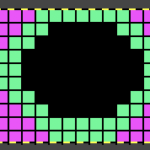
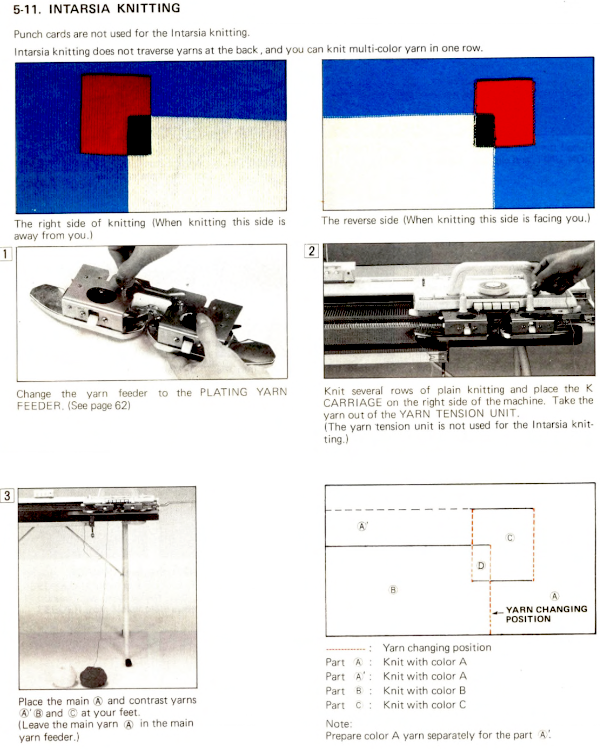
My first attempt to use a 3 color automatic separation was with img2track.
The default selector setting is for a single motif, perhaps on the assumption that the main use would primarily be for large-scale, nonrepetitive images.
In standard dbj the built-in separation, when KRC is activated, the first preselection row is made from left to right, and the first color knits for only one row on moving from the right side to the left, but if 2 colors with the same selection are required at the start, one row of the 2 rows is technically eliminated as a result, resulting in patterning errors.
The first preselection row in these knits is made from right to left, each color in each row will be knit twice.
As soon as a row begins to be knit, the numbers change in the memo window, indicating that the machine is using this pass to select the needles for the next row. As the carriage passes the midpoint of the bed, the row number will begin flashing indicating that this is the row you will be knitting next. The process is repeated as the carriage reverses direction.
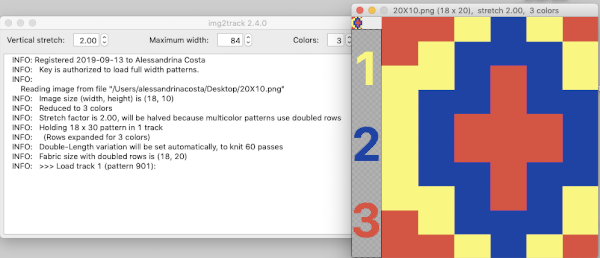
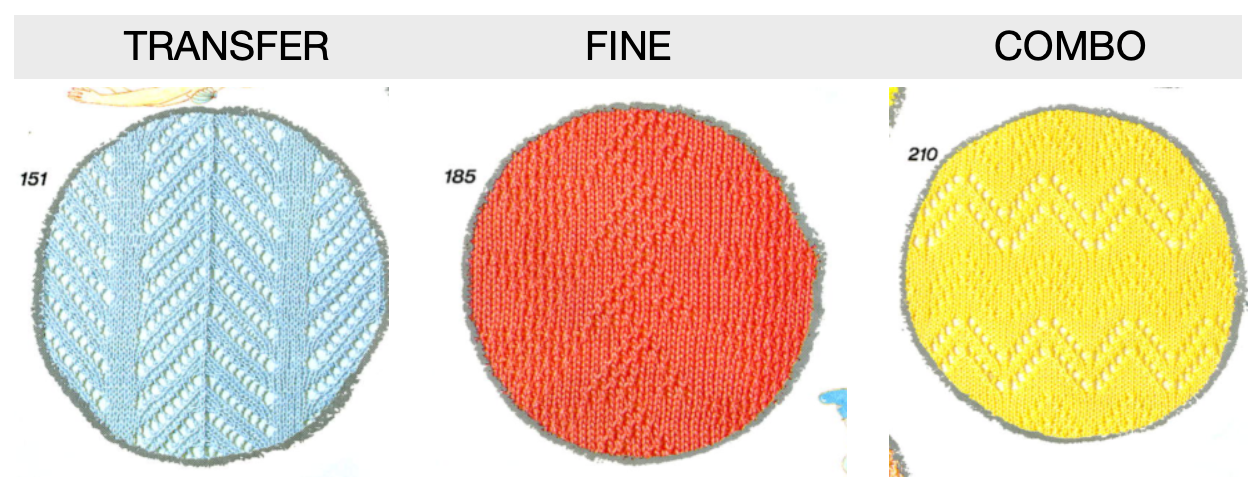
I had expected to use 3 shades of grey, a pleasant surprise: the program can import 3 colors other than grays. The test was using the 11-stitch repeat 
 Using Gimp, images worked in RGB can be reduced to indexed 3 colors for this purpose. If there are rows where no color is represented, then as explained later in the post, the indexing should be to 4 colors, not 3 for the planned import to work properly.
Using Gimp, images worked in RGB can be reduced to indexed 3 colors for this purpose. If there are rows where no color is represented, then as explained later in the post, the indexing should be to 4 colors, not 3 for the planned import to work properly. 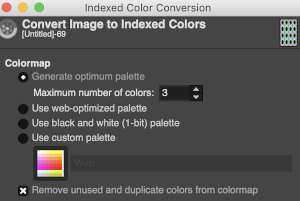 The design is automatically flipped vertically, so it will appear as intended on the knit side of the fabric.
The design is automatically flipped vertically, so it will appear as intended on the knit side of the fabric.
Yarn colors may be placed in the color changer matching the order in the assigned color numbers to match the placements in the original image.
The program automatically adjusts for the vertical stretch, which changes the aspect ratio of the shapes.
The double height variation button is activated automatically.
On my 930 I received prompts on which color to change to before doing so, eliminating any confusion.
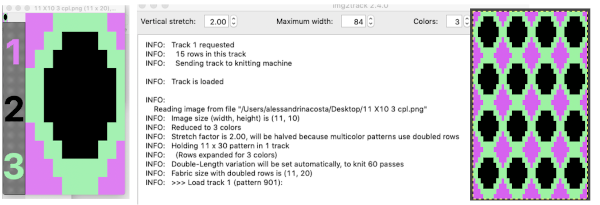
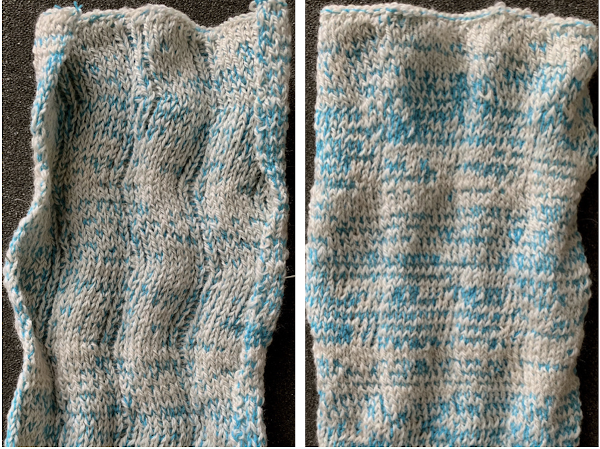
With no such prompts generally one can tell which color was knit last because it will appear on top of the previously used one on the left of the knit. With a stretch factor of 1 selected in img2track, the image height was reduced by half. 
 To achieve a look closer to the intended shape, the repeat needs to be rendered twice as long, or the stretch factor can be adjusted in the program itself to 2.0
To achieve a look closer to the intended shape, the repeat needs to be rendered twice as long, or the stretch factor can be adjusted in the program itself to 2.0
 In the past, I have preferred to elongate the design prior to importing with plans for download rather than to rely on memory for changing settings either in the download program or in the machine itself in future uses of the same design.
In the past, I have preferred to elongate the design prior to importing with plans for download rather than to rely on memory for changing settings either in the download program or in the machine itself in future uses of the same design. 
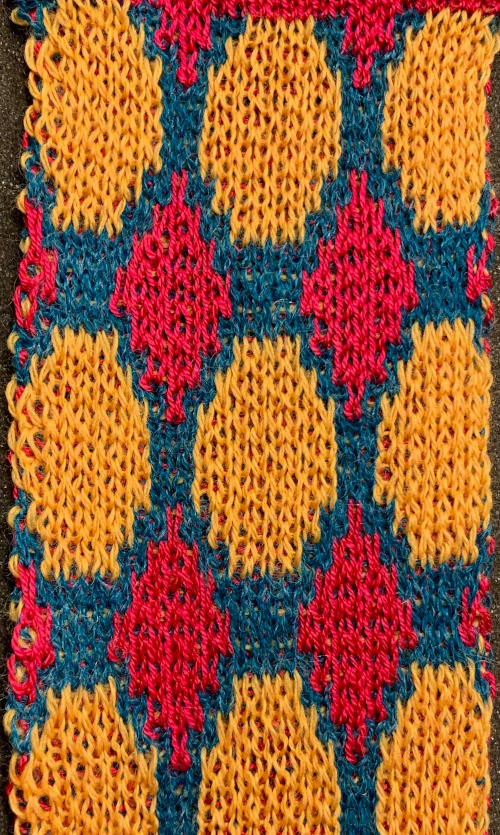
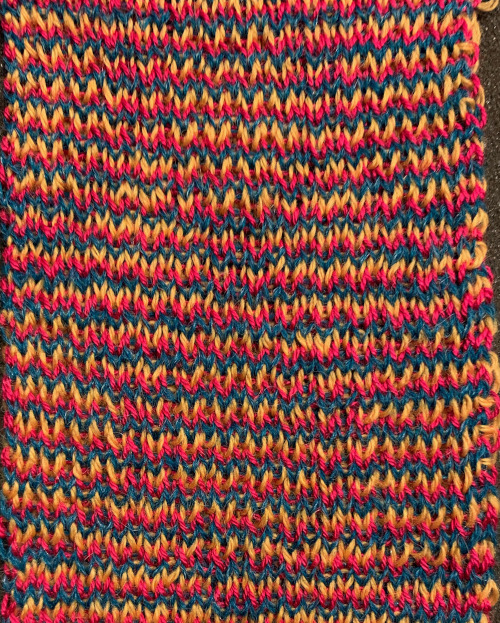

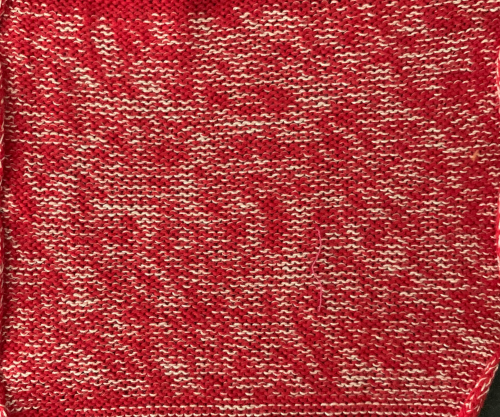
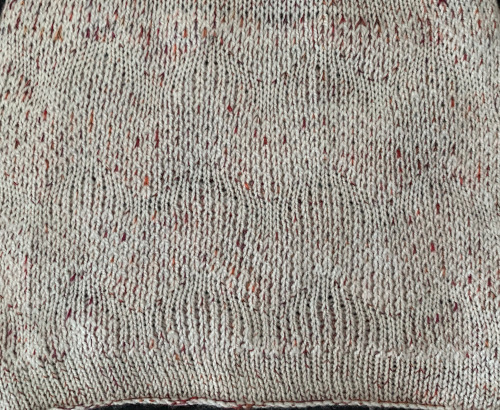
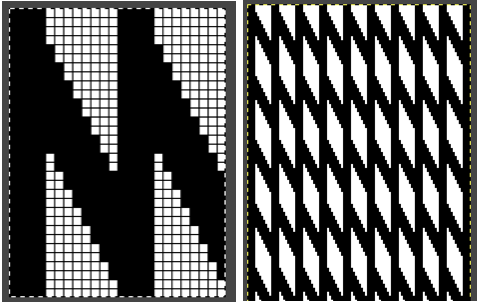
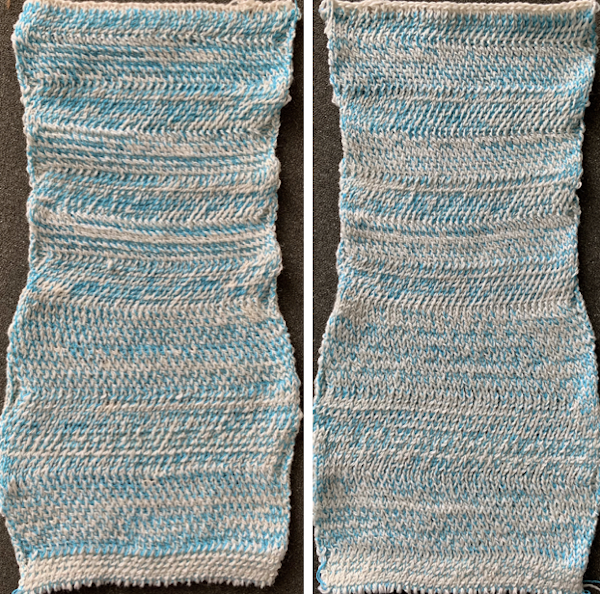
 The same yarns, tension, the total number of carriage passes, and settings were used showing the difference in aspect ratio between single color per row knitting and the img2track built-in color separation.
The same yarns, tension, the total number of carriage passes, and settings were used showing the difference in aspect ratio between single color per row knitting and the img2track built-in color separation.  The width of both swatches is essentially identical.
The width of both swatches is essentially identical.
Images may be loaded into the program without the cable being connected to the machine. Error messages do appear with download attempts if the cable is not properly in place. The machine also needs to be powered on before the program is launched if a download is planned. I am working in Mac OS Mojave 10.14.6, have no present desire to upgrade to Catalina.
Executing fabrics that will knit each color in each row only once for every 2 passes on the main bed: back to that original repeat  Here it is used as drawn, note vertical stretch set at 2, will be cut in half by the software, getting the image back to the original height l0 X 3 = 30 rows required for all colors to knit in turn; there will be 60 carriage passes to complete one single repeat.
Here it is used as drawn, note vertical stretch set at 2, will be cut in half by the software, getting the image back to the original height l0 X 3 = 30 rows required for all colors to knit in turn; there will be 60 carriage passes to complete one single repeat. 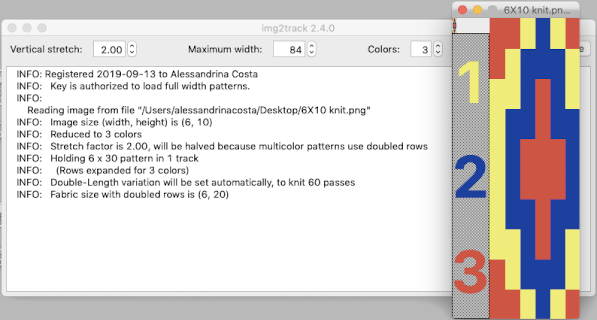 The 930 will provide prompts for the next color to be selected by pushing the matching number button on the color changer, avoiding any confusion in terms of what should be picked up next. img2track will also flip the design horizontally automatically so the image will appear as originally drawn on the knit side. Images are loaded as single motifs, so the change in the selector needs to be made manually for an all-over pattern.
The 930 will provide prompts for the next color to be selected by pushing the matching number button on the color changer, avoiding any confusion in terms of what should be picked up next. img2track will also flip the design horizontally automatically so the image will appear as originally drawn on the knit side. Images are loaded as single motifs, so the change in the selector needs to be made manually for an all-over pattern.
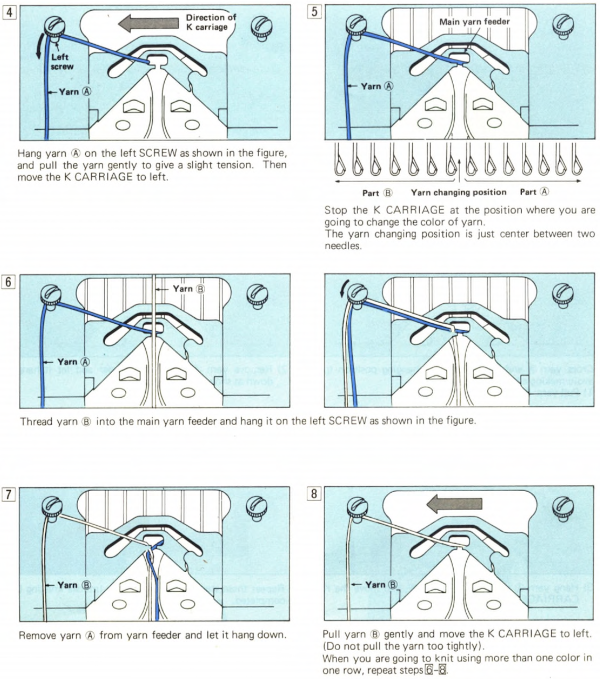
To have each color in each row knit only once: cast on with preferred method and color. Set up the machine so that the yarn colors are placed in the color shown in the image presented by the program to match your design. End with the machine on the left-hand side for the first preselection row.
COL: set both carriages to slip in both directions and all its needles in the B position, set lili buttons if not already in use, and pick up color 1
knit one row to the right
COR: knit to the left, color 1 will knit for a single row
**COL: change color, STOP! Push back any needles on the top bed back to B position, as you knit to the right the ribber only will be knitting, knit one row to the right
COR: preselected needles will be knit in the color last picked up on the way back to the color changer, knitting only one row in that color on the main bed as you return to the left**
repeat the last ** 2 steps throughout. One can get into a rhythm. A cast-on comb, part of a garter bar, or any tool of adequate width can make it a quick process of pushing needles back to B when needed to
trust the software, not the selection expected by your eyes.
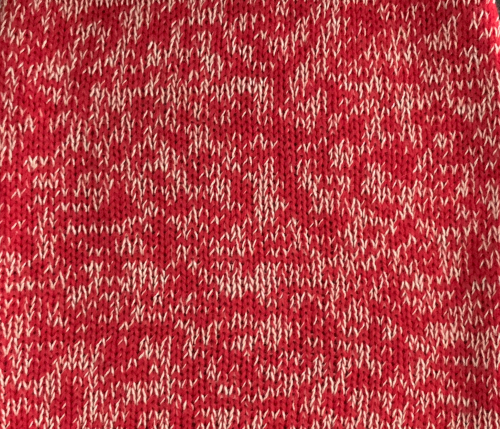
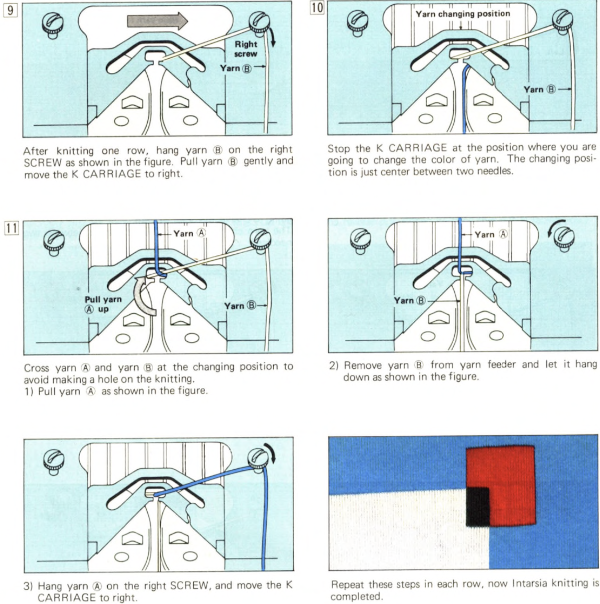
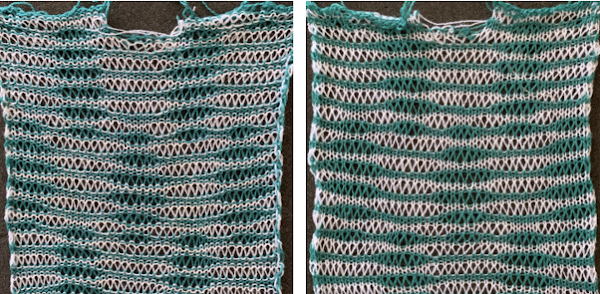
My swatch seemed to be growing in length at a faster rate than I remembered in the last exercise, here the results are shown side by side with the fabric executed previously 
 Obviously a success in terms of the single row for each color reducing elongation of the design shape. While knitting occurs using the same yarns, at the same tensions, there is a clear difference in the length of each stitch on the main bed and their appearance. The reverse. Checking the ribber carriage I noticed on the left side it was set to knit only, not to slip: OOPS!
Obviously a success in terms of the single row for each color reducing elongation of the design shape. While knitting occurs using the same yarns, at the same tensions, there is a clear difference in the length of each stitch on the main bed and their appearance. The reverse. Checking the ribber carriage I noticed on the left side it was set to knit only, not to slip: OOPS!  N is king, so the ribber set as shown is knitting every other needle when moving to the right, but even with lili buttons in use, it knits on every needle when moving back to the left. Every other needle on the ribber will then be knitting for 2 rows as a result. The more knitting on the ribber for each pair of rows, the longer the stitches on the opposite bed. The backing is an interesting variation (half) birdseye. The elongated stitches on the main bed show more of the backing in between their shapes, it is referred to as bleedthrough. In some instances, the result can make the knit surface resemble weaving and its appearance far less familiar in a surprising, pleasant way. Beauty is in the eye of the beholder.
N is king, so the ribber set as shown is knitting every other needle when moving to the right, but even with lili buttons in use, it knits on every needle when moving back to the left. Every other needle on the ribber will then be knitting for 2 rows as a result. The more knitting on the ribber for each pair of rows, the longer the stitches on the opposite bed. The backing is an interesting variation (half) birdseye. The elongated stitches on the main bed show more of the backing in between their shapes, it is referred to as bleedthrough. In some instances, the result can make the knit surface resemble weaving and its appearance far less familiar in a surprising, pleasant way. Beauty is in the eye of the beholder.
Remember always to double-check all settings at the start of any process in case something was missed or magically moved, and keep notes.
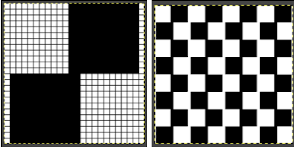
I was asked on Facebook whether the technique shown here is the same as the 3 color slip (skip) stitch patterns in the Stitchworld pattern book, my response: some of the StitchWorld patterns for 3 color slip are designed for or may be used on the double bed (often single bed as well). For instance, patterns 392 and 394. The original designs are rendered color-separated. The numbers on the left suggest the order for color changes to achieve a look similar to that in the swatch photos. Assuming the pattern is not easily accessible because of its being built-in your machine’s memory, it would have to be entered into a paint program manually to make it available for import and in turn for download. Note that the color-changing sequence may change throughout knitting the image, so prompts or notes of some sort would be needed to keep it correct. Each color in each row knits twice after each color change. My goals in my blog posts so far have been to keep a constant color-changing sequence with each color in each row of any personal design knitting only once. I did it first with my color separation, then, in turn, used the 3 color separation feature in img2track to achieve my desired result. Here are 2 images from the Stitchworld section in question  The images could be replicated as given in a paint program, using only one color for the squares, but “should be reduced to black and white”. Attempting to import an indexed 2-color image drawn in a color other than BW may result in strange results.
The images could be replicated as given in a paint program, using only one color for the squares, but “should be reduced to black and white”. Attempting to import an indexed 2-color image drawn in a color other than BW may result in strange results. 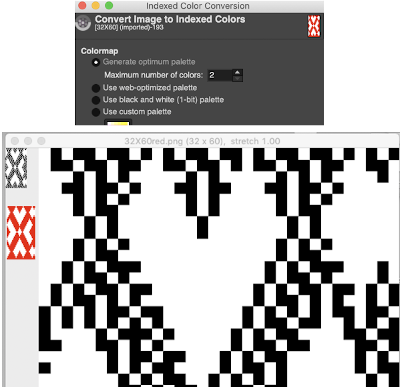 That said, if glitched knits are the goal, the above could work just fine. Curiously, here is the same process, using a different color, and a successful import. Checking again, I had forgotten to save the image after indexing it from RGB mode to 2 colors.
That said, if glitched knits are the goal, the above could work just fine. Curiously, here is the same process, using a different color, and a successful import. Checking again, I had forgotten to save the image after indexing it from RGB mode to 2 colors.  and a test with another color
and a test with another color 
Drop stitch lace periodically comes up, I have written several posts on the technique, now considered the possibility of producing it in 3 colors. The resulting fabric tends to be long, thin, and in need of blocking. There is no way to avoid the striped ground. Passap knitters often refer to this type of knitting as “summer fair isle”. I adjusted the repeat width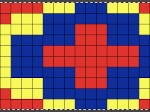
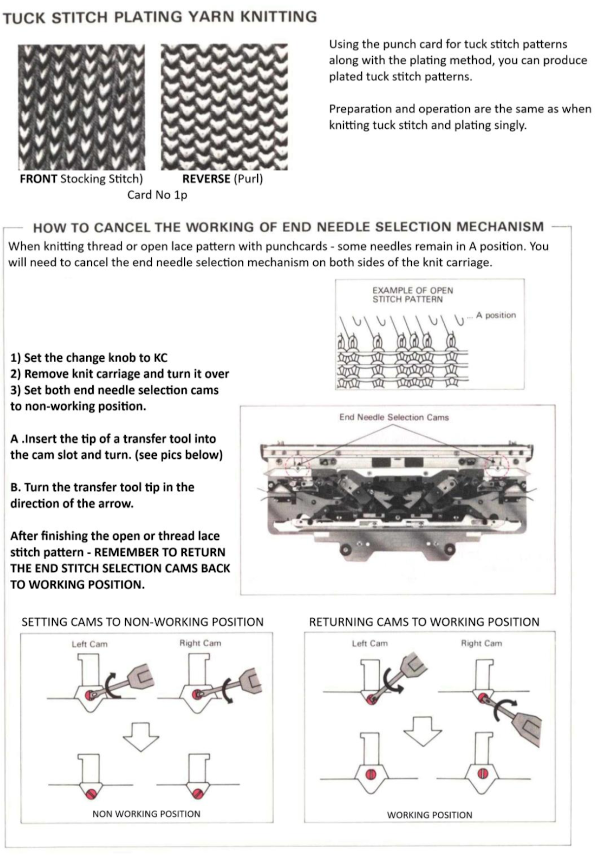
 Note to self: if you are determined to use a punchcard carriage on your electronic machine remember there is no KCII to cancel end needle selection!
Note to self: if you are determined to use a punchcard carriage on your electronic machine remember there is no KCII to cancel end needle selection!
To knit this fabric, stitches must be cast on in whatever method you prefer, but before any patterning, all stitches must be transferred down to the ribber, and the main bed needles are placed in the work position but are empty. Because of the single-row knit for the first 2 design rows of color one, the start is a bit finicky. Alternative start follows lower in post
COL: KC II, main bed set to slip <– –>, ribber stays on N throughout, no lili buttons. Knit one row with color 1 (ribber only)
COR: as you knit to return to the left, the color 1 preselected needles will knit, while the ones corresponding to color 2 will preselect
COL: carefully drop any stitches on needles with color 1 on them without disturbing the new needle selection for color 2
**COL: change color, knit to right
COR: drop the stitches knit in the new color, make certain all needles are empty and in B position, knit back to left, and needles will be pre-selected for the next color**
Repeat the ** to**
Again, the resulting fabric is narrow and long, so it may take a bit of squinting to recognize the design.
If each color is not represented in each design row, the ribber only will knit with no selection on the top bed corresponding to those no-pixel rows.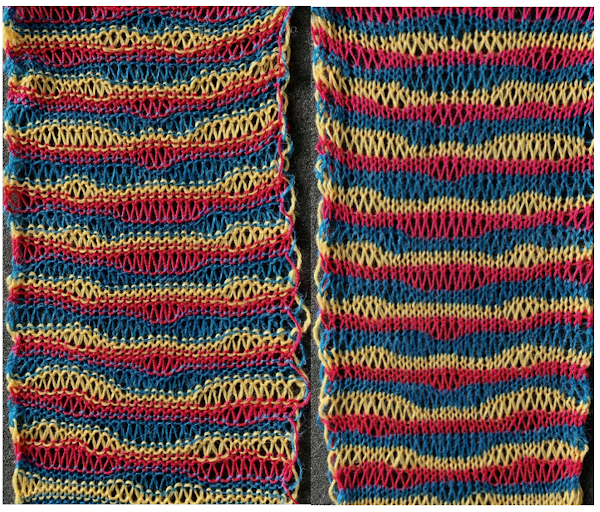  A single repeat results in about 3.5 by 9 inches of knitting, a far cry from what might have resulted in a single row per color design row dbj virtually shown here in a tiled format
A single repeat results in about 3.5 by 9 inches of knitting, a far cry from what might have resulted in a single row per color design row dbj virtually shown here in a tiled format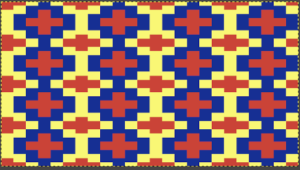
The question then comes up about dropping only one of the 3 colors. Using the manual selection described above, the knitting on the top bed would need to be canceled on every color, every row except for the single row in the chosen drop stitch color. To my mind, that is too much to keep track of for any length of time. It would be easier achieved with specific self-drawn color separations.
There is a lot of testing that can go into developing any fabric in unfamiliar techniques that may or may not meet our expectations or our “like”, it all contributes to learning regardless of whether the tests evolve into projects.
My last post on drop stitch lace from single color to two: revisiting the techniques on brother machines
2022: returning to the topic, exploring drop stitch lace in multiple colors
Reviewing what happens within the program one more time, highlighting significant items to verify before beginning to knit 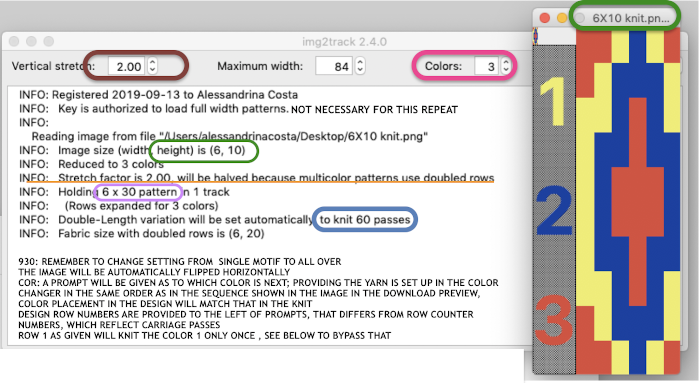 Getting that first row to knit twice instead of a single time if that matters in your technique or is your preference:
Getting that first row to knit twice instead of a single time if that matters in your technique or is your preference:
advance design row to last one in the sequence, in this case, 30
in the 930 when the pattern is loaded, using the down arrow key gets to the last row in the downloaded pattern more quickly
COL: set machine to preselect pattern, the next 2 passes would need to not knit, so both carriages are set to slip in both directions
knit one row to the right
COR: number 30 design row flashes
knit one more free pass to the left, row 1 of color 1 will preselect as you knit
COL: number 1 design row flashes
check all settings, main bed set to slip <– –>, ribber set to slip <– –> with lili buttons, and with an even number of needles in work for standard dbj 
 pick up color 1 in yarn changer
pick up color 1 in yarn changer
the resulting knit design will be elongated
COL: knit one row to the right.
As you knit the first row of color 1 design row 1 will knit, row 2 of color one design row 1 will preselect
COR: knit back to the left
as you knit back to left row 2 of color 1 design row 1 will knit, row 1 of color 2 design row 1 will preselect
COL: pick up color 2,
continue in pattern changing colors every 2 rows
In designing your own, small repeats can easily be rendered even in a simple paint program. Larger, more complex ones, may best be worked using layers and masking in a variety of programs ie. Photoshop or Gimp. It is possible to combine 2 color dbj and 3 color dbj in the same piece simply by using different color separations for each segment, but the look of the fabric in terms of the length of each stitch on the knit side may be quite different when moving from one segment to the next. Of course, the backing will change as well. Though the aspect ratio of the design changes in terms of height when one knits 2 rows for each color in each design row, it remains the easiest separation method. Adding the hand selection as described above so that the main bed knits in one direction only helps reduce some of the extra height, making the original image more recognizable. There is no option within img2track to perform the action automatically in terms of adding the necessary blank rows to replace some of the colored ones in the separation.
Passap knitters are not left out of this idea. Passap preselects pushers. On the E 6000 Tech 179 emulates the built-in KRC option in Japanese model machines. My guess was that technique 180 for 2 colors, perhaps 197 with both arrow keys on the back may work for 3 colors. TBD in my next spurt of knitting activity on it. That said, the console’s built-in designs may be used cross-brand. It is possible in Passap to layer repeats in order to add the third color to the mix. Here is one sample reworked for use on Brother and downloaded into img2track. 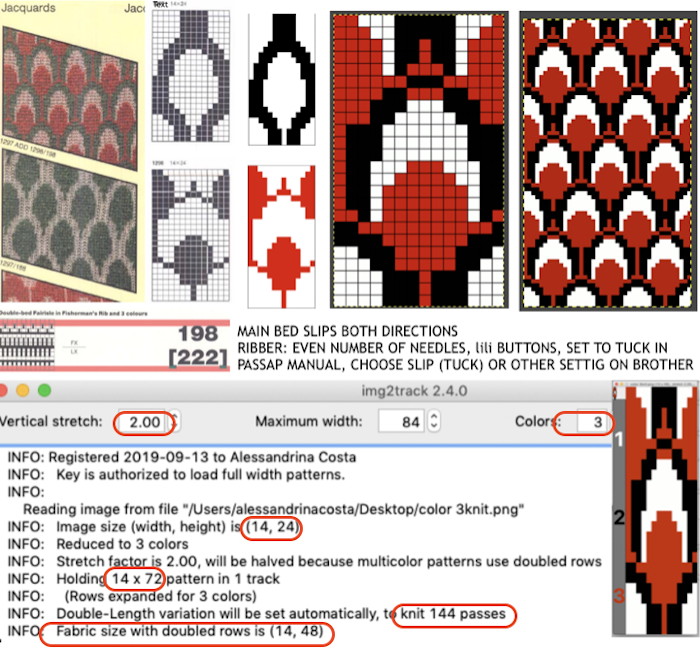 If black and white repeats are already in your library, one may easily recycle them adding a third color. Here I did so with a repeat intended for a very different topic in future posts. The image was altered and tiled in Gimp for a repeat alignment test and is also shown imported into img2track for possible knitting.
If black and white repeats are already in your library, one may easily recycle them adding a third color. Here I did so with a repeat intended for a very different topic in future posts. The image was altered and tiled in Gimp for a repeat alignment test and is also shown imported into img2track for possible knitting.  What about using images published in punchcard machine references? It is probably best to start with smaller repeats. That said, this is from a Deco pattern book. Deco punchcards were 40 stitches wide, and could be joined together in length as can those for the Japanese models
What about using images published in punchcard machine references? It is probably best to start with smaller repeats. That said, this is from a Deco pattern book. Deco punchcards were 40 stitches wide, and could be joined together in length as can those for the Japanese models 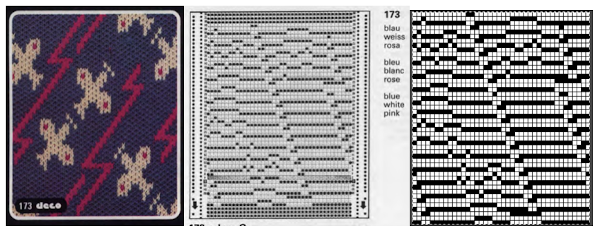 The image of the separation on the above right has not been proofed for accuracy. If it were, the next step would be to elongate it X 2 for color changes every 2 rows. One method is to elongate the original in a paint or photo processing program. The width is fixed (40), the height is scaled X 2. The resulting BW indexed image may be imported, using a 1.0 stretch factor, it remains unchanged. When I tried to elongate the unstretched image in img2track by 2.0 my first try failed. It turned out the reason was I had saved the import without first indexing it to 2 colors. With that corrected, the result matched the one from scaling X 2 in height in the paint program
The image of the separation on the above right has not been proofed for accuracy. If it were, the next step would be to elongate it X 2 for color changes every 2 rows. One method is to elongate the original in a paint or photo processing program. The width is fixed (40), the height is scaled X 2. The resulting BW indexed image may be imported, using a 1.0 stretch factor, it remains unchanged. When I tried to elongate the unstretched image in img2track by 2.0 my first try failed. It turned out the reason was I had saved the import without first indexing it to 2 colors. With that corrected, the result matched the one from scaling X 2 in height in the paint program
 For years now I have been doing color separations which at first could be extremely slow, one pixel at a time. With increasing familiarity with Gimp and Mac Numbers over time, I have been able to decrease the speed to achieve them immensely. So here, with img2track I now have a program that can work with and separate multiple colors at a time (up to 6 in its pull-down menu option). Here I returned to my first separation in 3 colors for the now-familiar repeat A, elongated it in the paint program B and imported A into img2track choosing 2.0 stretch and 3 colors C. I can totally live with the fact the colors are not the same. The color changer can be set up with my chosen colors in any order I choose
For years now I have been doing color separations which at first could be extremely slow, one pixel at a time. With increasing familiarity with Gimp and Mac Numbers over time, I have been able to decrease the speed to achieve them immensely. So here, with img2track I now have a program that can work with and separate multiple colors at a time (up to 6 in its pull-down menu option). Here I returned to my first separation in 3 colors for the now-familiar repeat A, elongated it in the paint program B and imported A into img2track choosing 2.0 stretch and 3 colors C. I can totally live with the fact the colors are not the same. The color changer can be set up with my chosen colors in any order I choose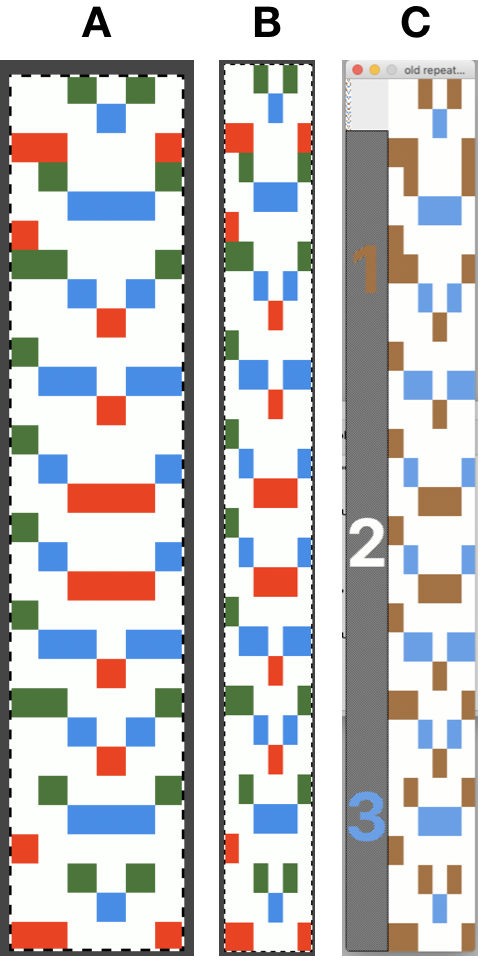
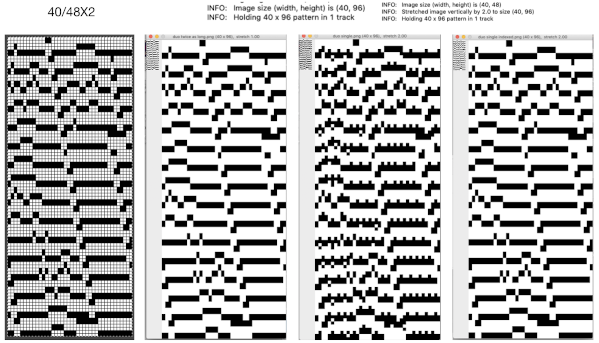
In my first tests with charting a repeat missing any color in some rows, I had scaled the original image taken from a spreadsheet to the wrong size in Gimp, so operator error resulted in crazy results in img2track.  Here the image is scaled properly for each color represented for a single row in height and also scaled again for double height for possible knitting in Gimp. The Gimp scaling failed to be accurate for me (second image from left) until I indexed the original to 4 colors as well instead of 3. The no-color rows as we view them serve as a fourth color in the separations. Importing the proper size PNG into img2track for the separation of 4 colors per row now gives results that make sense: note the daunting estimate for the total number of carriage passes for a single repeat height
Here the image is scaled properly for each color represented for a single row in height and also scaled again for double height for possible knitting in Gimp. The Gimp scaling failed to be accurate for me (second image from left) until I indexed the original to 4 colors as well instead of 3. The no-color rows as we view them serve as a fourth color in the separations. Importing the proper size PNG into img2track for the separation of 4 colors per row now gives results that make sense: note the daunting estimate for the total number of carriage passes for a single repeat height
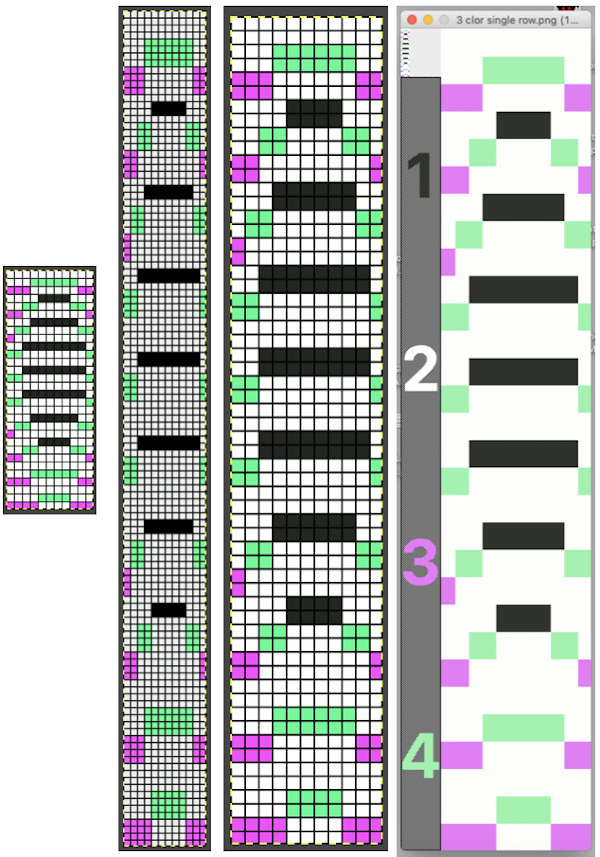 If the ribber has knit on every needle by its return to the color changer and the machine is set to slip both ways with no needle selection on the main bed, the “no color” can be executed as an empty yarn holder in the color changer combined with no yarn in the feeder. The rows involved should simply not knit on the top bed, with no dropping of any of its stitches since no needles will have been selected thus coming forward with the yarn in the hooks and traveling behind the latches and in turn, slipping off the needles as a carriage with no yarn pushes the needles with now empty hooks back to B position.
If the ribber has knit on every needle by its return to the color changer and the machine is set to slip both ways with no needle selection on the main bed, the “no color” can be executed as an empty yarn holder in the color changer combined with no yarn in the feeder. The rows involved should simply not knit on the top bed, with no dropping of any of its stitches since no needles will have been selected thus coming forward with the yarn in the hooks and traveling behind the latches and in turn, slipping off the needles as a carriage with no yarn pushes the needles with now empty hooks back to B position.
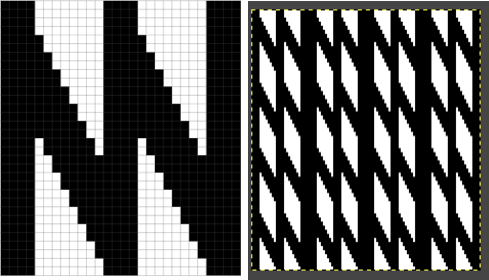
In testing concepts, I prefer to work initially with small repeats. Punchcard books can be an excellent source, but the Stitchworld books have the advantage of actually showing a single repeat for each design, so an 8 stitch repeat, for example, would be shown as such and it would not be up to the person using it shown in a 24 stitch card one to isolate it. I randomly chose pattern 394. I realize that if used from a built-in library of patterns in any machine model the prompts may be provided by the machine, but here I am looking at simply duplicating the pattern for import into img2track.
 After duplicating the repeat and associated numbering using Numbers, these were some of my results. A pleasing surprise was that colors in the 2 color import need not be only black and white. That said, the pale green failed, the red did not, and the results from importing both the red/white and the black/white were identical. Another future time saver for me to keep in mind.
After duplicating the repeat and associated numbering using Numbers, these were some of my results. A pleasing surprise was that colors in the 2 color import need not be only black and white. That said, the pale green failed, the red did not, and the results from importing both the red/white and the black/white were identical. Another future time saver for me to keep in mind. 
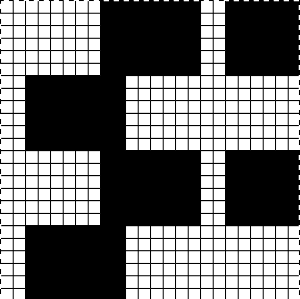
If colors were assigned to each pair rows representing each color used, the white squares were read as an added color on import, and the only way to have those few blocks for the 4th color to show up in the visual representation in an imported repeat was to assign a 5 color separation, resulting in a scrambled pattern. Removing the few squares in color 4 will produce inaccurate separations for actual knitting of the given pattern whether imported to be rendered for 3 colors or 4. The black and white on the right is the “correct” match, leaving any prompts for use of shifting color changers to be tracked somehow by the knitter. 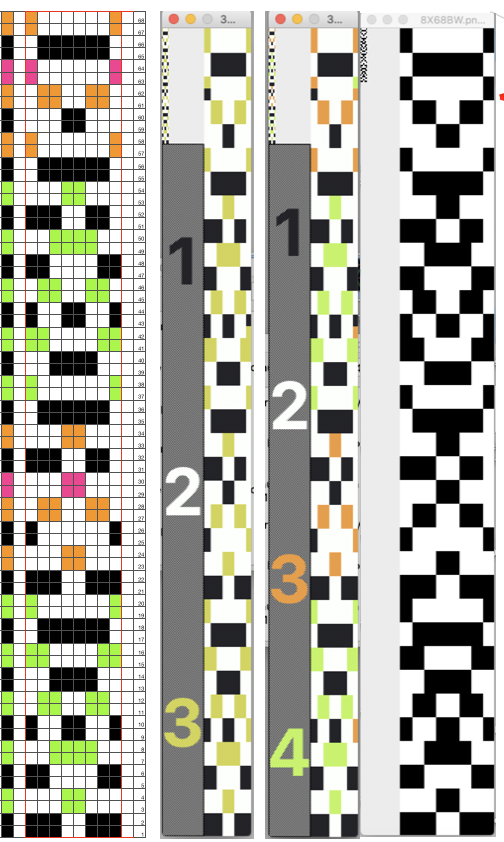 Punchcard knitters may have the easiest knitting variable color sequences since cards may be visually marked up with colored pencils matching needed change locations and taking into account your eyes are several rows above the row being read by the card reader. This number depends on the machine’s brand and model.
Punchcard knitters may have the easiest knitting variable color sequences since cards may be visually marked up with colored pencils matching needed change locations and taking into account your eyes are several rows above the row being read by the card reader. This number depends on the machine’s brand and model.
Some spreadsheets that may help with tracking row color changes or other regular actions on paper: 2018/04/tracking-rows-1.pdf
I have been asked about the position of the slide lever being fixed in my dbj illustrations. I have found the alternate positions can be wild cards, would rather make adjustments in carriage settings if needed rather than let the factory settings do some of the work for me. If the settings are accidentally in the wrong place as multiple pieces are knit, or in knitting ribber bands for garment pieces, the gauge is changed if the alternate setting is not adjusted and kept constant, and that may not be noticed until the piece of knitting in question is completed, needing a restart. With 15-20 machines active in each studio class and lab session, I tried to reduce as many variables as possible.
A video resource on using img2knit for 3 colors per row knitting with blank color rows in the design by Tanya Cunningham, and a Ravelry thread on the topic
 At least on my machine, I am giving up on the idea of using it, even if only to preselect needles, let alone make transfers.
At least on my machine, I am giving up on the idea of using it, even if only to preselect needles, let alone make transfers.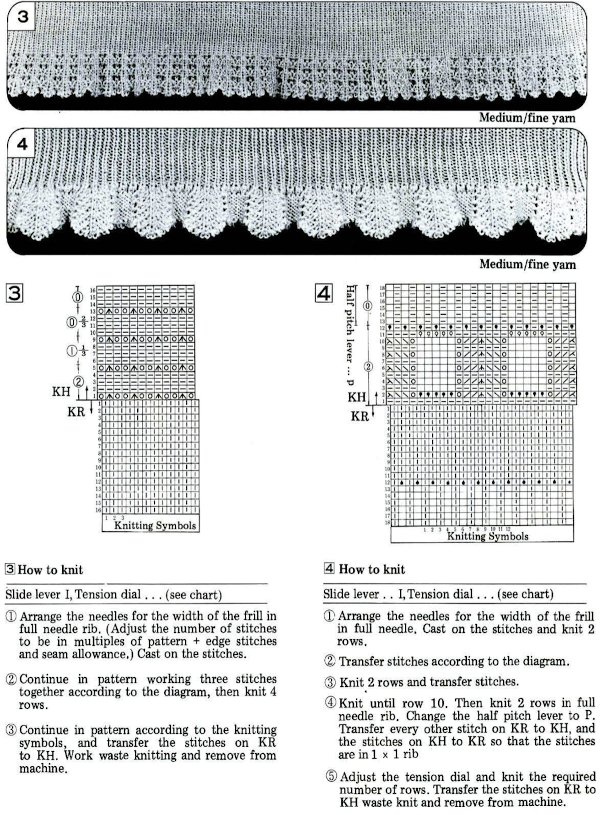
 The same work could be done using only one knit carriage as well, but that would require changing the cam buttons from slip in both directions to knit and back to slip at the appropriate points, one of the methods that make it possible to knit lace on the 260 bulky machines
The same work could be done using only one knit carriage as well, but that would require changing the cam buttons from slip in both directions to knit and back to slip at the appropriate points, one of the methods that make it possible to knit lace on the 260 bulky machines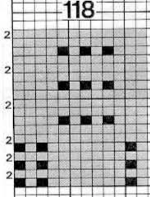

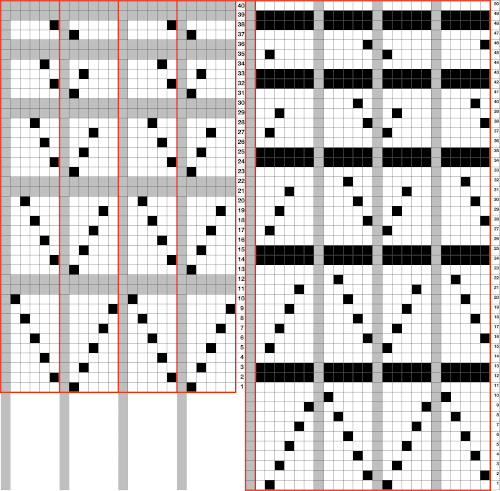 This explains some of the desired knitting actions
This explains some of the desired knitting actions 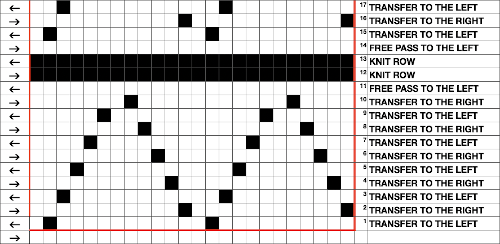 Using the method described in other posts, this was the screengrab imported into Gimp. The grey line is a reference point. Cropping the image to content will allow the last blank row to be preserved by having the grey one there. After the crop, it can be bucket filled with white, or when the image is, in turn, bitmapped to B/W, you may find it disappears. Image scale is then used to reduce the repeat for knitting.
Using the method described in other posts, this was the screengrab imported into Gimp. The grey line is a reference point. Cropping the image to content will allow the last blank row to be preserved by having the grey one there. After the crop, it can be bucket filled with white, or when the image is, in turn, bitmapped to B/W, you may find it disappears. Image scale is then used to reduce the repeat for knitting. 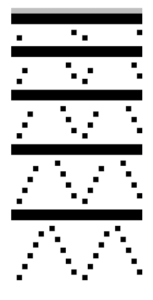 This is the repeat used to knit the swatch in my 930. If working from it, punchcard knitters need to mirror designs from an electronic source such as this and will find it easier to do so by turning the card over, marking the holes that require punching on that side, doing so, and then inserting the card in the reader in its usual orientation.
This is the repeat used to knit the swatch in my 930. If working from it, punchcard knitters need to mirror designs from an electronic source such as this and will find it easier to do so by turning the card over, marking the holes that require punching on that side, doing so, and then inserting the card in the reader in its usual orientation.  The 930 .png:
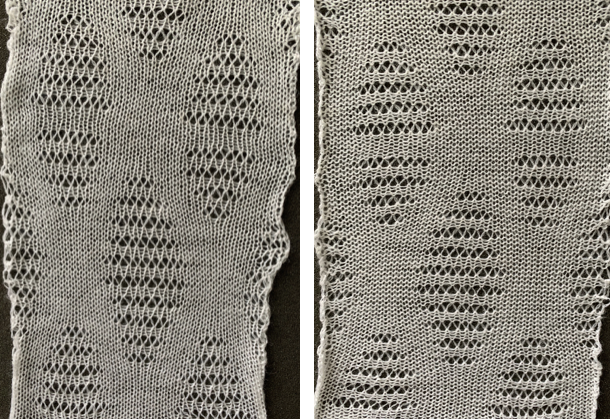
The 930 .png: ![]() Prior to knitting the pattern using the ribber, it pays to test the repeat single bed to get a sense of where the knit rows occur and to make certain the transfers are happening in the correct direction and in what place on the needle bed. There should be no side by side empty needles, and in this design, the first pairs of transfers result in 3 stitches on one needle in the center of each shape, not side by side holes as seen here in the false start prior to mirroring the image
Prior to knitting the pattern using the ribber, it pays to test the repeat single bed to get a sense of where the knit rows occur and to make certain the transfers are happening in the correct direction and in what place on the needle bed. There should be no side by side empty needles, and in this design, the first pairs of transfers result in 3 stitches on one needle in the center of each shape, not side by side holes as seen here in the false start prior to mirroring the image  Making things work: both carriages will be operating to and from the left-hand side. The process is facilitated by the use of an extension rail and a color changer. The knit carriage alone will operate to preselect the needles that will need to be hand transferred to create the lace pattern. With the following modification of the repeat, all transfers are made moving away from the knit carriage. So if the KC is on the right, transfer to the left, if it is on the left, transfer to the right. The paired carriages will create the two all-knit rows between lace segments. The blank rows above and below the two all punched or black pixel rows are there to return the carriages to the proper, left side to begin preselection for the next row of transfers. If any end needles are preselected on the knit bed, push them back to B.
Making things work: both carriages will be operating to and from the left-hand side. The process is facilitated by the use of an extension rail and a color changer. The knit carriage alone will operate to preselect the needles that will need to be hand transferred to create the lace pattern. With the following modification of the repeat, all transfers are made moving away from the knit carriage. So if the KC is on the right, transfer to the left, if it is on the left, transfer to the right. The paired carriages will create the two all-knit rows between lace segments. The blank rows above and below the two all punched or black pixel rows are there to return the carriages to the proper, left side to begin preselection for the next row of transfers. If any end needles are preselected on the knit bed, push them back to B. Begin with a zig-zag row from left to right, knit 2 circular rows, carriages will be on the right. Knit a sealing row to the left, followed by 2 all knit rows, ending with carriages once more on the left side.
Begin with a zig-zag row from left to right, knit 2 circular rows, carriages will be on the right. Knit a sealing row to the left, followed by 2 all knit rows, ending with carriages once more on the left side.
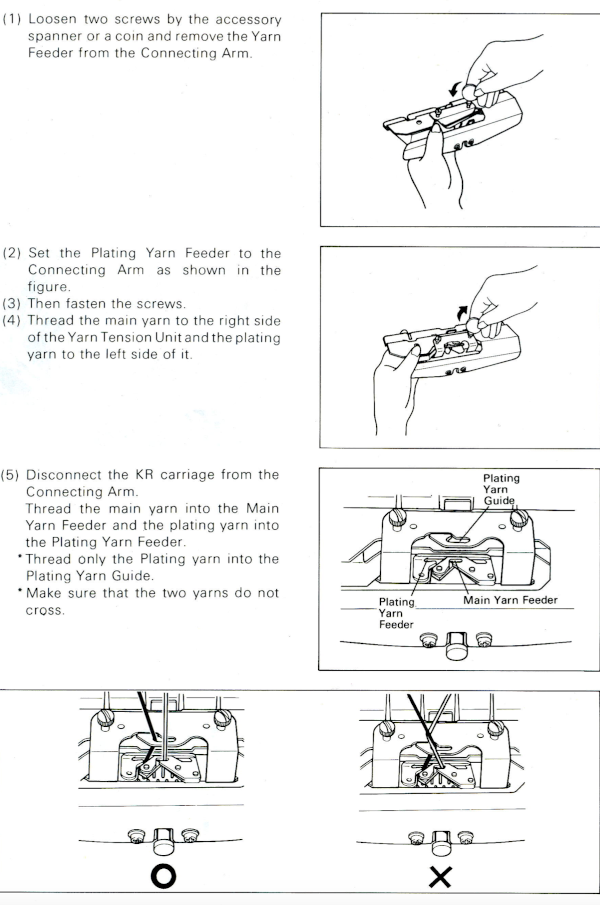
 plaiting with yarns swapped in feeders for reversible striped effect
plaiting with yarns swapped in feeders for reversible striped effect 

 Striping created by reversing yarn positions in plaiting feeder
Striping created by reversing yarn positions in plaiting feeder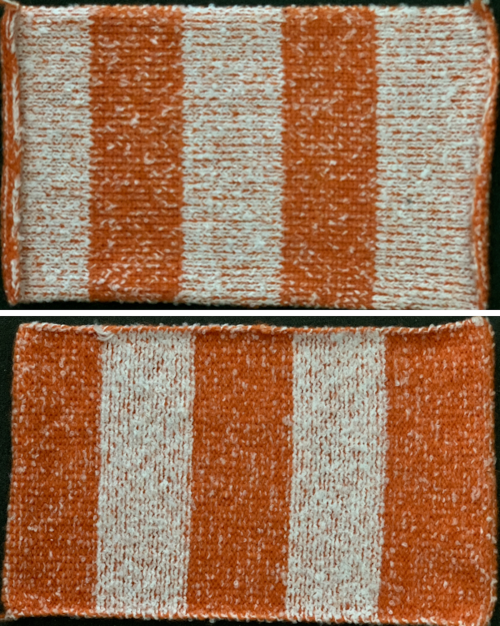 


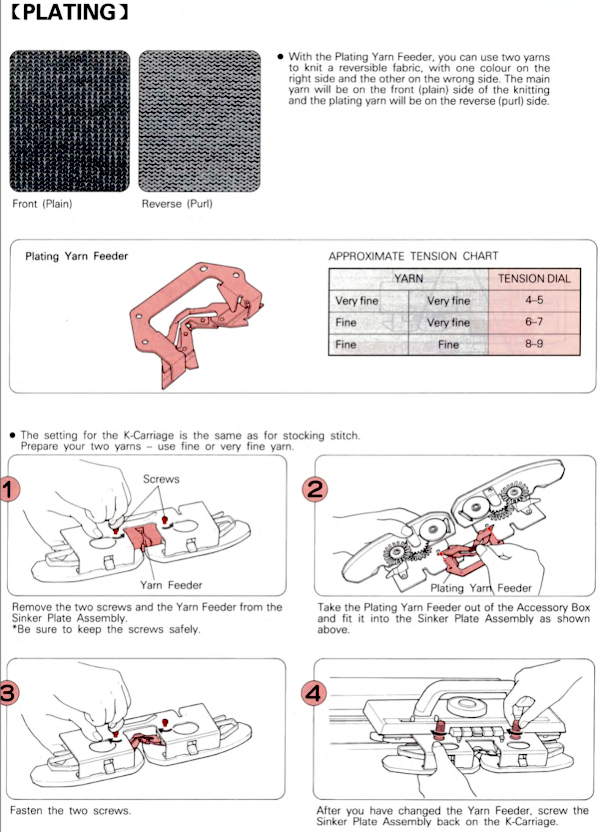
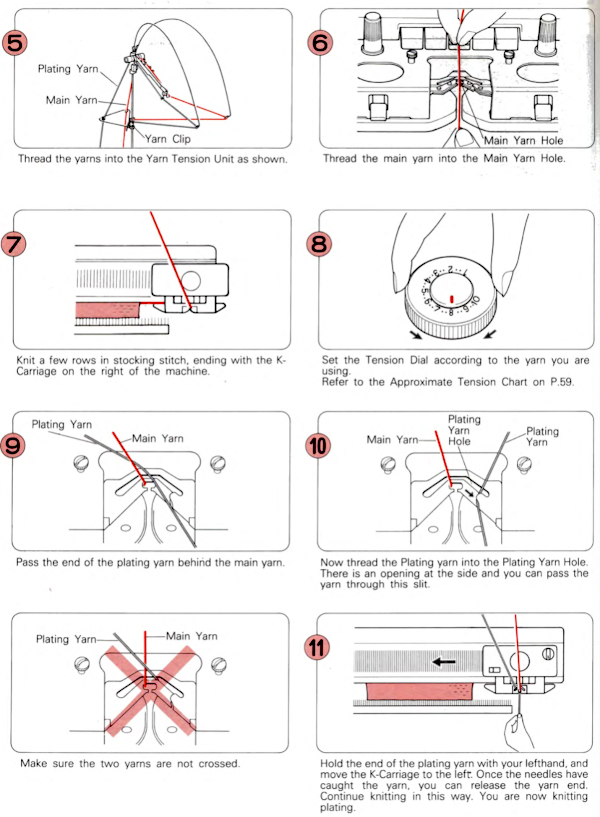
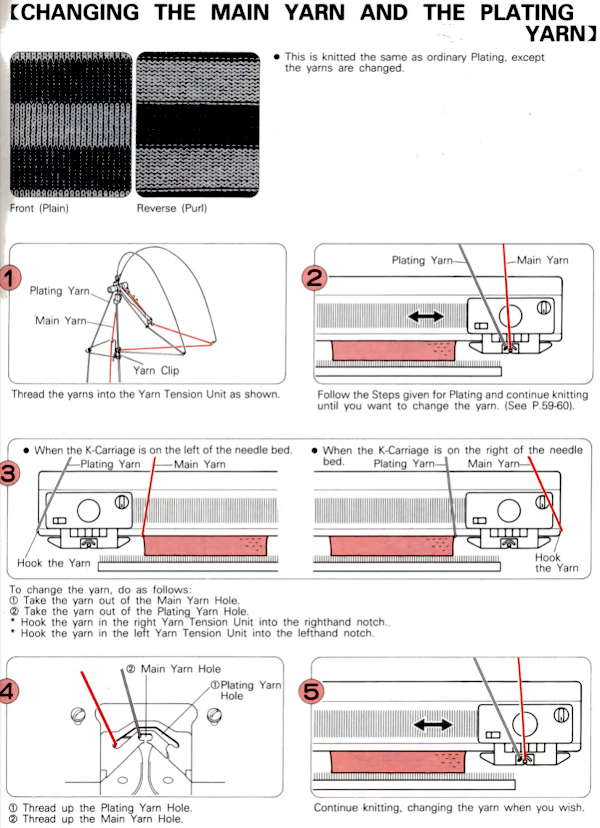
 If your sinker plate has rubber wheels, check them and move them to the proper position if needed.
If your sinker plate has rubber wheels, check them and move them to the proper position if needed. 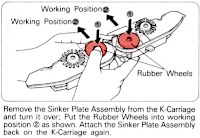
 More random, ancient swatches: stocking stitch using equal-weight yarns in a single bed tuck stitch
More random, ancient swatches: stocking stitch using equal-weight yarns in a single bed tuck stitch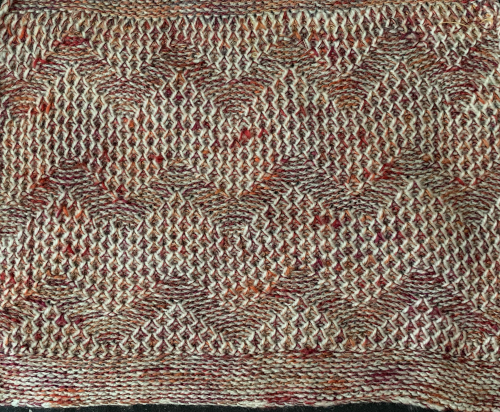
 double bed every needle rib tuck stitch using the same pattern repeat
double bed every needle rib tuck stitch using the same pattern repeat 


 Shadow lace
Shadow lace  Pleated pattern
Pleated pattern 


 An experimental double bed fabric using the plaiting feeder and thread lace setting double bed
An experimental double bed fabric using the plaiting feeder and thread lace setting double bed 

 The suitable dbj separation is the one where each color in each row knits for 2 rows, whether performed by hand, using the 3 colors per row separation in img2track or the default separation in Passap. The Ayab HOP separation is awesome, works for any 3 color design with as little elongation as possible, but is not suited for this purpose. How-tos for DIY separations and their automated versions by programs for knitting more than 2 colors per row have been discussed in other posts.
The suitable dbj separation is the one where each color in each row knits for 2 rows, whether performed by hand, using the 3 colors per row separation in img2track or the default separation in Passap. The Ayab HOP separation is awesome, works for any 3 color design with as little elongation as possible, but is not suited for this purpose. How-tos for DIY separations and their automated versions by programs for knitting more than 2 colors per row have been discussed in other posts.
 A similar process on the Passap allows for playing easily with both racked colors because of the possible arrow and pusher settings on the back bed, but on Brother, this would require hand selection on the ribber on every row or a specific color separation for needle selection on the top bed
A similar process on the Passap allows for playing easily with both racked colors because of the possible arrow and pusher settings on the back bed, but on Brother, this would require hand selection on the ribber on every row or a specific color separation for needle selection on the top bed Seeking automation, keeping things simple, here is a basic zigzag pattern in a repeat also executable on punchcard machines. The ribber is now set to knit throughout (N/N), the main bed to slip in both directions. End needle selection must be canceled when using the slip setting selectively or when working patterning with needles completely out of work
Seeking automation, keeping things simple, here is a basic zigzag pattern in a repeat also executable on punchcard machines. The ribber is now set to knit throughout (N/N), the main bed to slip in both directions. End needle selection must be canceled when using the slip setting selectively or when working patterning with needles completely out of work 
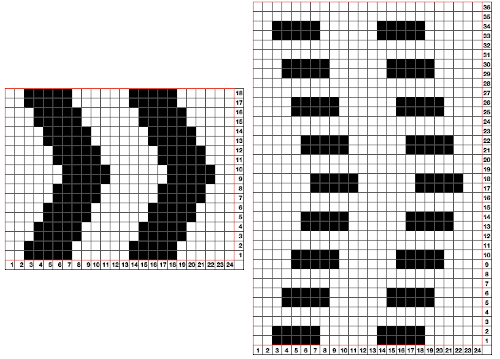
 The process using 3 colors: the patterning color will be knit on needles preselected on the top bed. As shaping is about to begin, in this pattern, one needle preselected out indicates the location for an “increase”, one preselected back to B position a decrease
The process using 3 colors: the patterning color will be knit on needles preselected on the top bed. As shaping is about to begin, in this pattern, one needle preselected out indicates the location for an “increase”, one preselected back to B position a decrease  To perform the decrease, using a double eye tool to transfer the B position stitch down onto the ribber needle adjacent to the first needle in D position on the top bed
To perform the decrease, using a double eye tool to transfer the B position stitch down onto the ribber needle adjacent to the first needle in D position on the top bed



 The repeat and the knit shown on both sides:
The repeat and the knit shown on both sides: 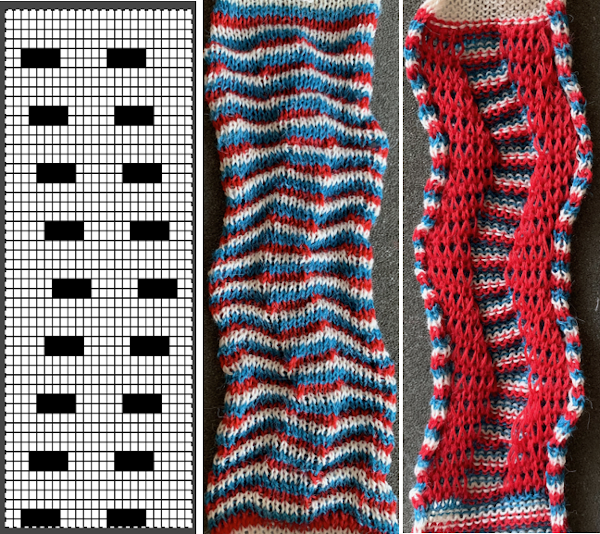 Comparing the 2 color and 3 color versions: aside from the obvious increase in length, note that the slipped segments in red on the 3 color swatch are now composed of longer stitches since they are held for 2 additional rows, and the overall fabric is more puckered than the 2 color version. The curling at the sides is the nature of edge stitches, especially if the yarn used is wool. At times that may be used intentionally, as a decorative edge.
Comparing the 2 color and 3 color versions: aside from the obvious increase in length, note that the slipped segments in red on the 3 color swatch are now composed of longer stitches since they are held for 2 additional rows, and the overall fabric is more puckered than the 2 color version. The curling at the sides is the nature of edge stitches, especially if the yarn used is wool. At times that may be used intentionally, as a decorative edge.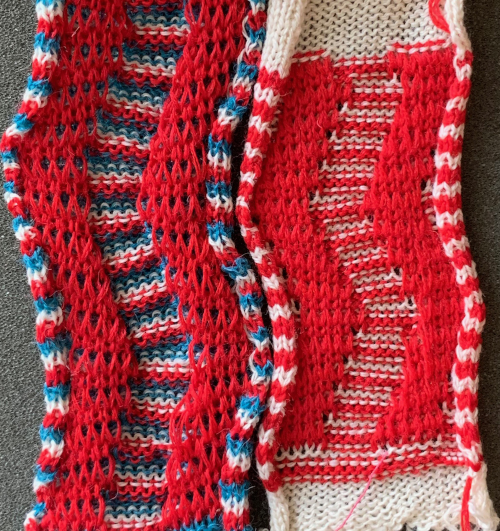
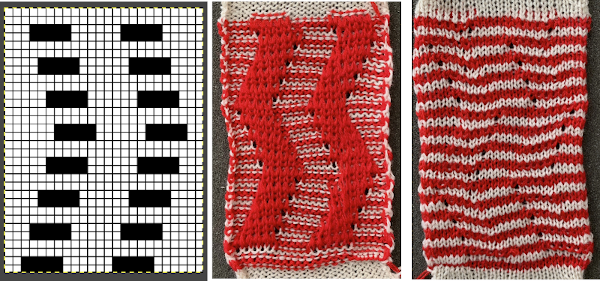
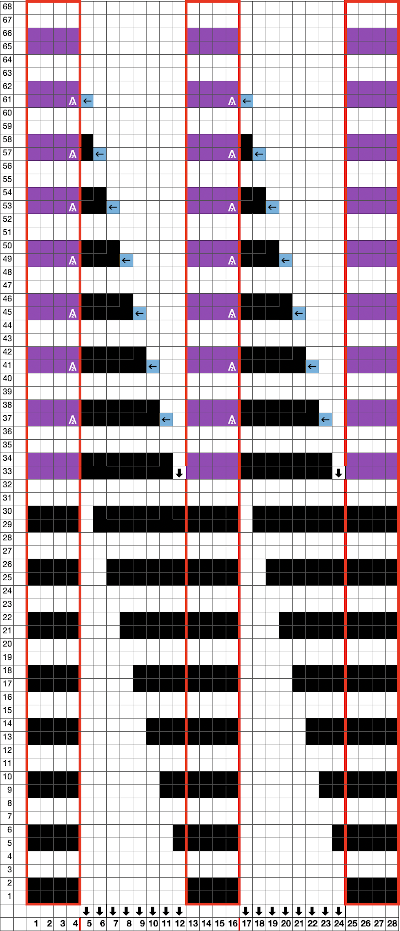
 Using the same color separation as for the simple zig-zag shape, the design is expanded to include knit bed rows that will be skipped completely, resulting in the ribber alone knitting in the second color for those rows. It is now twice as long as the original, 24X64
Using the same color separation as for the simple zig-zag shape, the design is expanded to include knit bed rows that will be skipped completely, resulting in the ribber alone knitting in the second color for those rows. It is now twice as long as the original, 24X64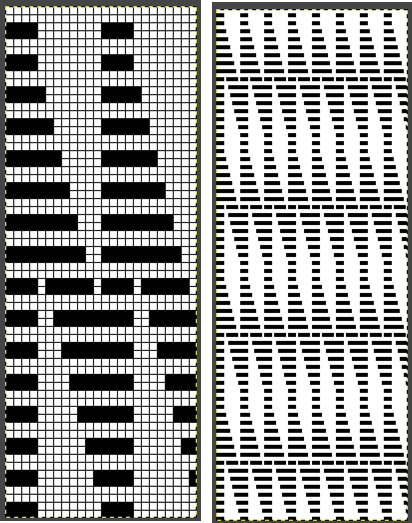 The planned proof of concept added a 4 stitch border on the right for a 28 stitch swatch centered with 14 stitches either side of 0. Tiling the repeat X2 again in height made it easier for me to plan how to manage transfers to expose the varying stripes in the ground. Visual comparison to the movement in the inspiration knit:
The planned proof of concept added a 4 stitch border on the right for a 28 stitch swatch centered with 14 stitches either side of 0. Tiling the repeat X2 again in height made it easier for me to plan how to manage transfers to expose the varying stripes in the ground. Visual comparison to the movement in the inspiration knit:  As the number of needles in work on either of the 2 beds is increased, it is likely tension or yarn changes may be required. The first preselection row is from the right, toward the color changer. The stitches on the non selected needles are transferred to the bottom bed
As the number of needles in work on either of the 2 beds is increased, it is likely tension or yarn changes may be required. The first preselection row is from the right, toward the color changer. The stitches on the non selected needles are transferred to the bottom bed 
 with the color change, only preselected needles will knit on both the top and bottom beds moving to the right
with the color change, only preselected needles will knit on both the top and bottom beds moving to the right  and will do so again on the return to the left while preselecting an all blank row
and will do so again on the return to the left while preselecting an all blank row  on the next pass to the right only the ribber knits in the ground color;
on the next pass to the right only the ribber knits in the ground color; 


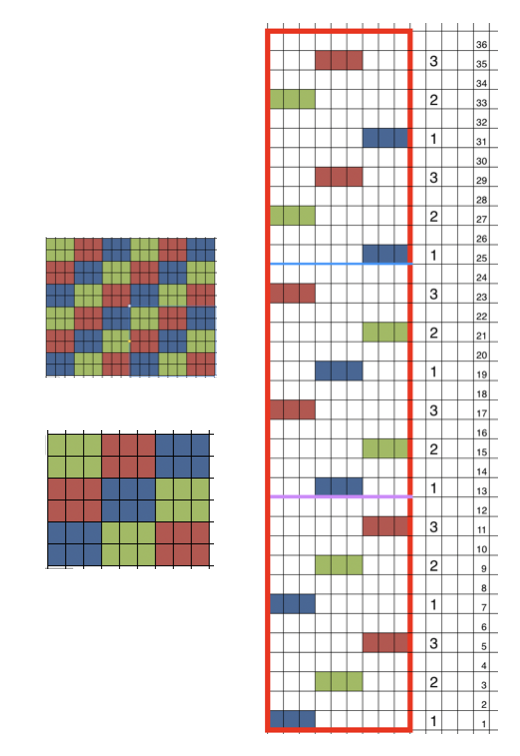
 Back to the drawing board in order to reduce the number of hand manipulations involved, with a shift in the center transition, the repeat in my spreadsheet is now 24 stitches wide, plus an additional 4 stitch border, and gets marked up with colors. I prefer to program the width of my knitting as opposed to a single repeat for all over patterning
Back to the drawing board in order to reduce the number of hand manipulations involved, with a shift in the center transition, the repeat in my spreadsheet is now 24 stitches wide, plus an additional 4 stitch border, and gets marked up with colors. I prefer to program the width of my knitting as opposed to a single repeat for all over patterning 
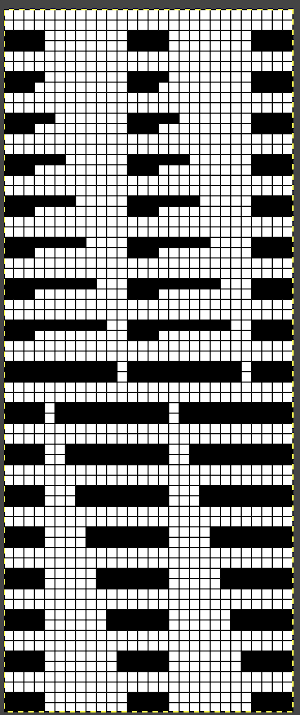 The choice can be made based upon the preference of moving stitch groups to the right or to the left with the horizontal direction of the repeat adjusted for your KM model or software used.
The choice can be made based upon the preference of moving stitch groups to the right or to the left with the horizontal direction of the repeat adjusted for your KM model or software used.  I planned the transfers in this swatch toward the color changer after picking up the proper color, white, and before knitting the next row using it. The 930 png:
I planned the transfers in this swatch toward the color changer after picking up the proper color, white, and before knitting the next row using it. The 930 png: 
 When the top of the repeat is reached, row 68, the only needles selected will be those of the 4 stitch vertical columns and the design repeat will return to its start
When the top of the repeat is reached, row 68, the only needles selected will be those of the 4 stitch vertical columns and the design repeat will return to its start My proof of concept swatch is 3.75 inches wide
My proof of concept swatch is 3.75 inches wide 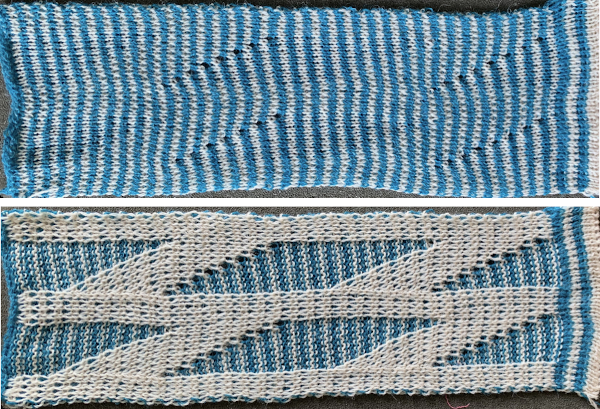 The inspiration sweater was knit using a wider repeat and significantly thicker yarn, reflected here in the small number of repeats composing the sweater body front
The inspiration sweater was knit using a wider repeat and significantly thicker yarn, reflected here in the small number of repeats composing the sweater body front 
 The off white yarn used here was the same thickness but not fiber content as in the previous swatch, 2/18 wool-silk vs Australian wool in the former. It is not as smoothly spun. The result shows an interesting similarity in length, though there are 16 additional rows in the pattern repeat. This time I programmed my repeat for stitch transfers on the knit bed to move away from the color changer.
The off white yarn used here was the same thickness but not fiber content as in the previous swatch, 2/18 wool-silk vs Australian wool in the former. It is not as smoothly spun. The result shows an interesting similarity in length, though there are 16 additional rows in the pattern repeat. This time I programmed my repeat for stitch transfers on the knit bed to move away from the color changer.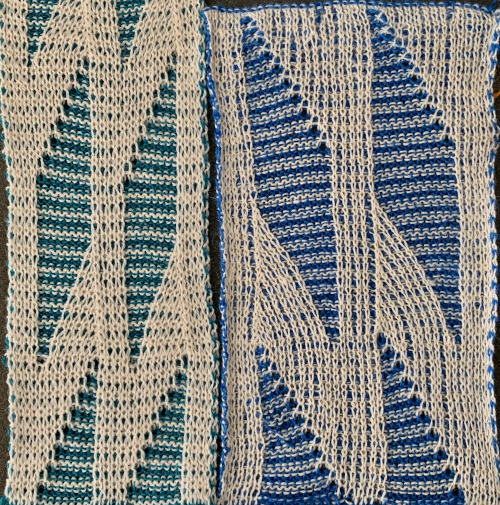  Eliminating the border on one side, a double repeat (30 stitches) measure 4 inches in width. To put the difference in scale to the sweater in perspective, an oversize garment with 40 inches in chest diameter would require 20 inches in width for the front piece. Ten single repeats, as opposed to the inspiration’s sweater 4, bring the total required the number of stitches to 150. With the added border of 5 stitches for matching side edges, the fabric is in the realm of possibility for producing a garment on the home knitting machine. My tension was set at 3/3 for all the swatches, with some teasing required on occasion to encourage stitches on the main bed to knit off properly. Ribber height adjustment can also have an effect on those numbers. I tend to do all my knitting with the slide lever in the center position. The double 30X84 repeat with no added border
Eliminating the border on one side, a double repeat (30 stitches) measure 4 inches in width. To put the difference in scale to the sweater in perspective, an oversize garment with 40 inches in chest diameter would require 20 inches in width for the front piece. Ten single repeats, as opposed to the inspiration’s sweater 4, bring the total required the number of stitches to 150. With the added border of 5 stitches for matching side edges, the fabric is in the realm of possibility for producing a garment on the home knitting machine. My tension was set at 3/3 for all the swatches, with some teasing required on occasion to encourage stitches on the main bed to knit off properly. Ribber height adjustment can also have an effect on those numbers. I tend to do all my knitting with the slide lever in the center position. The double 30X84 repeat with no added border


 There have previous posts on automated lace edging on Brother machines, ie
There have previous posts on automated lace edging on Brother machines, ie 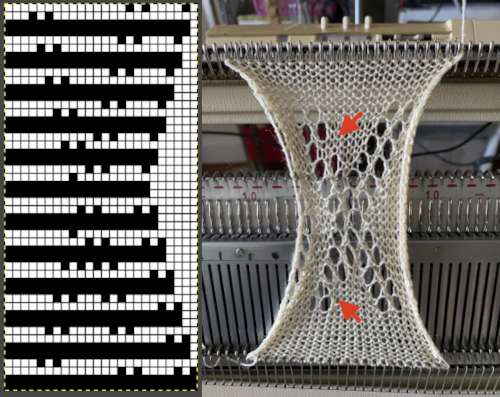
 Here the same pattern was executed on the same number of stitches with the white wool used above, but the elastic was plied with a 2/24 acrylic yarn and knit as DBJ with the blue, stretchy combination creating the solid color backing.
Here the same pattern was executed on the same number of stitches with the white wool used above, but the elastic was plied with a 2/24 acrylic yarn and knit as DBJ with the blue, stretchy combination creating the solid color backing. 
 The same pattern repeat knit with striper backing is far less interesting
The same pattern repeat knit with striper backing is far less interesting 


 The appearance of the fabric when stretched and weighted, still between the beds
The appearance of the fabric when stretched and weighted, still between the beds  and off
and off  Going the far more traditional route of traditional dbj with the use of the color changer, striper backing with the ribber set to N/N yields a wider, flatter fabric with an interesting purl side
Going the far more traditional route of traditional dbj with the use of the color changer, striper backing with the ribber set to N/N yields a wider, flatter fabric with an interesting purl side 
 The birdseye version had more of a bent on
The birdseye version had more of a bent on

 Adding a third ply of elastic was disastrous at any tension. Better results occurred simply by increasing the ribber tension by 2 whole numbers, the knit tension by 1, and reverting to the previous yarn usage. There is a single dropped stitch in the elastic, and the result has much more of a 3D effect.
Adding a third ply of elastic was disastrous at any tension. Better results occurred simply by increasing the ribber tension by 2 whole numbers, the knit tension by 1, and reverting to the previous yarn usage. There is a single dropped stitch in the elastic, and the result has much more of a 3D effect. 


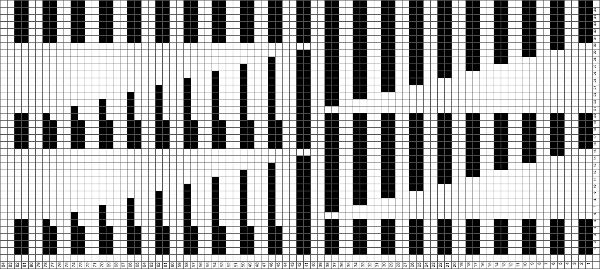
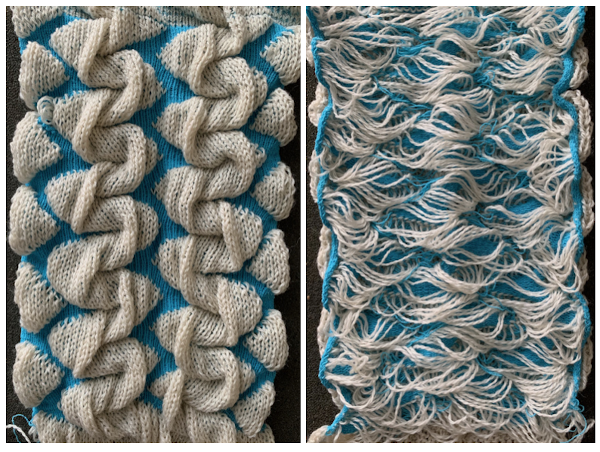
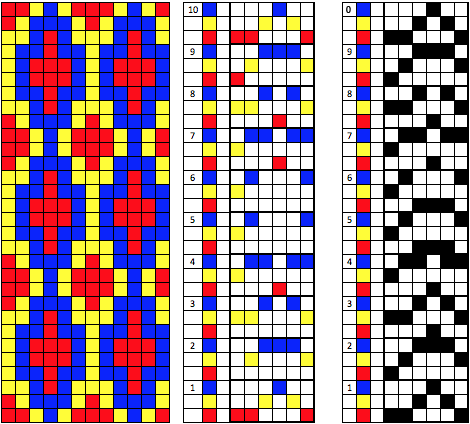
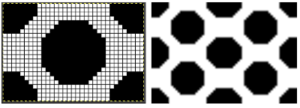 Increments in height need to happen at sequences of 2 rows each, so the design was then doubled in height, resulting in a scaled image now 33 stitches by 46 rows in height, with a planned horizontal repeat X2 = 66. Note: the sidebar offers start and end needles are given for pattern placement on the needle bed. Sampling may occur on fewer stitches than that. Since the number of repeats programmed to add up to an even number and center alignment is chosen, the number of needles is even on each side of 0.
Increments in height need to happen at sequences of 2 rows each, so the design was then doubled in height, resulting in a scaled image now 33 stitches by 46 rows in height, with a planned horizontal repeat X2 = 66. Note: the sidebar offers start and end needles are given for pattern placement on the needle bed. Sampling may occur on fewer stitches than that. Since the number of repeats programmed to add up to an even number and center alignment is chosen, the number of needles is even on each side of 0.  In my second series of swatches, I decided to try for a smaller “circular” shape, with the repeat now measuring 15 wide by 20 high, and a planned horizontal repeat X3 = 45. If centered, the software places the odd number of needles on the right-hand side of 0.
In my second series of swatches, I decided to try for a smaller “circular” shape, with the repeat now measuring 15 wide by 20 high, and a planned horizontal repeat X3 = 45. If centered, the software places the odd number of needles on the right-hand side of 0. 

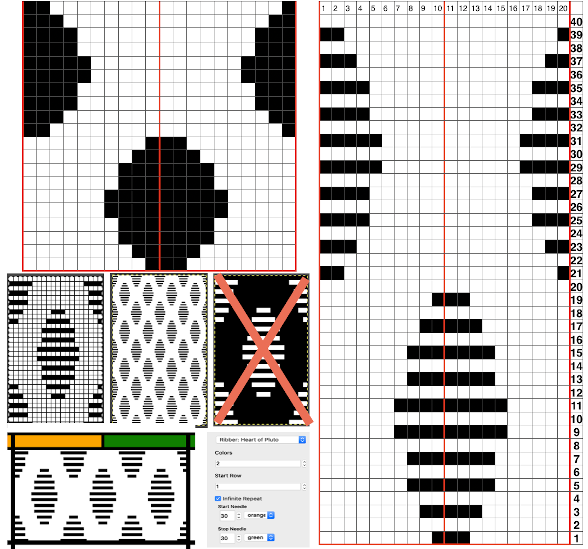
 The wider horizontal band of all knit stitches was due to operator error, happened when I pushed back preselection an extra time, resulting in the ribber only knitting extra rows. For the sake of added clarity, I have added color to the chart below, assigning yellow and grey to all-white design areas in the pattern. The black squares are what I choose to drop. For illustration purposes, this is only a segment of the repeat.
The wider horizontal band of all knit stitches was due to operator error, happened when I pushed back preselection an extra time, resulting in the ribber only knitting extra rows. For the sake of added clarity, I have added color to the chart below, assigning yellow and grey to all-white design areas in the pattern. The black squares are what I choose to drop. For illustration purposes, this is only a segment of the repeat. 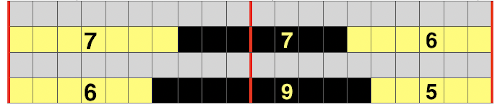



 drop the loops, return needles to B position. At this point, since all needles are in B a modified stitch ditcher may be used for 2 passes, dropping the loops on the first pass and returning the whole series back to B on the second.
drop the loops, return needles to B position. At this point, since all needles are in B a modified stitch ditcher may be used for 2 passes, dropping the loops on the first pass and returning the whole series back to B on the second. 
 COL: push all preselected needles back to B, as you knit back to the right the next group of white squares (yellow) in the next design row will be preselected
COL: push all preselected needles back to B, as you knit back to the right the next group of white squares (yellow) in the next design row will be preselected
 COL: knit to the right in order to form loops on the main bed, continue for the desired number of repeats and end as suggested for the two-color version.
COL: knit to the right in order to form loops on the main bed, continue for the desired number of repeats and end as suggested for the two-color version.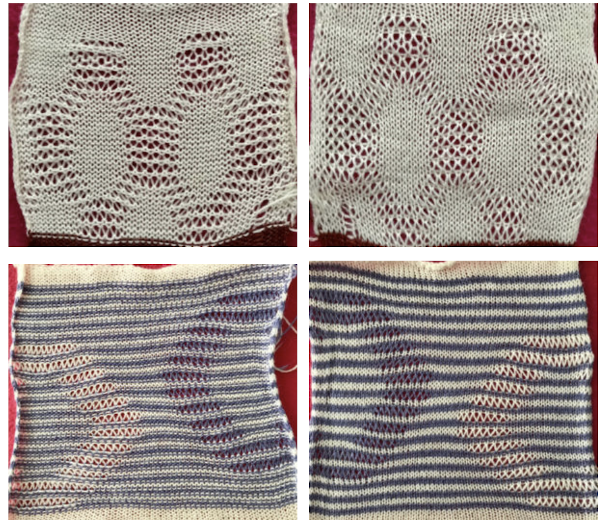




 and its accompanying punchcard repeat:
and its accompanying punchcard repeat: UKI is no longer available. I recently acquired some
UKI is no longer available. I recently acquired some 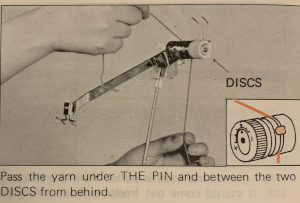 Here the white yarn shows position beneath the pin
Here the white yarn shows position beneath the pin  and scotch tape in place to adjust the amount of pressure exerted on the elastic.
and scotch tape in place to adjust the amount of pressure exerted on the elastic. 
 Thread lace produces a single set of floats (in this case the elastic), the white border is not visible in the repeat below, it is the same as the above fabric, with colors reversed. I prefer the single float backing. In addition, for these fabrics the elastic is placed in the A feeder, the yarn in B
Thread lace produces a single set of floats (in this case the elastic), the white border is not visible in the repeat below, it is the same as the above fabric, with colors reversed. I prefer the single float backing. In addition, for these fabrics the elastic is placed in the A feeder, the yarn in B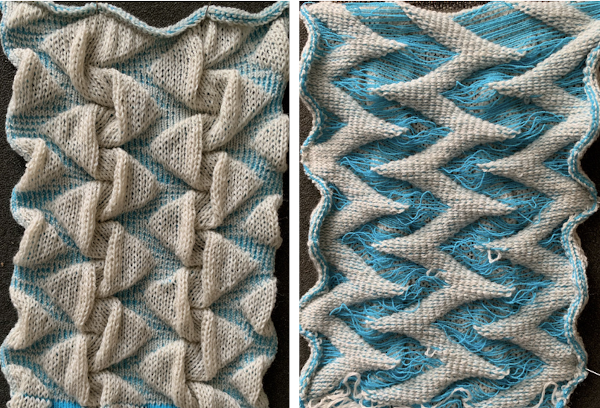
 A second thread lace variation:
A second thread lace variation: The multiple folds and creases, as opposed to smooth blister in all the above, are very interesting to me.
The multiple folds and creases, as opposed to smooth blister in all the above, are very interesting to me.
 The spots, where the elastic and yarn knit together, are compressed, so the results are quite different than what might be expected from studying the chart
The spots, where the elastic and yarn knit together, are compressed, so the results are quite different than what might be expected from studying the chart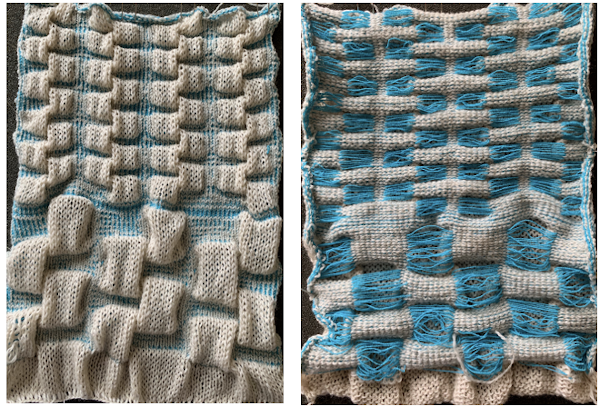  A quick, imperfect sample using a fine cotton and a single strand of the elastic, each with its own upper tension disk adjustments.
A quick, imperfect sample using a fine cotton and a single strand of the elastic, each with its own upper tension disk adjustments.
 I was curious to try a pattern previously tested in an all wool
I was curious to try a pattern previously tested in an all wool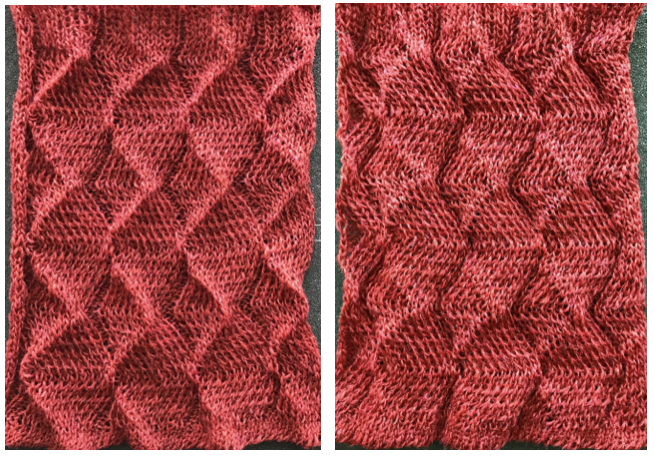



 Working with a similar arrangement I decided to try having patterning on the top bed, with the aim to tuck on the single needles in work in the repeat (bottom line of black squares). Not all ideas are an immediate success. Wanting to see the effect on the single-ply wool I began with that at the tension that appeared to be required for knitting it along with the elastic and stitches were far too loose.
Working with a similar arrangement I decided to try having patterning on the top bed, with the aim to tuck on the single needles in work in the repeat (bottom line of black squares). Not all ideas are an immediate success. Wanting to see the effect on the single-ply wool I began with that at the tension that appeared to be required for knitting it along with the elastic and stitches were far too loose.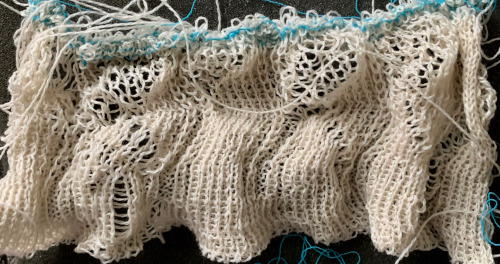 I had more success and a bit better definition of the fabric by knitting with both strands together from the bottom up. In an effort to attempt to have better color distribution I used the plating feeder and had some issues with stitches not knitting off properly. The result was not significantly different than that obtained by simply feeding both yarns together. When using plating feeders both on the single and the double beds one of the yarns may have a tendency to jump out, to prevent that from happening here is one “hack”.
I had more success and a bit better definition of the fabric by knitting with both strands together from the bottom up. In an effort to attempt to have better color distribution I used the plating feeder and had some issues with stitches not knitting off properly. The result was not significantly different than that obtained by simply feeding both yarns together. When using plating feeders both on the single and the double beds one of the yarns may have a tendency to jump out, to prevent that from happening here is one “hack”.

 The same yarn as above, also knit in tuck setting, showing the difference in size and dimension between slip setting on left, tuck on right
The same yarn as above, also knit in tuck setting, showing the difference in size and dimension between slip setting on left, tuck on right  As with any knitting, keeping an eye on what your yarn is doing still matters. Such as this will lead to a series of circumstances that may bring your project to a far earlier end than planned ;-(
As with any knitting, keeping an eye on what your yarn is doing still matters. Such as this will lead to a series of circumstances that may bring your project to a far earlier end than planned ;-( A very last effort at attempting the scales with elastic and wool knit at a far looser tension that in previous tests, ended when elastic broke as a result of above, IMO an unremarkable fabric
A very last effort at attempting the scales with elastic and wool knit at a far looser tension that in previous tests, ended when elastic broke as a result of above, IMO an unremarkable fabric  For more swatches and information see post on
For more swatches and information see post on 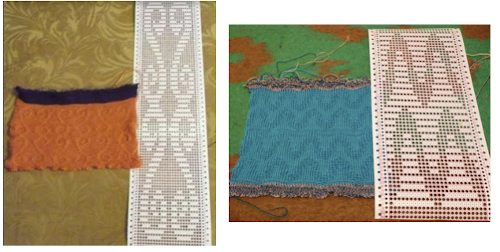
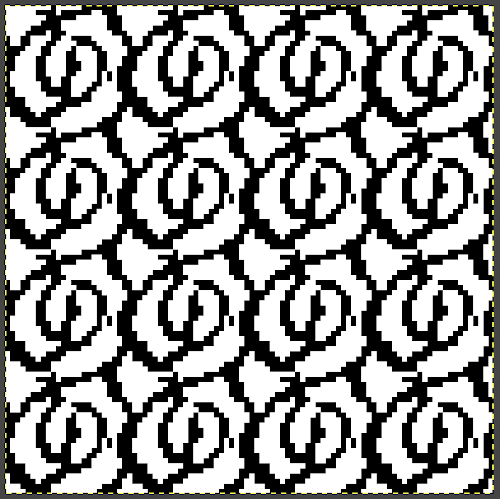





 The “striped” repeat produces essentially the same fabric. The knit carriage may be set to slip in both directions when using it since the row of all punched holes or black pixels will knit every stitch on every needle selected while in the previous samples the cam button set to knit in one direction performed that function regardless of any markings on the design repeat. The ribber is set to knit in one direction, slip in the other. Reversing sides for cam button settings produces the same fabric
The “striped” repeat produces essentially the same fabric. The knit carriage may be set to slip in both directions when using it since the row of all punched holes or black pixels will knit every stitch on every needle selected while in the previous samples the cam button set to knit in one direction performed that function regardless of any markings on the design repeat. The ribber is set to knit in one direction, slip in the other. Reversing sides for cam button settings produces the same fabric 

 The
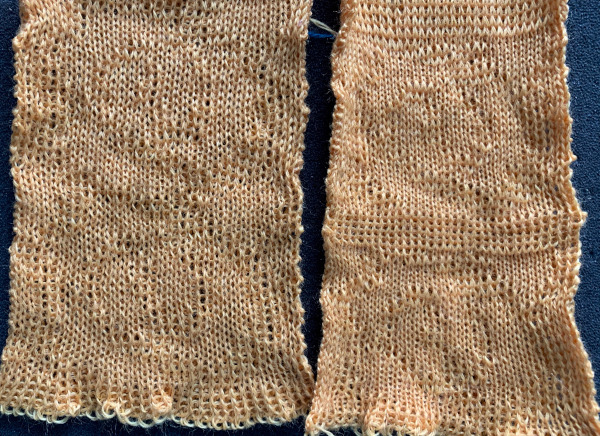
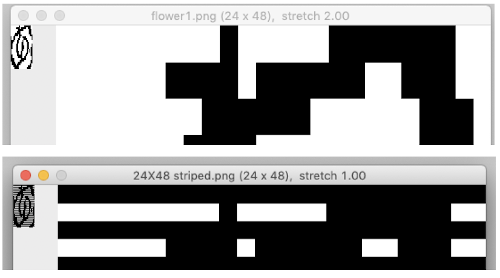
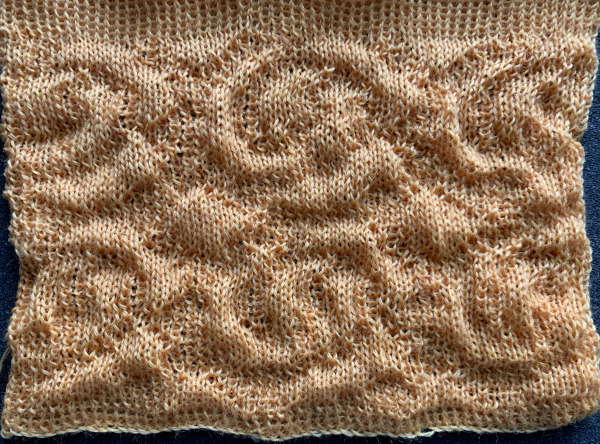
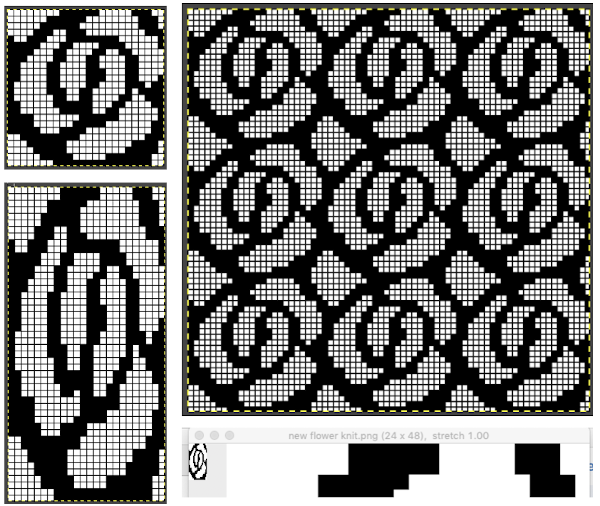
The  The repeat I chose is designated as suitable for the Garter Carriage. It is 24 stitches wide by 48 rows high, shown below as provided, charted in Gimp as .png for download, and tiled to help visualize how continuous repeats might line up. The image .png was downloaded with img2track to my 930, with a stretch factor of 1.0, retaining the original repeat size
The repeat I chose is designated as suitable for the Garter Carriage. It is 24 stitches wide by 48 rows high, shown below as provided, charted in Gimp as .png for download, and tiled to help visualize how continuous repeats might line up. The image .png was downloaded with img2track to my 930, with a stretch factor of 1.0, retaining the original repeat size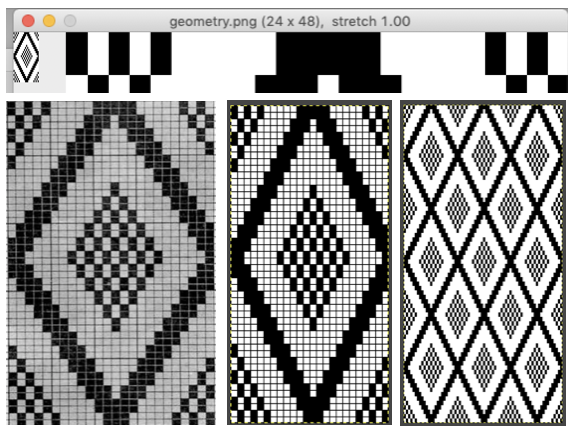




 The design is automatically flipped vertically, so it will appear as intended on the knit side of the fabric.
The design is automatically flipped vertically, so it will appear as intended on the knit side of the fabric.

 In the past, I have preferred to elongate the design prior to importing with plans for download rather than to rely on memory for changing settings either in the download program or in the machine itself in future uses of the same design.
In the past, I have preferred to elongate the design prior to importing with plans for download rather than to rely on memory for changing settings either in the download program or in the machine itself in future uses of the same design. 


 The same yarns, tension, the total number of carriage passes, and settings were used showing the difference in aspect ratio between single color per row knitting and the img2track built-in color separation.
The same yarns, tension, the total number of carriage passes, and settings were used showing the difference in aspect ratio between single color per row knitting and the img2track built-in color separation.  The width of both swatches is essentially identical.
The width of both swatches is essentially identical.
 The 930 will provide prompts for the next color to be selected by pushing the matching number button on the color changer, avoiding any confusion in terms of what should be picked up next. img2track will also flip the design horizontally automatically so the image will appear as originally drawn on the knit side. Images are loaded as single motifs, so the change in the selector needs to be made manually for an all-over pattern.
The 930 will provide prompts for the next color to be selected by pushing the matching number button on the color changer, avoiding any confusion in terms of what should be picked up next. img2track will also flip the design horizontally automatically so the image will appear as originally drawn on the knit side. Images are loaded as single motifs, so the change in the selector needs to be made manually for an all-over pattern.
 Obviously a success in terms of the single row for each color reducing elongation of the design shape. While knitting occurs using the same yarns, at the same tensions, there is a clear difference in the length of each stitch on the main bed and their appearance. The reverse. Checking the ribber carriage I noticed on the left side it was set to knit only, not to slip: OOPS!
Obviously a success in terms of the single row for each color reducing elongation of the design shape. While knitting occurs using the same yarns, at the same tensions, there is a clear difference in the length of each stitch on the main bed and their appearance. The reverse. Checking the ribber carriage I noticed on the left side it was set to knit only, not to slip: OOPS!  N is king, so the ribber set as shown is knitting every other needle when moving to the right, but even with lili buttons in use, it knits on every needle when moving back to the left. Every other needle on the ribber will then be knitting for 2 rows as a result. The more knitting on the ribber for each pair of rows, the longer the stitches on the opposite bed. The backing is an interesting variation (half) birdseye. The elongated stitches on the main bed show more of the backing in between their shapes, it is referred to as bleedthrough. In some instances, the result can make the knit surface resemble weaving and its appearance far less familiar in a surprising, pleasant way. Beauty is in the eye of the beholder.
N is king, so the ribber set as shown is knitting every other needle when moving to the right, but even with lili buttons in use, it knits on every needle when moving back to the left. Every other needle on the ribber will then be knitting for 2 rows as a result. The more knitting on the ribber for each pair of rows, the longer the stitches on the opposite bed. The backing is an interesting variation (half) birdseye. The elongated stitches on the main bed show more of the backing in between their shapes, it is referred to as bleedthrough. In some instances, the result can make the knit surface resemble weaving and its appearance far less familiar in a surprising, pleasant way. Beauty is in the eye of the beholder. The images could be replicated as given in a paint program, using only one color for the squares, but “should be reduced to black and white”. Attempting to import an indexed 2-color image drawn in a color other than BW may result in strange results.
The images could be replicated as given in a paint program, using only one color for the squares, but “should be reduced to black and white”. Attempting to import an indexed 2-color image drawn in a color other than BW may result in strange results.  That said, if glitched knits are the goal, the above could work just fine. Curiously, here is the same process, using a different color, and a successful import. Checking again, I had forgotten to save the image after indexing it from RGB mode to 2 colors.
That said, if glitched knits are the goal, the above could work just fine. Curiously, here is the same process, using a different color, and a successful import. Checking again, I had forgotten to save the image after indexing it from RGB mode to 2 colors. 


 Note to self: if you are determined to use a punchcard carriage on your electronic machine remember there is no KCII to cancel end needle selection!
Note to self: if you are determined to use a punchcard carriage on your electronic machine remember there is no KCII to cancel end needle selection!

 Getting that first row to knit twice instead of a single time if that matters in your technique or is your preference:
Getting that first row to knit twice instead of a single time if that matters in your technique or is your preference:
 pick up color 1 in yarn changer
pick up color 1 in yarn changer If black and white repeats are already in your library, one may easily recycle them adding a third color. Here I did so with a repeat intended for a very different topic in future posts. The image was altered and tiled in Gimp for a repeat alignment test and is also shown imported into img2track for possible knitting.
If black and white repeats are already in your library, one may easily recycle them adding a third color. Here I did so with a repeat intended for a very different topic in future posts. The image was altered and tiled in Gimp for a repeat alignment test and is also shown imported into img2track for possible knitting. 
 The image of the separation on the above right has not been proofed for accuracy. If it were, the next step would be to elongate it X 2 for color changes every 2 rows. One method is to elongate the original in a paint or photo processing program. The width is fixed (40), the height is scaled X 2. The resulting BW indexed image may be imported, using a 1.0 stretch factor, it remains unchanged. When I tried to elongate the unstretched image in img2track by 2.0 my first try failed. It turned out the reason was I had saved the import without first indexing it to 2 colors. With that corrected, the result matched the one from scaling X 2 in height in the paint program
The image of the separation on the above right has not been proofed for accuracy. If it were, the next step would be to elongate it X 2 for color changes every 2 rows. One method is to elongate the original in a paint or photo processing program. The width is fixed (40), the height is scaled X 2. The resulting BW indexed image may be imported, using a 1.0 stretch factor, it remains unchanged. When I tried to elongate the unstretched image in img2track by 2.0 my first try failed. It turned out the reason was I had saved the import without first indexing it to 2 colors. With that corrected, the result matched the one from scaling X 2 in height in the paint program

 Here the image is scaled properly for each color represented for a single row in height and also scaled again for double height for possible knitting in Gimp. The Gimp scaling failed to be accurate for me (second image from left) until I indexed the original to 4 colors as well instead of 3. The no-color rows as we view them serve as a fourth color in the separations. Importing the proper size PNG into img2track for the separation of 4 colors per row now gives results that make sense: note the daunting estimate for the total number of carriage passes for a single repeat height
Here the image is scaled properly for each color represented for a single row in height and also scaled again for double height for possible knitting in Gimp. The Gimp scaling failed to be accurate for me (second image from left) until I indexed the original to 4 colors as well instead of 3. The no-color rows as we view them serve as a fourth color in the separations. Importing the proper size PNG into img2track for the separation of 4 colors per row now gives results that make sense: note the daunting estimate for the total number of carriage passes for a single repeat height If the ribber has knit on every needle by its return to the color changer and the machine is set to slip both ways with no needle selection on the main bed, the “no color” can be executed as an empty yarn holder in the color changer combined with no yarn in the feeder. The rows involved should simply not knit on the top bed, with no dropping of any of its stitches since no needles will have been selected thus coming forward with the yarn in the hooks and traveling behind the latches and in turn, slipping off the needles as a carriage with no yarn pushes the needles with now empty hooks back to B position.
If the ribber has knit on every needle by its return to the color changer and the machine is set to slip both ways with no needle selection on the main bed, the “no color” can be executed as an empty yarn holder in the color changer combined with no yarn in the feeder. The rows involved should simply not knit on the top bed, with no dropping of any of its stitches since no needles will have been selected thus coming forward with the yarn in the hooks and traveling behind the latches and in turn, slipping off the needles as a carriage with no yarn pushes the needles with now empty hooks back to B position.

 Punchcard knitters may have the easiest knitting variable color sequences since cards may be visually marked up with colored pencils matching needed change locations and taking into account your eyes are several rows above the row being read by the card reader. This number depends on the machine’s brand and model.
Punchcard knitters may have the easiest knitting variable color sequences since cards may be visually marked up with colored pencils matching needed change locations and taking into account your eyes are several rows above the row being read by the card reader. This number depends on the machine’s brand and model.
 the initial method:
the initial method:




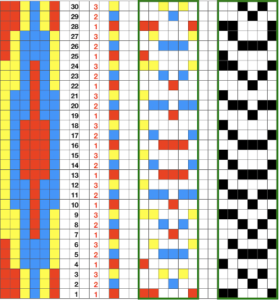 following that up, I planned for the 60 rows needed to complete the repeat, hid 30 rows, using this menu
following that up, I planned for the 60 rows needed to complete the repeat, hid 30 rows, using this menu copied and pasted the black and white repeat on the above right, then unhid the 30 hidden rows (see previous posts using command key selections), having a new color separation repeat, created the final 2 color BMP in Gimp (whew!)
copied and pasted the black and white repeat on the above right, then unhid the 30 hidden rows (see previous posts using command key selections), having a new color separation repeat, created the final 2 color BMP in Gimp (whew!)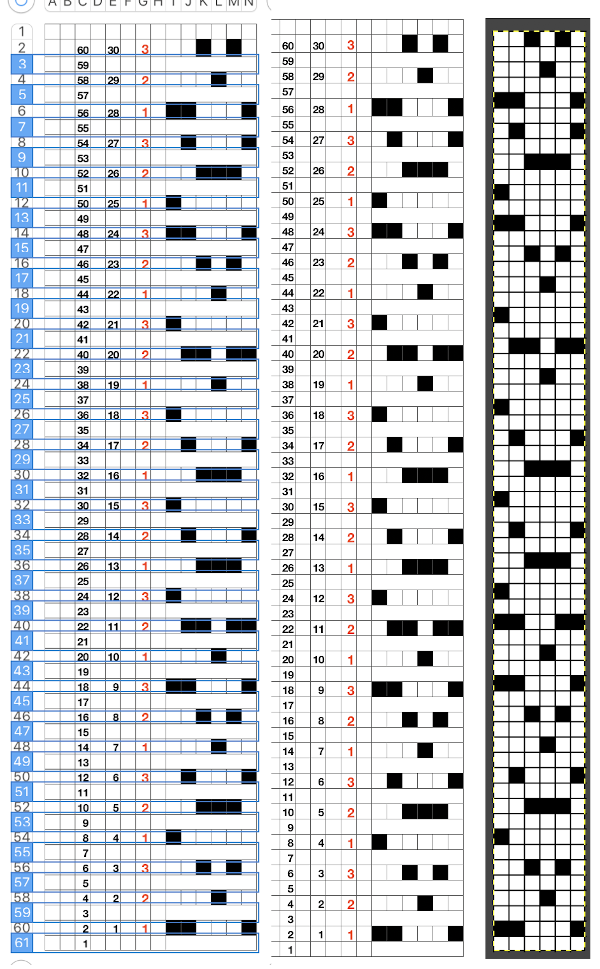 Since my separation is planned on 2-row sequences, I began with COR and my preselection row was from right to left.
Since my separation is planned on 2-row sequences, I began with COR and my preselection row was from right to left. 
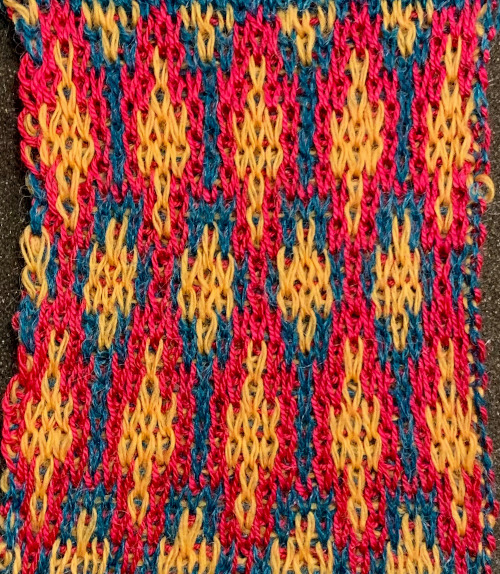
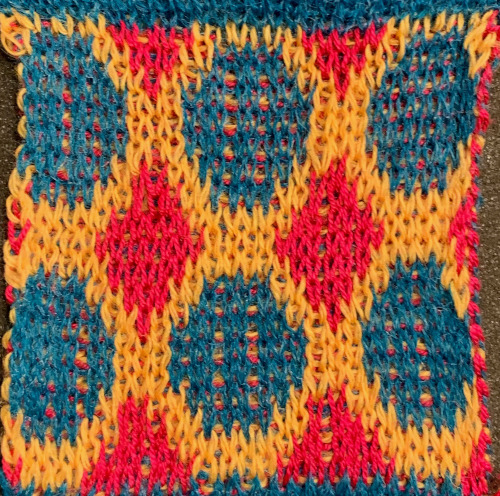


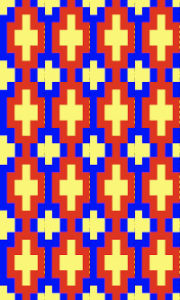

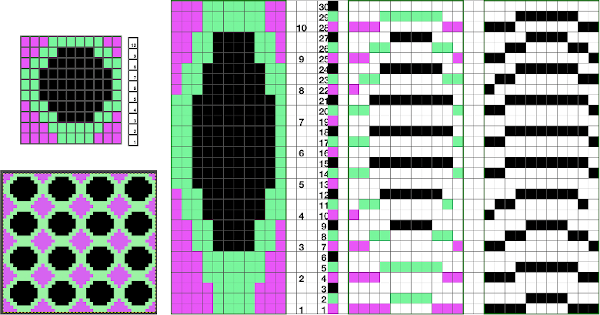

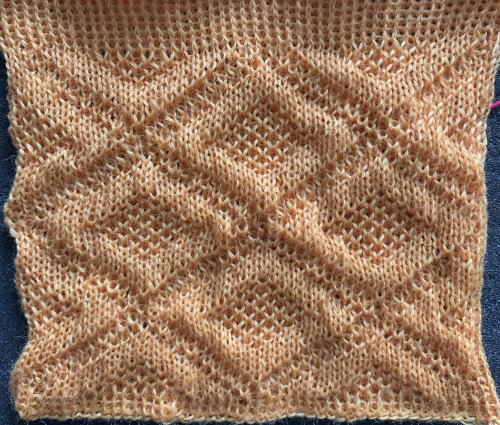
 Again, there is some bleed-through, and even with this technique there is some elongation of each of the shapes, but less so than with other techniques. The backing of all these fabrics produces single lines in each color used
Again, there is some bleed-through, and even with this technique there is some elongation of each of the shapes, but less so than with other techniques. The backing of all these fabrics produces single lines in each color used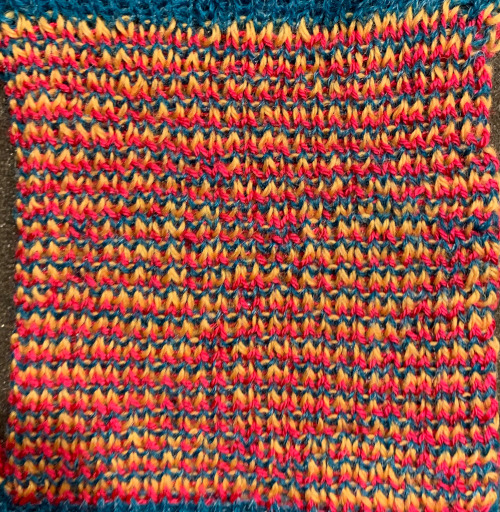  Even fairly small repeats can take time to color separate in this manner. The technique, however, is the only method available to punchcard knitters. Electronic machines with download cables and varying software open a very different world in terms of ease and range in repeat size possibilities.
Even fairly small repeats can take time to color separate in this manner. The technique, however, is the only method available to punchcard knitters. Electronic machines with download cables and varying software open a very different world in terms of ease and range in repeat size possibilities.