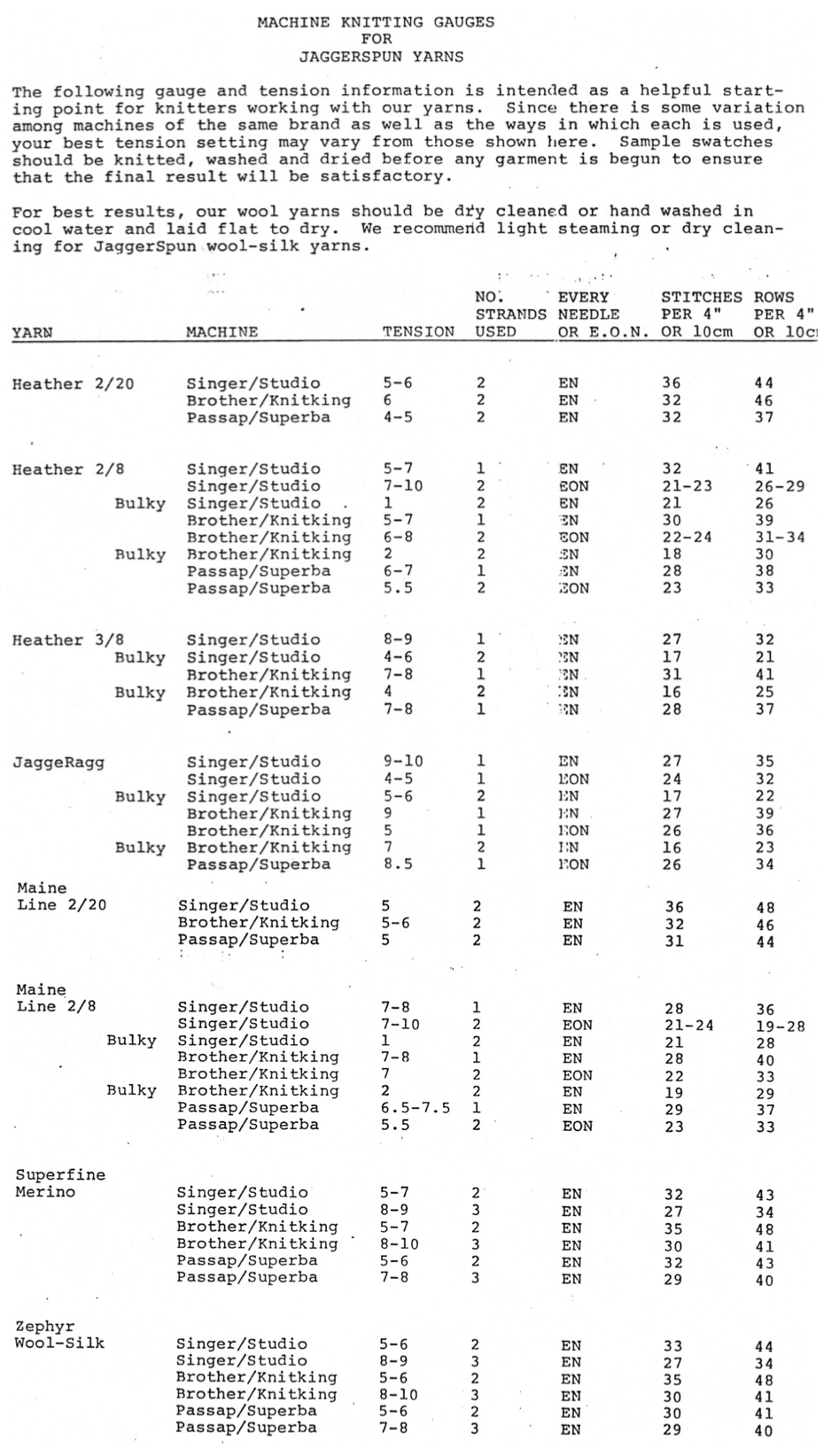
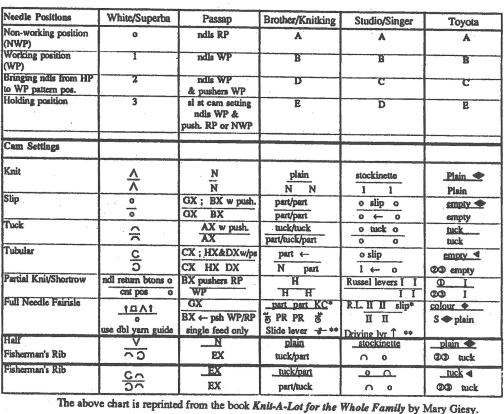
Additional information may be found in previous posts on ribber adjustments and color changers
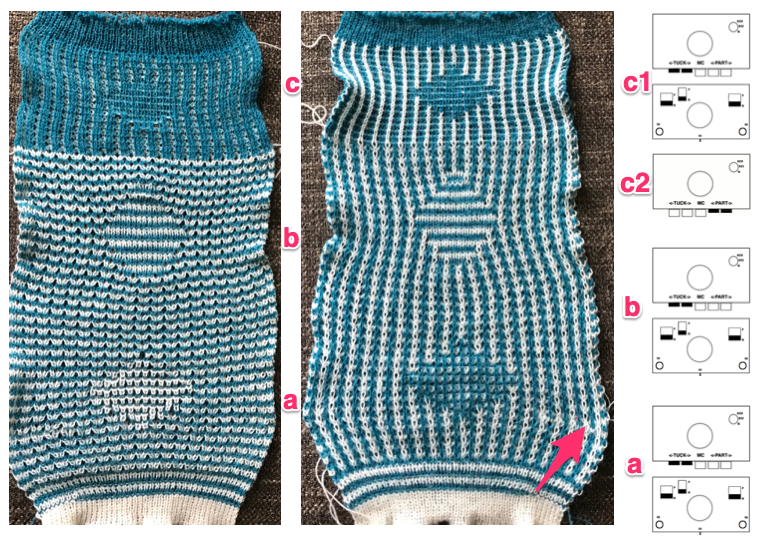
Recently I began to be curious as to how long, non-repetitive images might be handled when knitting on both Brother and Passap. The subject is not out of reach for punchcard knitters. In the early art-to-wear days when the options were for 24 or 40-stitch repeats, many artists joined punchcards in length to the desired height, and knit them in width + seam allowances, joining long panels together to form the large images, or hanging them as panels in tapestry format. One such artist was Nicky Hitz Edson. I have avoided working with such images since my bit knitter knit from screen days eons ago. Also, I always preferred DBJ variations on the Passap. I used the KRC function only in my very early Studio Electronic days, prior to acquiring the Passap or any of my Brother machines. Tools and machines available to me at present: 910 with EMS kit and Ayab software, old fashioned mylars also for the 910, an unknown capacity for accurate knitting “rehabilitated” 930 accompanied by img2track consultations for the moment with Tanya Cunningham, and Passap E6000 using technique 179.
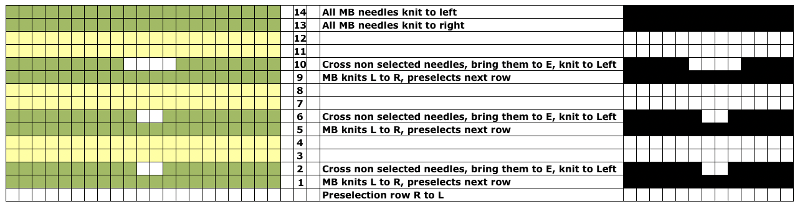
Reviewing some basics: the KRC function built into the 910 performs this separation automatically. It is the default dbj separation in Ayab and uses the built-in KRC button with img2track on the 930. Repeats must be an even number of rows in height.
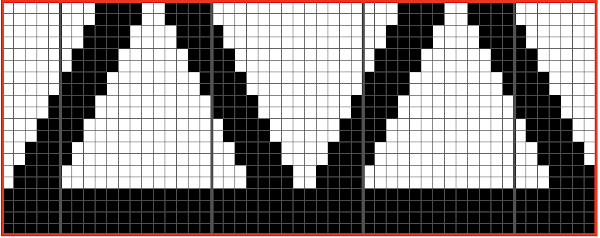
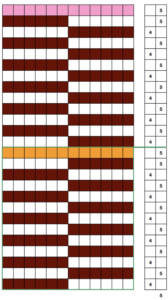
Here the simple shape illustrated in some of my previous is shown in color and repeating twice vertically. Note: the first color used knits only once, toward the color changer 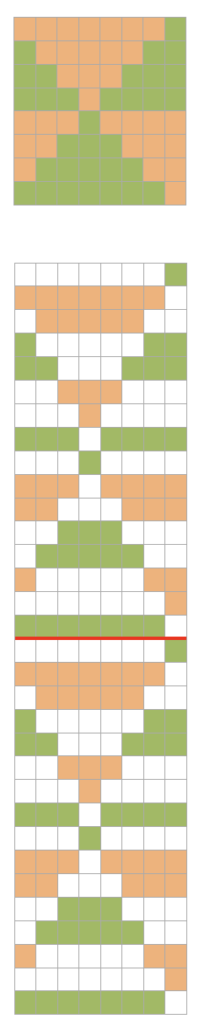 This means the first preselection row needs to happen from left to right, with color knitting beginning from right to left, and subsequently every 2 rows. Pertinent reminders from the 910 manual: in any pattern knitting
This means the first preselection row needs to happen from left to right, with color knitting beginning from right to left, and subsequently every 2 rows. Pertinent reminders from the 910 manual: in any pattern knitting
and when knitting DBJ with factory mylar (or self-drawn patterns) White pixels knit first when images are drawn in black and white squares
White pixels knit first when images are drawn in black and white squares
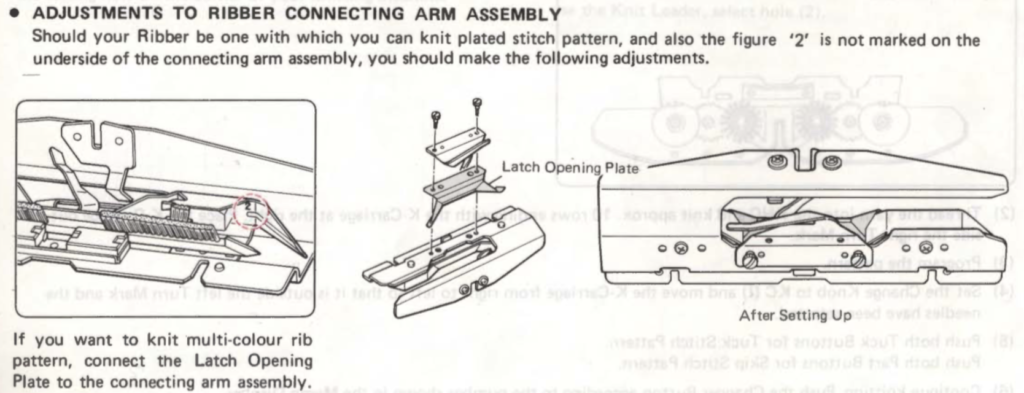
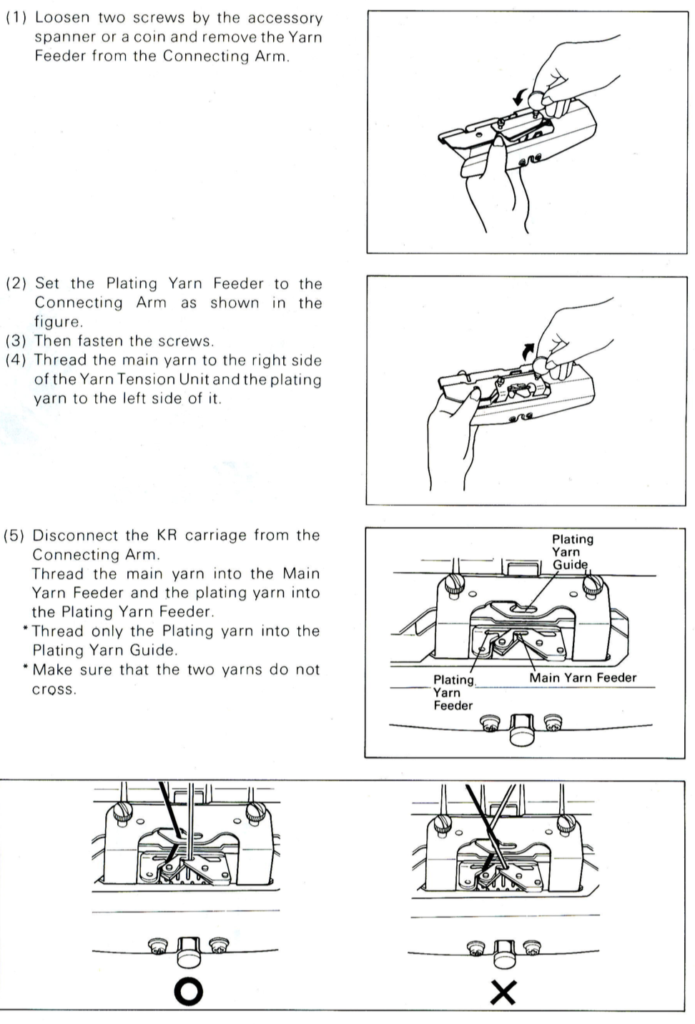
KC I or II may be used, needle arrangements can vary depending on the look one prefers on the edges. The 930_940 directions get a bit more elaborate, and show usage of an accessory “latch opening tool” (I have never used it on my 910, may have to give it a test in the future); img2track downloads to the machine’s built-in brain, the equivalent of downloading to the Passap console, which will hold the pattern program in memory until altered or erased. In re-reading manuals, I noted I have had a chronic habit since I began knitting of referring to the ribber “connecting arm” as its “sinker plate”.
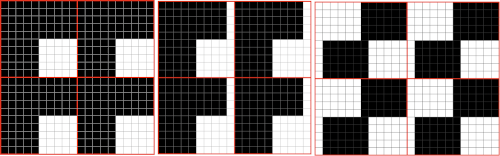
I have several sinker plates. In reference to the above, this photo illustrates the location of #2 when present vs. not 
here the latch opening plate has been secured into place in the connecting arm without the #2 marking, where it makes a noticeable change, bringing the unit closer to needles when on the machine during knitting
A reminder: if the needle presser bar on the ribber (all plastic) is to be removed, it is reinserted back in with ridges facing, and flat side down
When the pattern selector is down, the pattern is centered on green #1 (right of 0). If a pattern is an odd number of stitches and the pattern limits are yellow 12 and green 13, the center is green #1. AYAB color sequence is reversed from the Brother convention of white pixels being color #1, and black pixels being color #2. It chooses black as color #1, and white as color #2. The first pass to the right is set up with the “black” yarn. The first pass to the right preselects for the first row of black squares, which will be knit on the first pass from right to left. With an odd number of needles, Ayab places the larger number of needles on the left, its orange (yellow) side.
The closest relative to the KRC button in the PassapE6000 is Technique 179, intended for emulating single bed 2 color FI on Japanese machines, but it may be used with every needle rib and varied back lock settings to produce far less elongated DBJ than its standard built-in DBJ color separations. In single bed knitting GX/LX is used, for DBJ use every needle rib, and set back bed settings and pushers for desired backing (GX is the Passap equivalent of a free pass, with the bed in that setting not knitting any stitches, whether or not any needles are in use or holding yarn). The repeat must be an even number of rows in height. The instructions in the company publications are that color reverse must be used, swapping the background and motif colors. The color-changing sequence is the usual one. Both KRC and 179/ col rev knit white pixels first. When knitting a row in Brother machines the K carriage must pass the center of the needle bed, or the pattern will not advance properly. In Passap, programmed end needles for the pattern on each side must be cleared or error messages will be received, and a pattern “correction” will be required before continuing.
I am planning to begin by using a 2 color, large repeat factory mylar scanned and reduced to a downloadable image, details on how to in a previous post. The goal is to knit segments that are part of a continuous, “longer” image. My ultimate goal: is to knit scarves that are 70-84 stitches wide, with nonrepeating patterns for 12-1400 rows. My understanding is that such an image in img2track would be broken into tracks by the software, with each track programmed in turn as separate segments, and the software warning one when the last row for each track is reached. In Passap the segments will be entered as patterns A, B, and C, with no warnings at repeat ends, they are calculated based on math. Segments will be 30 pixels in height as “pretend” longer file components, for the sake of knitting speed.
That row back to the color changer knitting row one again would show up as an error/ extra row below row 1 color 1 of the subsequent pattern. 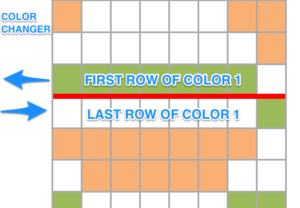 Looking at it in terms of black and white squares, what happens the same repeats when stacked continuously above each other
Looking at it in terms of black and white squares, what happens the same repeats when stacked continuously above each other
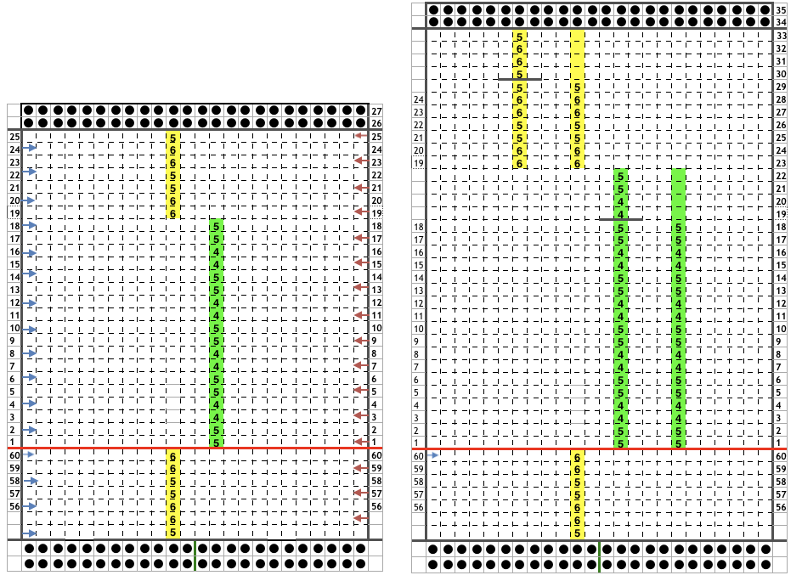
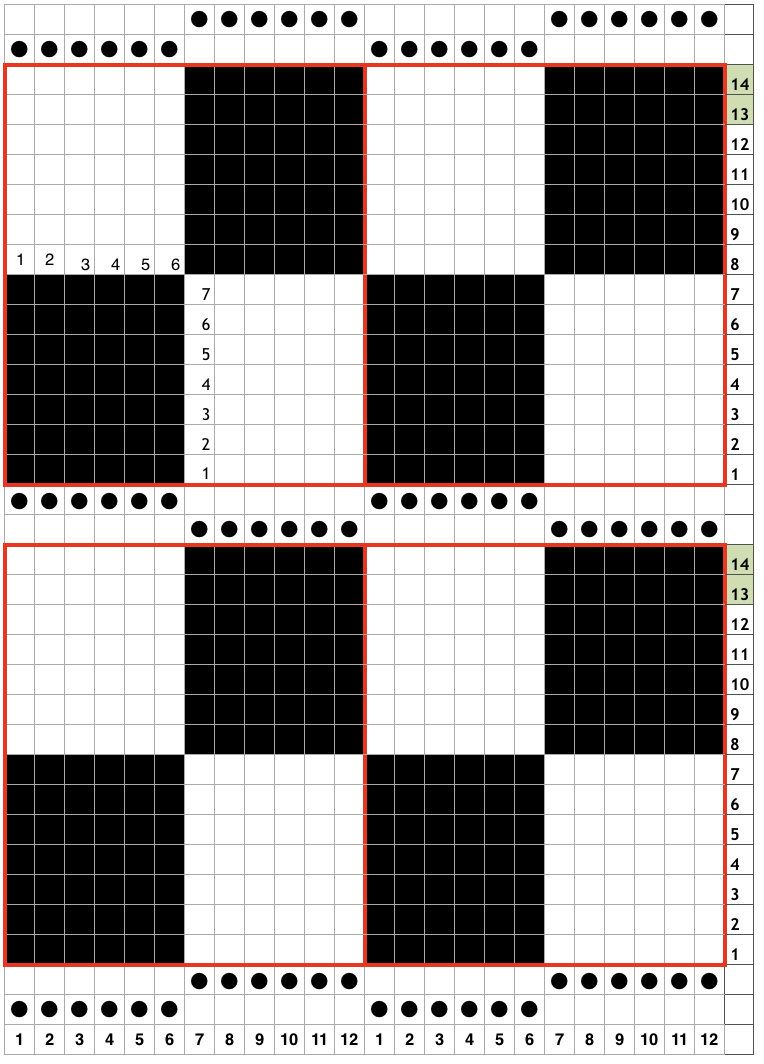
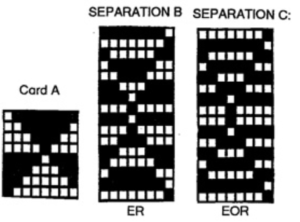
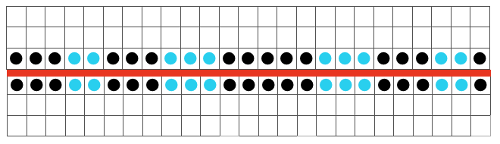
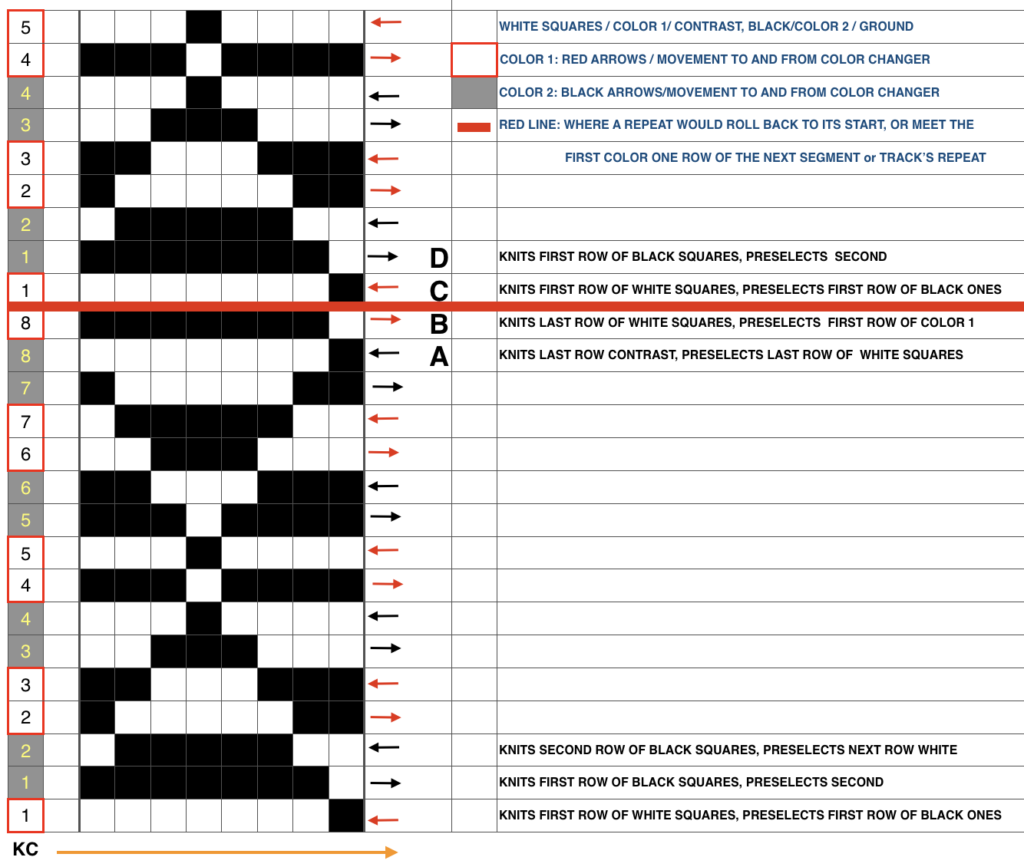 The problem comes at the intersection of the 2 different patterns; the assumption with the KRC separation is that you start with one row of color 1 opposite the color changer and if you are knitting a continuous, “looping/repeating” pattern, knit the last row of color 1 away from the color changer (B), and will start with row 1 color one again toward the color changer on the left in Brother (C). One approach is to stop knitting in pattern opposite the color changer, (red line), program the second piece of the “longer” design, and start to knit the first row of color 1 again for that pattern segment, going from right to left/ toward the color changer(C). Color changing then follows every 2 rows until the top of the second pattern piece is reached, repeating as needed.
The problem comes at the intersection of the 2 different patterns; the assumption with the KRC separation is that you start with one row of color 1 opposite the color changer and if you are knitting a continuous, “looping/repeating” pattern, knit the last row of color 1 away from the color changer (B), and will start with row 1 color one again toward the color changer on the left in Brother (C). One approach is to stop knitting in pattern opposite the color changer, (red line), program the second piece of the “longer” design, and start to knit the first row of color 1 again for that pattern segment, going from right to left/ toward the color changer(C). Color changing then follows every 2 rows until the top of the second pattern piece is reached, repeating as needed.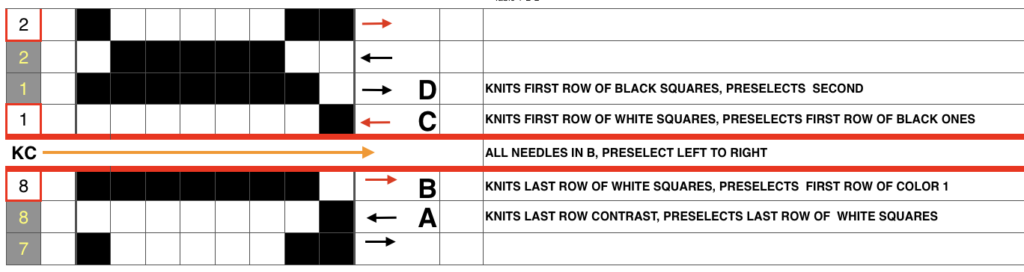
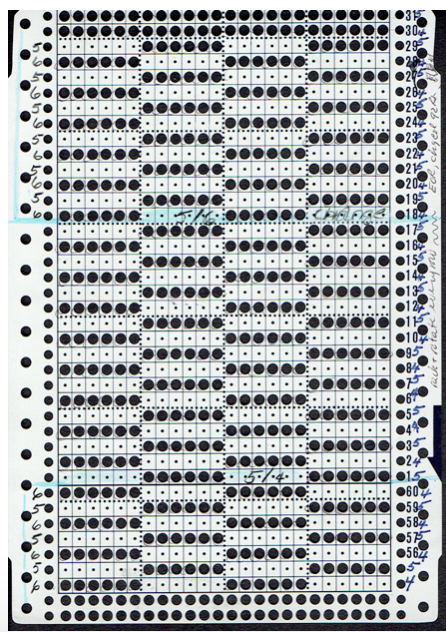
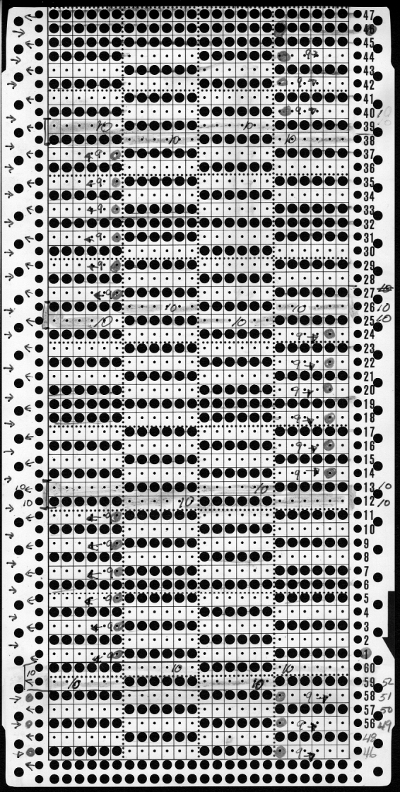
The full mylar repeat scanned and processed for use as images to be eventually downloaded via cable is shown in the top image. Below it segments 1-40 stitches, rows 1-30, 41-60, and 61-90 are shown as selected, cropped in turn, with corresponding .bmps saved for cable download. AYAB users can work with image software like Paint, Gimp, etc. to process and save them as b/w bitmap, png, etc. Img2track accepts common image formats (jpg, gif, png, .bmp, tiff). Both software programs may be used on PCs and Macs. Wincrea Win_Crea can open files in .cut (Passap), .bmp, or .wmf formats, and can be saved in .cut and .bmp. Passap and the 930s hold the segments in their own memory, while ayab knits from the screen. Stitch Painter (2.0) prior to the latest release used to have limited import and export formats, including .cut. There now is a new website for the program, and a new release, and I could not find info on exports beyond “There are now numerous export file formats including PDF, JPG, TIF, PNG, and other popular formats.”
The full mylar 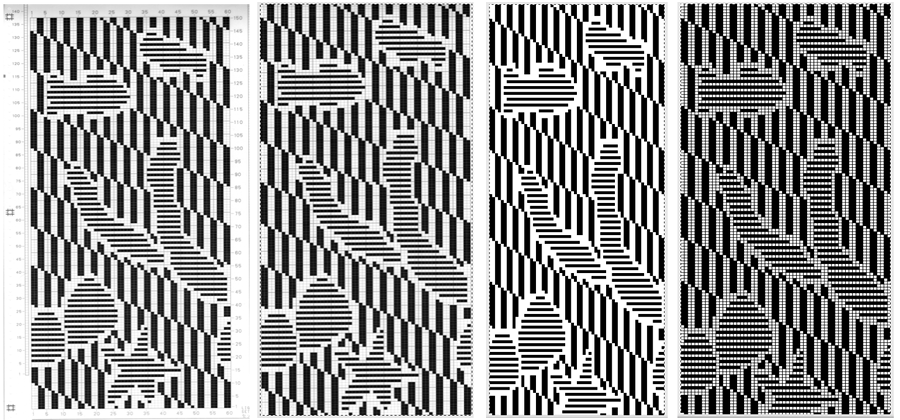 three segments, selected from its bottom left
three segments, selected from its bottom left 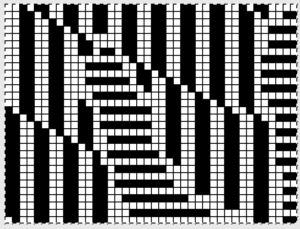
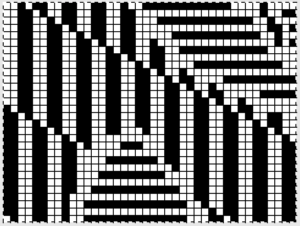

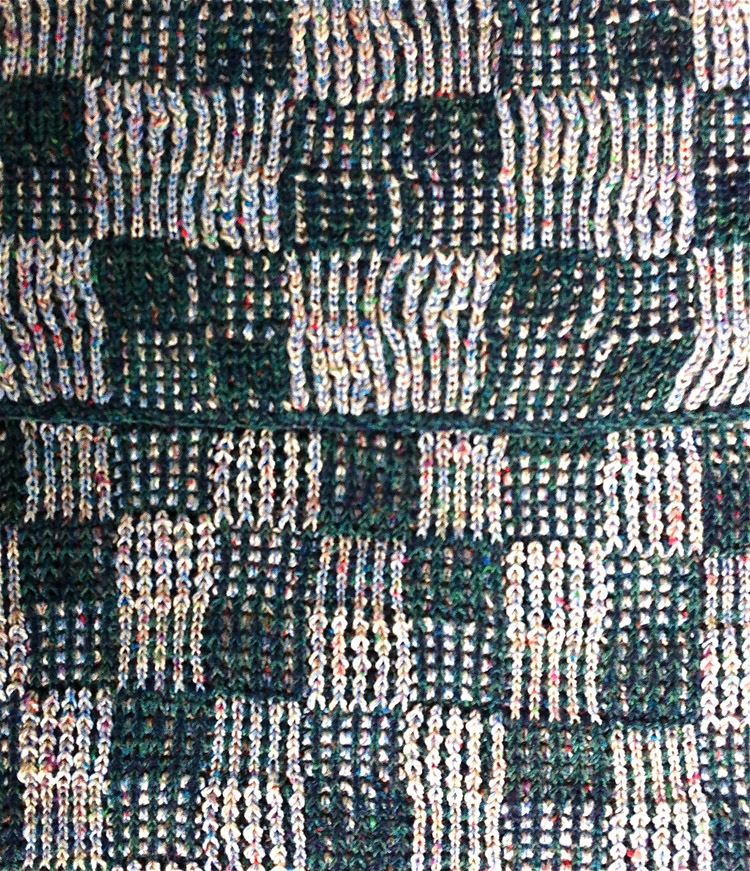
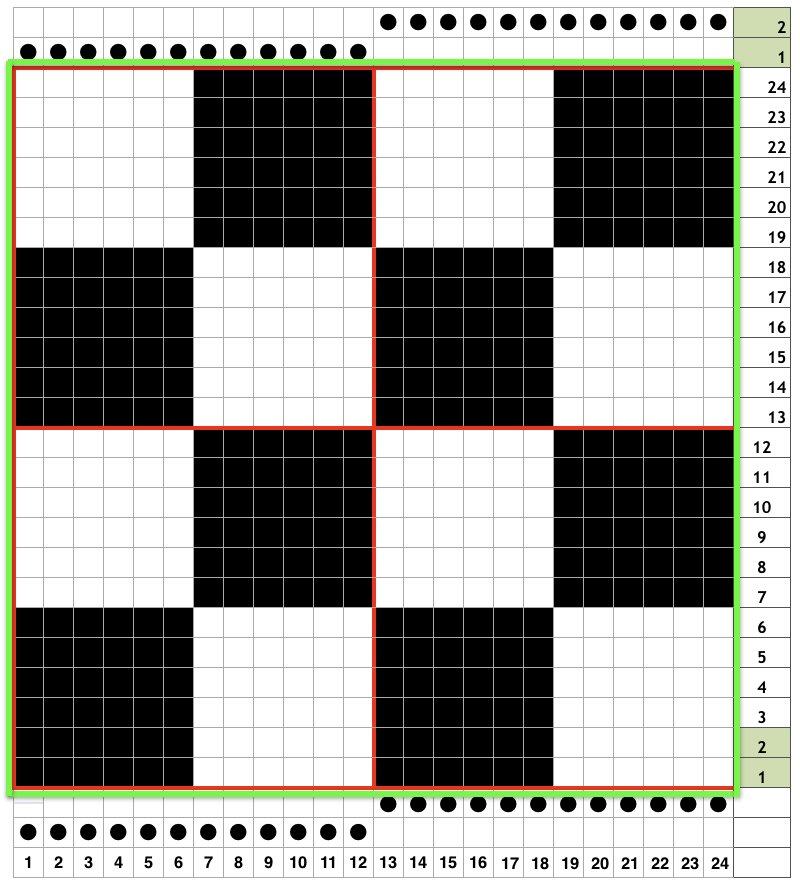
Proof of concept swatch on 910 using the mylar, programmed consistently in width on needles 1-40, with height for each segment 1-30, 31-60, 61-90. I was knit in a throw-away yarn, in unfamiliar DBJ tension settings, so I had some dropped stitches seen in the left, the bottom of the swatch image that were resolved with adjustments in settings. Note the image is reversed vertically by the program automatically with all variation levers down with the exception of the KRC one
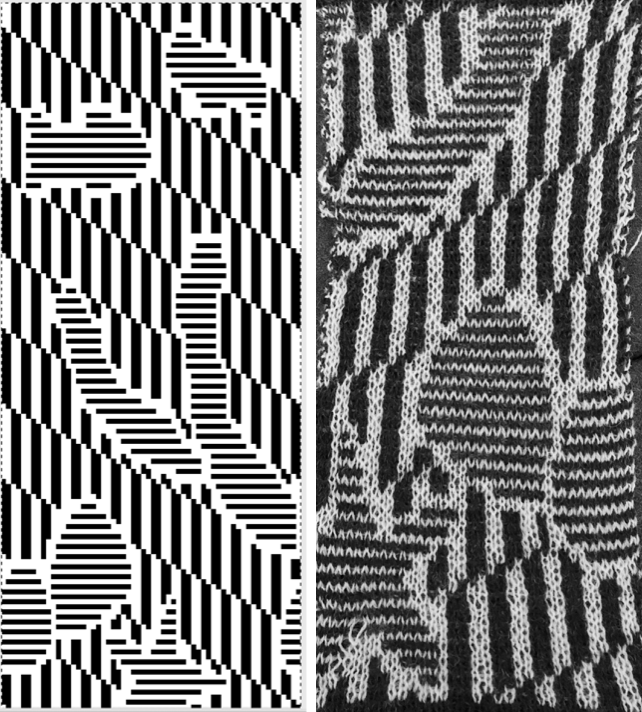
One develops preferred ways of handling images as their knitting experience increases and varies. I have always done my own scaling prior to any actual knitting. Software programs at times offer to adjust the height based on knitting technique and either real or estimated gauge. Passap has a smooth edge feature to decrease stepped effects if the image is enlarged in multiples by the console. In double bed work, sample swatches are often much larger than when working on a single bed, at least 100 stitches by 100 rows. Because DBJ lengthens the image by default (every single row of design now requires 2 passes of the carriage), a separation for a 30-row design would require 60 rows of knitting on the machine to complete the repeat. Ribber settings can help reduce elongation in addition to any scaling of the motif. One alternative would have the ribber knitting in one direction, slipping in the other. This means that every other row the main bed will create floats for the non-knitting color, get caught between beds on the next pass.
In my test design, such floats are quite long in sections of the motif, resulting in problems, so that left me with choosing the lili setting.
Lili buttons on Brother machines behave like a 1X1 punchcard does on the main bed. There is no free pass with ribber set to slip in both directions if lili buttons are engaged. It is the equivalent of making such a pass on the main bed with every other needle selected, where any stitches on selected needles would be dropped if there is no yarn in use. Also, one may not slip on the same needles continually, so needles in use on the ribber must total an even number, in pairs of what I refer to as dash and blank or blank and dash markings on the needle tape. The pusher selection on the Passap selections operates differently, so an even vs. odd total # rule doesn’t apply.
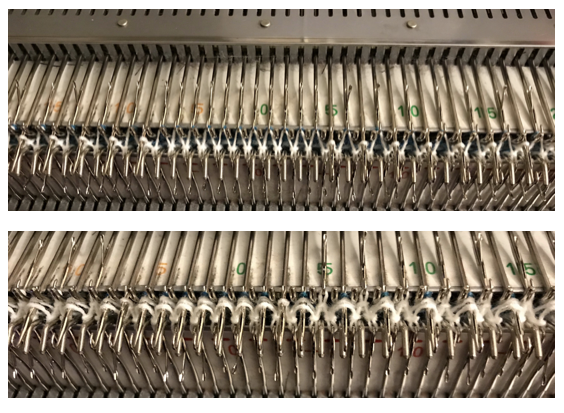
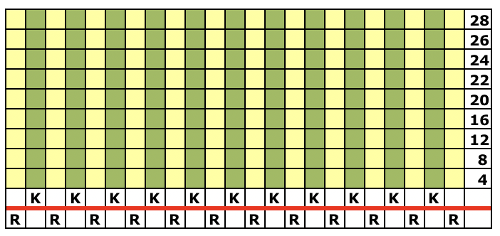
These photos illustrate needle selection on ribber, first beginning with a dash on the left, ending with a blank on the right, the second beginning with a blank on the left, and ending with a dash on the right. It is the second needle on the carriage side that gets selected in each direction, regardless of the starting mark for needle pairs. Here the blank knits to the right, the dash knits to the left,  and its reverse, with dash knitting to the right, and blank knitting to the left. There is no way without operator intervention to get that first needle to be the one knitting (such adjustments are made to achieve striper backing as opposed to birdseye, a different topic altogether
and its reverse, with dash knitting to the right, and blank knitting to the left. There is no way without operator intervention to get that first needle to be the one knitting (such adjustments are made to achieve striper backing as opposed to birdseye, a different topic altogether
I programmed my first repeat segment after casting on, ending with dark color, both carriages on the left side. The white squares (in this case knit in white yarn) need to be knit on the first row from right to left. Either remove the ribber carriage and move it to the opposite side or tilt it forward and move it to the right, being careful not to engage any needles. After it is in place, set it for birds-eye backing
The knit carriage is now brought to the left, set to slip in both directions, KCI or II, in proper placement outside the turn mark for the first preselection row to the right. Make a free pass to the right, needles will be selected in pattern for the first single row of white squares (needles on the main bed after cast on are already only in B position). Place the yarn properly in the feeder, couple the carriages, knit right to left, and change color every 2 rows.

At the row before the last row of the pattern (top row, color 1), the card is automatically returned to the starting position of the pattern. When the machine buzzer alerts with its sound that the end of the repeat is being reached, the contrast color 2 (black squares) will be on the right side. In my initial attempts, I used the approach: knit to left, change to white (color 1), knit a single color 1 row left to right, and stop. Do not cut the yarn. The next pass to the left needs to knit the first white squares row in the next segment. The ribber carriage remains on the right, the bird’s eye pattern on the back will not be interrupted. I took the knit carriage off on the right, moved it back to the left side, it will not be holding any yarn. Prepare for knitting the second segment. There will still be needles selected (they would have knit the first white row when moving from right to left if the repeat were a continuing one). They need to be manually pushed back to B or those stitches will be dropped on the free pass to the right. Program the new repeat segment, and as usual, pre-select to right, place white yarn back in the proper position in the feeder, engage both carriages, and knit repeating the process until once again, a first, single row of the white is knit at the top of the second segment. The machine sounds serve as reminders when you have reached the point where things require attention. The process is repeated until all necessary pieces have been knit, composing the much longer image. As I worked further, I believe the same method may be used as seen below with the mylar in place. Knit the last row with the ground color to the left, preselection for the white squares is made on the way. Do not disturb needle selection on the bed or settings on either carriage. COL. Program the next segment, begin on the far left outside the turn mark, and change color to color 1 (white squares). As the carriages move to the right, the last row of segment one knits, and the first row of segment 2 is preselected. As the carriages return to the left to begin color-changing sequence every 2 rows, row 1 color 1 segment next will knit, while the first row of the ground (black squares) will preselect.
I recently received a second EMS Ayab kit I am just now beginning to use. Here the same image, bottom segment only, is tested. Knowing Ayab selects black squares first in its ribber setting I used the action invert available in the program itself to color reverse (middle image) so white would knit first. The process remains essentially the same in terms of ribber and other settings prior to knitting color 1 design row 1. The difference here as compared to the sample knit with the built-in KRC, all other buttons down, is that the native 910 KRC image is reversed on the knit side, it is knit as it would appear on the purl side. The Ayab version automatically mirrors the motif to have the original appear on the knit side as drawn.  I did attempt to load the 3 segments into the program, and knit them using the single setting (left), and the infinite one (right). The single setting gives one alert when the top of the repeat is reached akin to the native buzzer, the infinite relies on the operator to know to stop. I had problems with the yarn I was using and dropping stitches after out of curiosity I decided to add the latch opening plate to my ribber carriage. They went away when I removed it in subsequent swatches. I was not successful again using the single setting. The arrows mark what appears to be needle selection errors in both series.
I did attempt to load the 3 segments into the program, and knit them using the single setting (left), and the infinite one (right). The single setting gives one alert when the top of the repeat is reached akin to the native buzzer, the infinite relies on the operator to know to stop. I had problems with the yarn I was using and dropping stitches after out of curiosity I decided to add the latch opening plate to my ribber carriage. They went away when I removed it in subsequent swatches. I was not successful again using the single setting. The arrows mark what appears to be needle selection errors in both series.  9/18/18 Because of space restrictions at the moment my ayab and 910 are in “storage”. As I kept working, it occurred to me this method might be the way to go when using Ayab as well, at present it is untested
9/18/18 Because of space restrictions at the moment my ayab and 910 are in “storage”. As I kept working, it occurred to me this method might be the way to go when using Ayab as well, at present it is untested 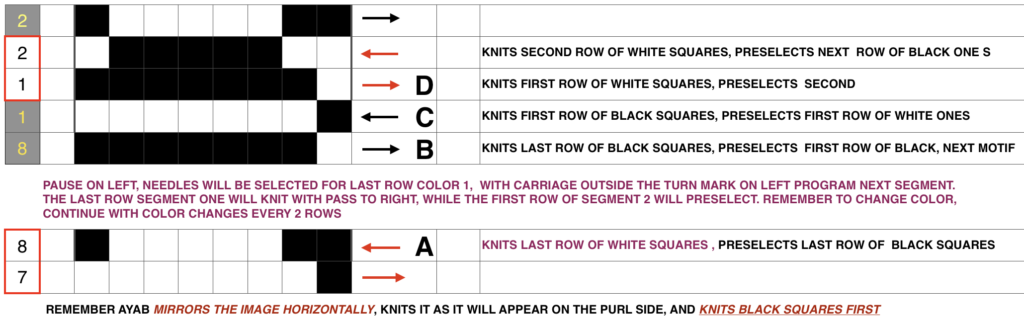
Here I attempted proof of concept with img2track on my 930 which is nice enough to track rows knit. As the top of the first segment was reached and the carriage began to reverse direction from the right, the machine made a warning sound, alerting me to the fact that the second row for row 30 of color 2 was about to be knit  as the carriage moved back toward the color changer selection was made for the last row of color 1
as the carriage moved back toward the color changer selection was made for the last row of color 1 making certain I did not disturb the needle selection in that row, I took the carriages to the far left, programmed the second segment in the repeat, with no other changes to carriage settings, changed to color 1. The above row is knit on the first pass to the right with color 1, while the preselecting row 1 for color 1 in the new segment and knitting it on the return to the color changer. The idea appeared sound, but then I ran into this: random dropped stitches. At first, I thought it might be a yarn issue (different fiber content and weight). After a break, I took the time to check all ribber adjustments, since this deconstruction was not part of the plan.
making certain I did not disturb the needle selection in that row, I took the carriages to the far left, programmed the second segment in the repeat, with no other changes to carriage settings, changed to color 1. The above row is knit on the first pass to the right with color 1, while the preselecting row 1 for color 1 in the new segment and knitting it on the return to the color changer. The idea appeared sound, but then I ran into this: random dropped stitches. At first, I thought it might be a yarn issue (different fiber content and weight). After a break, I took the time to check all ribber adjustments, since this deconstruction was not part of the plan.  Adjustments in ribber height (dropped a bit on each side) appeared to solve the problem. I began the swatch intentionally with plain knit stripes as an initial check, and switched color 2 to the other yarn to test any different behavior there as well. I had actually moved my ribber from my 910 to the 930 without checking alignment and spacing after doing so, lesson learned.
Adjustments in ribber height (dropped a bit on each side) appeared to solve the problem. I began the swatch intentionally with plain knit stripes as an initial check, and switched color 2 to the other yarn to test any different behavior there as well. I had actually moved my ribber from my 910 to the 930 without checking alignment and spacing after doing so, lesson learned.
A theoretical design as a starting point for more discussion in Facebook 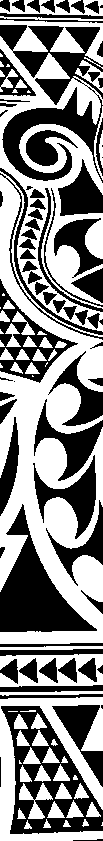
I cannot speak for img2track from personal experience. When I posed the question to the FB group as to how the program might handle a long, non-repetitive image, I supplied the image above. It is not knittable as is, 103X841(odd#) rows, from a random illustration, found online that would need a lot of “clean up”. Assuming it was knit ready, an even number of rows and other DBJ setup requirements are met does the 2 color separation work for the whole image length or must the image be divided into segments that are in turn knit and color separated separately? Tanya Cunningham, the creator of the group, was kind enough to respond in the forum, and I have her permission to share her response here. “Img2track creates a B&W pattern of the full length of the image. THAT file is useable in other applications. Many people create an image file with img2track, then load that image file into DAK to knit. Img2track does NOT create separate image files for the various tracks into which it breaks larger images. That happens when you request the pattern from the machine console. When img2track receives the request from the KM, it offers all tracks, and you select which one you wish to load. This image is already in a format such that it will not be altered by img2track (.bmp) (unless you restrict the width.) I selected it with img2track, and the resulting “pattern” was basically the identical image, just converted to a png.
The image was at first loaded in an uneven number of rows, and the software gave the warning “It will not end well!”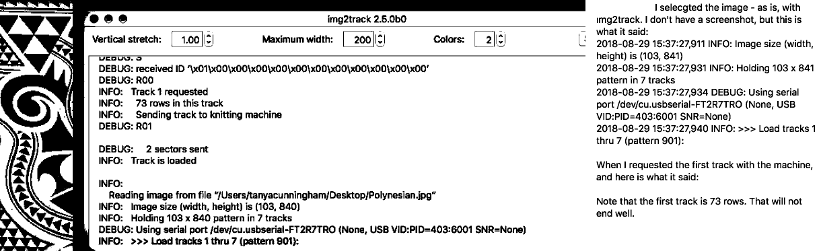

“As you knit the last row of each track (left to right) you will be selecting the needles for the first row of the next track. Thus, when you arrive at COR with color 1, you will be all set up for knitting the first row of the new track. Insofar as dividing up the pattern goes, that is done completely automatically by the software. You still have to load the successive tracks (and go outside the turn mark and select KRC). You just have to keep track of which tracks you’ve knitted. I write it down on a piece of paper each time I load a track, and how many rows it is. You can scroll back in the img2track window to see what was the last track knitted, unless img2track gets closed, and restarted, then it won’t show your previous activity unless you go to the img2track log..”
I put the same query to participants in the Facebook Ayab group. Ayab knits from the screen, so providing there is no interruption in power it appears some users are able to knit long, non-repetitive images without any subdivisions of the original pattern. Adrienne Hunter, an expert user, and great resource offered the following information: “there is effectively no length limitation in AYAB; the Arduino requests the next row as soon as it has finished selecting the current row, and the computer keeps sending the next row (color-separated as needed) until it reaches the top of the file. The pattern is in your computer’s memory which can be considered to be infinite; unlike a download to a 1980s self-contained knitting machine with very limited on-board memory. As you say, the computer must be set to stay awake, and as always you need to consciously wait for the beep on the right; the time it takes to do the color change is generally enough to cover the delay on the left.
I see occasional patterning errors in long narrow fair isle pieces too, but not in DBJ. That is because the errors can be prevented by crossing a turn mark every now and again, and with DBJ you cross a turn mark every two rows when you enter the color changer.
You will see the annoying UI bug where the display jumps back to the beginning of a long item so it isn’t showing you the section where it’s actually working. The knitting is doing the right thing, just not scrolling the display correctly to show it to you.” If accurate for the full image, this appears to be the ideal method to me.
Paint programs allow for easy manipulation of images that make it a bit easier to imagine the finished product. With the assumption I wish to knit a scarf no longer than 1200 rows using the above design, the first task is to reduce the repeat to a workable, even number of rows in height, no more than 600 rows. So I cropped the image to 94X536. It is well worth studying how the image might appear if the color reverse is used, as well as what effect mirroring it may have (especially if direction matters in your design). Pairs of mirrored images may produce interesting, far wider pattern variations. Know whether the program works first with black or white squares, and you can simply choose that color when color 1-row one begins to knit from the right. The color reverse option is built into most software and electronics. I prefer to save images as I want to knit them.  Notes to self-using ayab with images such as above: black squares knit first, so if I want the white to knit first, matching any Japanese pattern knit using KRC style separation use color reverse. If direction matters, remember that the image will be flipped vertically by the program so that it will appear on the knit side as drawn. Though technically I have no plan to knit the whole piece, I decided to test a portion of it with my new ayab board. I programmed the image on the left, wishing to get the effect noted on the right. Began on the right with color 1 = white for design row 1. I am not used to working in this scale. That said, the pattern was accurate up to the point I decided to stop because of time factors. Though the design is 94 wide, I knit only on its center 80 stitches
Notes to self-using ayab with images such as above: black squares knit first, so if I want the white to knit first, matching any Japanese pattern knit using KRC style separation use color reverse. If direction matters, remember that the image will be flipped vertically by the program so that it will appear on the knit side as drawn. Though technically I have no plan to knit the whole piece, I decided to test a portion of it with my new ayab board. I programmed the image on the left, wishing to get the effect noted on the right. Began on the right with color 1 = white for design row 1. I am not used to working in this scale. That said, the pattern was accurate up to the point I decided to stop because of time factors. Though the design is 94 wide, I knit only on its center 80 stitches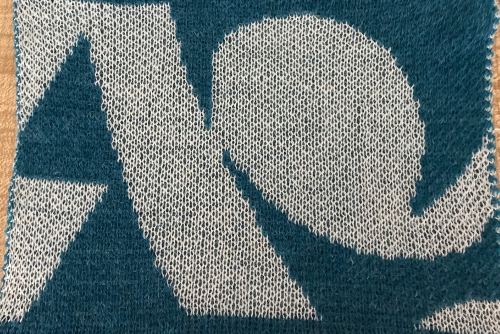
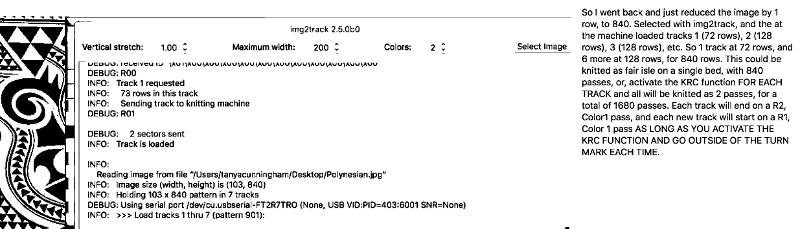
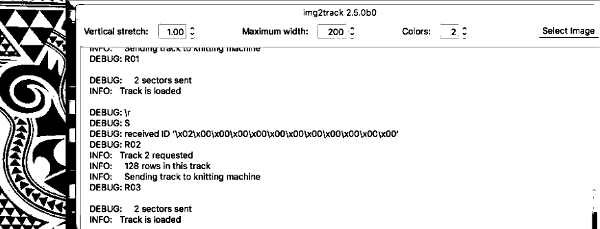
9/16/18 I received an orphan 930 which when first arrived had no movable parts related to patterning. The belt was frozen in place, and when that got liberated after cleaning and lubricating as much as I dared take apart at the time, after some initial errors the built-in patterns from several groups including lace knit perfectly, with only a slight squeak. After being stored again for a while, I tried built-in FI patterns again, and they displayed errors. I heard a new noise coming from the needle selector, exposed that, cleaned, and lubricated it, and it lost the added noise during operation. Tried built-in FI with resulting patterning errors once more. That said, test patterns in the service manual 881, 882, 884 knit perfectly. After another break for both of us, I got some built-in patterns to work again on both single and double beds and put working with them to rest. I began to work with img2track. I have not yet purchased a key. These were my first self-drawn single bed and dbj tests, none intended for any final piece.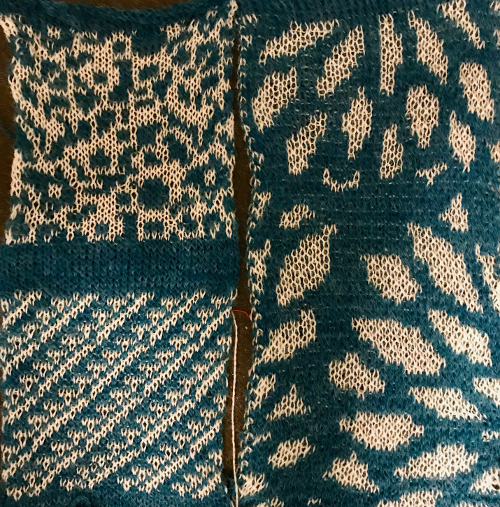 
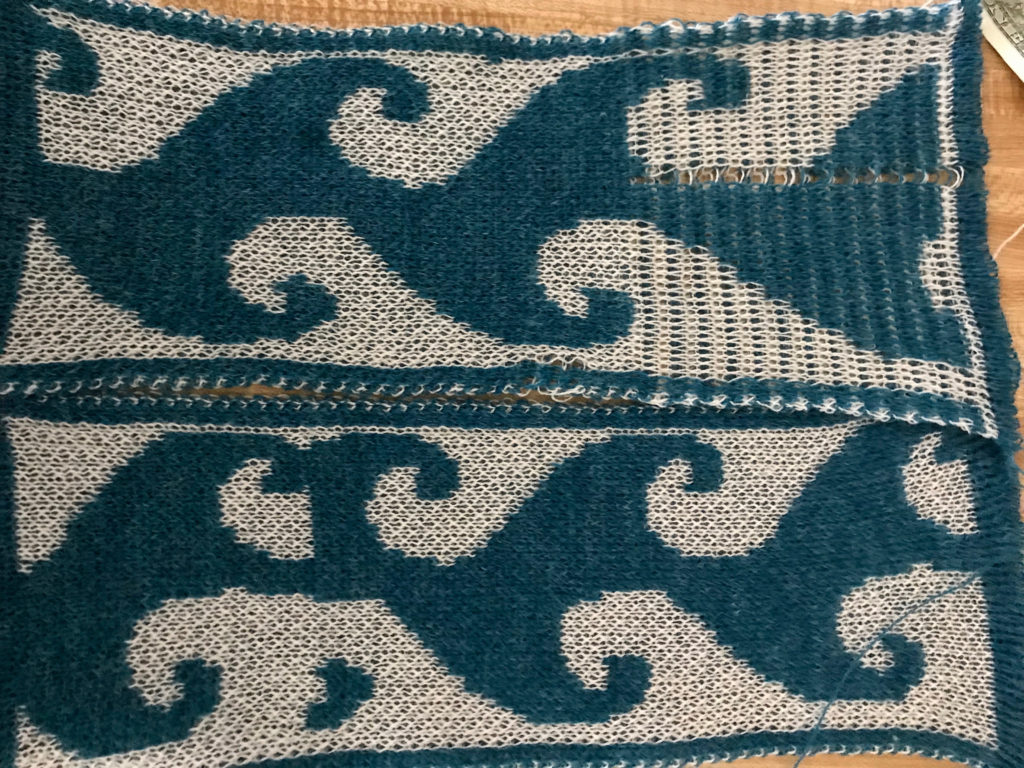
Here a quickly drafted long, narrow test design is shown with the first track self-repeating on the bottom, then with the second track programmed, and continuing on after the first (thanks to help and feedback in the FB group; long stitch striper backing and dropped stitches = extra “design features”. The program makes a sound when the last row of ground (black squares) is reached. The carriage is then moved to the left, knitting that last row of ground while selecting the last row of color 1 for that specific track. When on left, begin outside the turn mark, program the next track, change to color one, remember to set for KRC, knit to right (Cam button will already be set for KCI orII). As you do so, the last row of color 1 is knit, the first row of the next track for color 1 will be selected. The latter will knit on the way back to the color changer. Continue in pattern, changing colors every 2 rows. Knitting is uninterrupted by having to change carriage settings on either bed, the backing pattern is also uninterrupted. 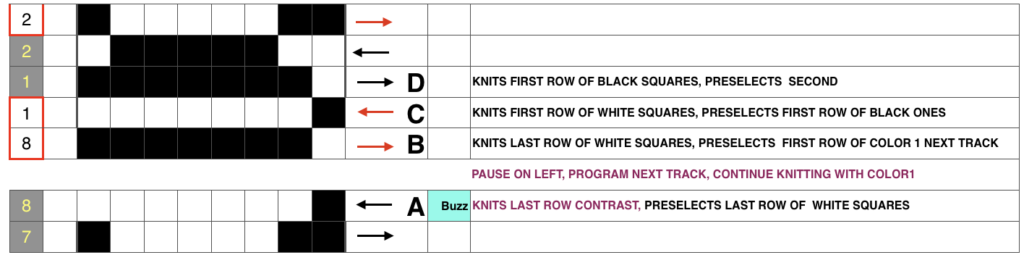

as described in the user guide: to download, launch program and select
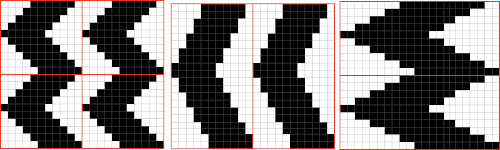
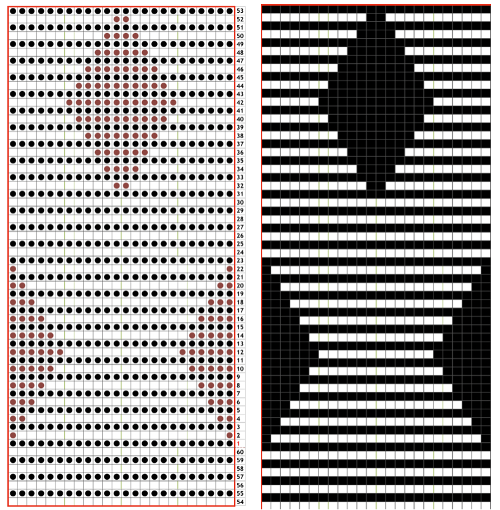
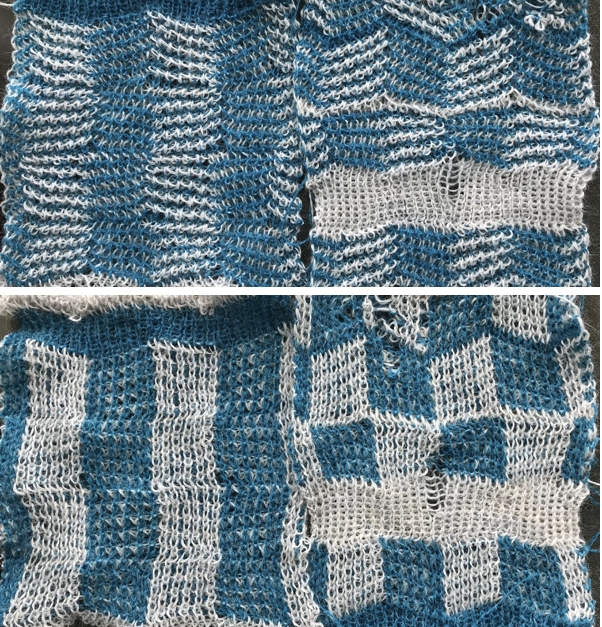
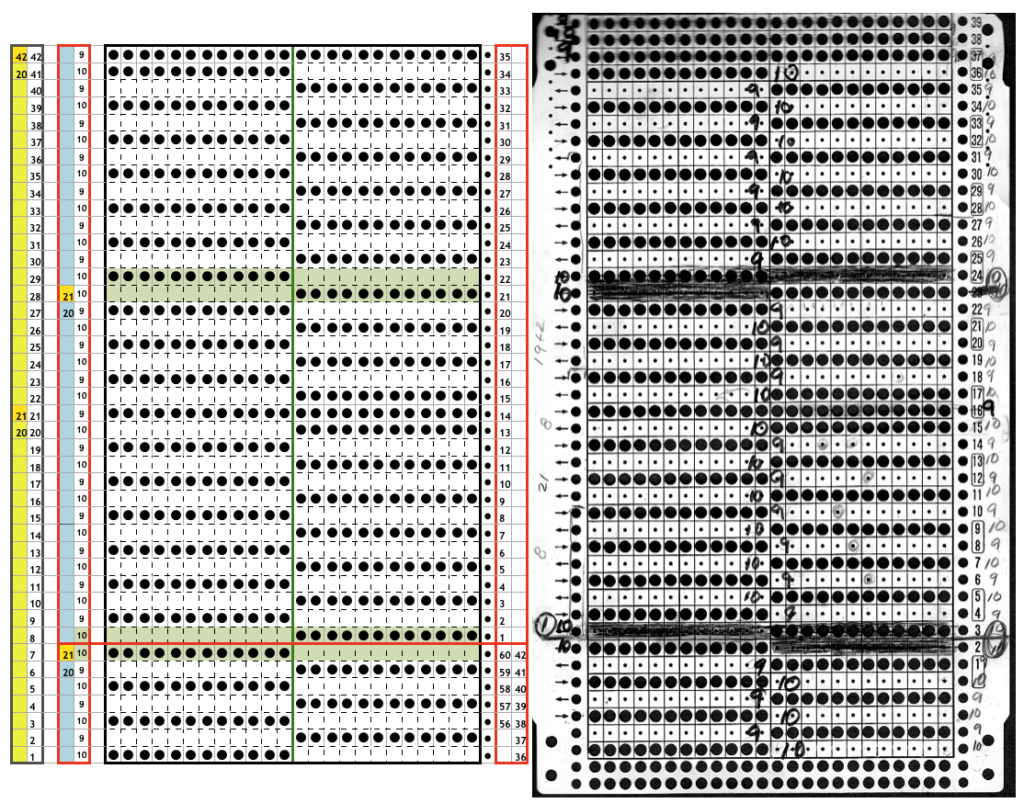
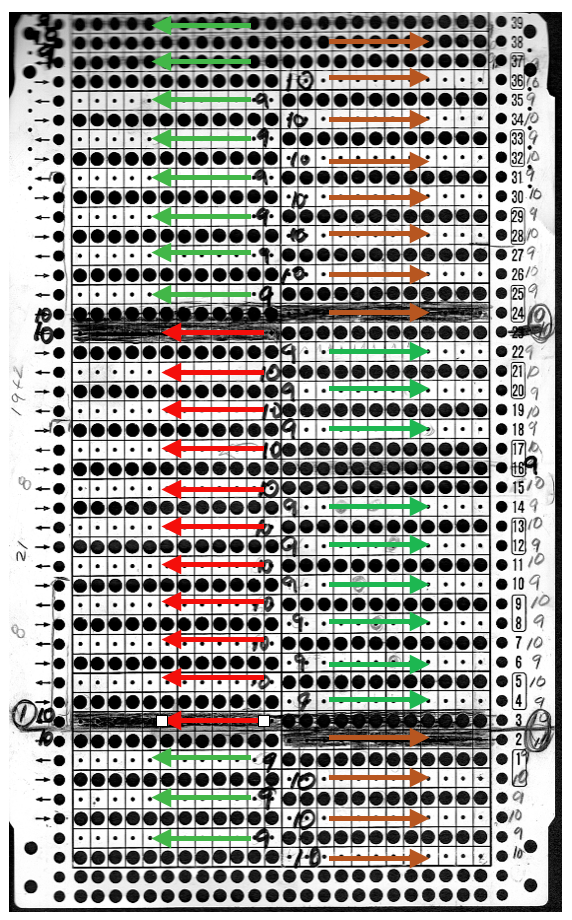
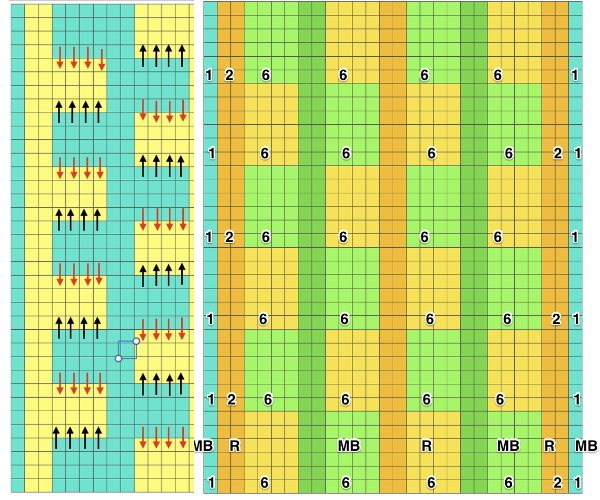
“The KH-930 takes just a few seconds to load the track because the memory holds only 2 KB of data (about 13000 stitches). Later models have a much larger memory (32 KB). The KH- 940 and KH-950i require 42 seconds to load a track.” “If your pattern was divided into more than one track, you will have to load successive tracks when completing the previous track. Listen for the beep from the knitting machine, indicating that the carriage is about to knit the next to the last row of the track, selecting needles for the last row of the track. Knit this second to the last row, and then STOP. (If you simply continue knitting at this point, the knitting machine will knit the last row of the track and select needles for the first row of the same track). To load the second track of the pattern, enter CE 551 STEP, and then 2 STEP prior to knitting the last row of the current track. (If your computer goes to sleep while you are knitting, you will be unable to load additional tracks. Be sure to check that your computer is not asleep before attempting to load successive tracks.) Before you begin to knit the last row and select needles for the first row of the next track, be sure that the carriage passes outside of the turn mark. The knitting machine will retain the loaded track in its memory until you alter it. You can turn it off, and later turn it on and resume where you left off.”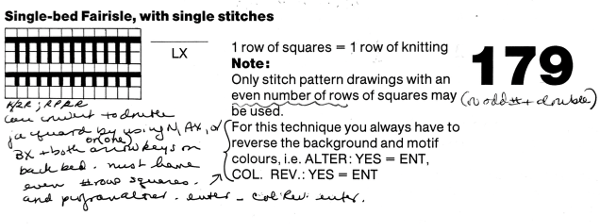 So what about Passap and using it for emulating the KRC 2 color DBJ? The Passap color changer to start with is on the right side rather than the left. All preselection of pushers (they will, in turn, drive the needles to move into work or not) always starts from the left. The first pass to the left after casting on and the pattern is programmed brings them all in to work in a flat line, the first preselection row is left to right, with color changes following every 2 rows. Settings for those 2 rows can vary, the console guides you through supposed 2 free passes with settings at SX/GX, the equivalent of Brother slip in both directions/ slip in both directions. Technique 179 is intended for simulating single-bed FI in Japanese machines, the manual recommends color reverse. In DBJ that would line up with KRC selecting white squares first. I like thinking of my black squares as my pattern ones, so I tend not to use the color reverse, and choose my contrast color accordingly. I decided to program the same built-in pattern twice, as A and B, each using tech 179, a repeat in which I thought it might see easily what happens when the “2 separate segments” intersect. Below is the pattern is seen charted in B/W, tiled, and knit. Notice in the knit swatch that the first row in each sequence repeats twice.
So what about Passap and using it for emulating the KRC 2 color DBJ? The Passap color changer to start with is on the right side rather than the left. All preselection of pushers (they will, in turn, drive the needles to move into work or not) always starts from the left. The first pass to the left after casting on and the pattern is programmed brings them all in to work in a flat line, the first preselection row is left to right, with color changes following every 2 rows. Settings for those 2 rows can vary, the console guides you through supposed 2 free passes with settings at SX/GX, the equivalent of Brother slip in both directions/ slip in both directions. Technique 179 is intended for simulating single-bed FI in Japanese machines, the manual recommends color reverse. In DBJ that would line up with KRC selecting white squares first. I like thinking of my black squares as my pattern ones, so I tend not to use the color reverse, and choose my contrast color accordingly. I decided to program the same built-in pattern twice, as A and B, each using tech 179, a repeat in which I thought it might see easily what happens when the “2 separate segments” intersect. Below is the pattern is seen charted in B/W, tiled, and knit. Notice in the knit swatch that the first row in each sequence repeats twice.  What appears to be happening, is that only that very first row is repeated twice for one time in the color separation at the very beginning of the knit. The arrows on the right indicate movements of the locks to and from the color changer, knitting my black squares. If row one is knit in that color twice only once, and the pattern subsequently is kept continuous, rolling back to row one for only a single pass, the 2-row color rotation can be maintained. The bold, green border outlines the single, full repeat. The separation is only for illustration of placement for the one color.
What appears to be happening, is that only that very first row is repeated twice for one time in the color separation at the very beginning of the knit. The arrows on the right indicate movements of the locks to and from the color changer, knitting my black squares. If row one is knit in that color twice only once, and the pattern subsequently is kept continuous, rolling back to row one for only a single pass, the 2-row color rotation can be maintained. The bold, green border outlines the single, full repeat. The separation is only for illustration of placement for the one color.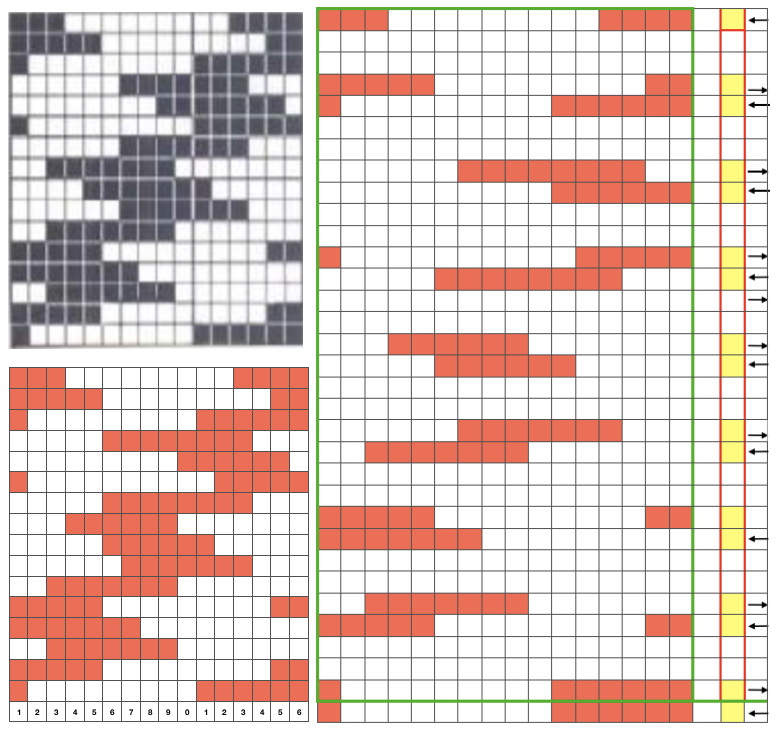
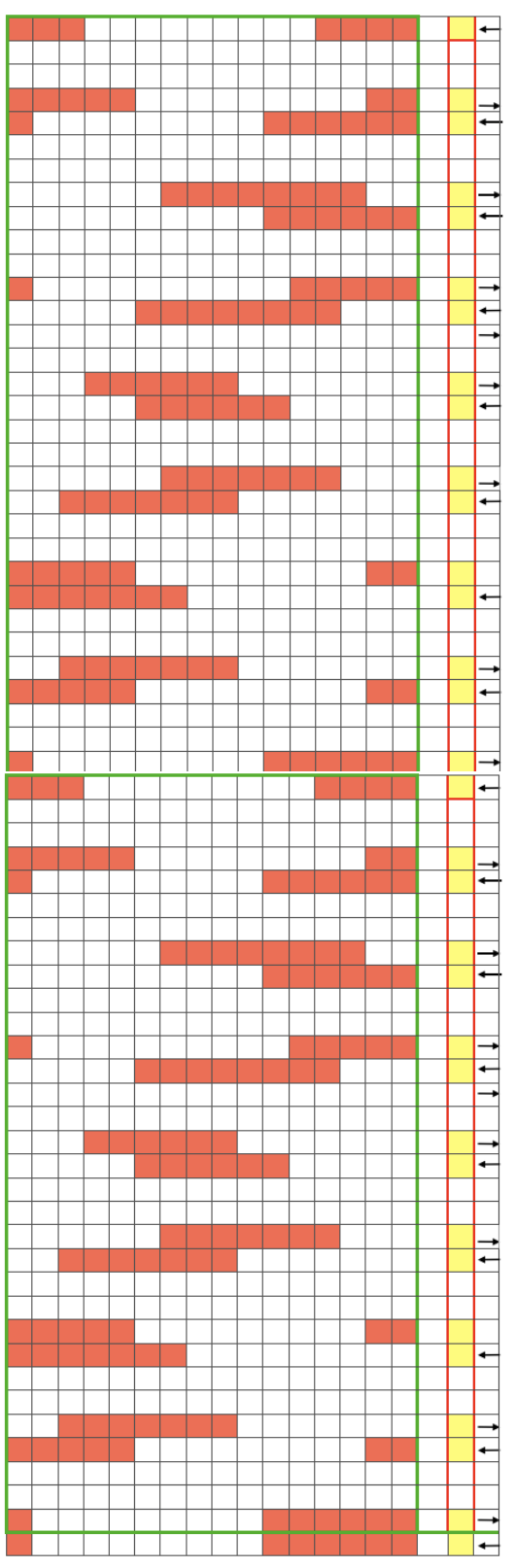
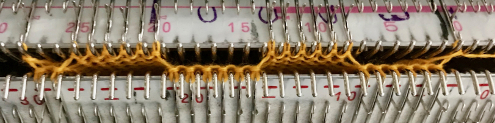
Swatching again with an attempt to produce it as 2 separate but continuous segments: I do not use color reverse, choose my color to match black squares, and that would be color 2 on the console prompt. In my first attempt, I followed other usual console prompts but used SX/GX settings for three rows rather than 2. The first pass will lift all pushers into work. The second pass preselects pushers for the first row of the pattern to the right. The third pass would normally knit the first row of the pattern, preselect for the second row to be knit from left to right, and so on. After the third SX/GX pass the locks are on the left side(LOL), I changed the settings for pattern knitting (LX/BX). On the right, make certain the empty yarn holder is up for the next color. On the left place the yarn into an eyelet, making certain it was positioned so it would not be crossing other color yarn on travel back to the color changer. Knit single row to the right, changed color, continued knitting in pattern unit the top of the segment was reached (row countX2, in this instance = 32). The design color knit its last pass, locks are on the right (LOR) Programmed second segment, repeated 3 rows of SX/GX. On the left, yarn in the feeder, proceed as above. This gave me correct continuous segments on the knit side of the fabric, but the bird’s eye backing was disrupted. On the bottom because of operator error in the lock setting, and the top because birds-eye normally knits EON for 2 rows, creating a bit jaggy, a single line of color after knitting on all needles when the second pass is knit, while here it EON for one row only, missing that second pass. Note yarn ends, the yarn would need to be cut to position it for those single-row passes from left.

It is really helpful to use colors that are in high contrast when testing patterns. Here color positions are reversed, the red is now my ground (white squares with no color reverse), and the blue at the segment change muddies things considerably to my eye. Maintaining the Birdseye selection is now sorted out and actually makes for easier knitting

 the resulting fabric
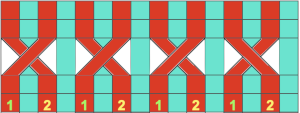
the resulting fabric  The method: both carriages are used to select needles, use lace extension rails on both sides of the machine. Cancel end needle selection on knit carriage underside if possible, or push end needles back manually if needed to avoid their corresponding stitches being transferred throughout the piece. Set up for knitting the pattern as usual, punchcard row 3 (marked in pencil) becomes row 1 of the design when the above card is used in the Brother machine. The arrows always indicate the direction the lace carriage will move across the knit to make transfers in the direction of that same arrow.
The method: both carriages are used to select needles, use lace extension rails on both sides of the machine. Cancel end needle selection on knit carriage underside if possible, or push end needles back manually if needed to avoid their corresponding stitches being transferred throughout the piece. Set up for knitting the pattern as usual, punchcard row 3 (marked in pencil) becomes row 1 of the design when the above card is used in the Brother machine. The arrows always indicate the direction the lace carriage will move across the knit to make transfers in the direction of that same arrow. double length
double length 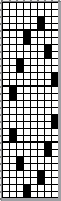 on the first row the LC selects, the next row it will transfer; LC always makes 2 passes first toward the KC, then away from it, even if those 2 rows in repeat have no needle selection. It is then removed from the bed to be returned to the bed on the opposite side after the knit row with KC that follows. In summary:
on the first row the LC selects, the next row it will transfer; LC always makes 2 passes first toward the KC, then away from it, even if those 2 rows in repeat have no needle selection. It is then removed from the bed to be returned to the bed on the opposite side after the knit row with KC that follows. In summary: This sample was knit beginning with lace carriage on left, as can be seen in marked areas, the alternating repeats have a different quality in the sets of transfers marked red vs green
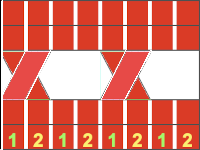
This sample was knit beginning with lace carriage on left, as can be seen in marked areas, the alternating repeats have a different quality in the sets of transfers marked red vs green  The successful swatch knit beginning with KC on the left, and LC on the right in the method described above
The successful swatch knit beginning with KC on the left, and LC on the right in the method described above  April 2019 I attempted the same repeat on the 930 with img2track. I mirrored the repeat horizontally and elongated it X 2 prior to knitting it. The arrows in the chart indicate the movement of the lace carriage, beginning with the first preselection row from the left
April 2019 I attempted the same repeat on the 930 with img2track. I mirrored the repeat horizontally and elongated it X 2 prior to knitting it. The arrows in the chart indicate the movement of the lace carriage, beginning with the first preselection row from the left 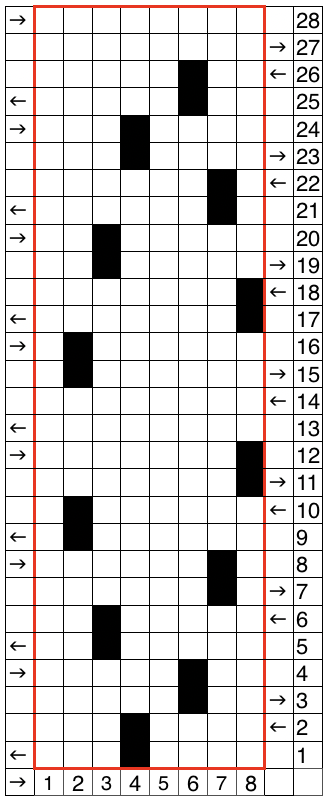 I had issues with the proper needles being selected (proofed also in fair isle), but with random stitches not being transferred. A switch in lace carriages, needle retainer bar, yarn, did not eliminate the problem. I finally had to perform some of the transfers by hand. This swatch also shows the joy of missed dropped stitches in lace knitting, the yarn used is a thin acrylic.
I had issues with the proper needles being selected (proofed also in fair isle), but with random stitches not being transferred. A switch in lace carriages, needle retainer bar, yarn, did not eliminate the problem. I finally had to perform some of the transfers by hand. This swatch also shows the joy of missed dropped stitches in lace knitting, the yarn used is a thin acrylic.  Different year (2023), even thinner yarn, with the image mirrored horizontally on the 930 using the method described above, the new knit proof of concept:
Different year (2023), even thinner yarn, with the image mirrored horizontally on the 930 using the method described above, the new knit proof of concept: 
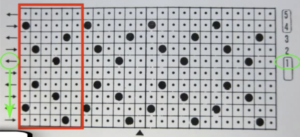 A comparison of my repeat using a single LC and the Knitlabo pattern expansion including memo options for use with 2 lace carriages
A comparison of my repeat using a single LC and the Knitlabo pattern expansion including memo options for use with 2 lace carriages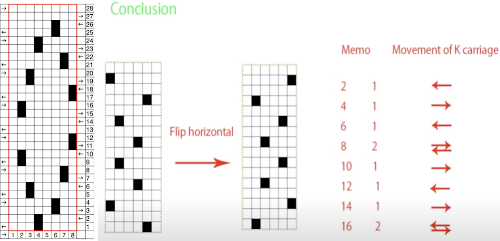

 113 has single rows between repeat segments, requiring added manipulation of the knit carriage
113 has single rows between repeat segments, requiring added manipulation of the knit carriage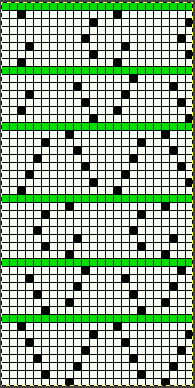 the 24X48 png
the 24X48 png![]() On a 930 with img2track use the # 1 variation key with the pattern repeat as shown, or flip horizontally before downloading.
On a 930 with img2track use the # 1 variation key with the pattern repeat as shown, or flip horizontally before downloading.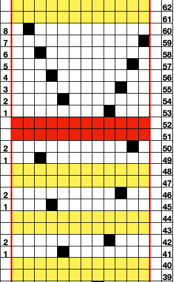
 The 12X104 png, on a 930 with img2track remember to use the # 1 variation key
The 12X104 png, on a 930 with img2track remember to use the # 1 variation key ![]() If one makes a choice or is required to repeat the width of the design to the number of needles used on the needle bed, it is easy to accidentally use the pencil in a paint program when working between windows. This test swatch clearly shows selection errors on a side edge only.
If one makes a choice or is required to repeat the width of the design to the number of needles used on the needle bed, it is easy to accidentally use the pencil in a paint program when working between windows. This test swatch clearly shows selection errors on a side edge only.  One way to check the repeat, handy when repeats are much larger or visually confusing: open the faulty one in Gimp, working in RGB mode, select by color and change black pixels to red, and make the white background color transparent by using Layer/Transparency/Color to Alpha. Open a new image, and carefully draw the design in repeat once more in the same location as in the first work window. Copy and paste the red pixels onto the black, revealing the missing pixels and the associated transfers on that edge. Fill red pixels with black, return the image to BW indexed mode, and save the new PNG to knit the piece.
One way to check the repeat, handy when repeats are much larger or visually confusing: open the faulty one in Gimp, working in RGB mode, select by color and change black pixels to red, and make the white background color transparent by using Layer/Transparency/Color to Alpha. Open a new image, and carefully draw the design in repeat once more in the same location as in the first work window. Copy and paste the red pixels onto the black, revealing the missing pixels and the associated transfers on that edge. Fill red pixels with black, return the image to BW indexed mode, and save the new PNG to knit the piece. 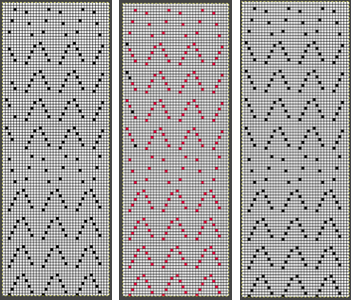 Redesigned for use on Brother machines with the LC operating from the left and the standard 2 knit rows between each design segment
Redesigned for use on Brother machines with the LC operating from the left and the standard 2 knit rows between each design segment 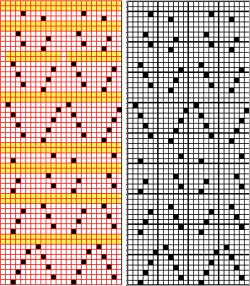 the 24X56 png
the 24X56 png ![]() knit mirrored horizontally on the 930, using a 2/18 wool
knit mirrored horizontally on the 930, using a 2/18 wool 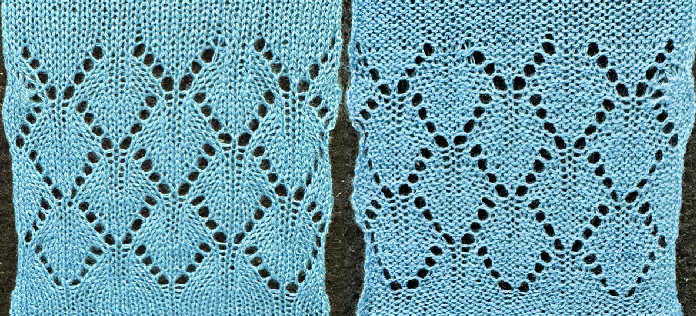 comparing both versions
comparing both versions  a cousin version executed as a bulky knit
a cousin version executed as a bulky knit Yet another method, illustrated in Swatches based on adapting random online published repeats
Yet another method, illustrated in Swatches based on adapting random online published repeats Mesh experiments using thread lace punchcards. This image also illustrates the yarn lines created in the eyelet spaces: a single thread when single rows are knit between repeats and twisted double threads when 2 rows are knit between transfers.
Mesh experiments using thread lace punchcards. This image also illustrates the yarn lines created in the eyelet spaces: a single thread when single rows are knit between repeats and twisted double threads when 2 rows are knit between transfers. 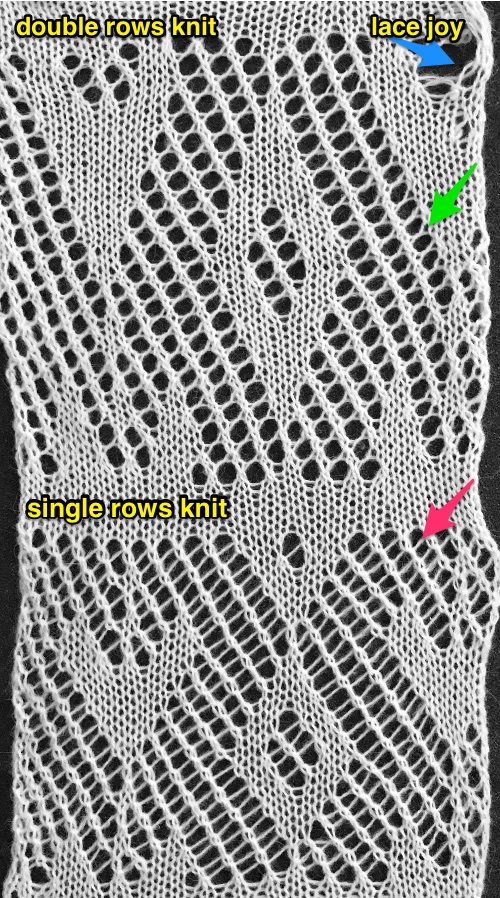 A later experiment Using StitchWorld #545
A later experiment Using StitchWorld #545 ![]()
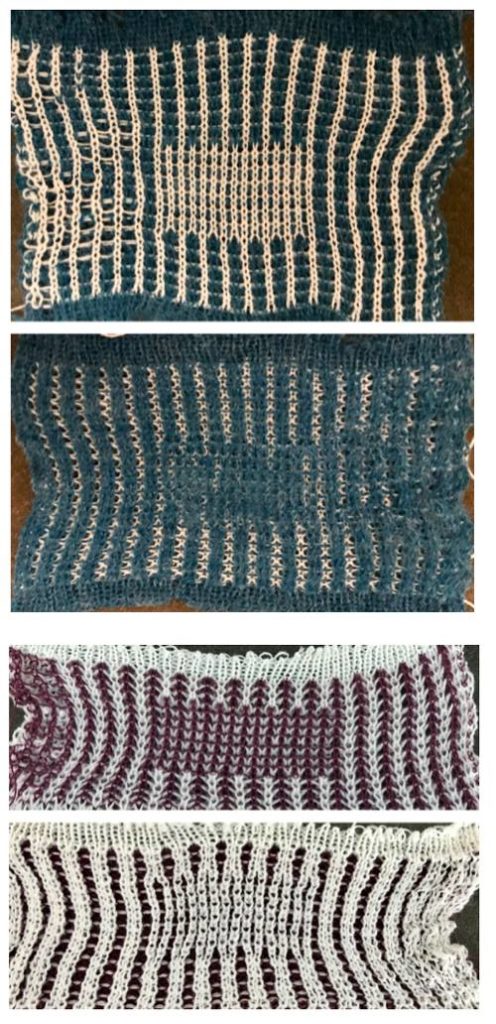
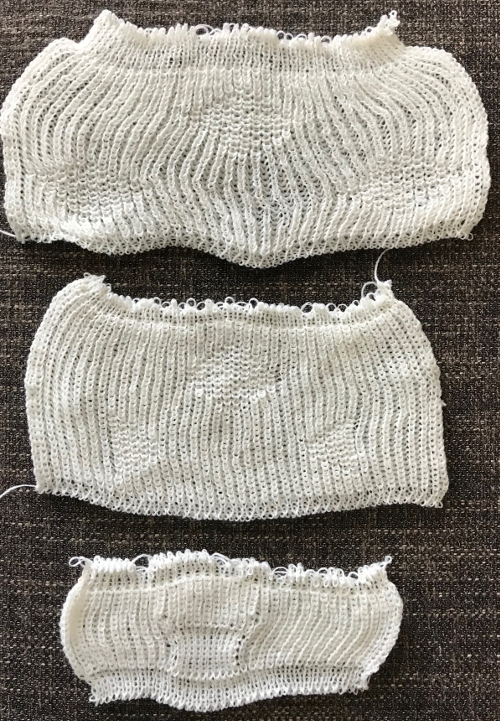
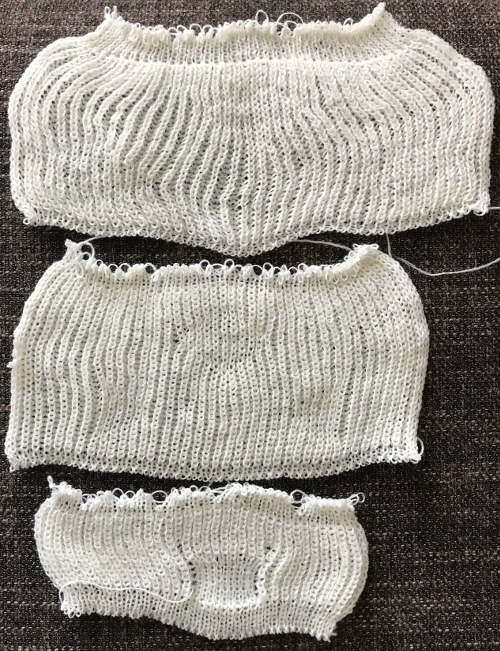


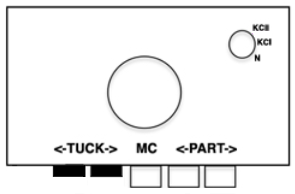
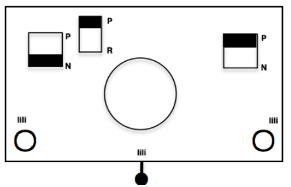
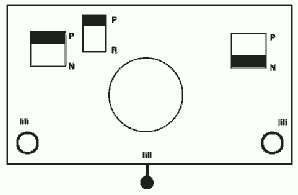
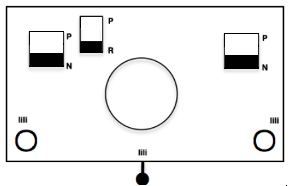







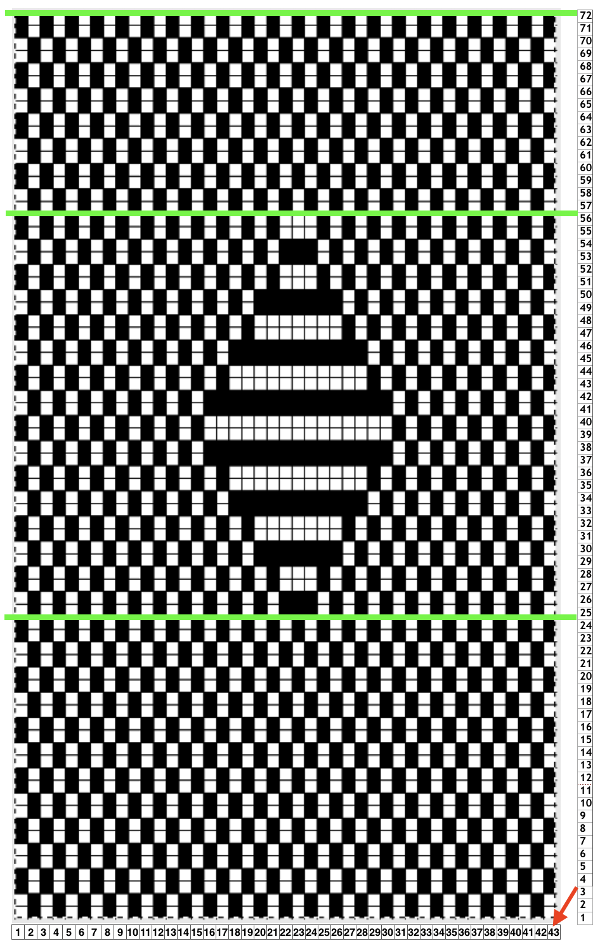
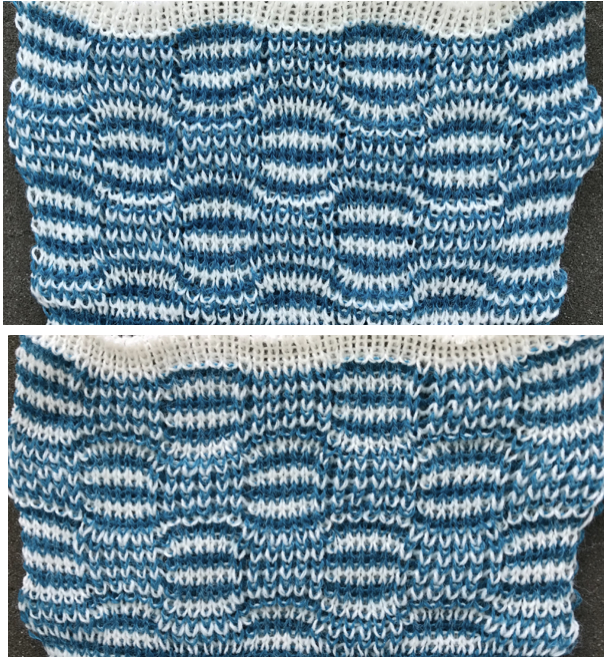
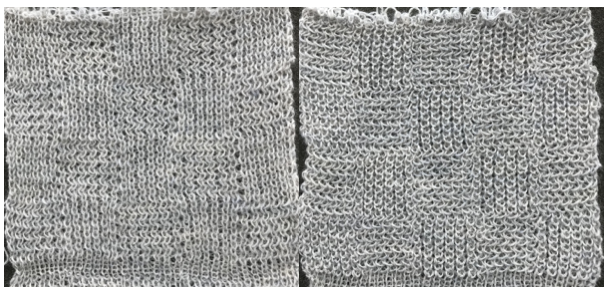
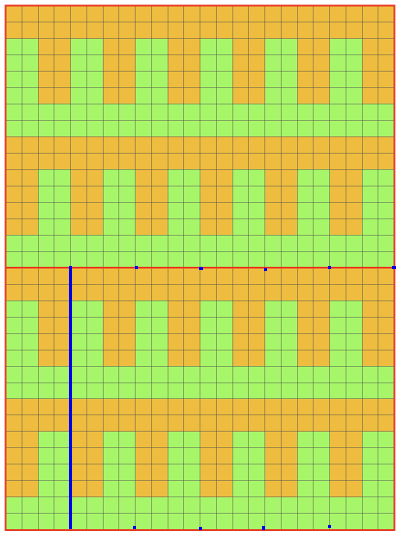
 Back to the original method used in the previous post where ribber settings are changed from knit to tuck <– –> every 2 rows along with color changes. I chose a design that would make it easy to identify the location of non-selected needles on the main bed in rows where the ribber will be set to tuck in both directions. The result is interesting, but the solid areas, narrower than the remaining knit, are in the opposite color to the dominant one on each side, the reverse of the inspiration fabric.
Back to the original method used in the previous post where ribber settings are changed from knit to tuck <– –> every 2 rows along with color changes. I chose a design that would make it easy to identify the location of non-selected needles on the main bed in rows where the ribber will be set to tuck in both directions. The result is interesting, but the solid areas, narrower than the remaining knit, are in the opposite color to the dominant one on each side, the reverse of the inspiration fabric.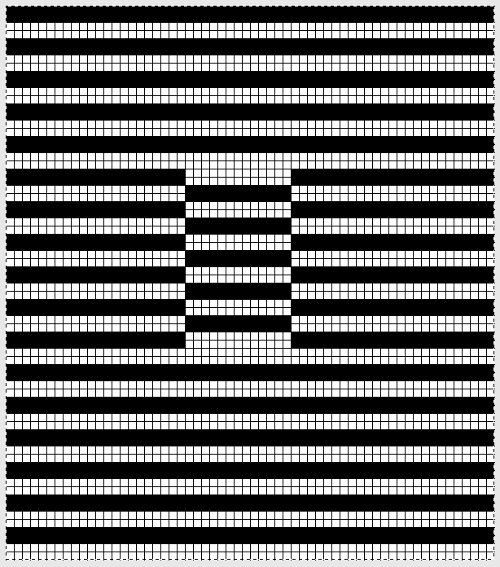
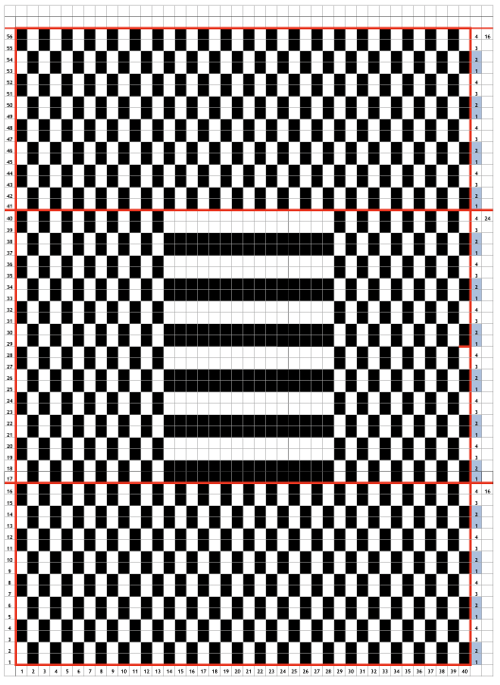
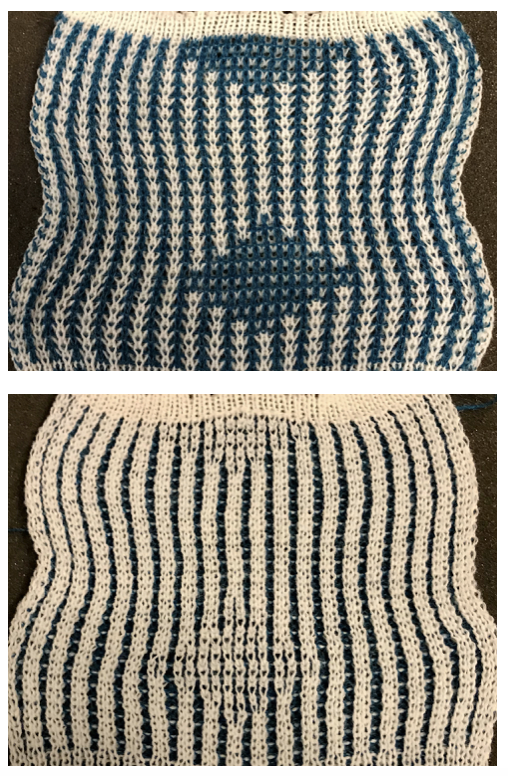


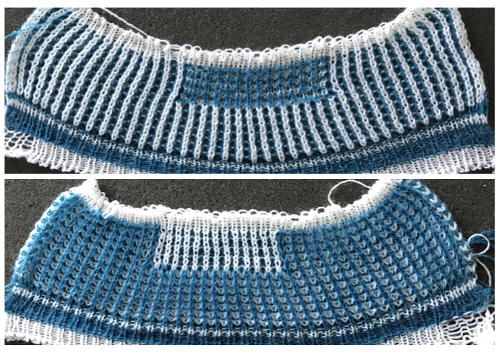











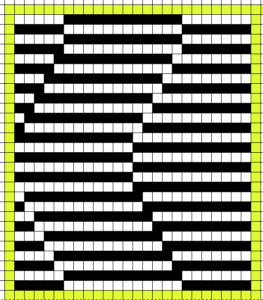

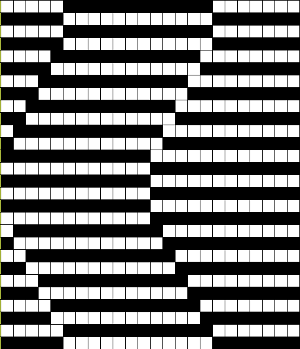
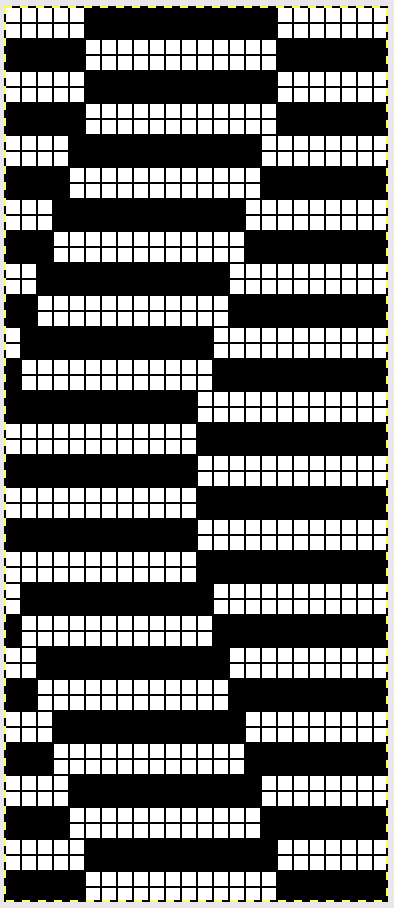
 The ribber remains set for knitting in both directions throughout, with the main bed set to tuck in both directions.
The ribber remains set for knitting in both directions throughout, with the main bed set to tuck in both directions.
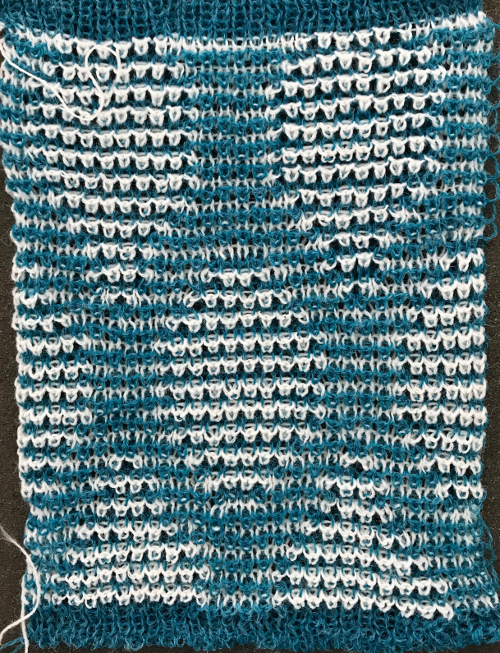
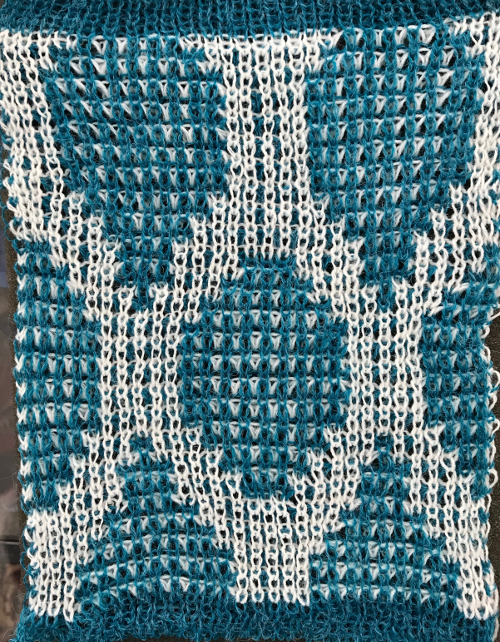






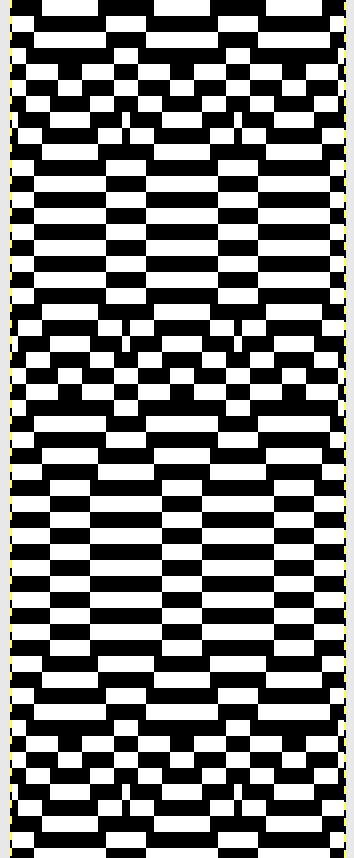 The single 14X84 png
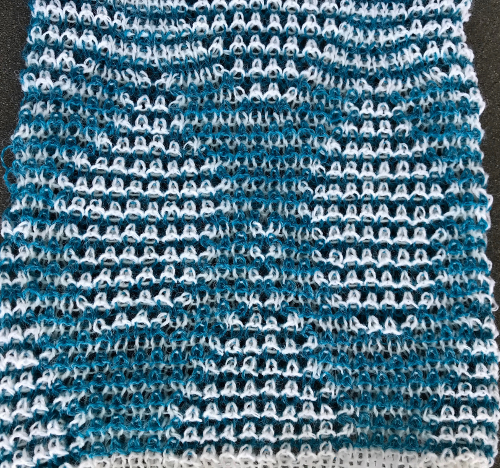
The single 14X84 png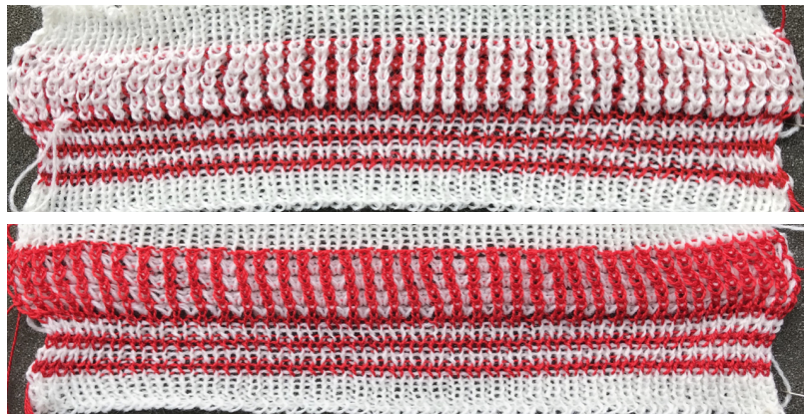  Each of the 2 colors tucks for 2 rows and in turn, knits for 2 rows alternately. Settings are changed manually as shown below after every 2 rows knit, following each color change on the left.
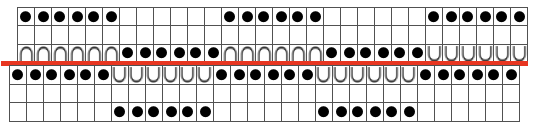
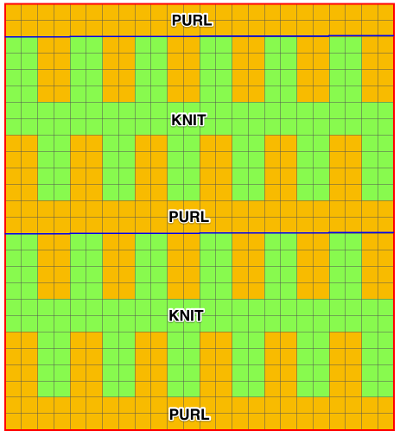
Each of the 2 colors tucks for 2 rows and in turn, knits for 2 rows alternately. Settings are changed manually as shown below after every 2 rows knit, following each color change on the left.  Making things a little easier: the top bed may be programmed on any machine, including punchcard models to avoid cam button changes in the knit carriage every 2 rows. With the main bed set to tuck <– —> throughout, black squares will knit for 2 rows, white squares will tuck, also for 2 rows. The first preselection row is toward the color changer. When no needles are selected on the top bed (white squares) the top bed will tuck every needle, the ribber is set to knit.
Making things a little easier: the top bed may be programmed on any machine, including punchcard models to avoid cam button changes in the knit carriage every 2 rows. With the main bed set to tuck <– —> throughout, black squares will knit for 2 rows, white squares will tuck, also for 2 rows. The first preselection row is toward the color changer. When no needles are selected on the top bed (white squares) the top bed will tuck every needle, the ribber is set to knit. 
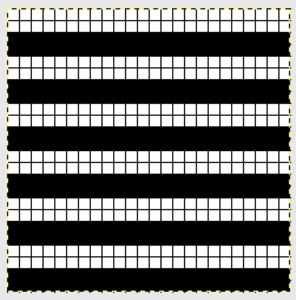


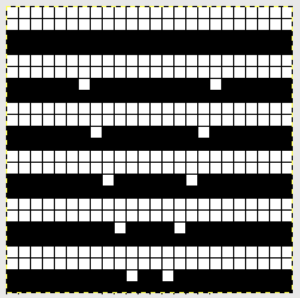

 Another attempt at cabling, 1X1 and 2X2. That white line in the bottom image on the right was caused by the color changer picking up and knitting both colors for part of the row before I noticed it. I got rid of the “wrong” color from the feeder and continued on. The wider 2X2 cables require “special handling” and eyelets are formed on columns aside from them after transfers are made.
Another attempt at cabling, 1X1 and 2X2. That white line in the bottom image on the right was caused by the color changer picking up and knitting both colors for part of the row before I noticed it. I got rid of the “wrong” color from the feeder and continued on. The wider 2X2 cables require “special handling” and eyelets are formed on columns aside from them after transfers are made. 
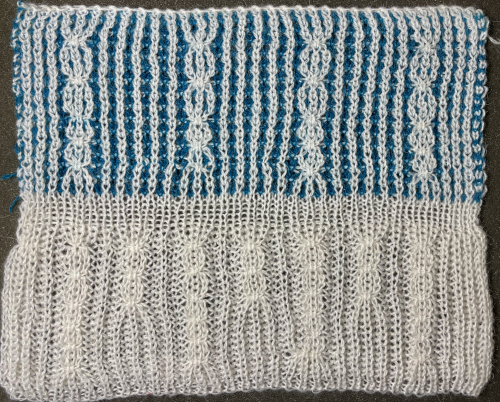




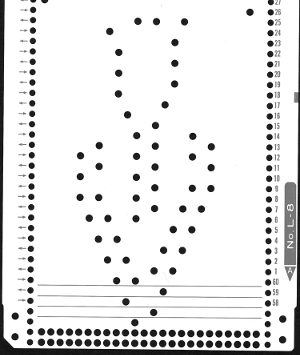
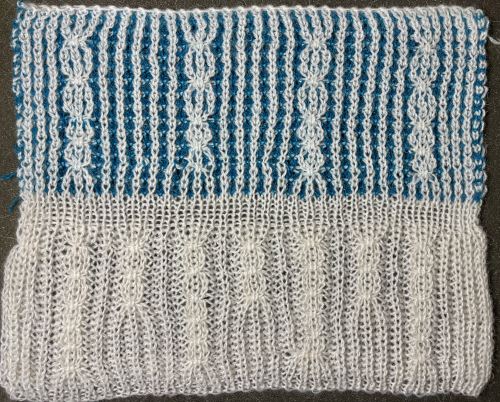
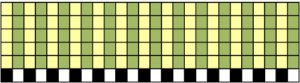
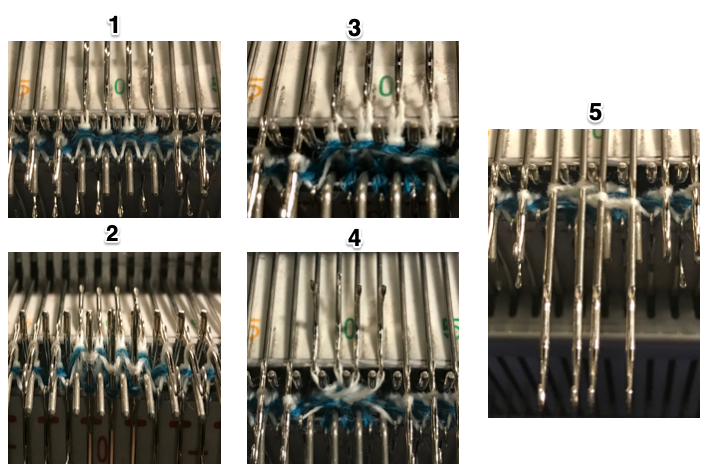
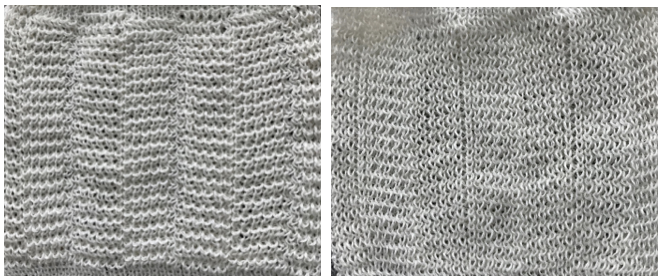
 The situation is different when working on single bed vertically striped fair isle designs. One of my ancient machine-knit demo FI swatches:
The situation is different when working on single bed vertically striped fair isle designs. One of my ancient machine-knit demo FI swatches: 
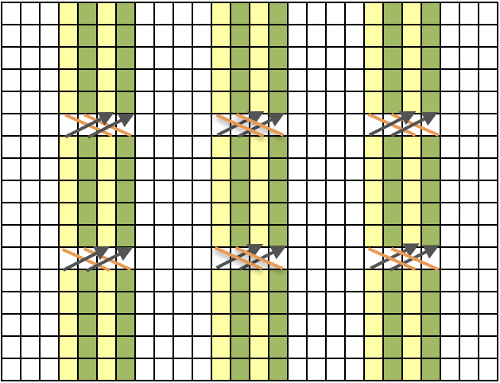
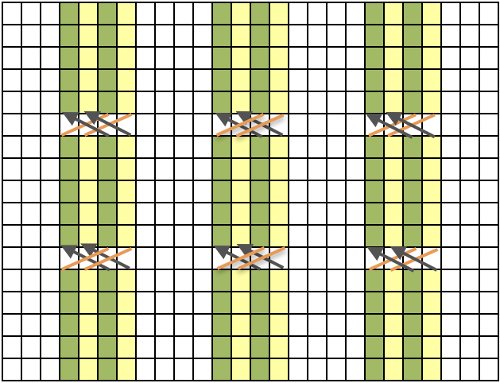
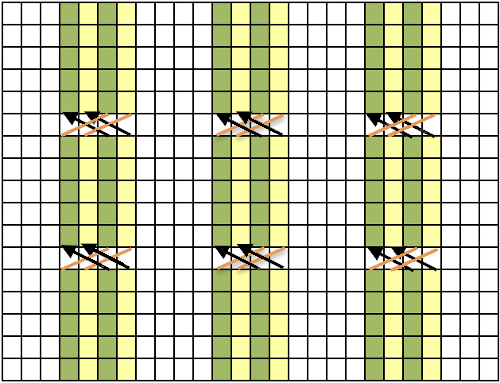

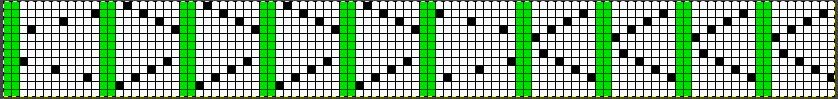
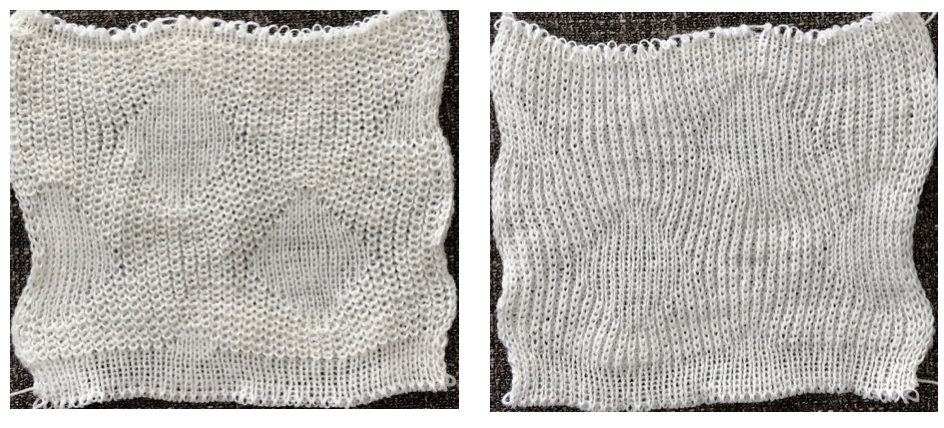
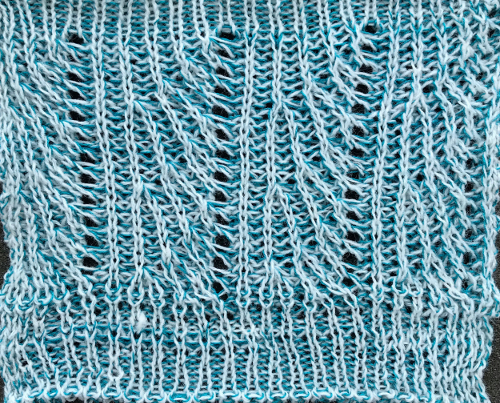
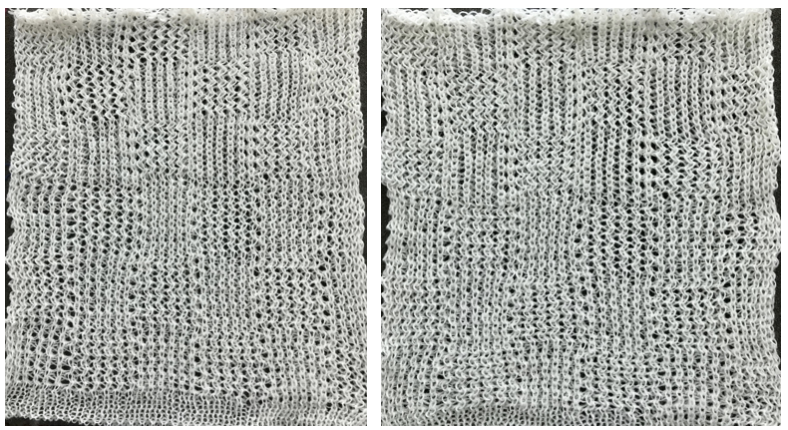
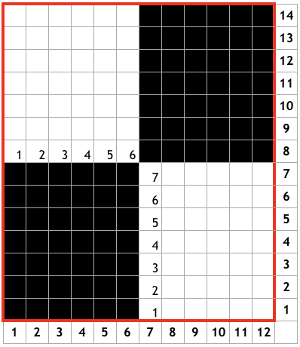
 The charted repeat on the left below when tiled shows the area of a patterning error, on the right with the missing blank rows added the problem is shown to be resolved, the repeat is now 24 X 84.
The charted repeat on the left below when tiled shows the area of a patterning error, on the right with the missing blank rows added the problem is shown to be resolved, the repeat is now 24 X 84. 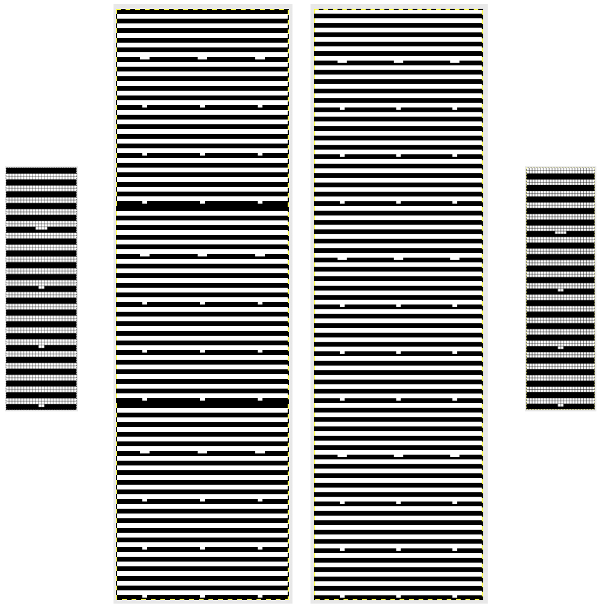


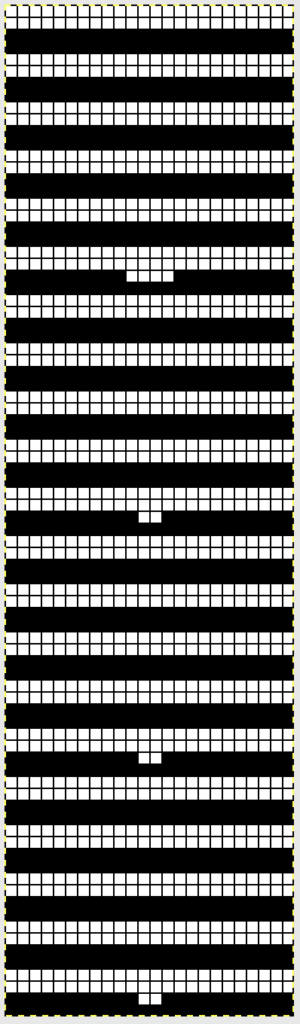
 Adding complexity, there is the possibility of
Adding complexity, there is the possibility of 
 Other related fabrics may be found in posts:
Other related fabrics may be found in posts: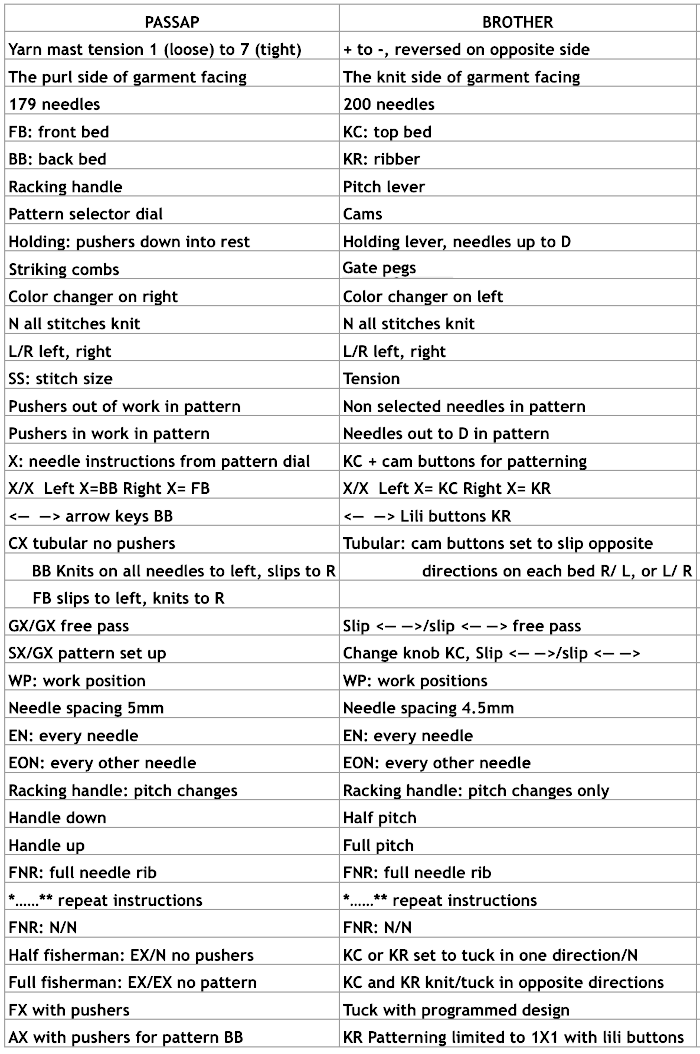











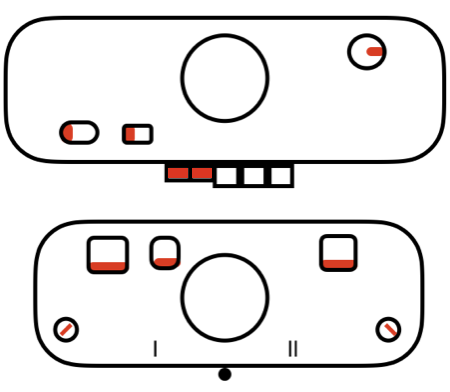













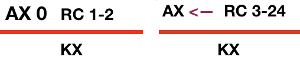



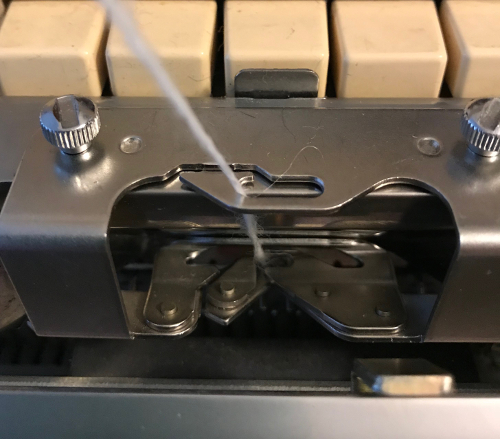
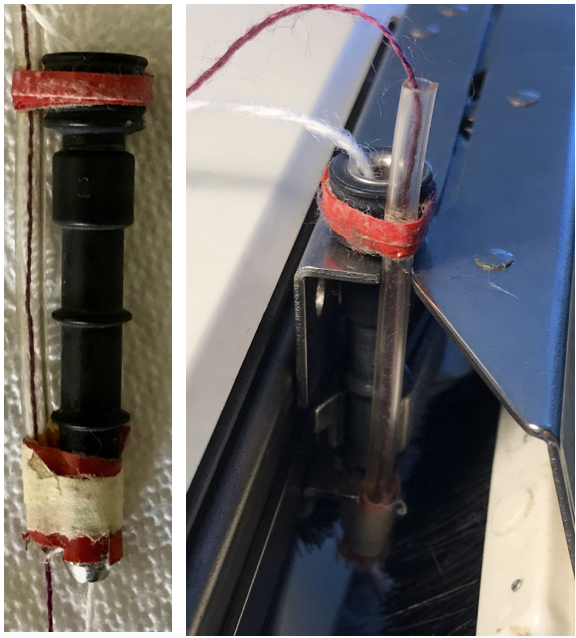
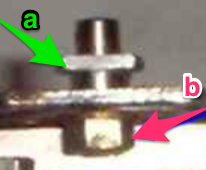
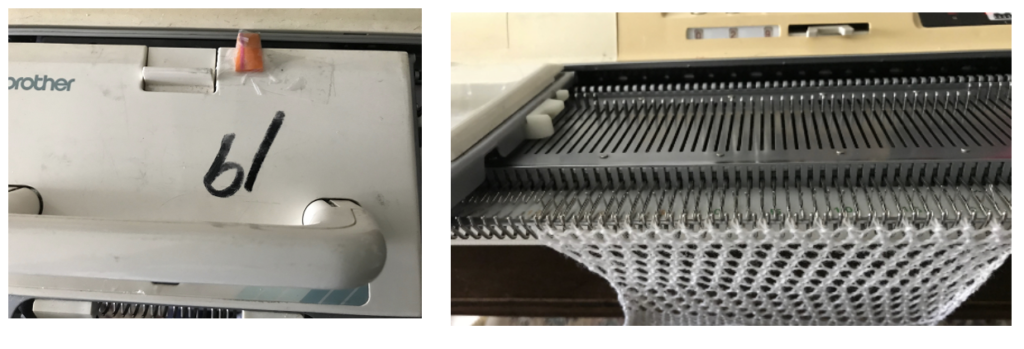 Here the 910 LC is also missing its magnet (left), gluing on a magnet in the position shown below made it usable on the electronic again.
Here the 910 LC is also missing its magnet (left), gluing on a magnet in the position shown below made it usable on the electronic again.
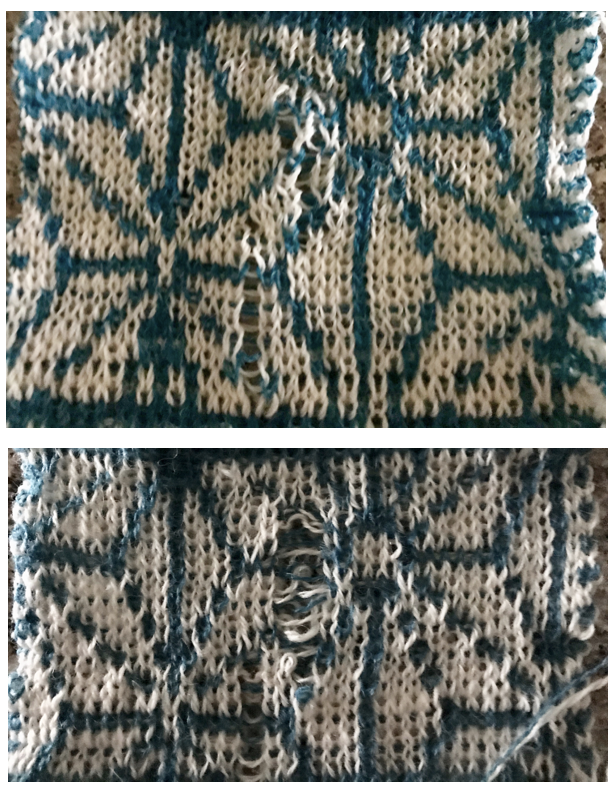
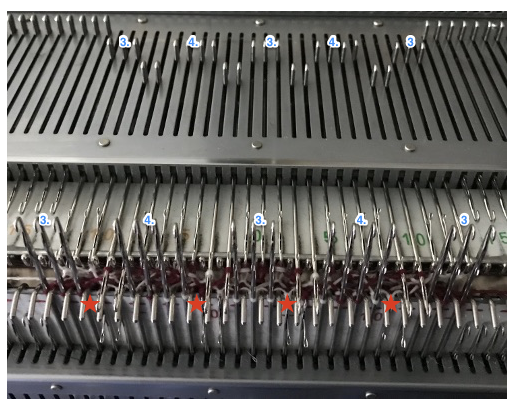
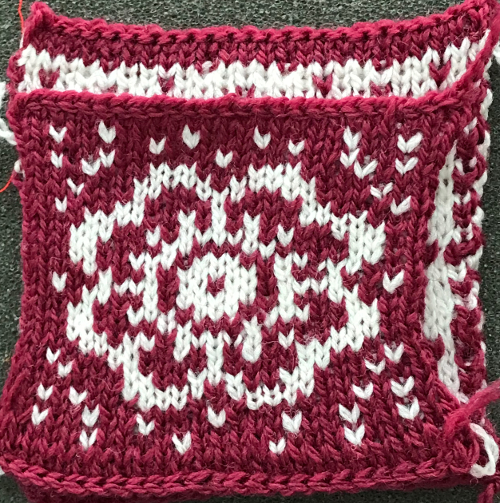
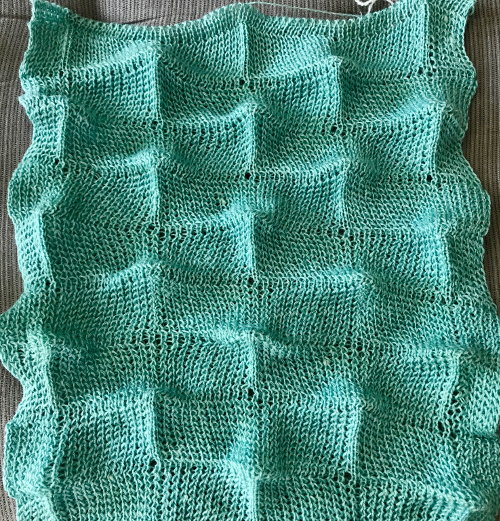
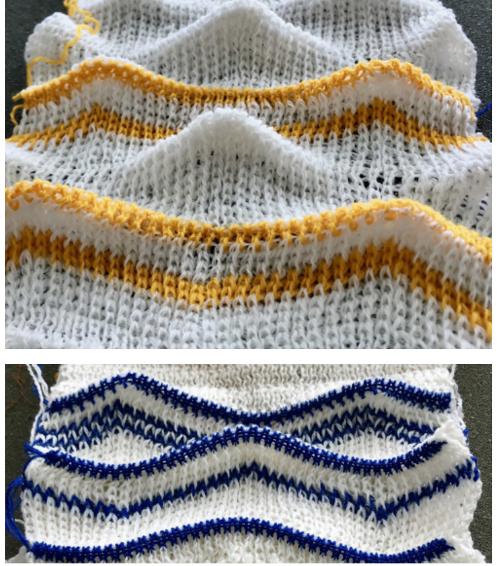
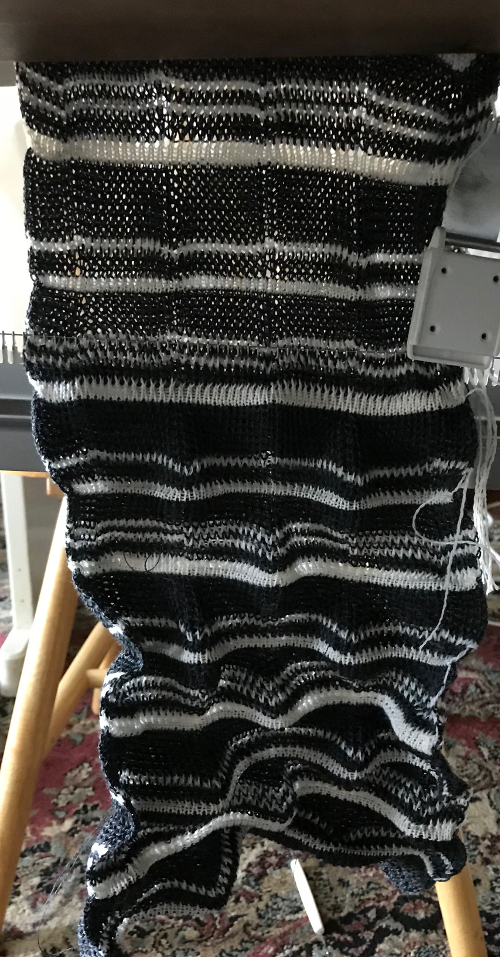
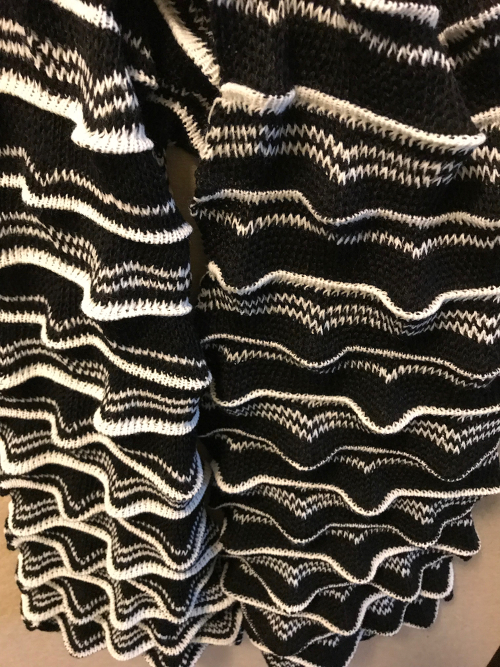
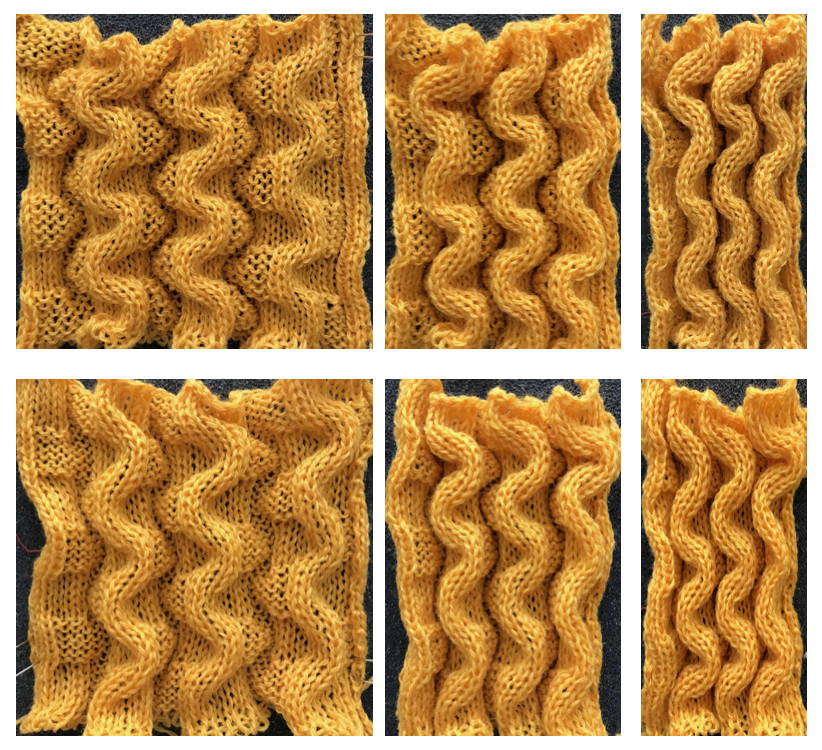












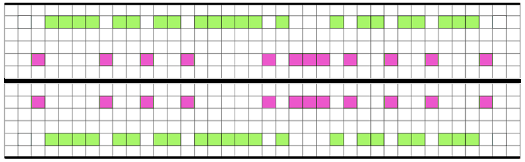



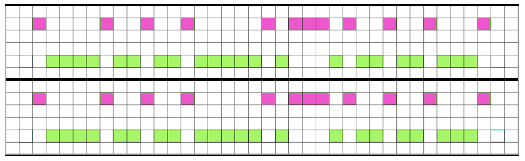
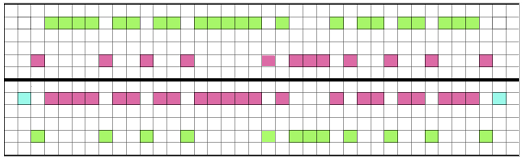






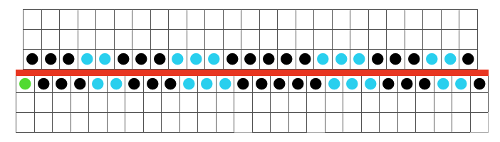

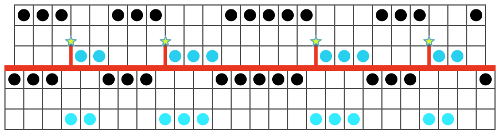


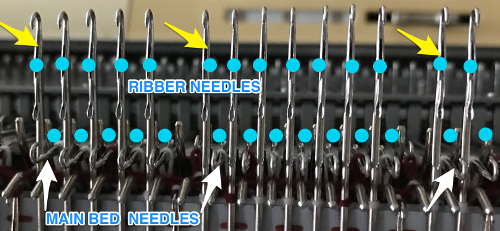


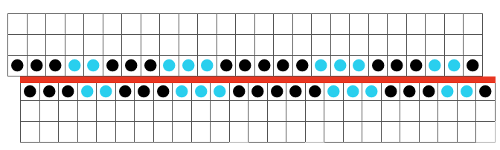

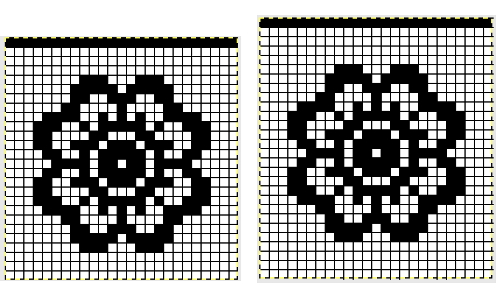






















































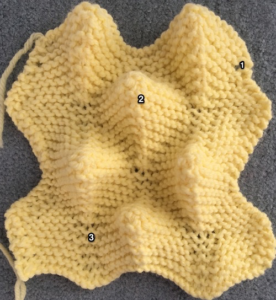
















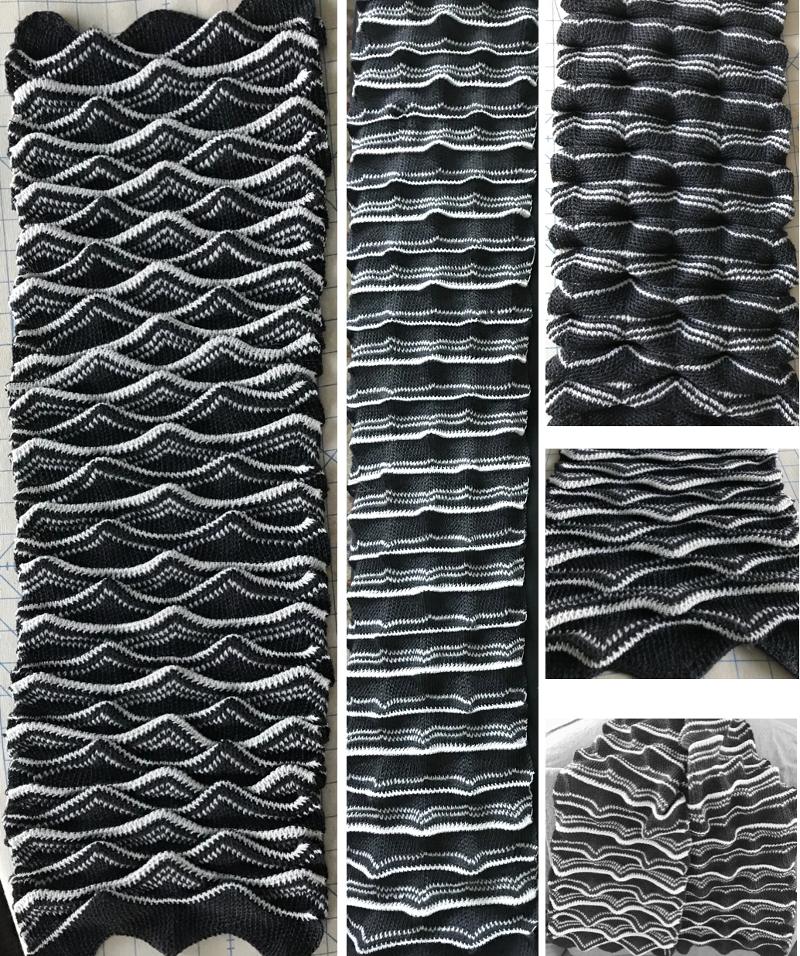





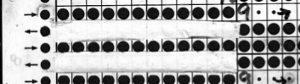

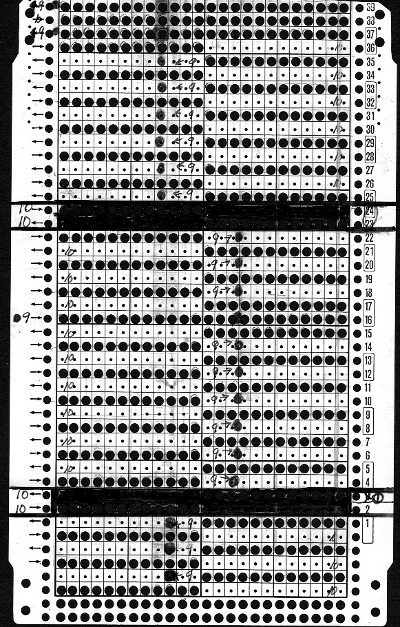
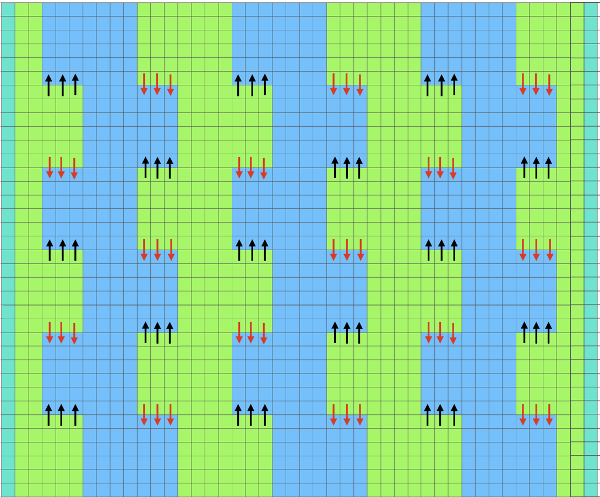








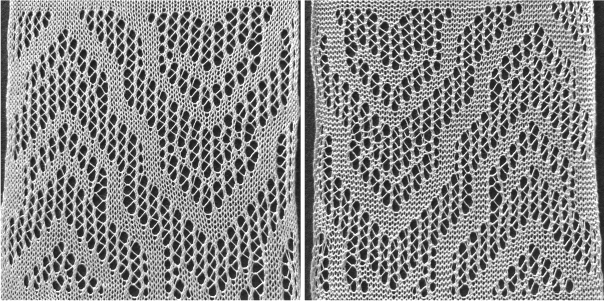
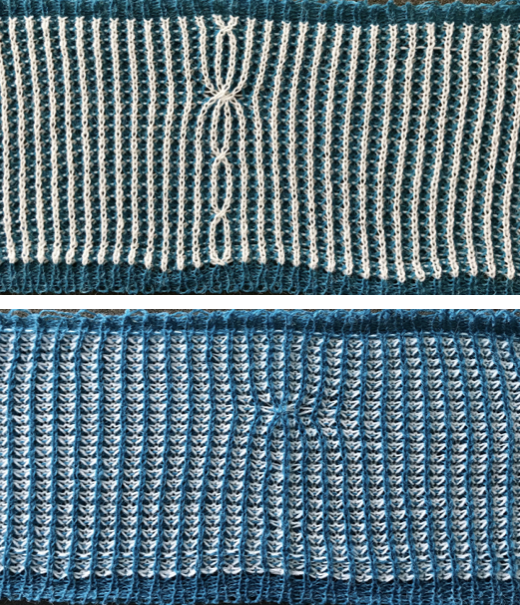
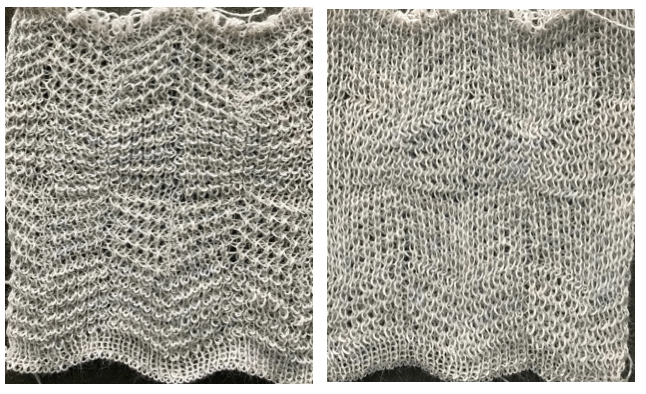
 and my small test swatch. The fold on each side and the swing in the pattern appear crisper and better defined to me
and my small test swatch. The fold on each side and the swing in the pattern appear crisper and better defined to me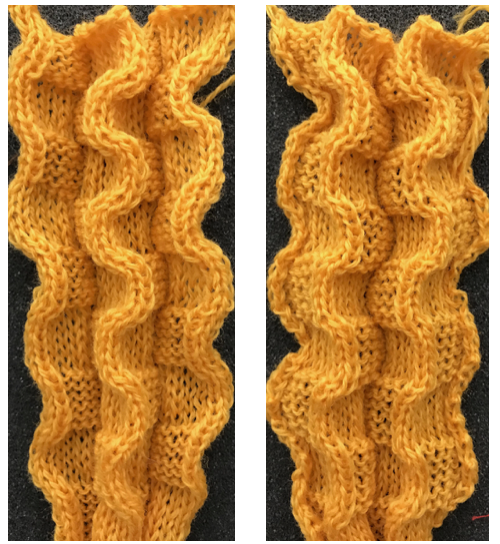
 an attempt at a side view
an attempt at a side view  an earlier
an earlier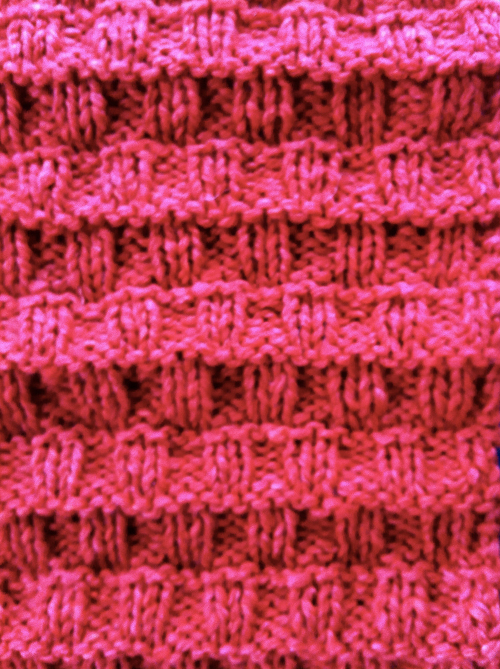  Another handknit swatch in worsted weight, perhaps suitable for G carriage
Another handknit swatch in worsted weight, perhaps suitable for G carriage