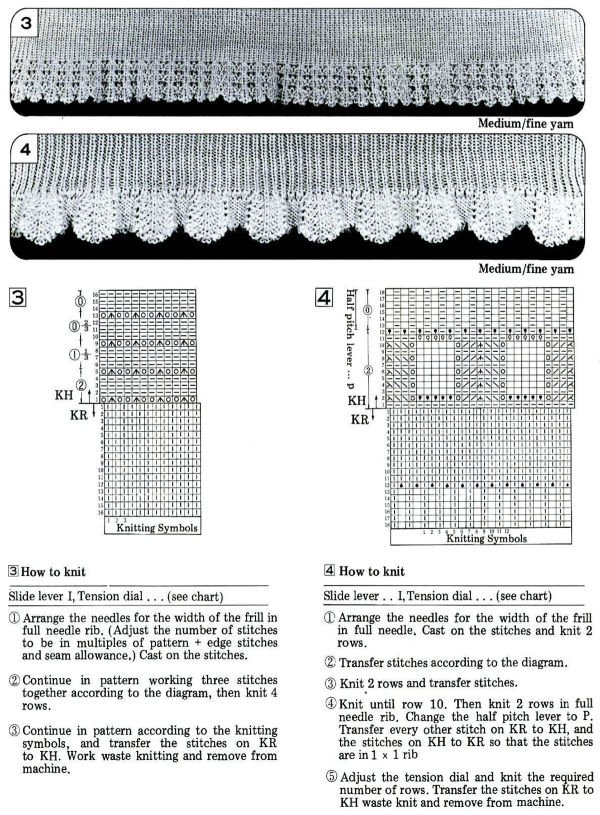
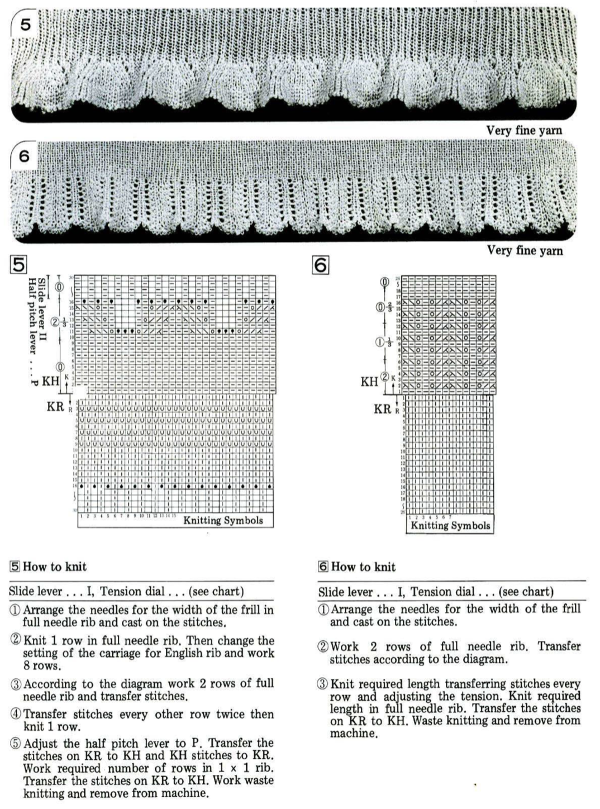 An intro to scallops: p.120
An intro to scallops: p.120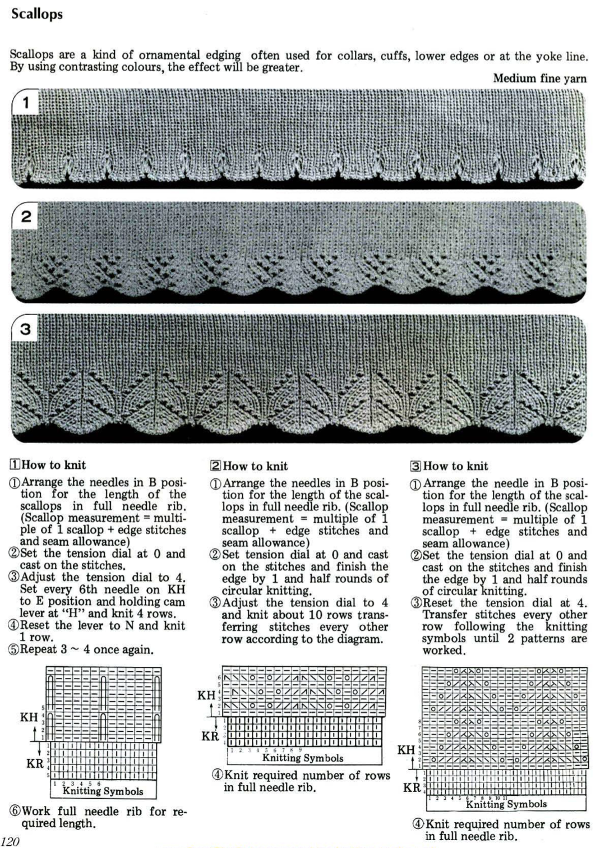



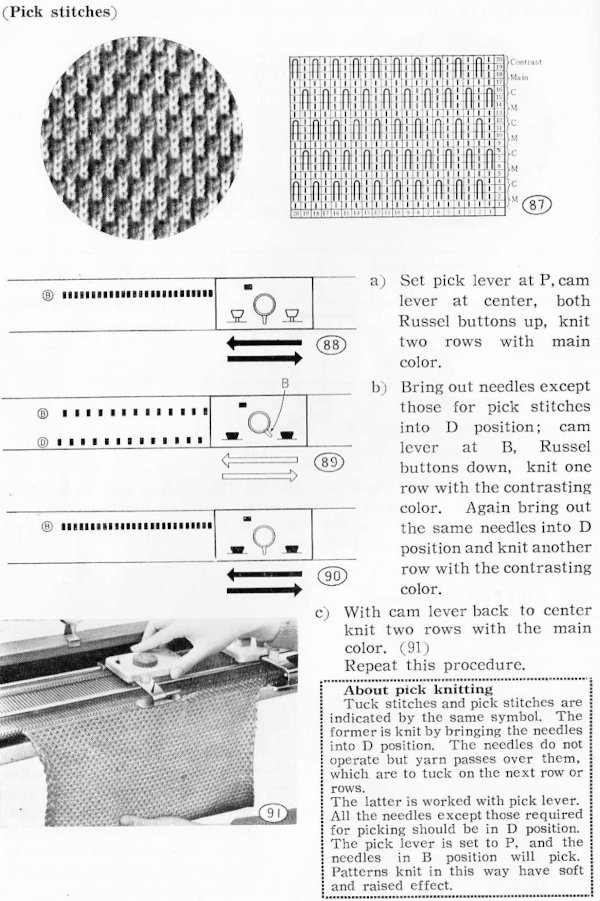 The identical pattern in later model machines may be produced by using the tuck setting. The image below shows the punchcard partial repeat and the isolated electronic repeat for use with the tuck setting.
The identical pattern in later model machines may be produced by using the tuck setting. The image below shows the punchcard partial repeat and the isolated electronic repeat for use with the tuck setting. 

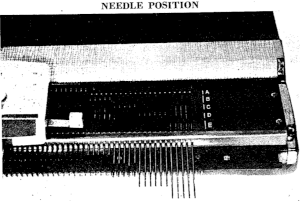
 The knit carriage appears to use “pick” as the name for what is now more commonly knows as the tuck setting.
The knit carriage appears to use “pick” as the name for what is now more commonly knows as the tuck setting.  A downloadable
A downloadable



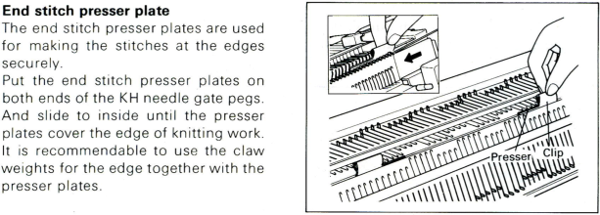
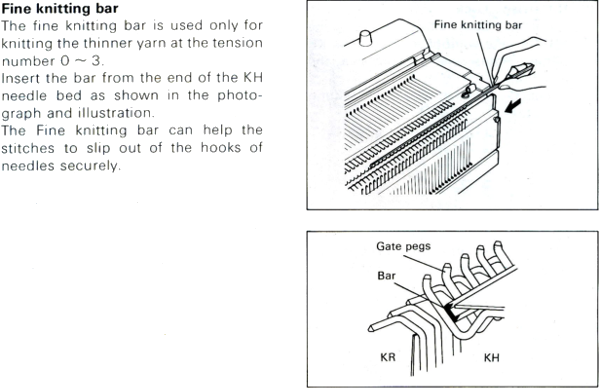


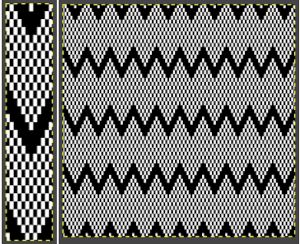
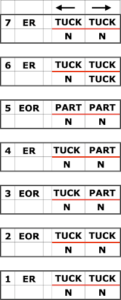


 Because, in most instances, the ribber is set to knit there are stitches on the ribber holding down tuck loops on the main bed, and typical tuck configuration rules may be broken. One such pattern to try: the punchcard repeat and the electronic one are identical
Because, in most instances, the ribber is set to knit there are stitches on the ribber holding down tuck loops on the main bed, and typical tuck configuration rules may be broken. One such pattern to try: the punchcard repeat and the electronic one are identical 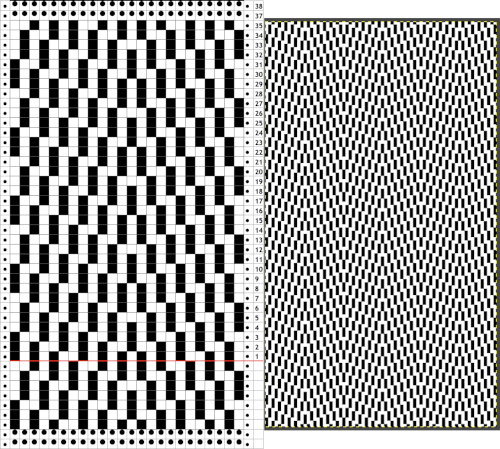
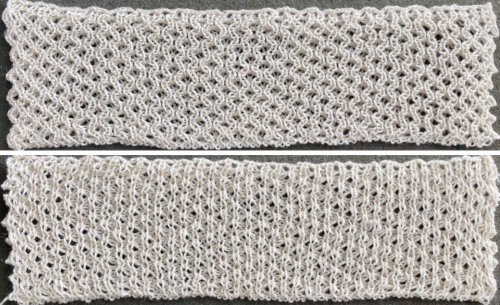 Adding color striping
Adding color striping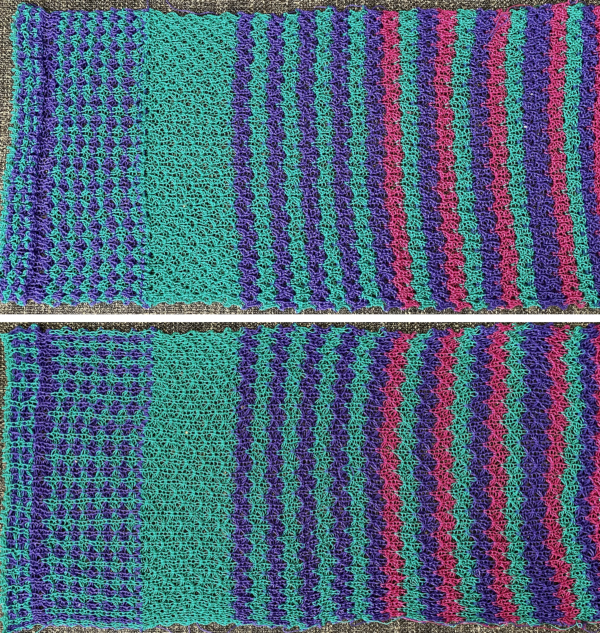 
 Using the stitch type to create edgings or ruffles
Using the stitch type to create edgings or ruffles
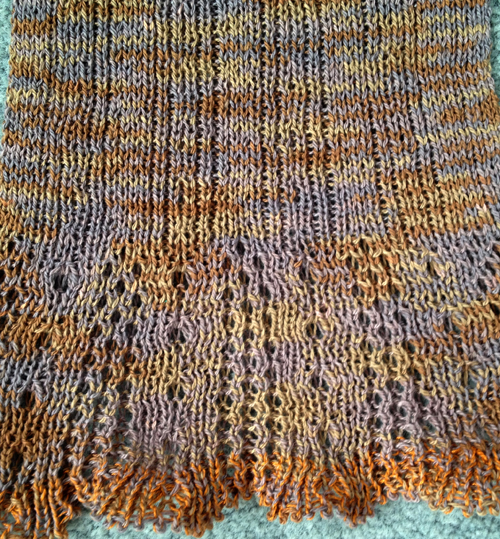
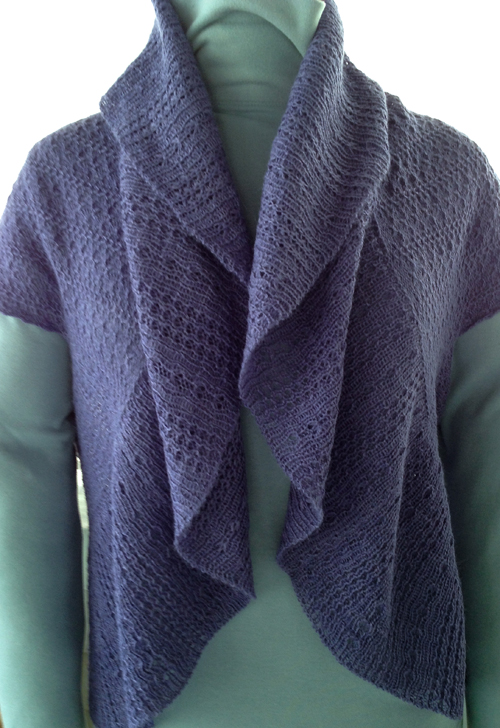


 See “
See “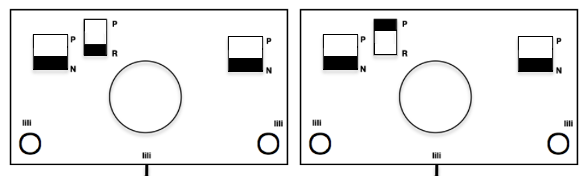
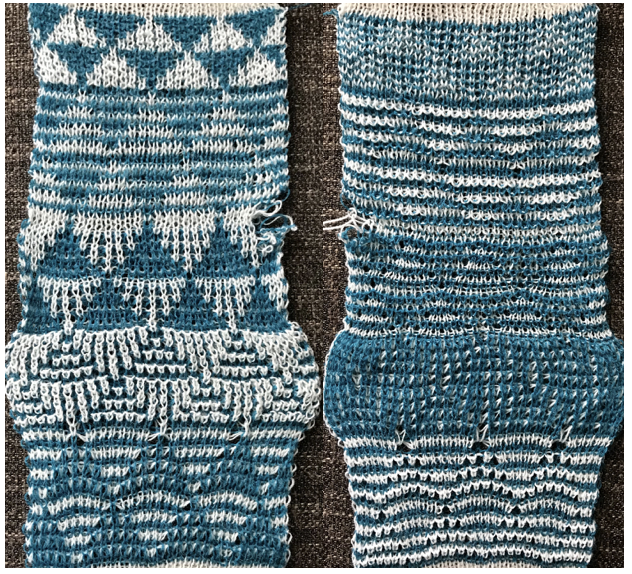








 Susanna classifies the subsequent separations as C1 and C2. Because each color in each row knits twice, there may be an odd number of rows in the initial design repeat.
Susanna classifies the subsequent separations as C1 and C2. Because each color in each row knits twice, there may be an odd number of rows in the initial design repeat. 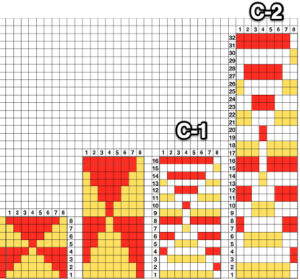
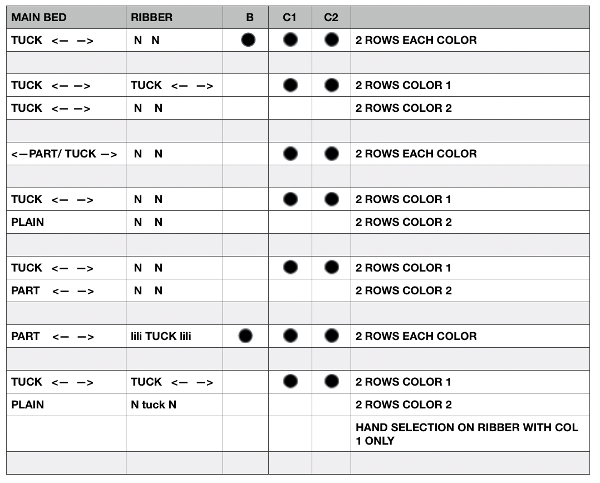
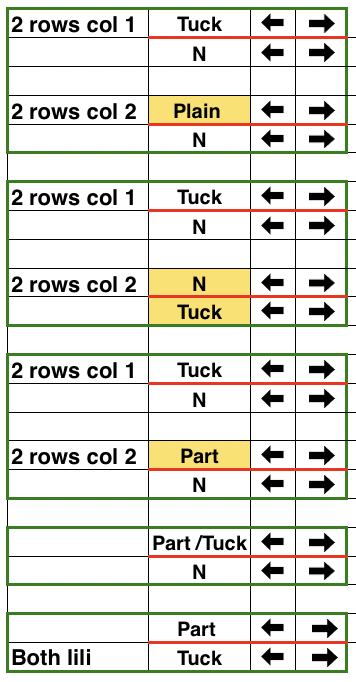
 Fisherman, aka full fisherman rib, is a tubular tuck with each bed tucking in one direction, knitting in the other
Fisherman, aka full fisherman rib, is a tubular tuck with each bed tucking in one direction, knitting in the other


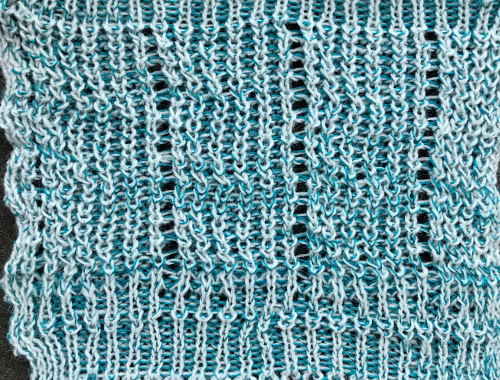
 Can plaiting give me 2 colors the “easy” way?
Can plaiting give me 2 colors the “easy” way?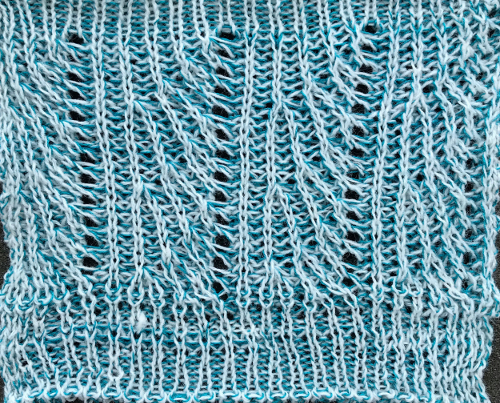 
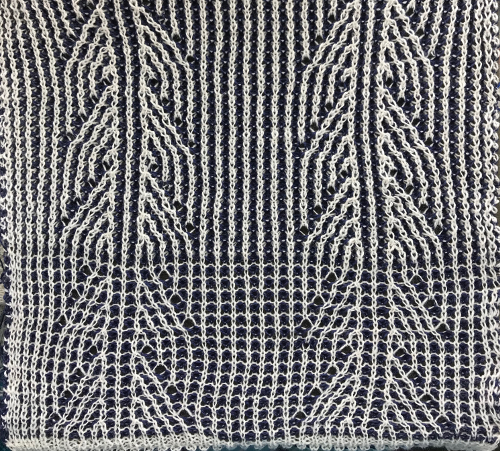
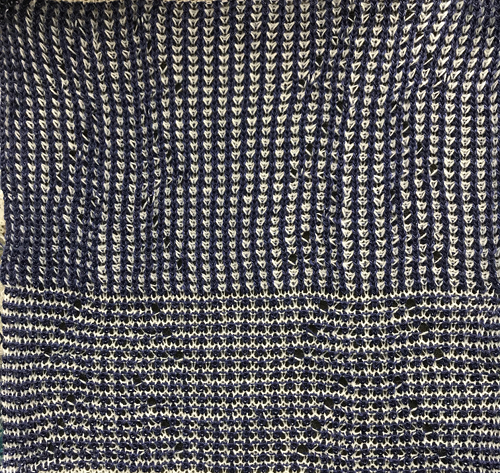
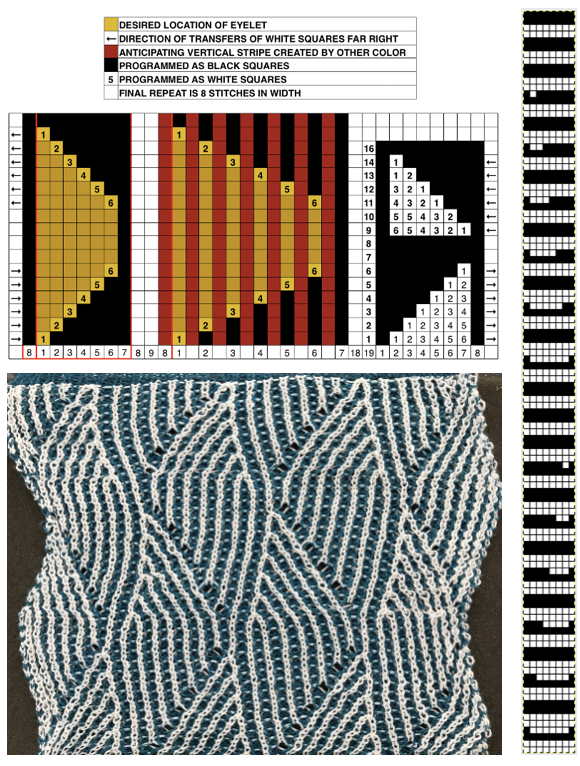
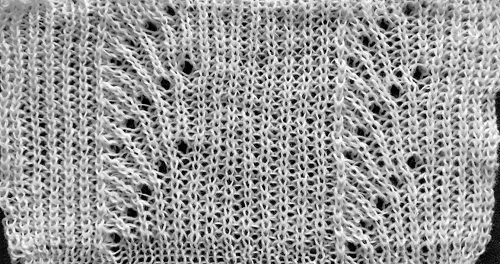














 its reverse side :
its reverse side :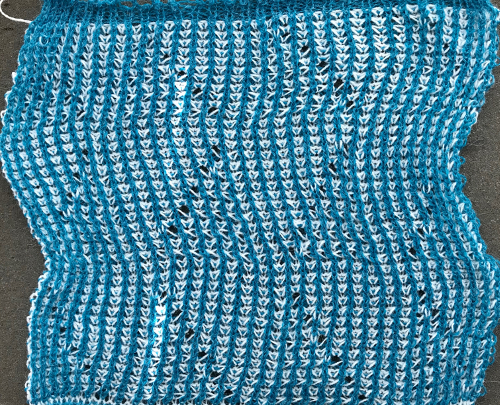



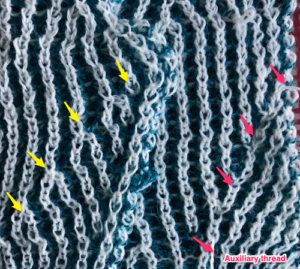 This is what happens when a new design is being tested, and the lili buttons “accidentally” happen to be engaged on the ribber
This is what happens when a new design is being tested, and the lili buttons “accidentally” happen to be engaged on the ribber 