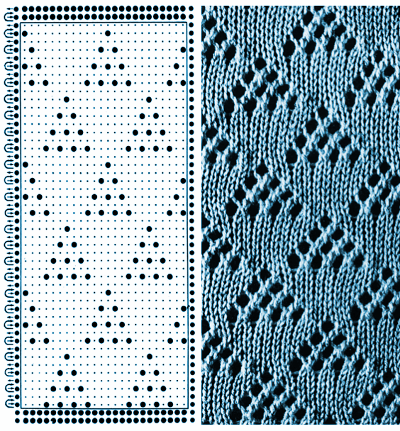
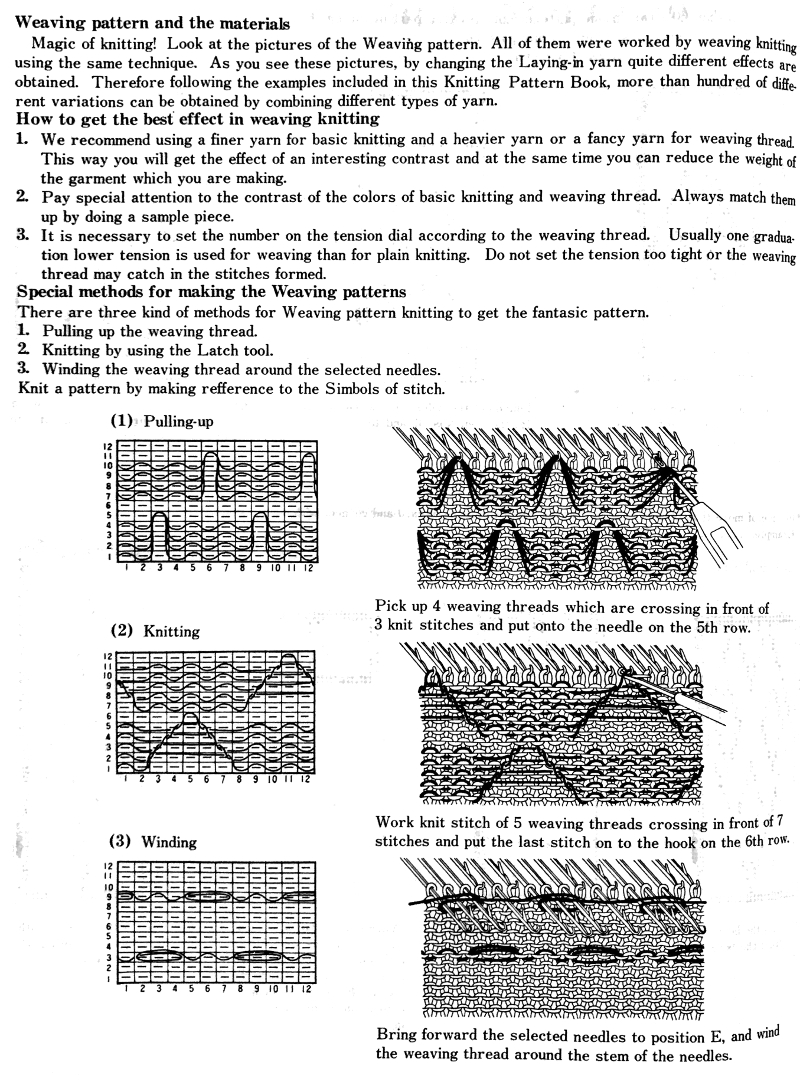
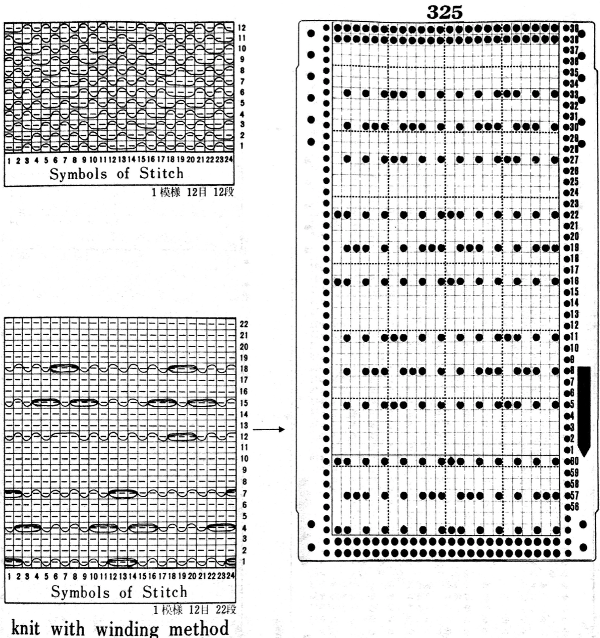
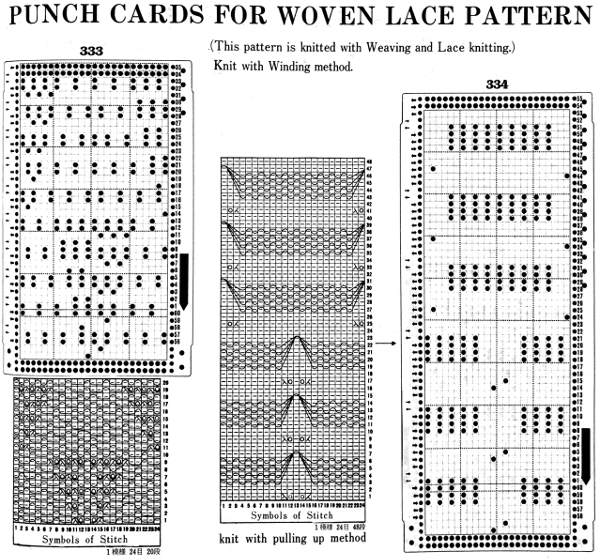
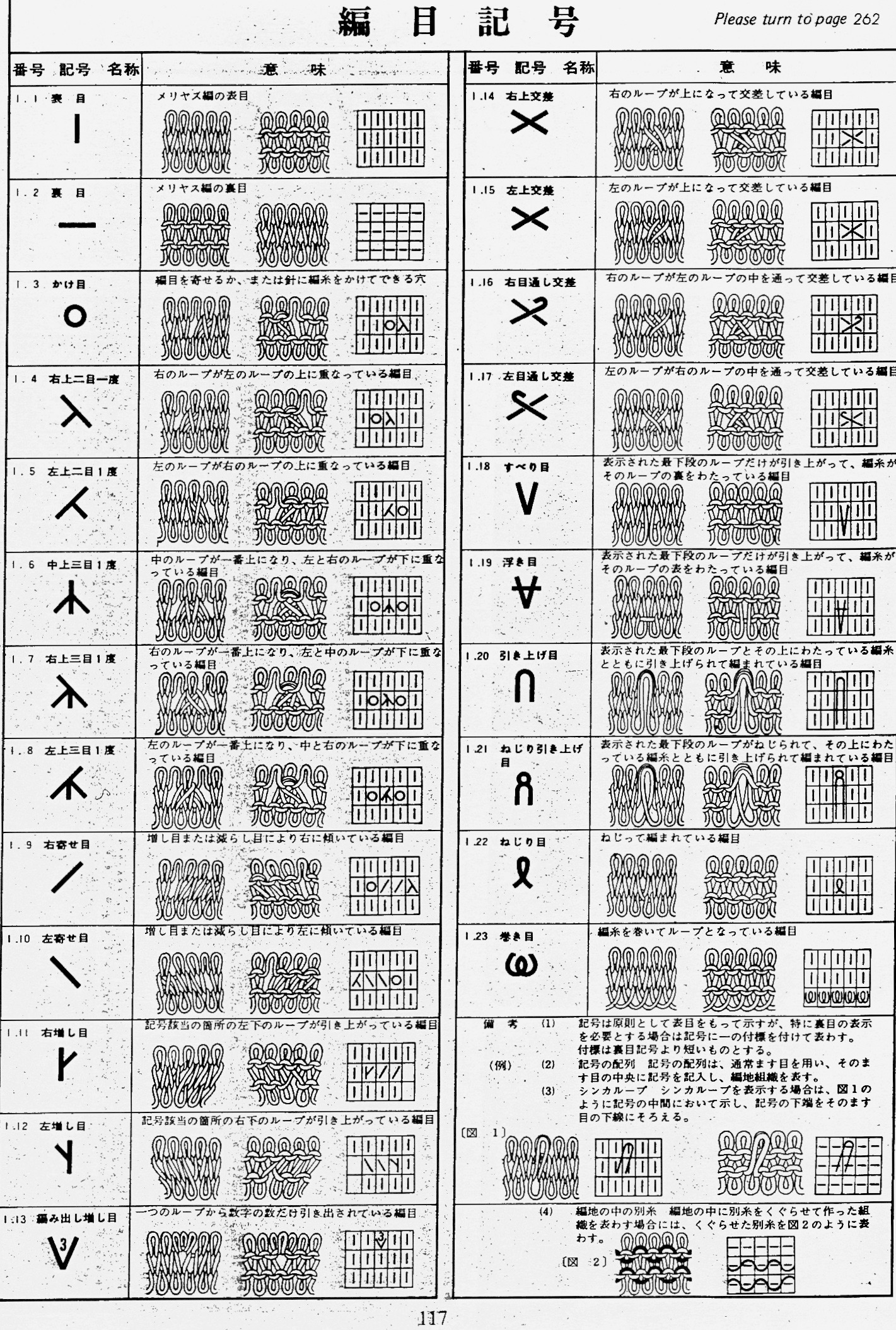
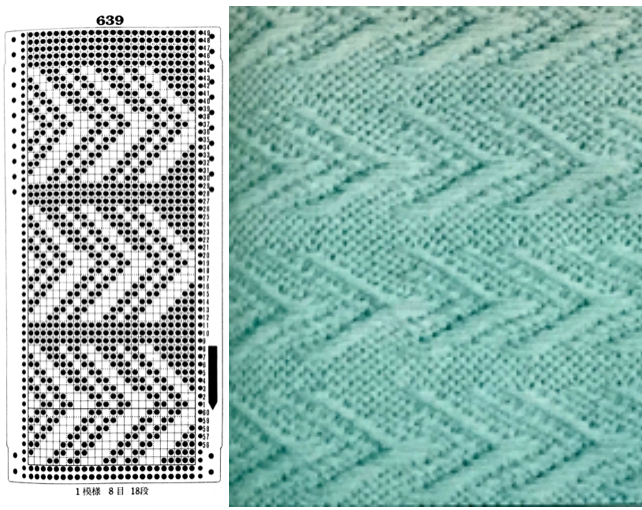
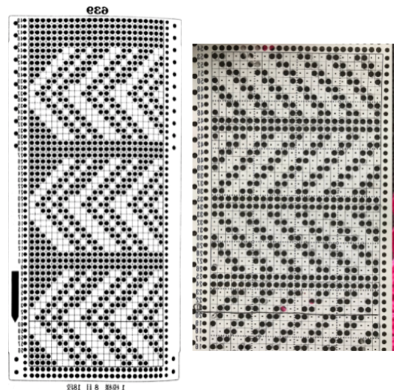
Some notes on how tubular software color separations such as the one automated in the ayab circular setting may be found in the previous post
In an effort to respond to a request I have had via my blog, I am sharing information on this topic as I have time to explore it. My first attempt when up and running with the Ayab software, was to reproduce an earlier sample I had created as a color separation originally intended for a hand-knit shadow knit experiment.
a chart from that blog post 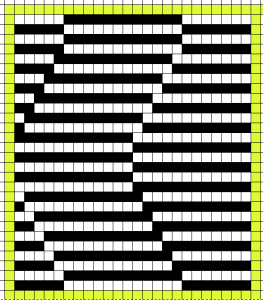 the resulting hand knit, on the purl side
the resulting hand knit, on the purl side
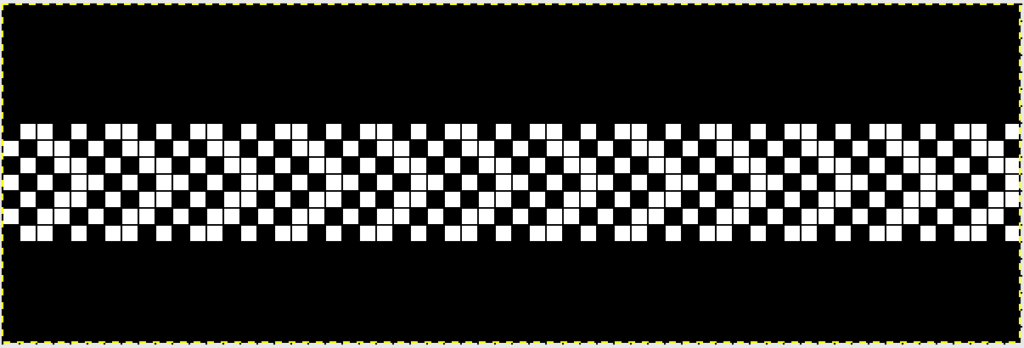
 the color-separated sample knit pre ayab
the color-separated sample knit pre ayab  the sample knit using the Ayab circular setting
the sample knit using the Ayab circular setting

Patterns predawn for shadow knitting, appear to be one published source for interesting 2 color drop stitch variations. What about geometric shapes or developing your own designs? Designs created using this technique lengthen considerably when off the machine. Both color sets of stitches become elongated as they are dropped, and that should be a consideration in planning your design. If your goal is a circle, the actual shape programmed may have to be closer to an egg laid horizontally rather than that of a “true” circle. The fabric also widens considerably when blocked and off the machine, making the cast on and bind off methods considerations another necessity. Design repeats may be drawn in Paintbrush or GIMP (both freeware), or Photoshop. I have been a long time GIMP user, and prefer to use it in tiling repeats as opposed to the copy and paste features in Paintbrush to accommodate the Ayab requirement of programming the repeats horizontally in the width of your piece.
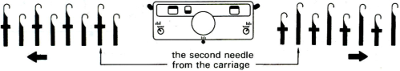
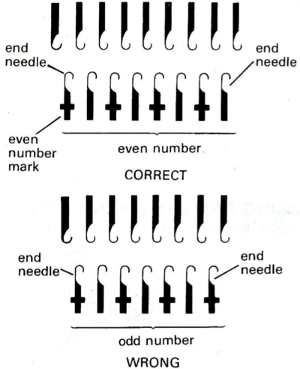
In my previous, how-to posts on designing your own 2 color drop stitch lace, part of the color separation required elongating the design X 2. The starting side in Ayab for needle selection always needs to be from left to right, and elongation of the motif is not required when using the Ayab circular option.
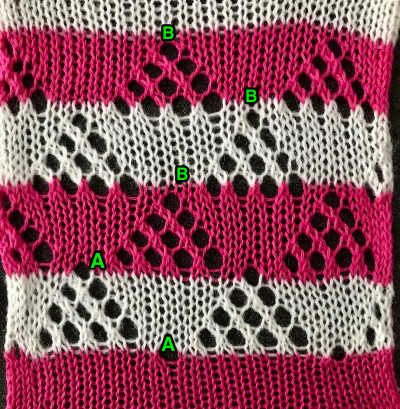
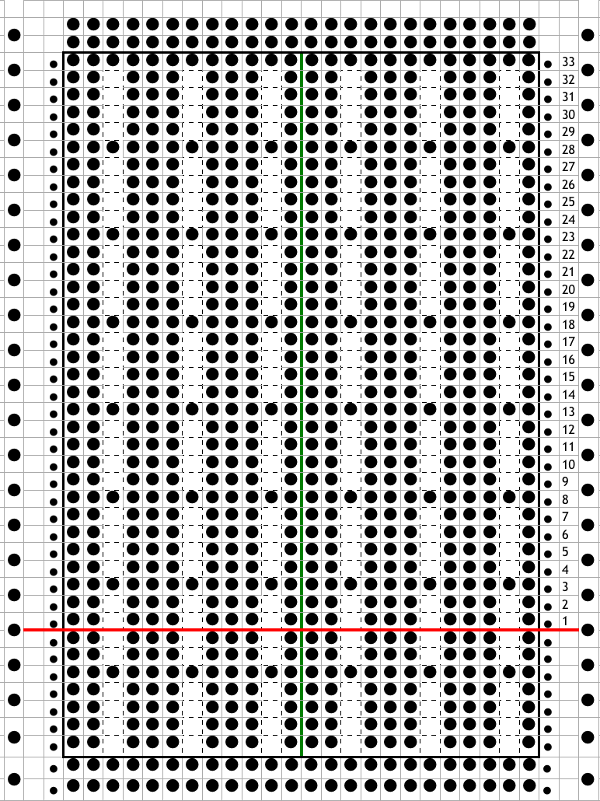
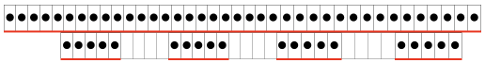
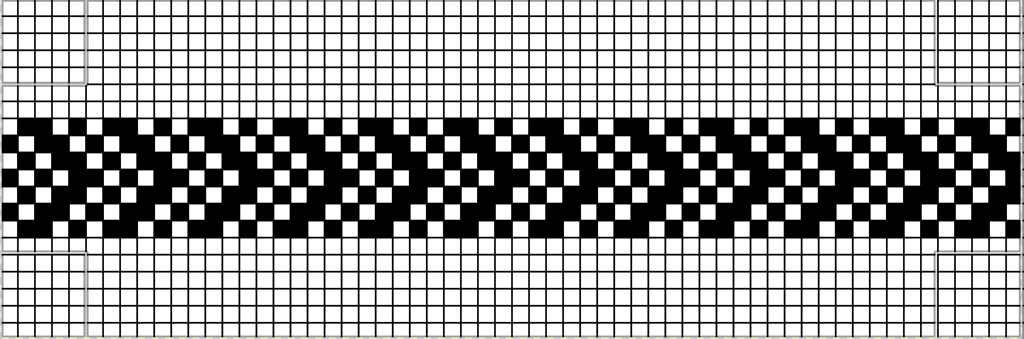
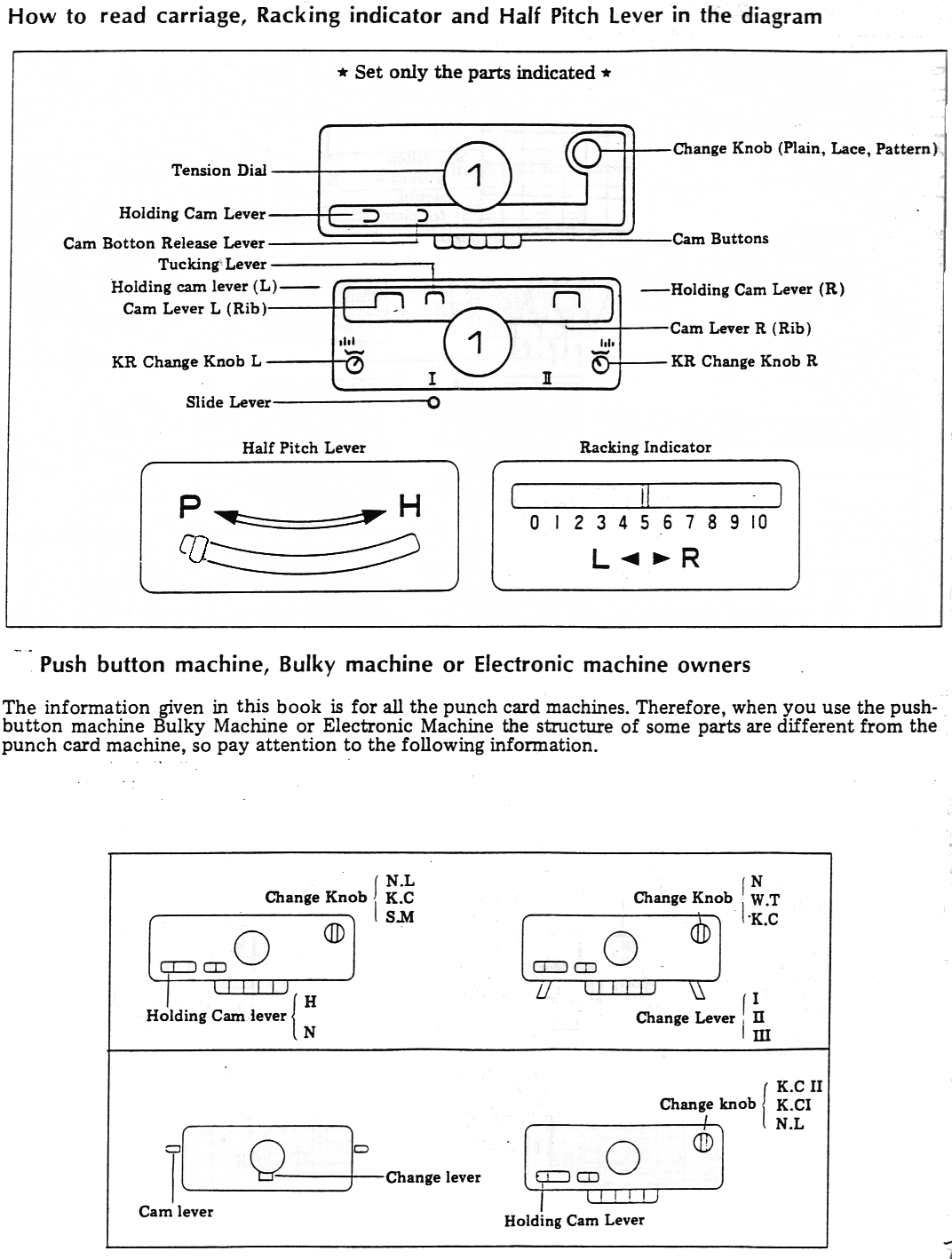
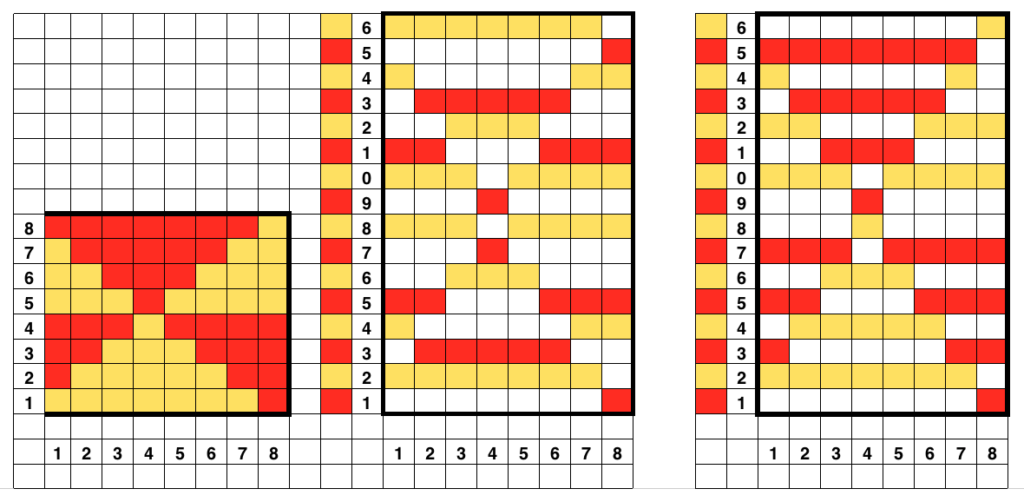
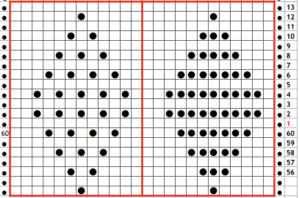
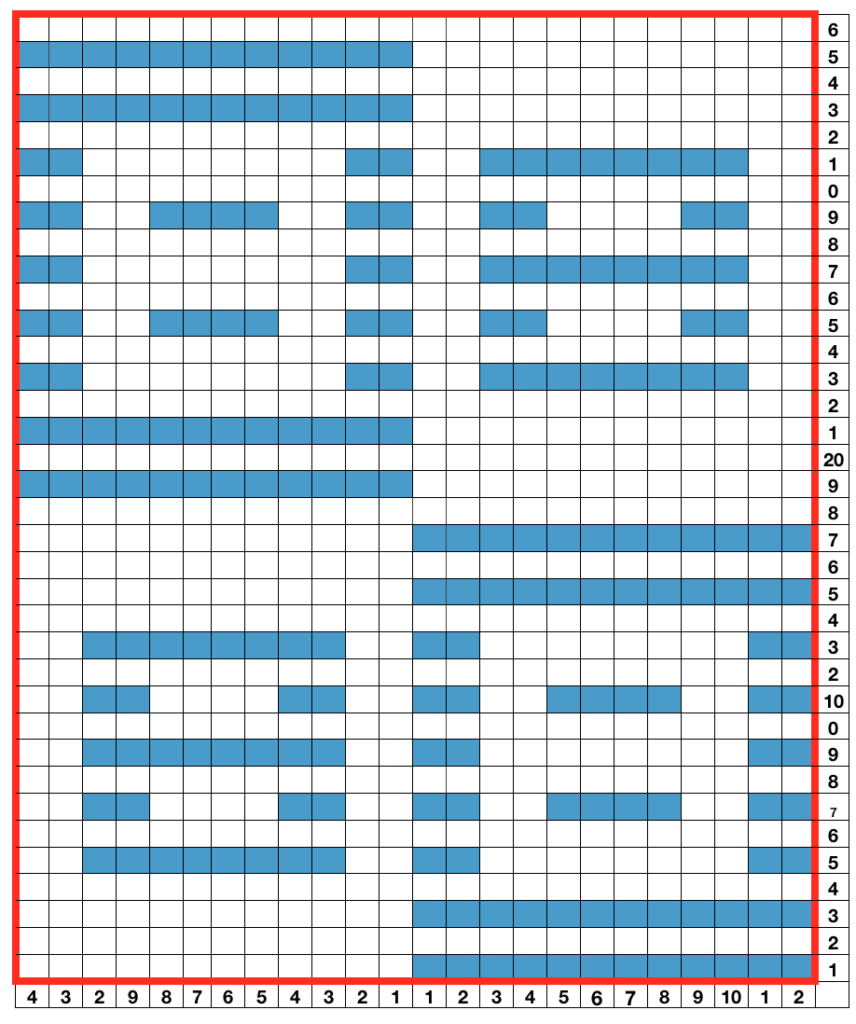
This was my first working repeat, A = repeat charted out. B = the working bitmap or png, etc. (which would be the only requirement for the mylar). C = the image tiled for the chosen number of stitches (again, Ayab requires the repeat to be programmed for the width of your knit piece). D = the image elongated, not usable for this fabric, it results in too much elongation. If you would like a knit border on either side, that can be achieved by having extra stitch(es) in work on the ribber. 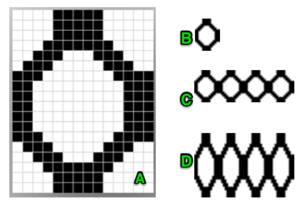 a possible ayab repeat, 56 stitches wide by 36 rows high
a possible ayab repeat, 56 stitches wide by 36 rows high
The results up to the point in which I had a yarn caught in brushes and stitches dropping on the left of the needle bed:
Drop stitch lace has been referred to over the years in other terms as well, such as release stitch, drive lace, and summer fair isle in Passapese. Passap knitters will recognize the results from this first method are akin to those produced using Technique 185.
Getting started: stitches intended to be dropped may be created on either bed. If the ribber is used to create loops, then the technique is a manual one. Using the main bed in Japanese machines to program dropped stitches increases accuracy and ease.
If you are swatching and testing, a permanent cast on is not necessary. The broken toe cast on is one of the two quickest on the Japanese machines, usable on either bed. It is fondly called that because if ribber cast on comb and weights are in the wrong place so that the wrong loops are dropped, everything falls to the floor, and likely on your toes. There is an online video by Diana Sullivan that shows its use for a tighter cast on row in 1X1 rib, but the use here is for a different purpose.
In producing this fabric you are technically knitting every needle rib. 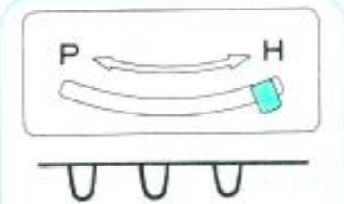 Cast on a fairly tight zig-zag row. The ribber comb wire needs to be placed so that it holds down the stitches on the bed on which you need to keep them. The principle and results are akin to the first row knit when you use a single bed cast on comb, and the second pass, with the first knit row anchors open loops before you continue to knit. Any loops not secured by the comb will result in dropped stitches. Any fabric, any time, when 2 stitches are empty side by side, stitches are not formed and the yarn is dropped off them creating a float or ladder. The red line indicates the ribber wire on top of the ribber loops in the zigzag row, placed so released knitting will be left on the ribber. Black lines your zig-zag yarn loops, blue dots the teeth of your ribber cast on comb. You can check placement by dropping just a few loops on the main bed before hanging your weights on the comb.
Cast on a fairly tight zig-zag row. The ribber comb wire needs to be placed so that it holds down the stitches on the bed on which you need to keep them. The principle and results are akin to the first row knit when you use a single bed cast on comb, and the second pass, with the first knit row anchors open loops before you continue to knit. Any loops not secured by the comb will result in dropped stitches. Any fabric, any time, when 2 stitches are empty side by side, stitches are not formed and the yarn is dropped off them creating a float or ladder. The red line indicates the ribber wire on top of the ribber loops in the zigzag row, placed so released knitting will be left on the ribber. Black lines your zig-zag yarn loops, blue dots the teeth of your ribber cast on comb. You can check placement by dropping just a few loops on the main bed before hanging your weights on the comb. ![]()
zigzag row showing the placement of cast on comb teeth, on each side of main bed needles
 with wire in place, anchoring ribber stitches
with wire in place, anchoring ribber stitches  testing out dropping a few stitches
testing out dropping a few stitches  all stitches now on the ribber in preparation for dropping stitches created on main bed
all stitches now on the ribber in preparation for dropping stitches created on main bed 
It is possible to also use a wired cast-on comb for an open stitch cast on the top bed only. Remove the wire from the comb. Bring the comb up and between needles to be used, and re-insert wire. Needles and latches will need to travel easily under the wire when the first knit row takes place. 
The knit carriage will not clear the comb properly because of the location of its brushes, etc. For the “cast on” row, exchange the sinker plate on your knit carriage for the one normally used with the ribber. The first photo below shows the approximate location for the comb during the first row knit. Needles are centered between the teeth, the teeth themselves line up with gate pegs. The comb needs to be manually held in place since there is no opposing bed in use to help balance it. Working with the ribber up would ease the process in wider pieces of knitting. The ribber sinker plate has no brushes or wheels to anchor knitting on the knitting bed. Any rows knit single bed using it, will need to have needles brought out to hold position prior to knitting each row for all stitches to be formed properly
the comb in position pass is made slowly with the ribber sinker plate in place
pass is made slowly with the ribber sinker plate in place  the comb is dropped
the comb is dropped  bring all needles out to hold position
bring all needles out to hold position  knit one more row, returning to starting position
knit one more row, returning to starting position  change sinker plate on knit carriage if needed, proceed with knitting
change sinker plate on knit carriage if needed, proceed with knitting
To use the same method with ribber in place: hold the appropriate ribber comb with the bump(s) up facing you, so that the teeth line up with gate pegs as shown above, and so the needles can come through the gaps. Leave the wire in, hold the bump(s) against the ribber, and tilt the comb against the knit bed. Hold the comb high enough to take the carriages across to the opposite side. Move carriages to the other side, drop the comb and weigh it. If continuing on the top bed only drop the ribber, switch sinker plates, and continue to knit.
For other purposes and an edge similar to a weaving cast-on executed on Japanese machines use EON for the cast-on row, then bring into work and add the rest of the needles prior to knitting the second row.
Use a cast-on comb appropriate for your knitting machine’s gauge ie 4.5mm, 5mm, etc., the brand is not relevant, only tooth spacing is. It is possible to cut ribber cast on combs into different widths for use when knitting is planned on fewer stitches than those accommodated by their available commercial widths.
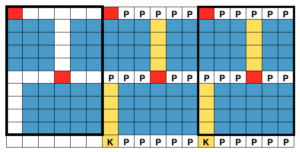
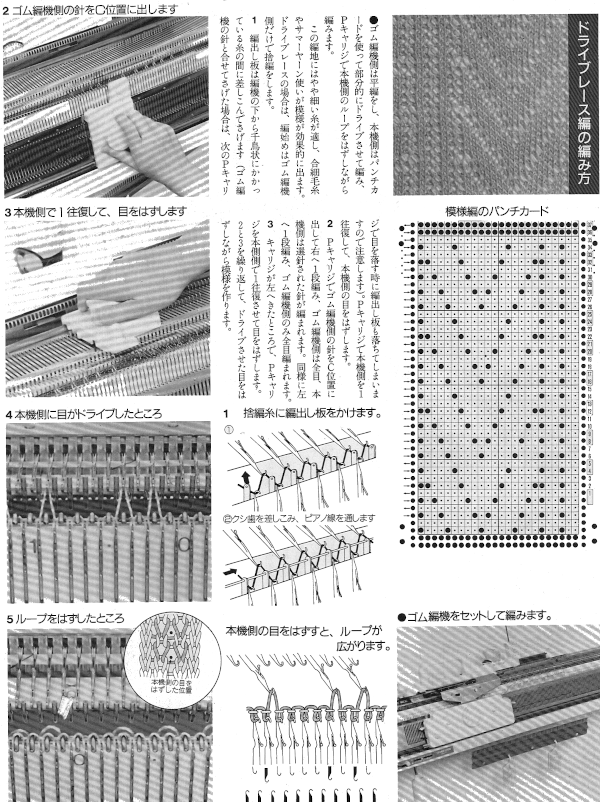
As for dropping those loops that will form the long stitches, one can do so manually with improvised tools. For more automatic dropping of stitches using knit carriage in Brother patterning, one may punch a card or draw a mylar with a method akin to color separation. A pass of the KH carriage across the knit is made with no yarn in the feeder, color 2 is actually no yarn/empty from left to right while establishing the proper needle selection on its return. The ribber would need to be reset to slip, or the ribber carriage separated from the knit one for the 2 passes to and from the color changer. This is the “scariest” option by far, more error-prone. It is not applicable when using the circular Ayab setting in creating the fabric. Without a specific tool, all stitches can be brought to E and back to B with a ruler, piece of garter bar, ribber cast on comb, or other handy ‘toy’. Dropping stitches is done while carriages are on the left, after the return to the color changer side. It is possible to modify the Studio accessory used to drop stitches

For 2 color drop stitch, the main bed is set to slip in both directions. Because not all needles on the main bed are used for patterning on every row, the KC II setting on the change knob is used, eliminating end needle selection on the 910. The ribber is set to knit every row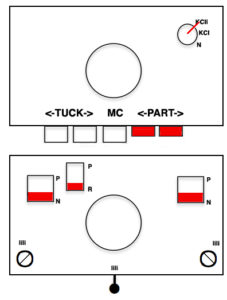
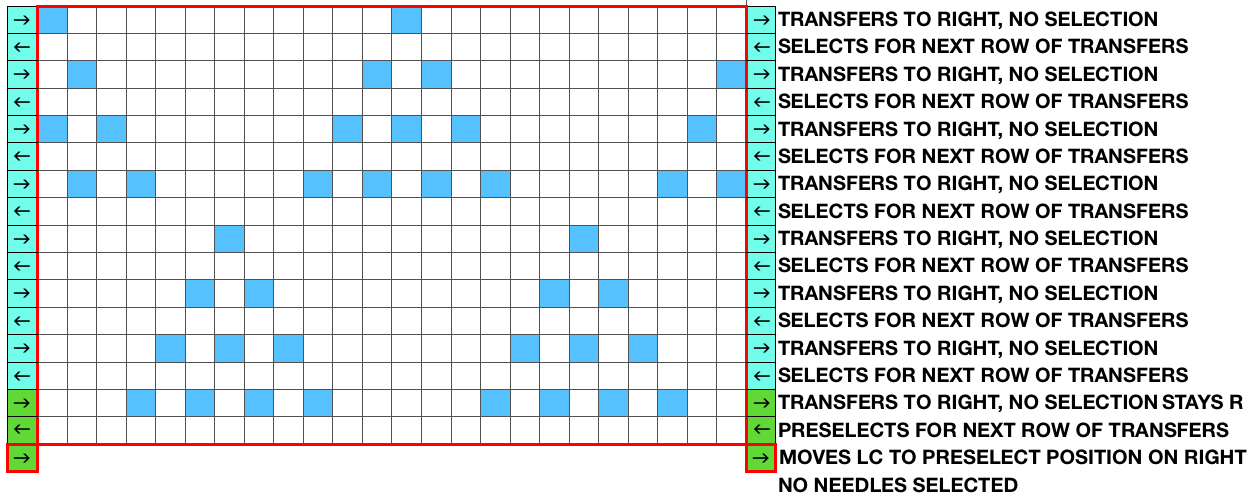
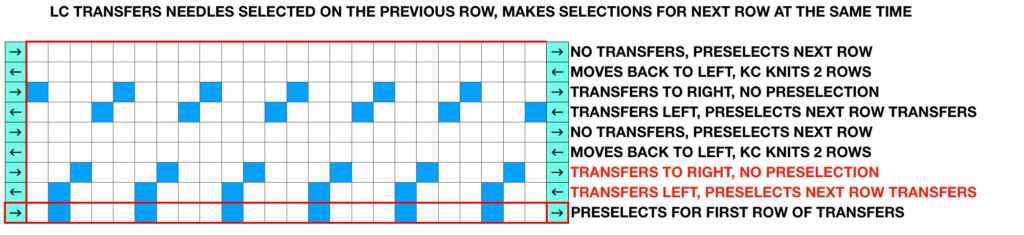
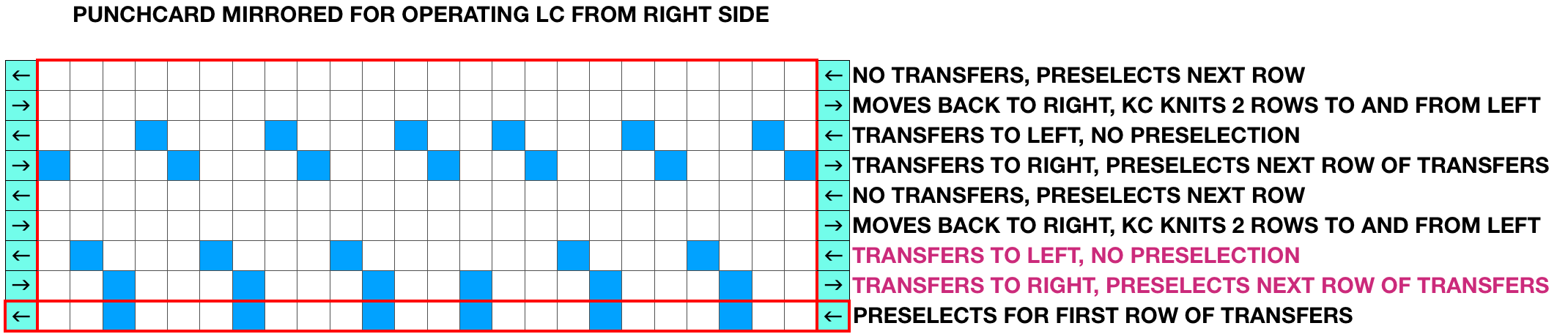
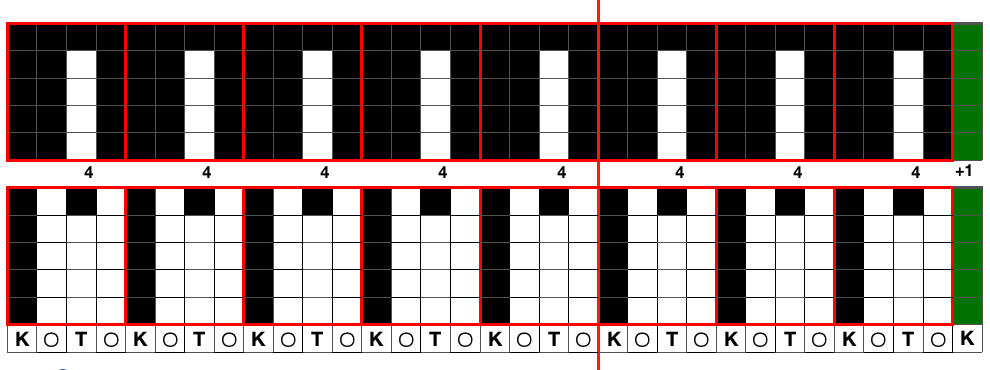
Ayab: begin your design repeat on your first row, choose its circular setting in machine type pull-down menu on the right
The first design row is preselected left to right
The main bed is set to slip <– –>, change knob on KC II (end needle selection is canceled)
Ribber is set to knit <– –> for the duration
COL: as you go from the left to right, needles are preselected on the top bed, they will knit, picking up loops that you will in turn drop on the subsequent passes of the knit carriage from right to left.
COR, the KC knits on preselected needles as it moves to the left.
Clear the color changer, set up your next color. Drop the stitches knit on that last pass
It may be necessary to push those loops down between the beds before you next pass, remember to pull down on your knitting periodically, visually check needle alignment on the main bed (all needles in B in the work area)
*With the new color move to the right, preselecting the next row of loops
Knit right to left, picking up loops on preselected needles, change colors, drop stitches,** and repeat * to ** steps in 2-row rotations
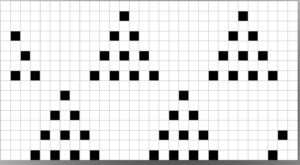
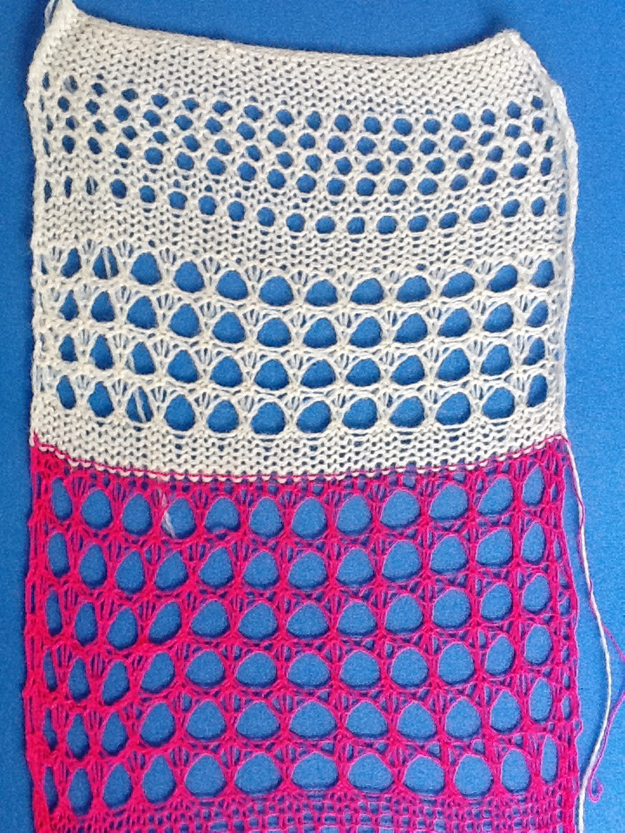
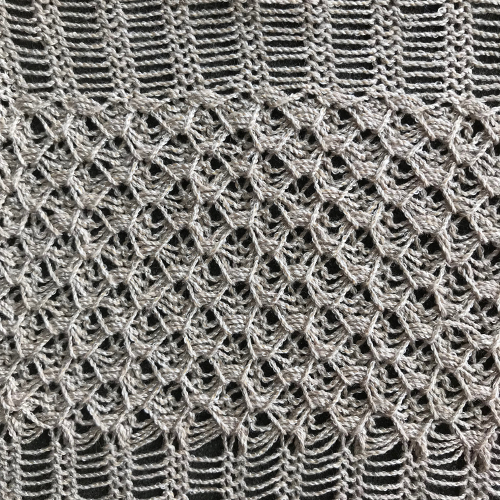
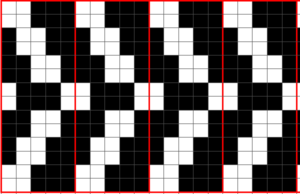
so I want circles, here is my test pattern 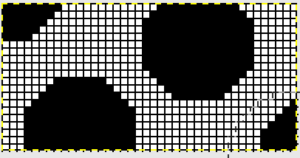 more like eggs, the black squares in shape appear as drawn on the purl side
more like eggs, the black squares in shape appear as drawn on the purl side  shapes are reversed as drawn on the knit side
shapes are reversed as drawn on the knit side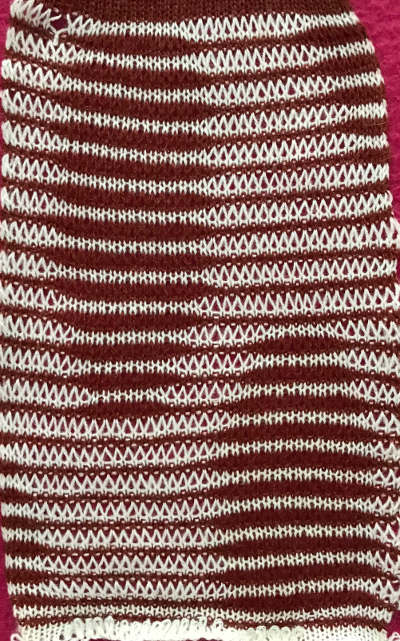 
It is possible using the circular setting to drop only one of the 2 colors, whether background or shape. I began by dropping the white ground. I used to encourage students to develop a tune/ repeat in their heads when regular actions needed to be taken. For me, in terms of yarn color, it was “white, knit, drop”, “brown = erase (push back to B), go back”. 1: white travels to the right, needles are pre-selected; 2: white travels to left, picking up loops 3: on left, change color, drop stitches. For brown: 1. travel to the right, needles are preselected 2: on the right, before traveling back to left push all selected needles back to B. Only the ribber knits on the way back to left, so brown will have knit 2 rows with no dropped stitches. I ran out of brown yarn, started over with the blue and white, planning on having the shape drop the stitches. There is a difference in the fabric width with the change in the distribution of stitches. I stopped knitting, not due to any mispatterning, but because I encountered another Ayab behavior that may be well known to punchcard knitters. Due to a yarn mast issue, I moved the knit carriage back to disentangle the yarn, and lo and behold the pattern advanced a row. Punchcard machines will advance a row with any movement of the carriage outside the edges of the knit. This was never an issue in the unaltered 910. At that point, I stopped knitting.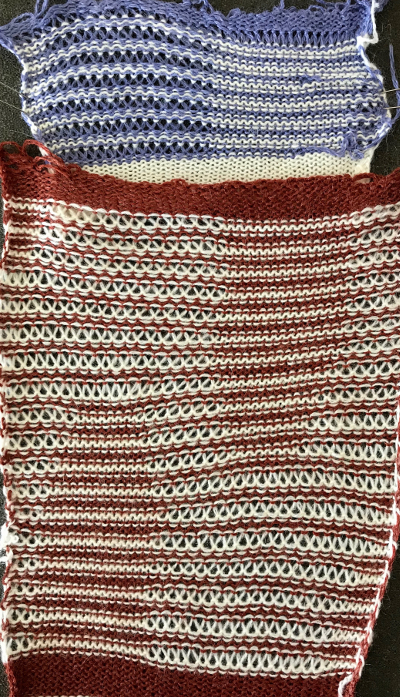 
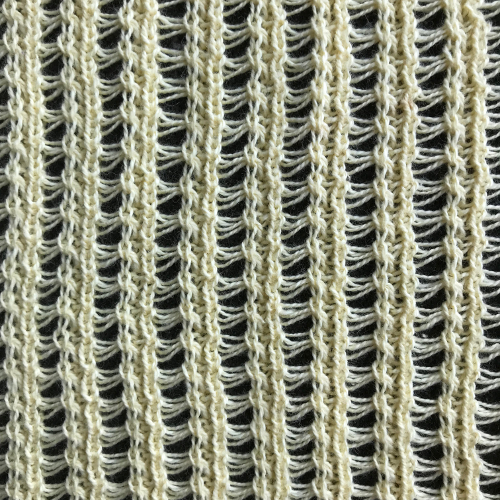
Not fond of stripes? prefer one color? the sample below was worked on 40 stitches in width, using the repeat charted for 56 stitches. Here decisions are made at the design phase of your repeat. For single color, drop stitch use an image double length, and single setting in the Ayab software. The process is the same: *preselect stitches left to right, knit on selected needles right to left, drop loops just picked up traveling to left**, repeat from * to **. Settings are the same as for the 2 color drop stitch, but the elongation depending on the number of stitches dropped is not as noticeable. The texture in my swatch is diminished after a quick press, the yarn is an acrylic blend. The charted repeat illustrated is wider, but I worked it on only the center 40 stitches. As always in slip stitch, the black squares knit and they represent the stitches that are dropped. If you wish to create the long stitches on the ground (white squares), reverse use Ayab Action Invert prior to knitting
the chart as viewed and explained at the top of the post



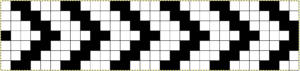
Sources of inspiration from studio publications vary, patterns designed for pile knitting make for suitable one color drop stitch. A partial punchcard repeat
and a punchcard pattern book, where markings emulate eyelets, usable only for single color knitting
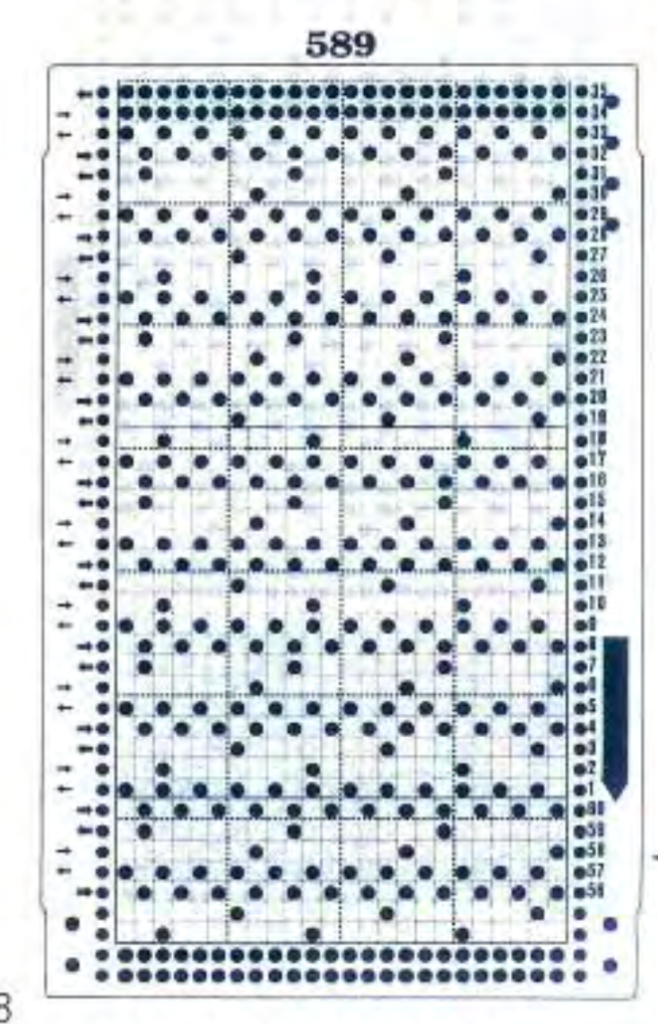
Note that in #2 card directly above, there is a solid row at the very start that is a design row (third all punched). In Ayab again, first-row preselection is left to right, you will be picking up loops on preselected needles going from right to left and then dropping them. That first design row needs to have punched holes or black squares/pixels in it. The color separation is essentially done for you in the source image. Do not use circular in Ayab, but rather, use “single” setting and follow instructions for creating the fabric as described above, with no color changes. The blank punchcard rows match the no selection rows in self-drawn color separations,
If double bed work is daunting, for a different stitch, worked single bed, that may cause interesting distortions in all knit, single bed fabrics see block stitch post.


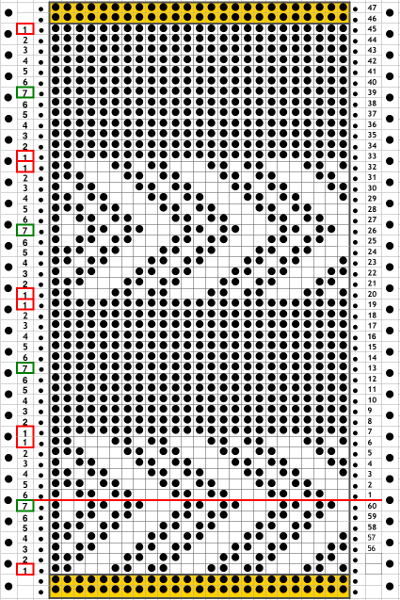
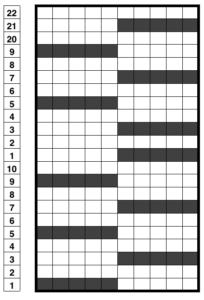
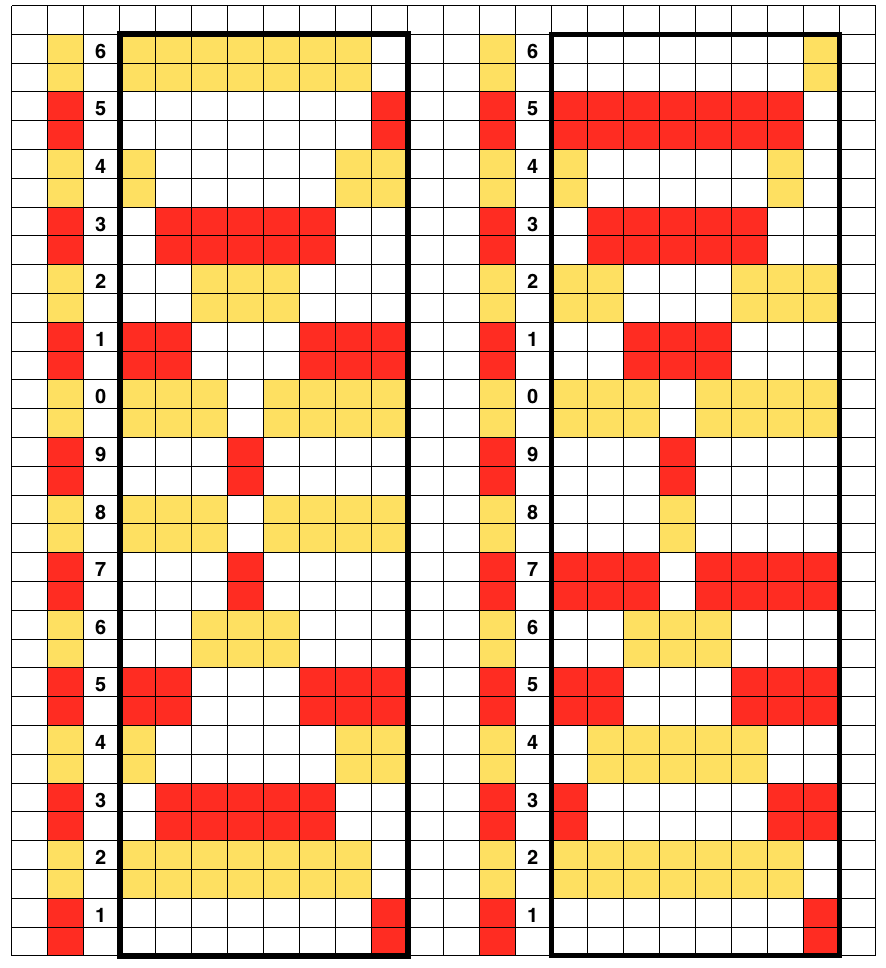
The self-drawn design repeats for 2 color drop stitch may be offset as well, resulting in colors being dropped alternately. The design shape needs to be created in 4-row blocks in order for the yarn to make it back and forth to the color changer with both colors to complete one design row. The second pairs of rows in each 4-row block is erased. In this instance as well, rows marked with black squares will pick up loops on the main bed, which are in turn dropped to create the long stitches. The second design repeat is offset to try to get sections of it to create loops to be dropped as well. The final motif must be a multiple of 8 rows in height if it is to be used as Ayab’s infinite repeat in length.
Color changes are indicated in the vertical strip in the center of the design. This was my starting idea
Elongation to 4 rows per block, erasing the second pair of rows for each color on right. The repeat on the right may be used if only one color is to be dropped; the 2 blank rows in the design field represent stitches that will knit only on the ribber for 2 rows. No stitches are dropped in color(s) used in sequential rows of blank squares in all “white” areas of the chart, including multiple rows above and below the design shape. Color changes every 2 rows continue, creating continuous stripes. 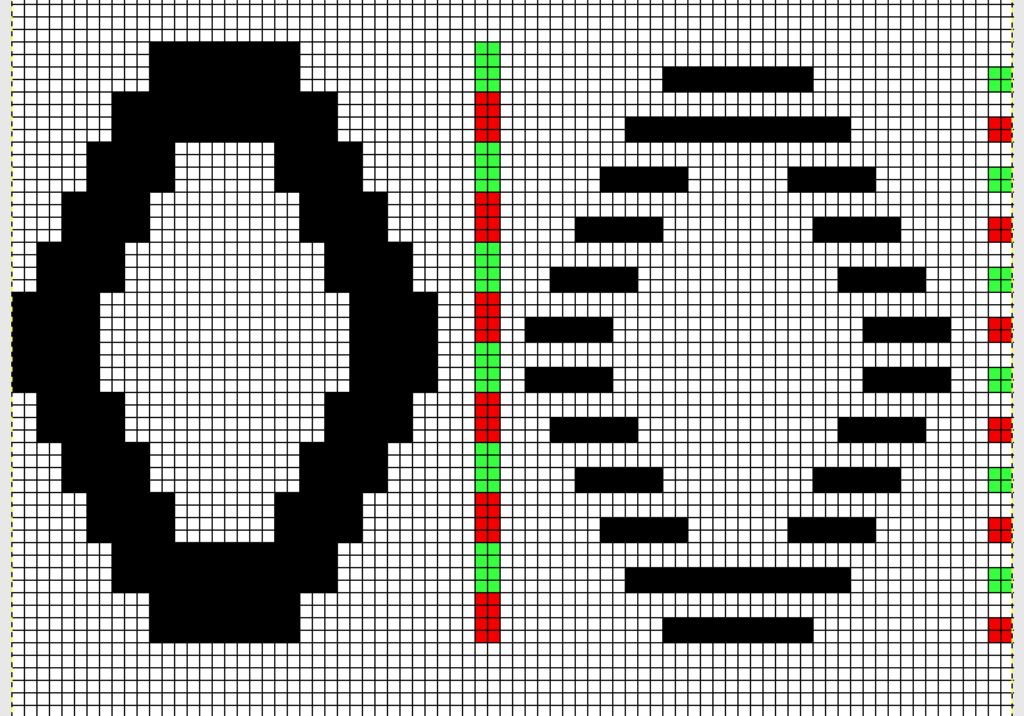 shapes staggered, visually checking for placement of alternately dropped stitches
shapes staggered, visually checking for placement of alternately dropped stitches 
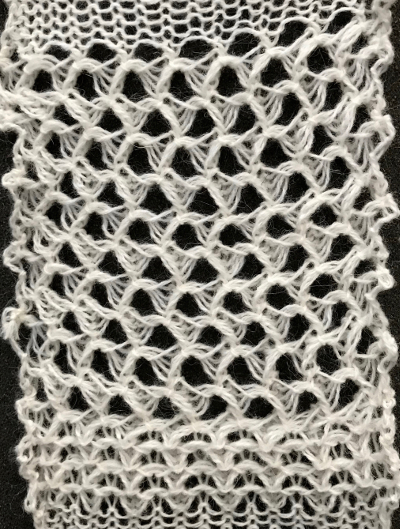
To accommodate the Ayab preselection for the first row to be knit from left to right, move the last blank row in the design to the first-row position. As the carriages travel from left to right and back to the color changer, the stitches will knit 2 rows only on the ribber. Continue knitting in steps as described earlier in the post, changing colors every 2 rows. On a larger knit ground such shapes may be arranged to suit. This was my working repeat, but I used a third fewer stitches in the swatch than in the chart. 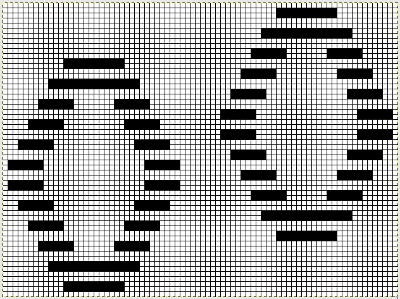 Note that the images will be reversed on the knit side, so if preferred, use Action Mirror to flip the image horizontally prior to knitting it
Note that the images will be reversed on the knit side, so if preferred, use Action Mirror to flip the image horizontally prior to knitting it
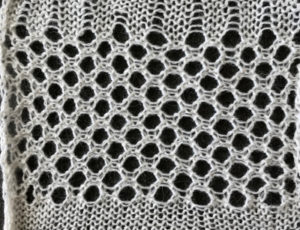
The swatch has been quickly pressed, so the texture is flattened out, but I am reminded of a few shadow knits when viewing its purl side. 
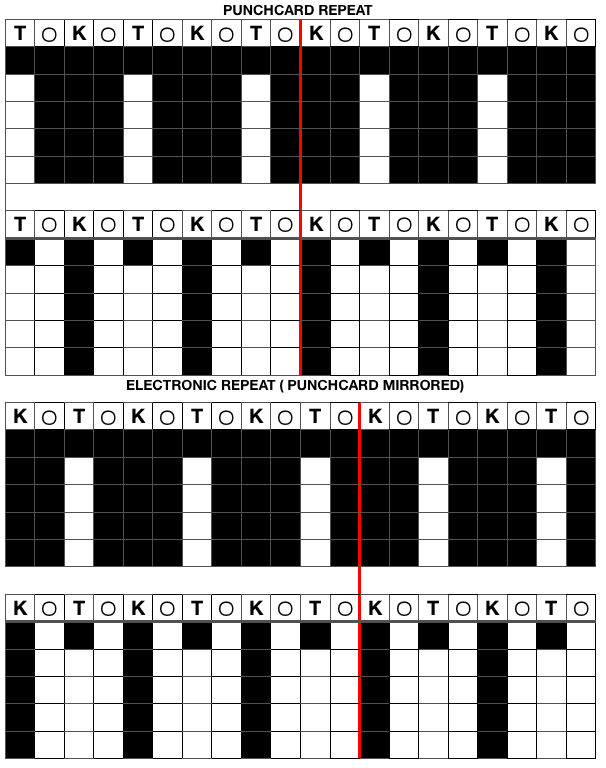
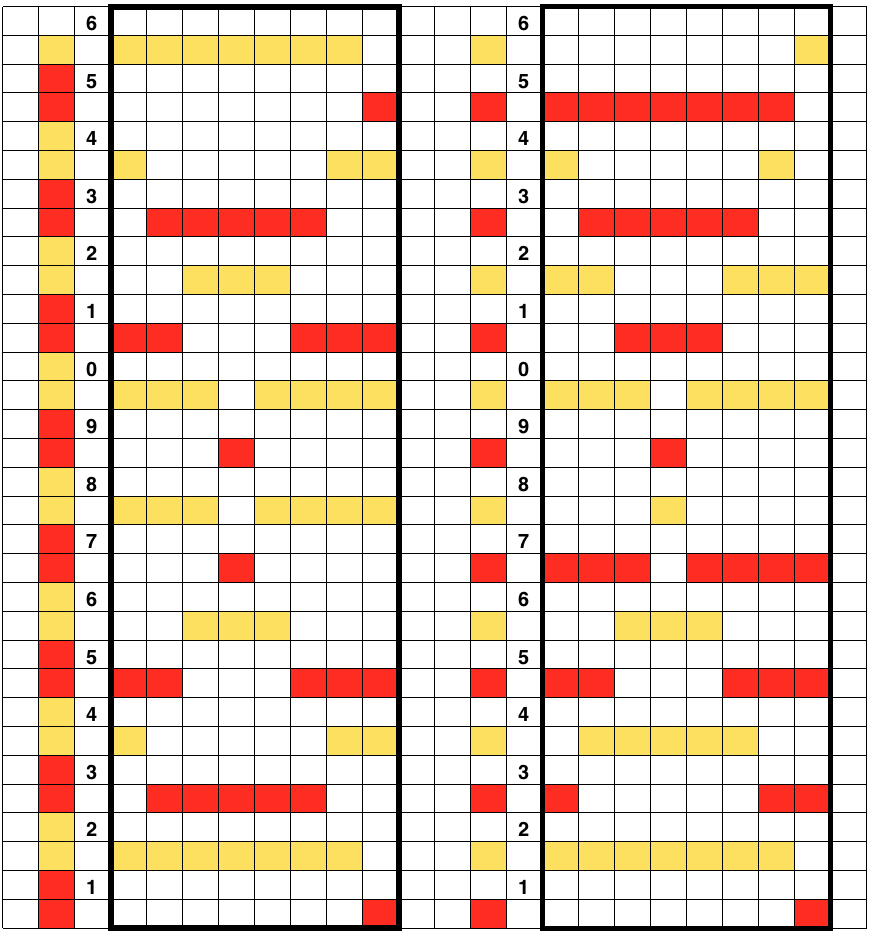
In an unaltered 910 with the ability to double the width of the programmed repeat, mylar users are not excluded from exploring a similar fabric. The repeat above may be rescaled to half the width, drawn that way, and then use the twice as wide built-in feature. Gimp does an “interesting” thing when scaling this design to half-width, note the right side of each repeat is an odd number of squares, the left side an even. The repeat may be used as-is or redrawn, adding or eliminating black squares if symmetry in each shape matters. Paintbrush produces the same image, mirrored.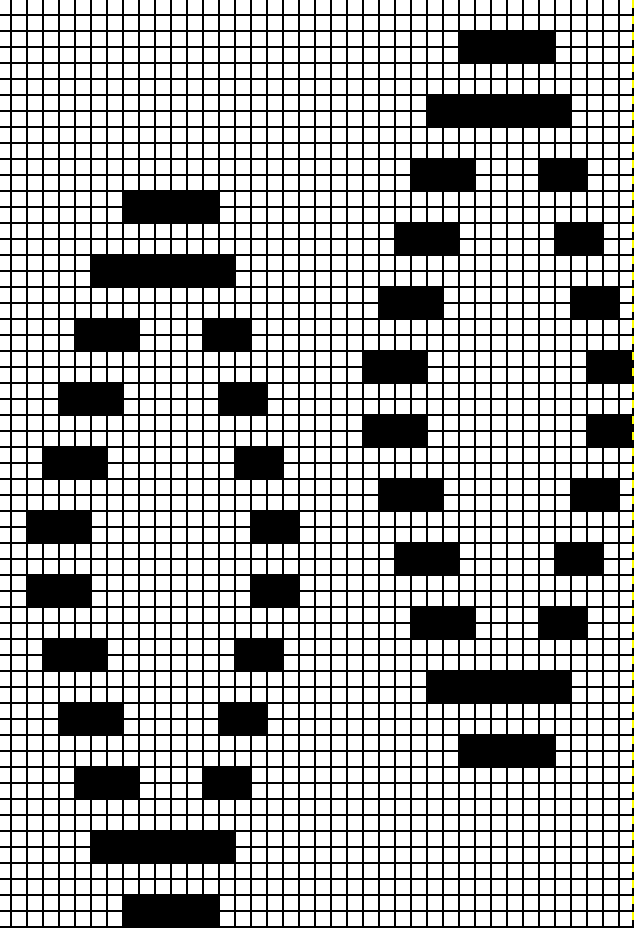
The explanation: further analysis of the original design reveals the fact that some of the pixel numbers in the design black square blocks are uneven in width. In this instance, 3.5 is half of 7, and half pixels cannot be rendered, so the software assigns the split to 4 and 3. 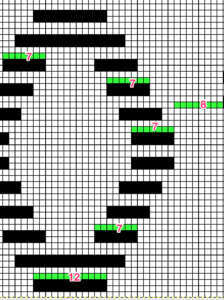
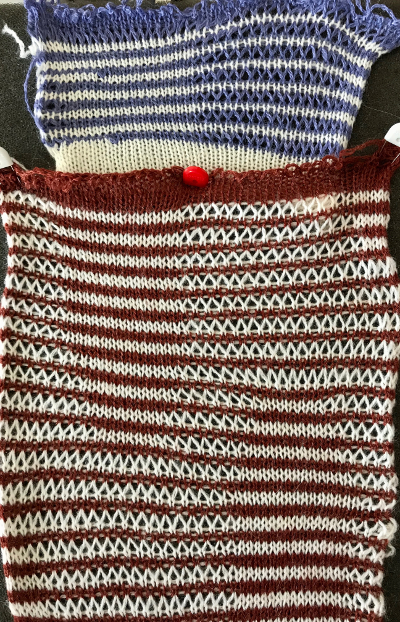
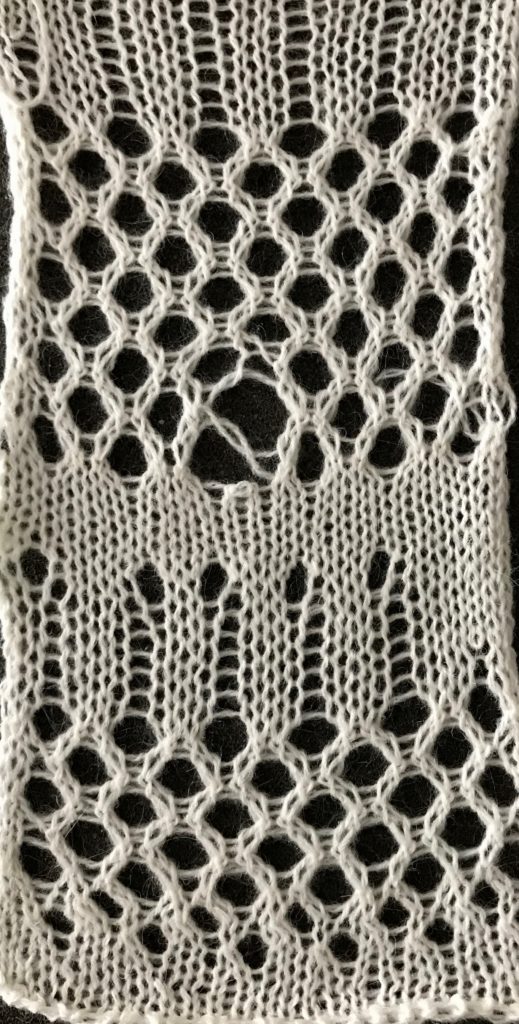














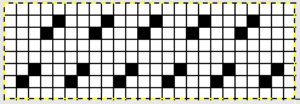



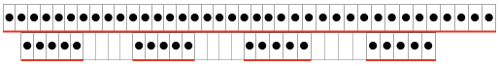
 The image tiled for the width of my knit, in this case, 32 stitches, a multiple of 8
The image tiled for the width of my knit, in this case, 32 stitches, a multiple of 8
 With the pattern flipped horizontally / mirrored, we now have the same results as in using the 589 punchcard
With the pattern flipped horizontally / mirrored, we now have the same results as in using the 589 punchcard



 no mirroring, software patterning errors in one of the test swatches
no mirroring, software patterning errors in one of the test swatches 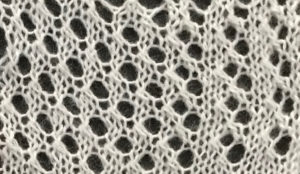
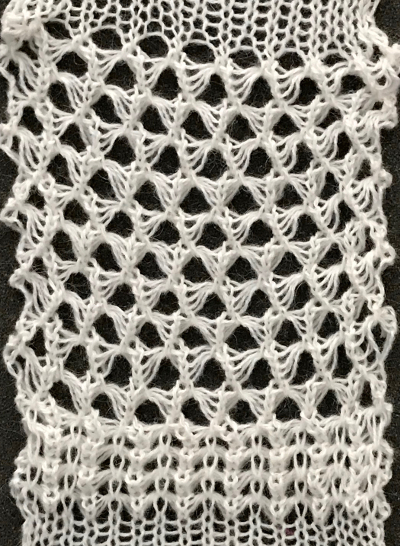
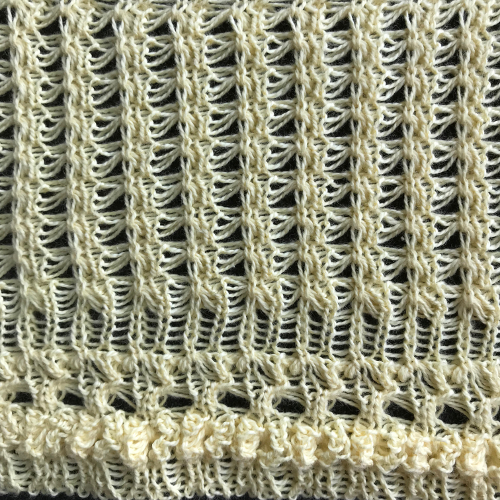
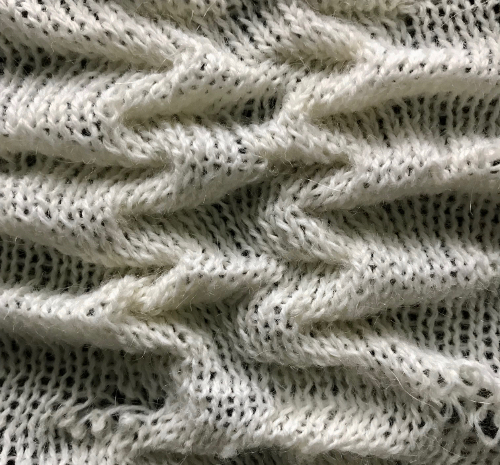

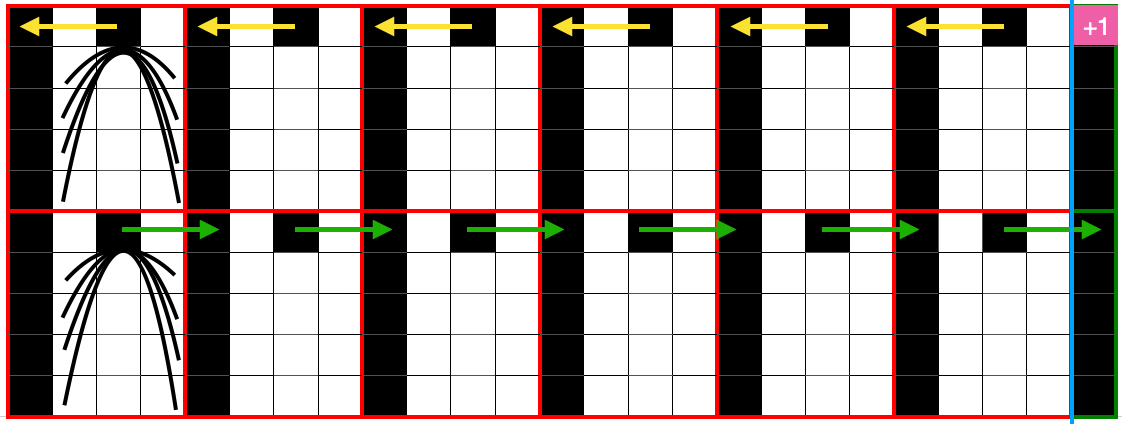






















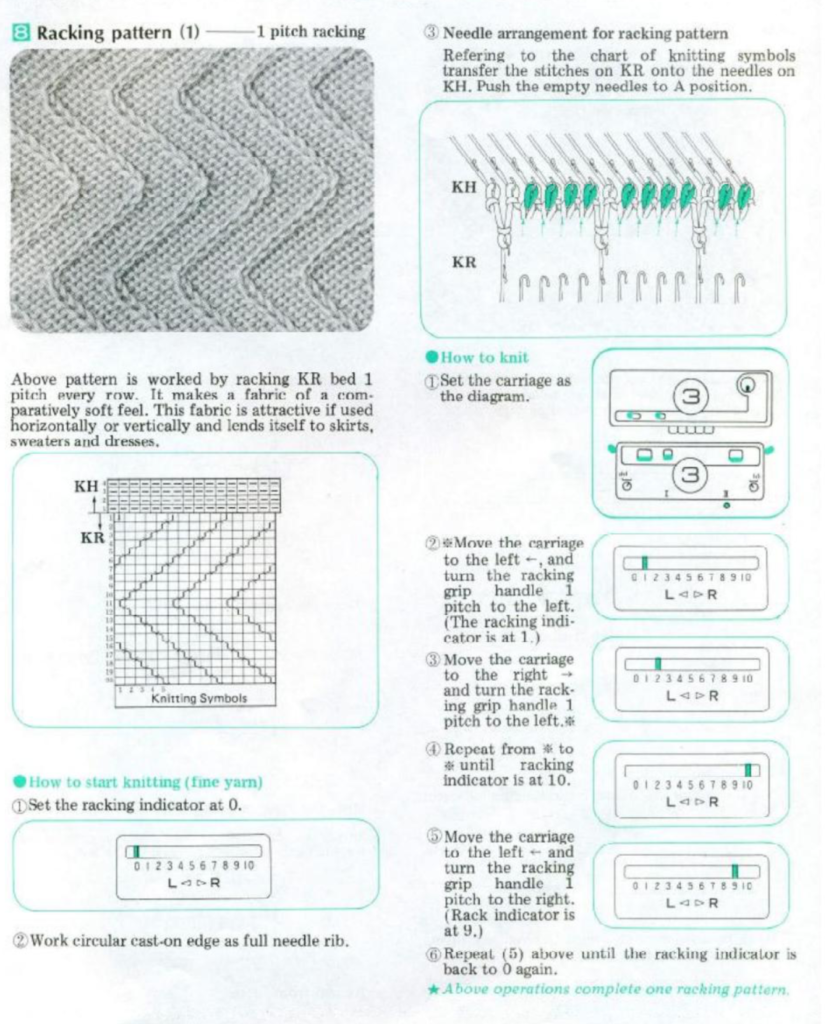


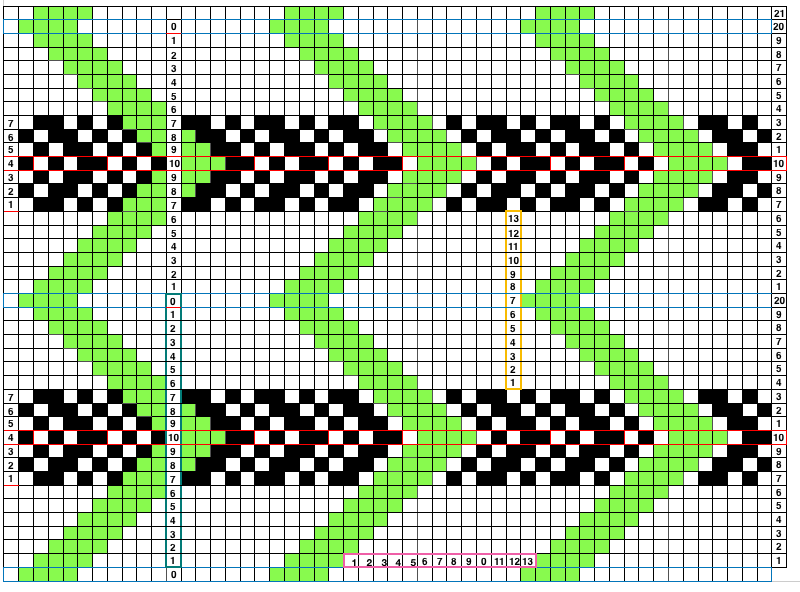
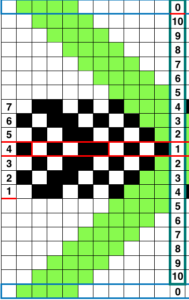
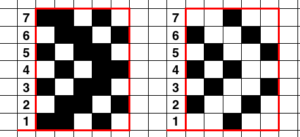



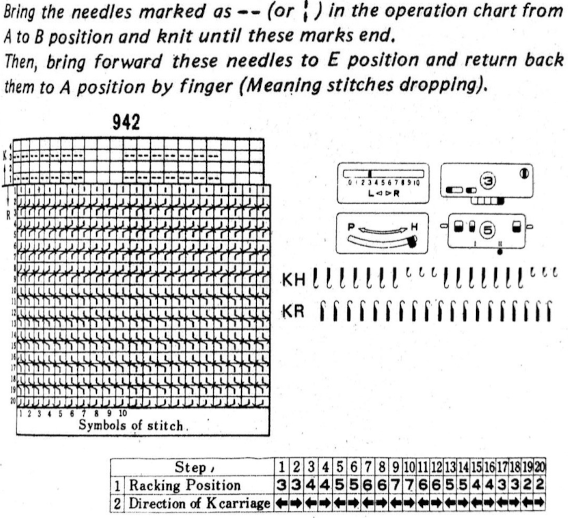
 The repeat required mirroring for use in my electronic 930. Experimenting with racking intersecting tuck stitch on multiple repeat png, stitches were picked up on the ribber aside from the first tuck stitch on the right, A, on the center, B, and on the left, C, of the knit stitch groups.
The repeat required mirroring for use in my electronic 930. Experimenting with racking intersecting tuck stitch on multiple repeat png, stitches were picked up on the ribber aside from the first tuck stitch on the right, A, on the center, B, and on the left, C, of the knit stitch groups.
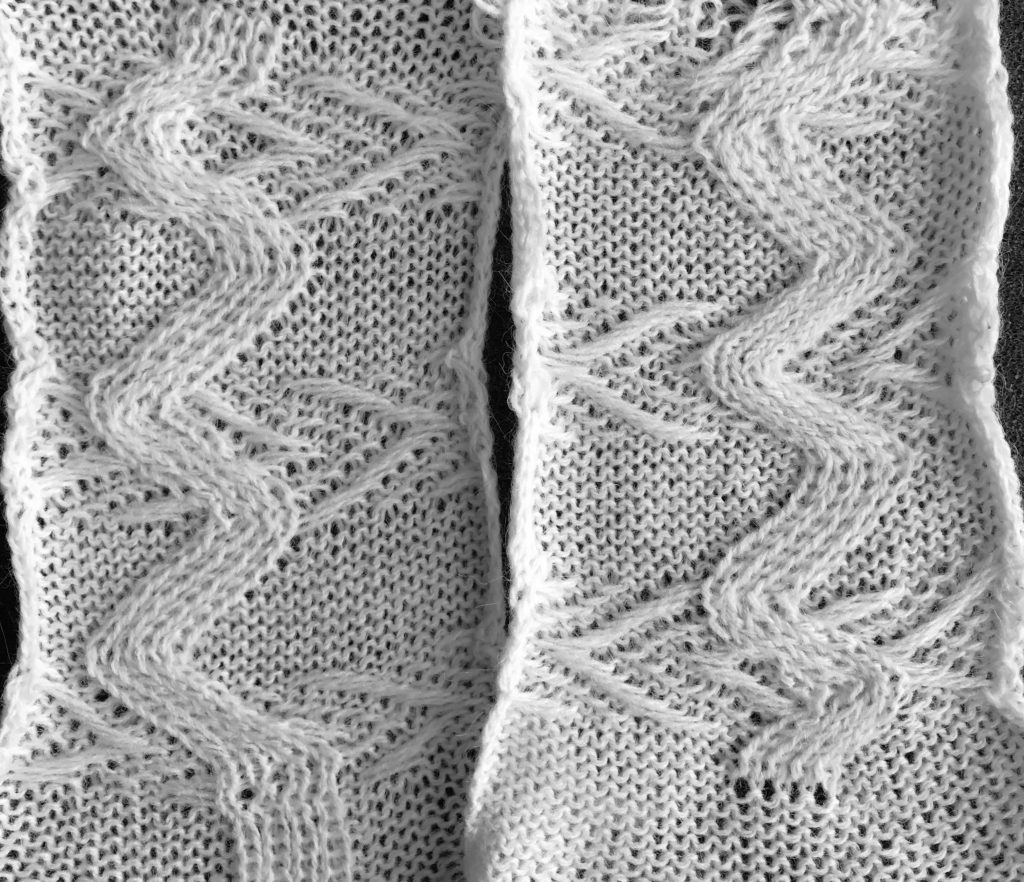
 changing ribber needle positions
changing ribber needle positions moving toward positioning the racked pattern further into the knit columns.
moving toward positioning the racked pattern further into the knit columns. 
 Good notes and documentation of the final needle arrangement will make the technique easily reproducible. The needles involved on the top bed always need to be returned to the patterning position after any shares.
Good notes and documentation of the final needle arrangement will make the technique easily reproducible. The needles involved on the top bed always need to be returned to the patterning position after any shares.  At any point in the knitting, it is easy enough to transfer stitches on the ribber up to the main bed, drop the ribber down, and check on the placement of the racked pattern. If the place is satisfactory, the moved stitches can be returned to the ribber and the work is continued. If not, transferred stitches can be left on the main bed, other stitches can be shared with the ribber and patterning can continue with racking in the new location. One such adjustment is seen toward the bottom of this swatch.
At any point in the knitting, it is easy enough to transfer stitches on the ribber up to the main bed, drop the ribber down, and check on the placement of the racked pattern. If the place is satisfactory, the moved stitches can be returned to the ribber and the work is continued. If not, transferred stitches can be left on the main bed, other stitches can be shared with the ribber and patterning can continue with racking in the new location. One such adjustment is seen toward the bottom of this swatch. 




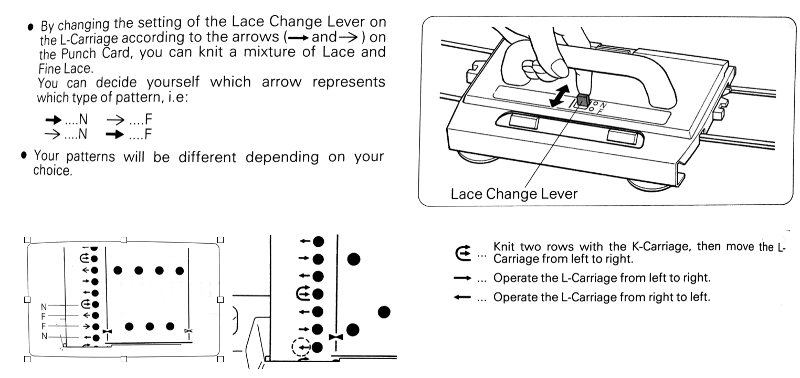







 the punchcard change knob has selections for single motif and pattern knitting (KC)
the punchcard change knob has selections for single motif and pattern knitting (KC)



 the start of the tube, needle selection for first pattern row
the start of the tube, needle selection for first pattern row 
 the start of a tube is evident if the ribber is dropped a bit
the start of a tube is evident if the ribber is dropped a bit  the tube dropped off the machine
the tube dropped off the machine  the FI created on the main bed
the FI created on the main bed  the pattern on the reverse, created by ribber
the pattern on the reverse, created by ribber



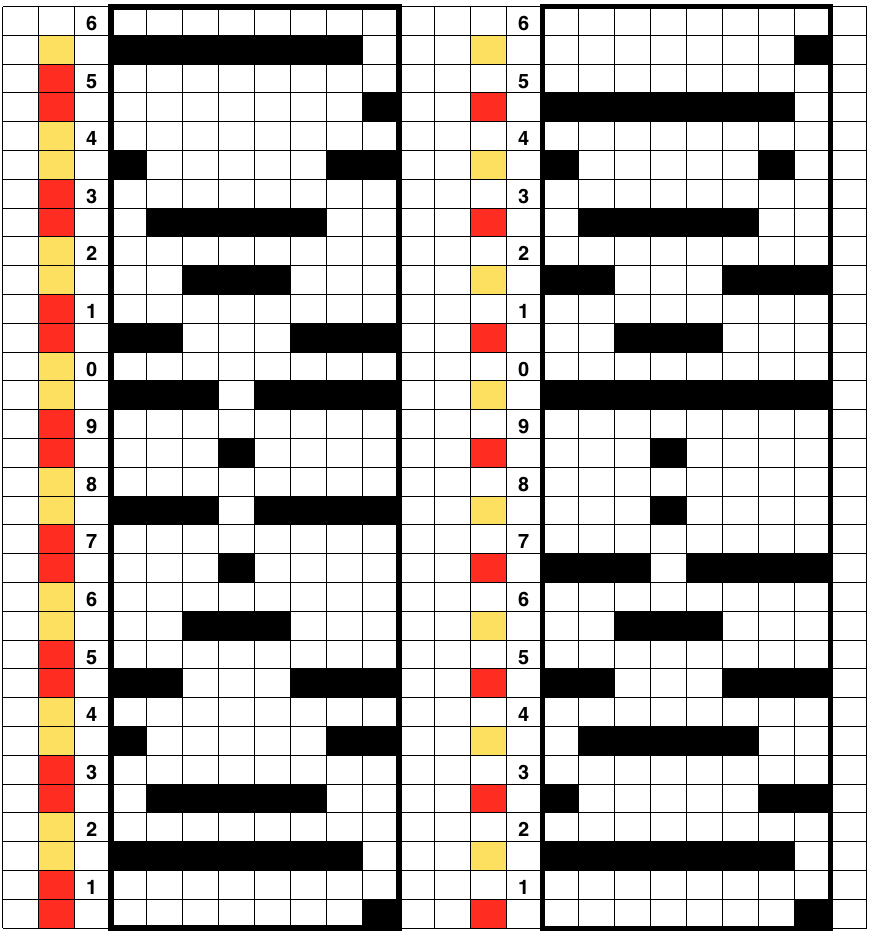
 this shows what happens when the first separation is collapsed into what actually gets knit by the carriages in this technique
this shows what happens when the first separation is collapsed into what actually gets knit by the carriages in this technique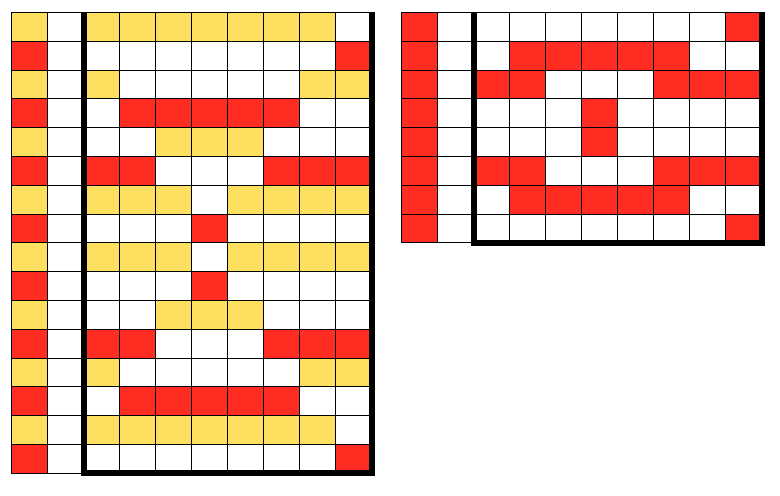 and the result in repeat in B/W like my swatch
and the result in repeat in B/W like my swatch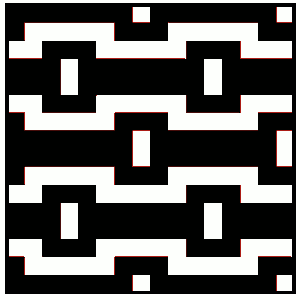



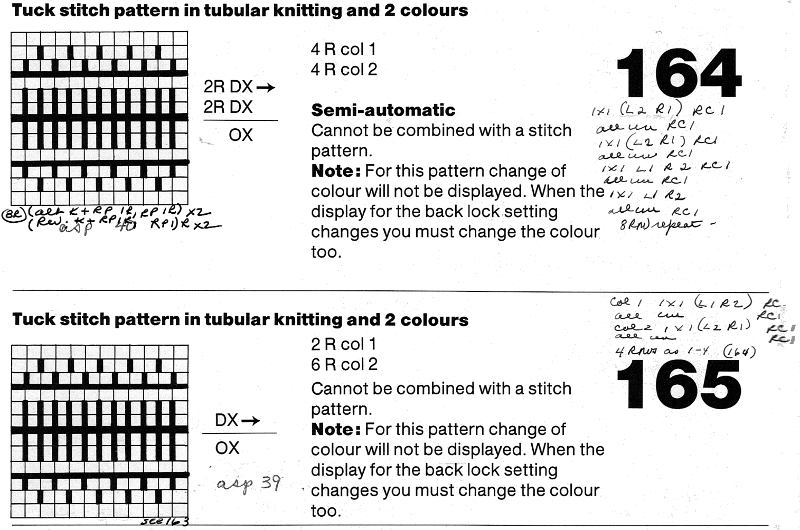 For tucked 2 colors fair isle use technique 185 with lock set on N/OX.
For tucked 2 colors fair isle use technique 185 with lock set on N/OX. 


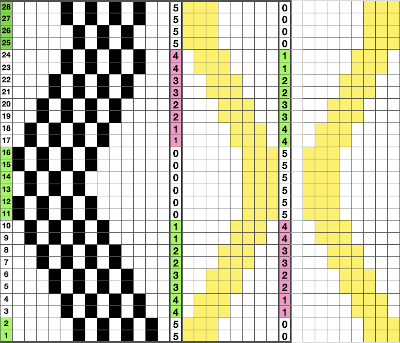
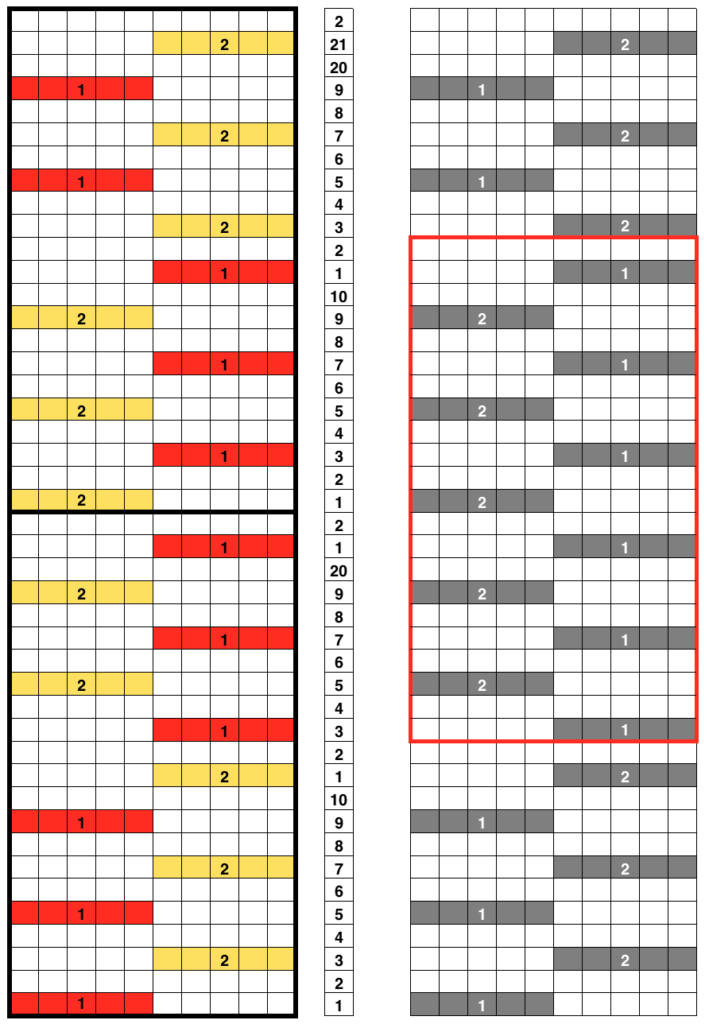
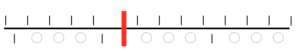
 This is my first experiment with gathered slip stitch floats on the purl side of the knit. To begin, this chart indicates one punchcard pattern’s full repeat in width. Four repeats in length would be required (the punchcard minimum repeat in length to achieve smooth continuous card feeding is 36 rows). Punch out blue squares, leaving white ones unpunched. A single repeat (outlined in black, 8 stitches by 12 rows) is for use in electronic patterning, where one may alternately draw or program white squares, then use color reverse. The red line represents 0 needle position in Brother KM
This is my first experiment with gathered slip stitch floats on the purl side of the knit. To begin, this chart indicates one punchcard pattern’s full repeat in width. Four repeats in length would be required (the punchcard minimum repeat in length to achieve smooth continuous card feeding is 36 rows). Punch out blue squares, leaving white ones unpunched. A single repeat (outlined in black, 8 stitches by 12 rows) is for use in electronic patterning, where one may alternately draw or program white squares, then use color reverse. The red line represents 0 needle position in Brother KM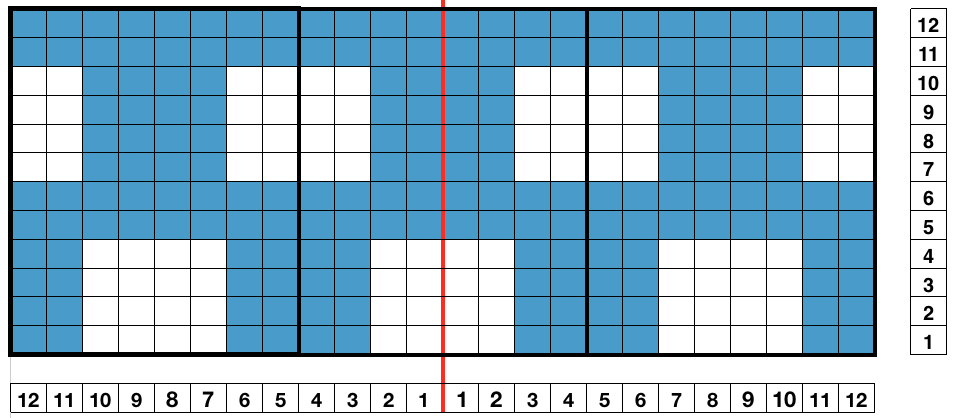
 result with color reverse
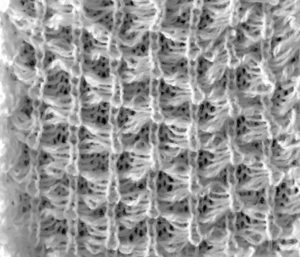
result with color reverse 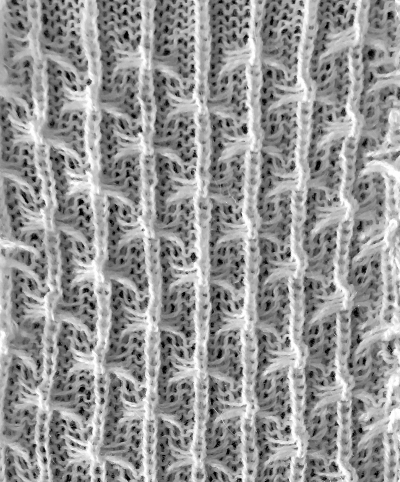 working out a mylar, electronic (unless DM 80 40 stitch width is in use) repeat for a variation of the fabric knit single bed. The stitch count is odd, allowing for a center stitch manipulation. KCI is used to make certain the first and last needles knit on each side. Floats created close to edges may be left without hooking them up. The fabric separates slightly along the “bowknot” edges
working out a mylar, electronic (unless DM 80 40 stitch width is in use) repeat for a variation of the fabric knit single bed. The stitch count is odd, allowing for a center stitch manipulation. KCI is used to make certain the first and last needles knit on each side. Floats created close to edges may be left without hooking them up. The fabric separates slightly along the “bowknot” edges 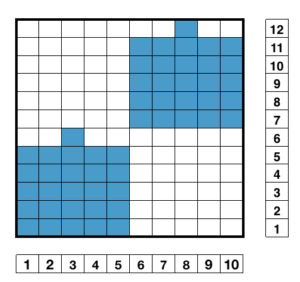

 lift them up and onto that single non selected needle, push that needle out to hold
lift them up and onto that single non selected needle, push that needle out to hold with the next pass the single needle and loops knit off together and become part of the alternating all knit block in the design
with the next pass the single needle and loops knit off together and become part of the alternating all knit block in the design the swatches are knit in a 2/15 wool, the fabric might be better served using a thicker yarn. Here the “blocks” creating “floats” are side by side
the swatches are knit in a 2/15 wool, the fabric might be better served using a thicker yarn. Here the “blocks” creating “floats” are side by side

 adding border stitches, and more theory on the placement of stitch type
adding border stitches, and more theory on the placement of stitch type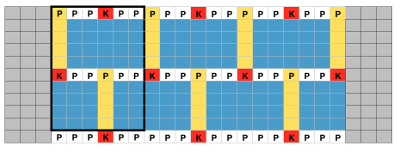 the result places “knit” stitches in the center of butterfly (magenta arrow), not at its sides, and I see and extra purl stitch (green arrow). Multiple stitch-wide borders create unwanted floats on one side
the result places “knit” stitches in the center of butterfly (magenta arrow), not at its sides, and I see and extra purl stitch (green arrow). Multiple stitch-wide borders create unwanted floats on one side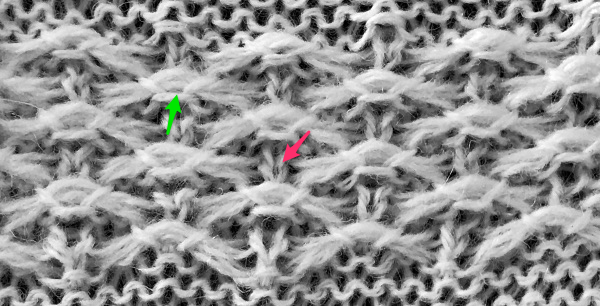 back to the drawing board and working things out first as a hand technique
back to the drawing board and working things out first as a hand technique
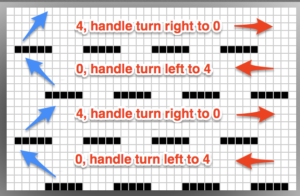
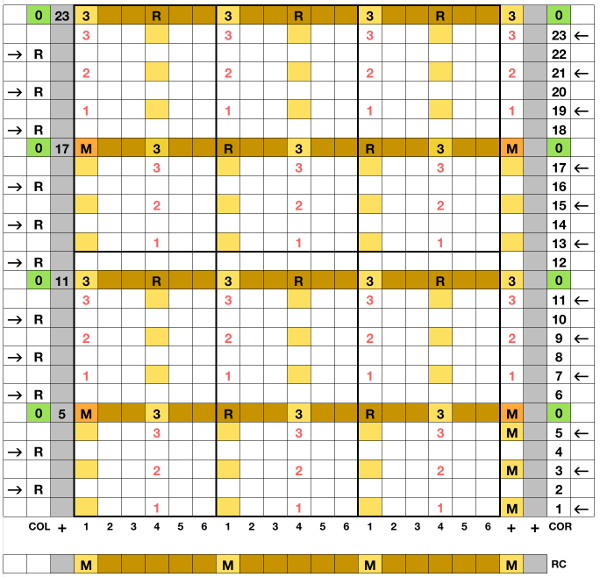 I began with my carriage on the right (COR), after setting up the repeat on a multiple of 6 stitches +3 as indicated above. The last stitch on either side on both beds is never transferred, and the short loops of every other set (rows 5 and 17 in the chart) are not hooked up. This will produce a slightly rolled edge on each side. The larger number of border stitches becomes problematic. The photos were taken while knitting 2 different swatches, so needle tape markings are not the same in all photos. To produce the circular knit, opposite part buttons are pushed in so with carriage on the right (COR), the settings would be
I began with my carriage on the right (COR), after setting up the repeat on a multiple of 6 stitches +3 as indicated above. The last stitch on either side on both beds is never transferred, and the short loops of every other set (rows 5 and 17 in the chart) are not hooked up. This will produce a slightly rolled edge on each side. The larger number of border stitches becomes problematic. The photos were taken while knitting 2 different swatches, so needle tape markings are not the same in all photos. To produce the circular knit, opposite part buttons are pushed in so with carriage on the right (COR), the settings would be



 after the three floats have been hooked up, with COL each time, the in-between main bed stitches are transferred back down to ribber
after the three floats have been hooked up, with COL each time, the in-between main bed stitches are transferred back down to ribber




 reducing main bed count so only one needle is left on either side of a selected one
reducing main bed count so only one needle is left on either side of a selected one  that needle (green arrow, gets transferred down to ribber
that needle (green arrow, gets transferred down to ribber  now the number of needles involved on both beds is evident on both beds
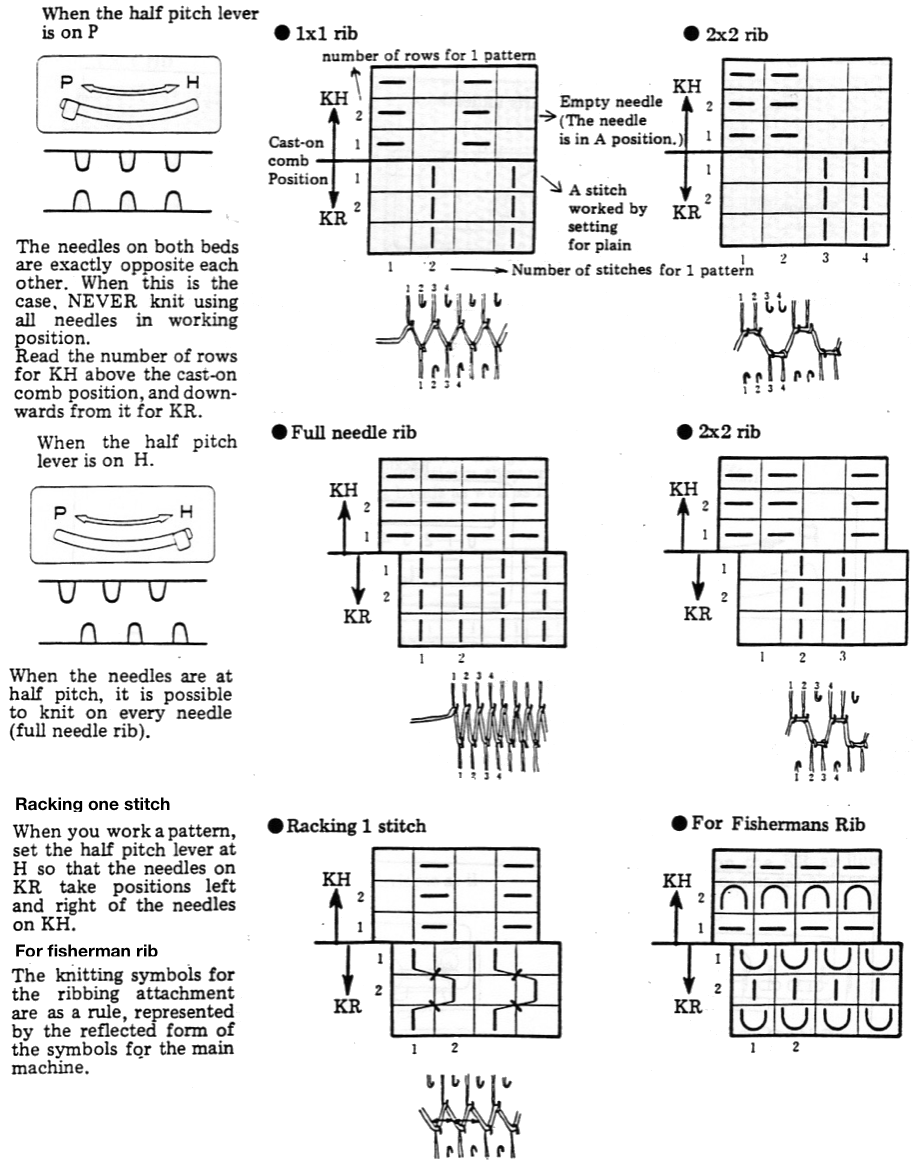
now the number of needles involved on both beds is evident on both beds While knitting in the pattern the ribber pitch is set on P (point to point) to keep stitches on opposing beds centered (P pitch also makes it easier to transfer directly from one bed to the other). If the cast-on is for every other needle rib with stitches then transferred between beds for pattern knitting set up, the cast-on and all rib rows need to be knit in H pitch, with a switch to P for transfers and knitting in pattern to be completed. With the first row set up on the selected segment of the needle bed, there are additional steps to take.
While knitting in the pattern the ribber pitch is set on P (point to point) to keep stitches on opposing beds centered (P pitch also makes it easier to transfer directly from one bed to the other). If the cast-on is for every other needle rib with stitches then transferred between beds for pattern knitting set up, the cast-on and all rib rows need to be knit in H pitch, with a switch to P for transfers and knitting in pattern to be completed. With the first row set up on the selected segment of the needle bed, there are additional steps to take.
 Hand techniques will now also occur when carriages are on the left, on RC 5, 11, etc as described in the hand technique chart, on rows with no needle selection. As in hand tech, transfers and multiple loops containing needles are brought out to hold before moving the carriages from left to right and selecting the needles for the next set of floats with that same pass.
Hand techniques will now also occur when carriages are on the left, on RC 5, 11, etc as described in the hand technique chart, on rows with no needle selection. As in hand tech, transfers and multiple loops containing needles are brought out to hold before moving the carriages from left to right and selecting the needles for the next set of floats with that same pass.
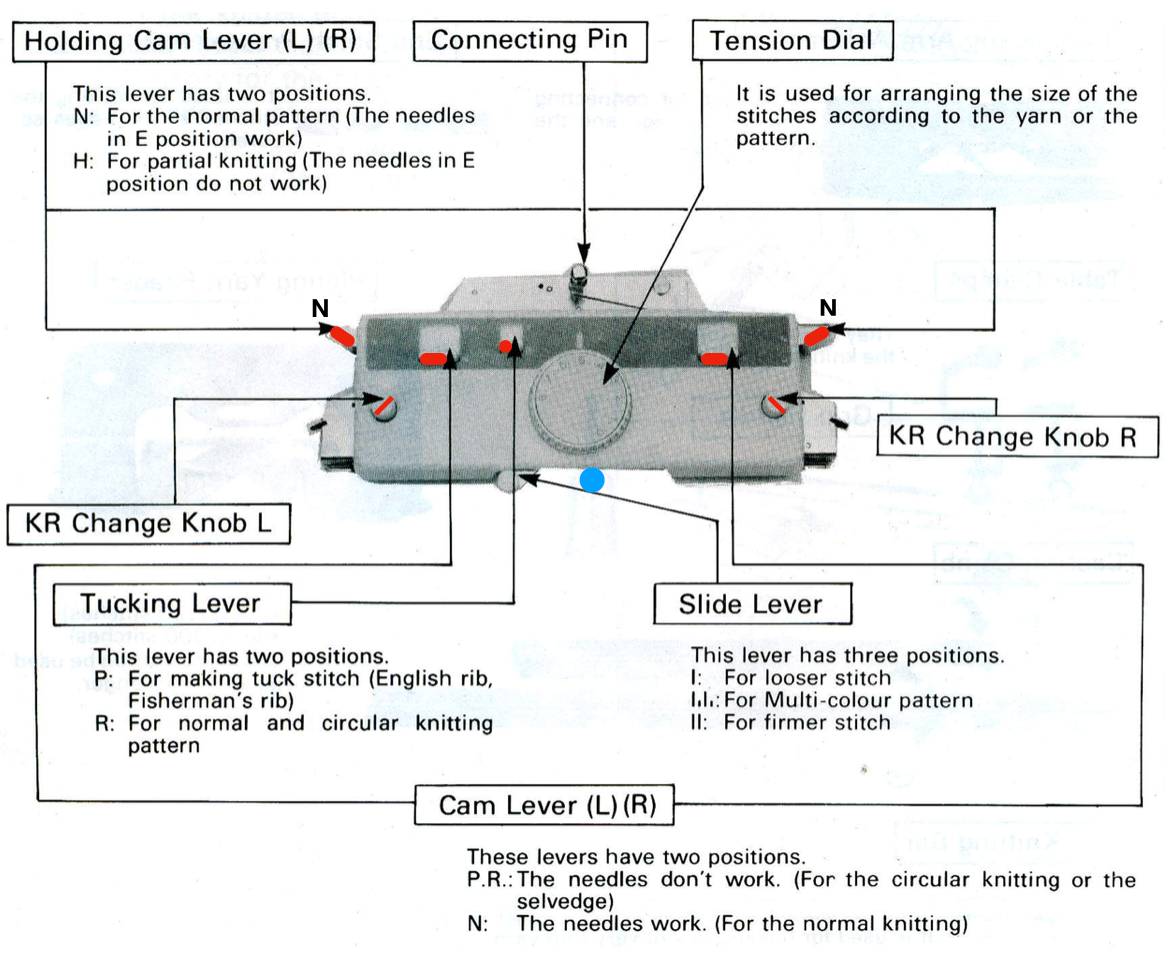 Back in 2015, I wrote on quilting on the machine, using the carriage representation below. Here lili buttons are positioned for use
Back in 2015, I wrote on quilting on the machine, using the carriage representation below. Here lili buttons are positioned for use
 slip to left
slip to left 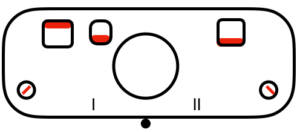 slip in both directions
slip in both directions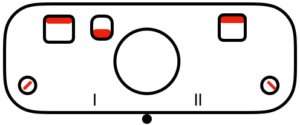
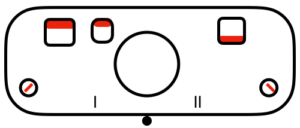 tuck to right
tuck to right 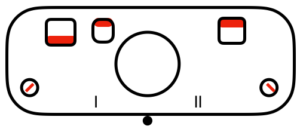 tuck in both directions
tuck in both directions
 tubular: either pair of opposite part buttons used
tubular: either pair of opposite part buttons used 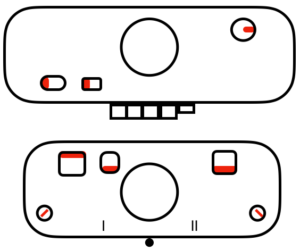
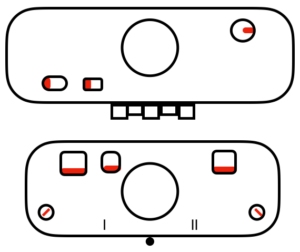 main bed <–> tucked jacquard: each needle on the ribber knits every row. Needles on the main bed knit in pattern according to punched holes, black squares on mylar, or programmed pixels. Non selected needles tuck. The patterns produced on the backside of the fabric are almost the reverse images of the front. Because so many tuck loops are formed the fabric is “short” and very wide, so cast ons and bind offs need to be planned accordingly
main bed <–> tucked jacquard: each needle on the ribber knits every row. Needles on the main bed knit in pattern according to punched holes, black squares on mylar, or programmed pixels. Non selected needles tuck. The patterns produced on the backside of the fabric are almost the reverse images of the front. Because so many tuck loops are formed the fabric is “short” and very wide, so cast ons and bind offs need to be planned accordingly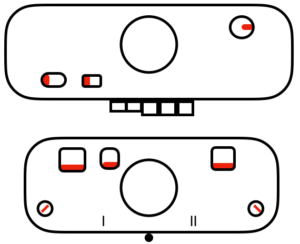 variation: tucking the main color, knitting the contrast, manual cam button reset every 2 rows
variation: tucking the main color, knitting the contrast, manual cam button reset every 2 rows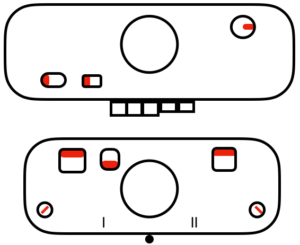
 full fisherman rib: tuck every needle alternately on both beds, in opposite carriage directions (below = L/R, or use R/L)
full fisherman rib: tuck every needle alternately on both beds, in opposite carriage directions (below = L/R, or use R/L)



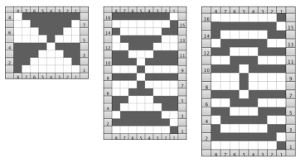
 revised with fewer single dots, and solid lines in the ground
revised with fewer single dots, and solid lines in the ground 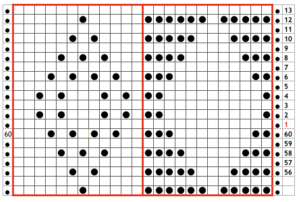
 using any method you prefer, set up knitting so all stitches are on the ribber. If you prefer to set up complete repeats prior to watching, “air knitting” prior to ribber set up or using the position option on the main bed if that is available, will help achieve that
using any method you prefer, set up knitting so all stitches are on the ribber. If you prefer to set up complete repeats prior to watching, “air knitting” prior to ribber set up or using the position option on the main bed if that is available, will help achieve that  set knit carriage to KC II (used when patterning does not occur on every needle across the needle bed), both part buttons pushed in for free pass to the opposite side of km, no knitting occurs but the first row of pattern knitting is selected. Ribber is set to N<–> throughout
set knit carriage to KC II (used when patterning does not occur on every needle across the needle bed), both part buttons pushed in for free pass to the opposite side of km, no knitting occurs but the first row of pattern knitting is selected. Ribber is set to N<–> throughout the carriages now move to the opposite side, selected needles on the main bed pick up loops, and nonselected needles stay empty. Ribber knits every stitch
the carriages now move to the opposite side, selected needles on the main bed pick up loops, and nonselected needles stay empty. Ribber knits every stitch  using a ribber cast on comb, stitch “dumper”, or another tool, move needles holding stitches forward to drop loops, and return empty needles to work position (B)
using a ribber cast on comb, stitch “dumper”, or another tool, move needles holding stitches forward to drop loops, and return empty needles to work position (B) as carriages move to the opposite side, needles are selected for next row of knit stitches to be knit on main bed
as carriages move to the opposite side, needles are selected for next row of knit stitches to be knit on main bed  carriages now move to the opposite side, loops are picked up on selected needles
carriages now move to the opposite side, loops are picked up on selected needles 

 carriages move to the opposite side, picking up loops
carriages move to the opposite side, picking up loops  before carriages move again, drop stitches formed. Watch loops after they are dropped, if tugging knitting it is not enough to pull them out of the way of needles returning to patterning, take a tool, or something like a credit card. Slide it from one side to the other between the beds, thus keeping loops clear away from the main bed
before carriages move again, drop stitches formed. Watch loops after they are dropped, if tugging knitting it is not enough to pull them out of the way of needles returning to patterning, take a tool, or something like a credit card. Slide it from one side to the other between the beds, thus keeping loops clear away from the main bed
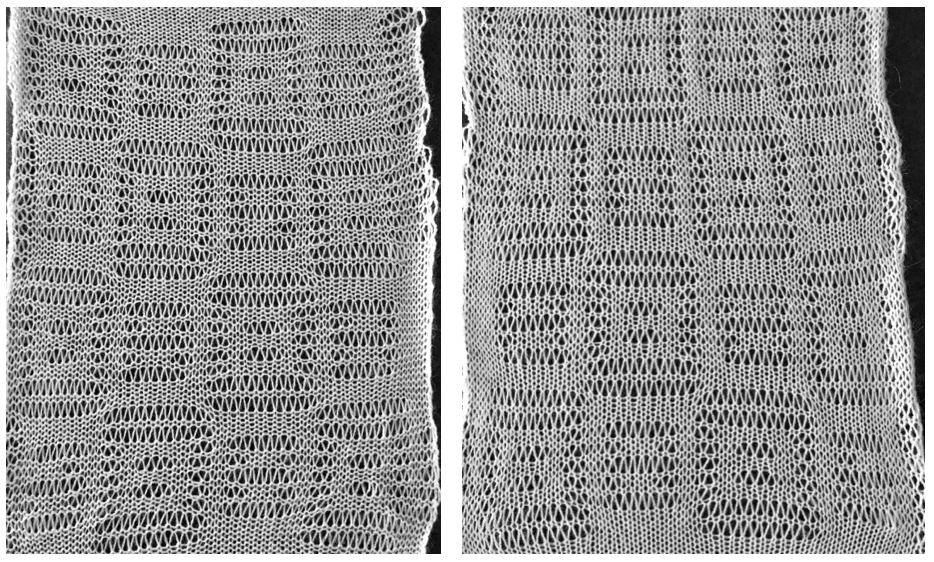
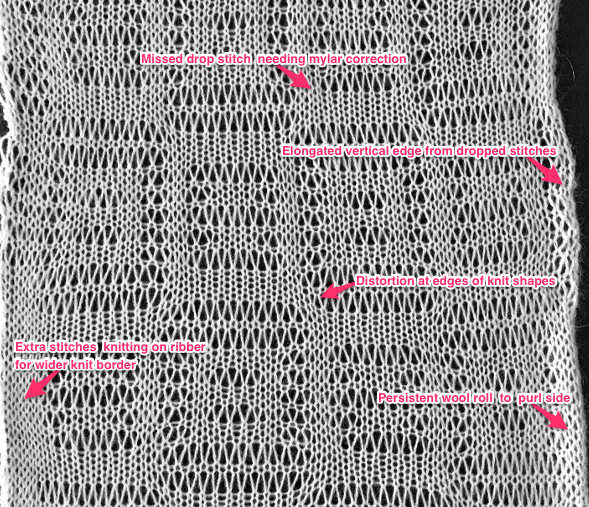
 purl side is shown first for each segment, followed by its knit
purl side is shown first for each segment, followed by its knit



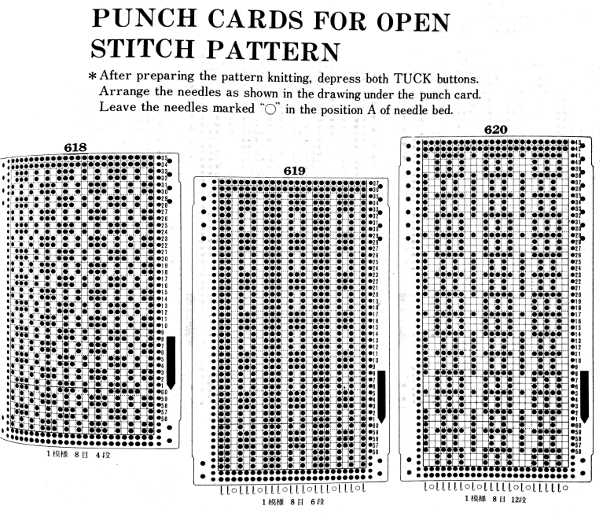
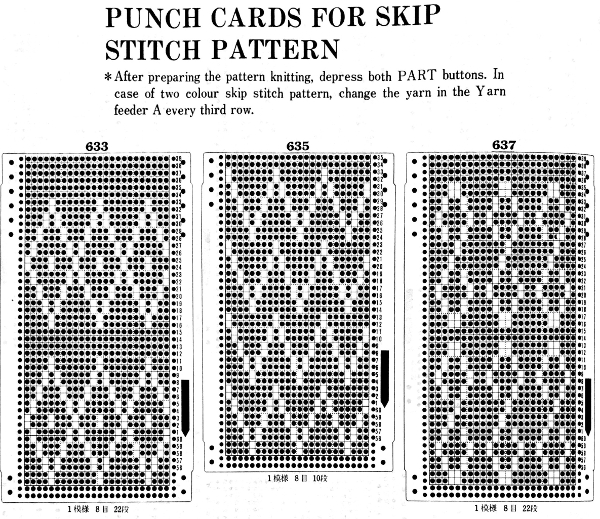
 If using punchcard machines, factory issue punch cards provided with the KM may be used
If using punchcard machines, factory issue punch cards provided with the KM may be used

 A slip stitch edge may be planned to keep edges of items such as scarves from rolling
A slip stitch edge may be planned to keep edges of items such as scarves from rolling  consider top and bottom edgings that include the technique (illustrated in the
consider top and bottom edgings that include the technique (illustrated in the 

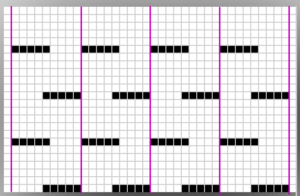
 An alternative way to produce this fabric on Brother is to use the knit carriage with no yarn to do the “stitch ditching”. The basic design programmed into any brother machine, electronic or punchcard will need to be altered. The intended design in my sample is a 4 X 4 square, colors represent what would be punched holes, black squares, or pixels. Simple block patterns such as these may be released upon completion of each “square” series, in this case, after 4-row segments.
An alternative way to produce this fabric on Brother is to use the knit carriage with no yarn to do the “stitch ditching”. The basic design programmed into any brother machine, electronic or punchcard will need to be altered. The intended design in my sample is a 4 X 4 square, colors represent what would be punched holes, black squares, or pixels. Simple block patterns such as these may be released upon completion of each “square” series, in this case, after 4-row segments. 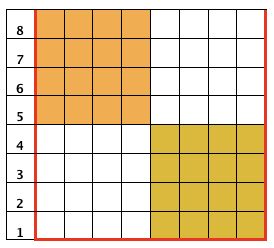
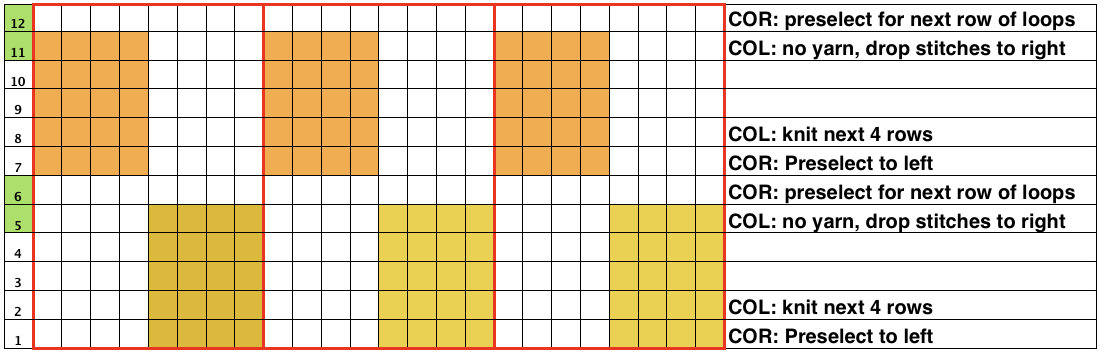 Rows 5 and 6, 11, and 12 are not part of the original repeat. The 5th design row provides needle selection, traveling from right to left. When the carriage passes in turn from left to right with no yarn, those preselected needles will drop while preselecting a blank design row (6) that allows the carriage to return to the left-hand side. As it moves back to the left, the carriage will preselect the first row of the design. With COL yarn is picked up in order to knit the next set of dropped stitches. A color change may be made while the carriage is on the left.
Rows 5 and 6, 11, and 12 are not part of the original repeat. The 5th design row provides needle selection, traveling from right to left. When the carriage passes in turn from left to right with no yarn, those preselected needles will drop while preselecting a blank design row (6) that allows the carriage to return to the left-hand side. As it moves back to the left, the carriage will preselect the first row of the design. With COL yarn is picked up in order to knit the next set of dropped stitches. A color change may be made while the carriage is on the left.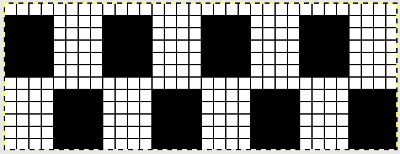
 More to try: the typical appearance to look for in the source inspiration is that of single-row horizontal geometric designs with all blank rows separating them from each other.
More to try: the typical appearance to look for in the source inspiration is that of single-row horizontal geometric designs with all blank rows separating them from each other.

 The yarn used here was a softly spun rayon that began eventually to split, and get partially caught up on gate pegs, leading to the ending of the swatch
The yarn used here was a softly spun rayon that began eventually to split, and get partially caught up on gate pegs, leading to the ending of the swatch 
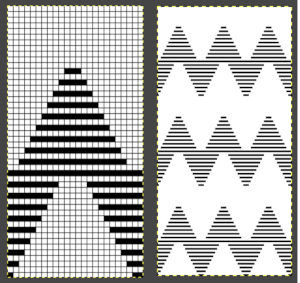
 Fair Isle
Fair Isle

 In Method 2/B: the separation occurs in two-row units.
In Method 2/B: the separation occurs in two-row units.
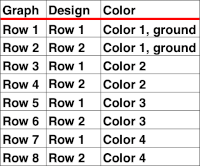
 Another former handout, intended for Passap knitters. Many of these fabric options could be emulated on the Brother machine, if separation method 1 were available, with a bit of interpretation. A
Another former handout, intended for Passap knitters. Many of these fabric options could be emulated on the Brother machine, if separation method 1 were available, with a bit of interpretation. A  Automated color separations preparations for download happen easily when using Ayab and img2 track software and accompanying cables. In addition to the familiar built-in KRC separation, there are a variety of other options. For more information please see
Automated color separations preparations for download happen easily when using Ayab and img2 track software and accompanying cables. In addition to the familiar built-in KRC separation, there are a variety of other options. For more information please see