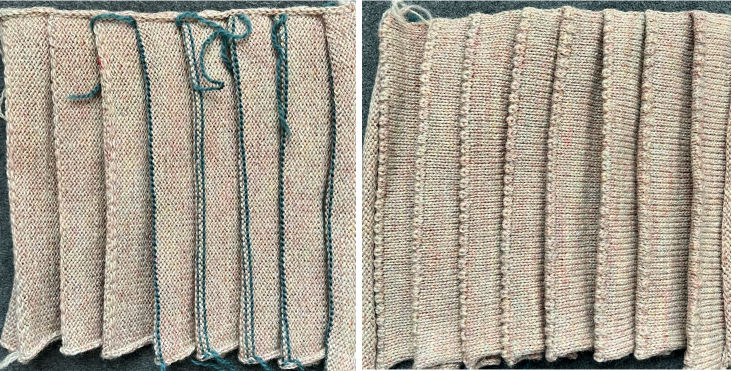
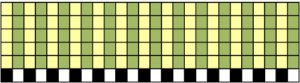
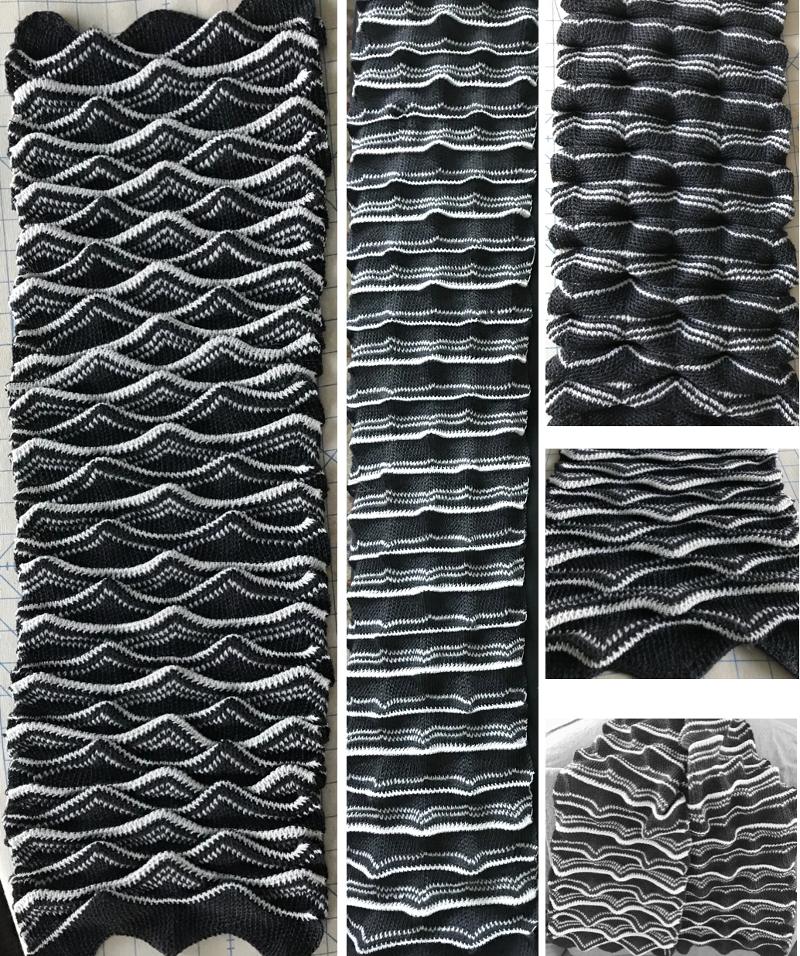
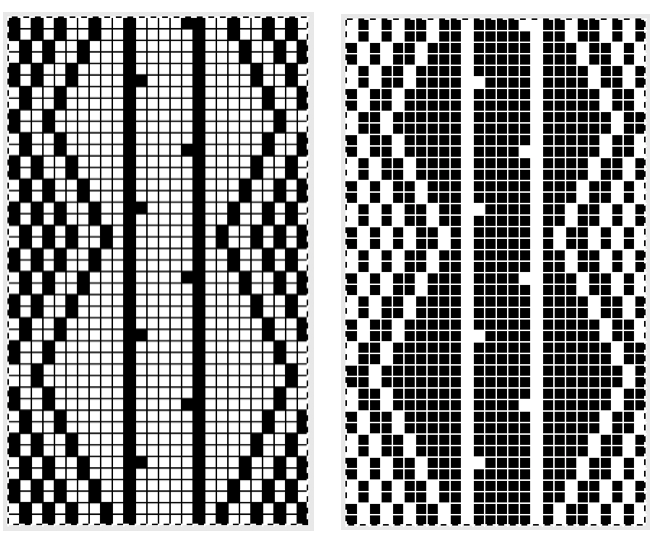
More than 6 years ago I produced a series of scarves that were double-sided, reversible, and were considered “manly” by some of the customers at my shows. Some were one color, some in 2. I found an early post with no clear instructions for them, but with this image and that of a punchcard marked for a racking pattern (given below). Coincidentally the question of checkerboard rib knit patterns came to light in a forum, and I found myself reviewing the technique, with part of the intent to reproduce this fabric. I have, over the years, been terrible at keeping good notes (if any). At times what I was working on was so “obvious” I had confidence I could rely on my memory. At others my attitude once the problems were worked out and a limited one of a kind series was produced, was that I was “done” with that particular fabric. Now here I am, years later, with a mystery pattern on my hands and a time-consuming quest, wishing I had documentation for how on earth I achieved it
 Definitely not “there” yet:
Definitely not “there” yet:
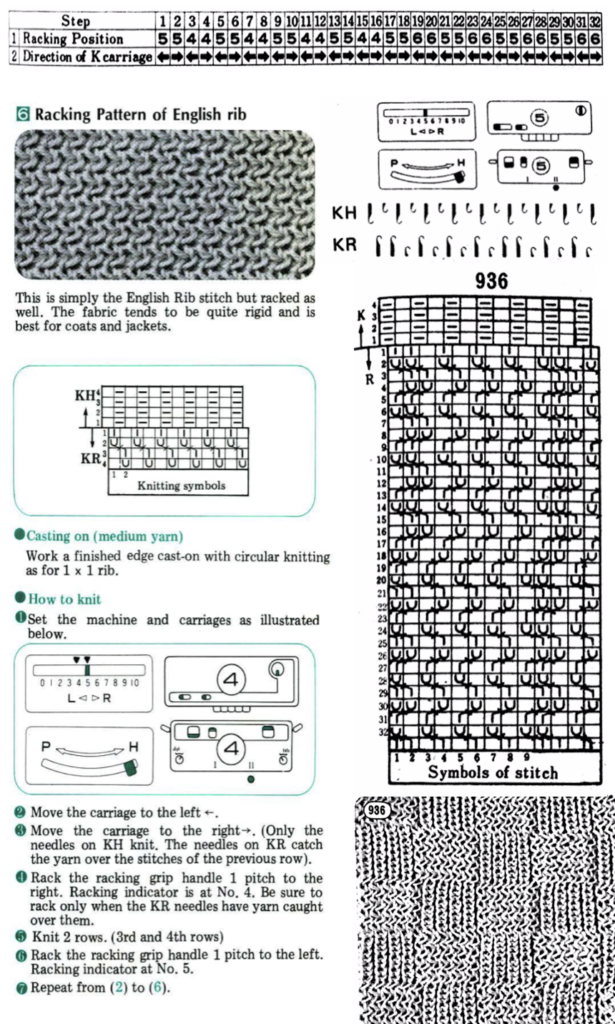
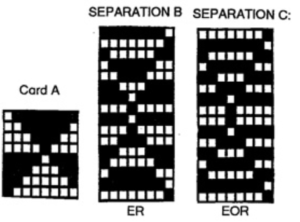
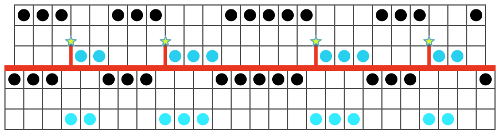
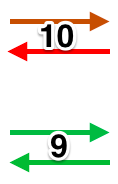
Early translations from the Japanese or German manuals did not always communicate clearly the meaning of symbols or actions required to be taken by the knitter. 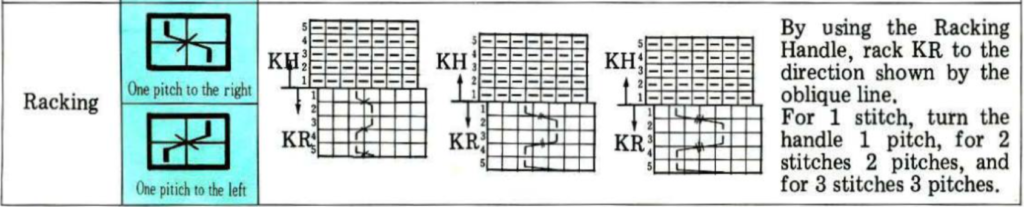 A bit clearer meaning may be gleaned from these instructions in Brother Punchcard Pattern Volume 5. The hatch marks on the racking symbol indicate the number of pitches the ribber is moved in either direction. The number of stitches moved corresponds to the number of needles in work on the ribber.
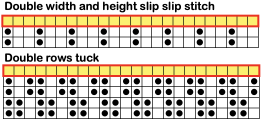
A bit clearer meaning may be gleaned from these instructions in Brother Punchcard Pattern Volume 5. The hatch marks on the racking symbol indicate the number of pitches the ribber is moved in either direction. The number of stitches moved corresponds to the number of needles in work on the ribber. 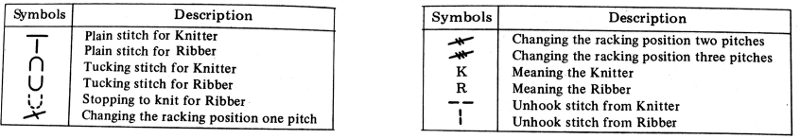 Recommended settings for English rib also known as half-cardigan, royal rib, or pearl-stitch, with no patterning or racking, the beds may be reversed. It is a 2-row repeat. One row is tucking on the main bed on every needle in one direction, knitting on every needle in the same bed upon return to the starting side. The opposite bed knits every row. There is one textured round followed by one of 1X1 ribbing. It is not a balanced structure, looks different on each side.
Recommended settings for English rib also known as half-cardigan, royal rib, or pearl-stitch, with no patterning or racking, the beds may be reversed. It is a 2-row repeat. One row is tucking on the main bed on every needle in one direction, knitting on every needle in the same bed upon return to the starting side. The opposite bed knits every row. There is one textured round followed by one of 1X1 ribbing. It is not a balanced structure, looks different on each side. 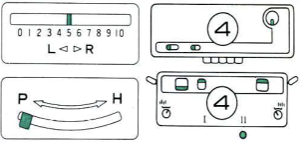 Variure denotes fabrics wherein the same bed is tucked for 2, 3, or even 4 rows followed by one or 2 rows of rib knitting every needle on both beds. The tucking bed may also be set up with needles out of work and with added racking as well.
Variure denotes fabrics wherein the same bed is tucked for 2, 3, or even 4 rows followed by one or 2 rows of rib knitting every needle on both beds. The tucking bed may also be set up with needles out of work and with added racking as well.
In fisherman’s rib, the settings are for a tubular tuck, with opposite tuck buttons set in the carriages. While a bed tucks on every needle, the opposite bed knits every needle, reversing the process on the return row. It is also a two-row repeat and referred to as full-cardigan stitch or polka rib.
It has the same appearance on both sides and does not contain any rows in all rib. 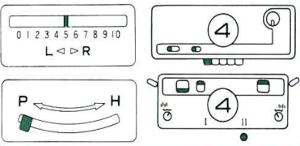 An additional illustration of both
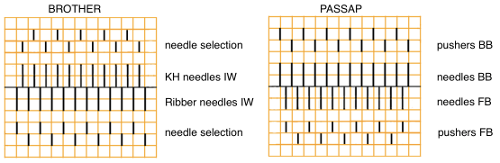
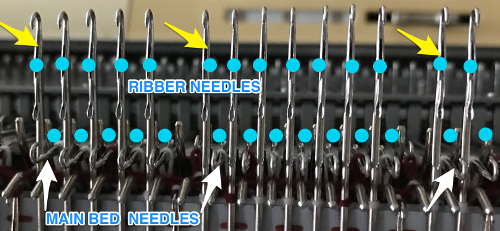
An additional illustration of both 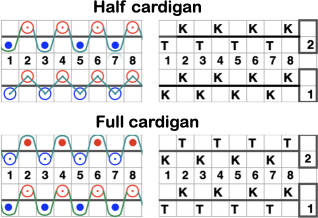 The recommended Brother ribber’s “needle rule”.
The recommended Brother ribber’s “needle rule”. More tuck rib variations may be found in posts on interlock 1, and 2.
More tuck rib variations may be found in posts on interlock 1, and 2.
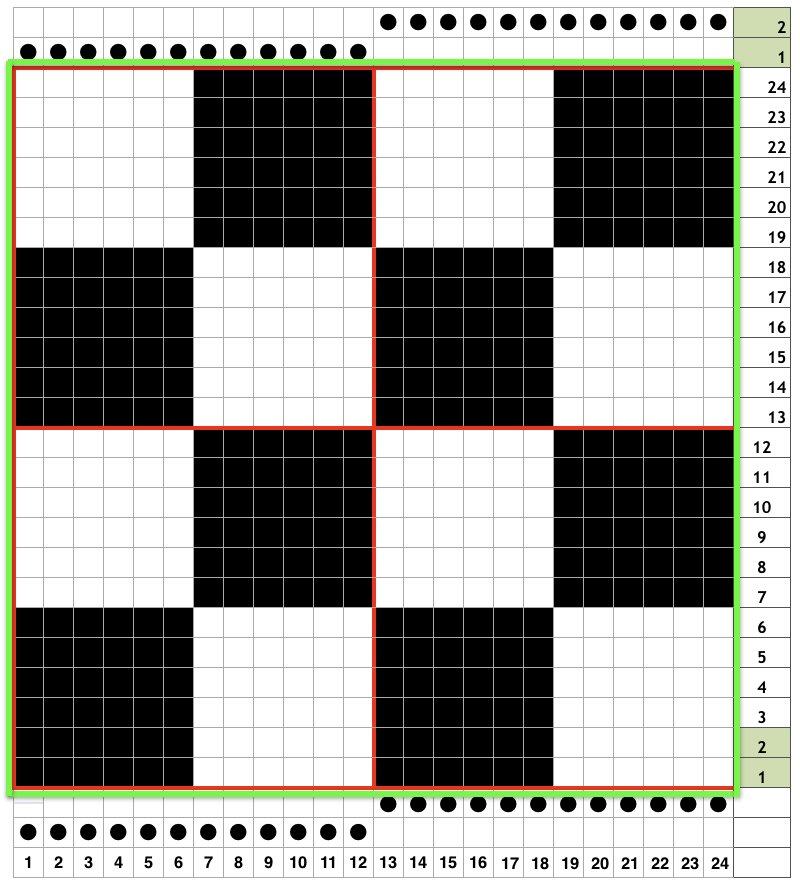
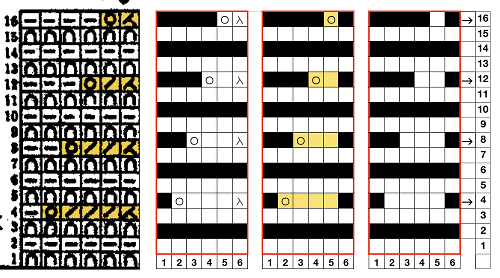
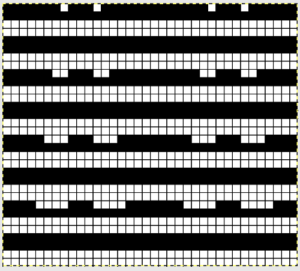
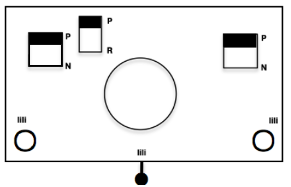
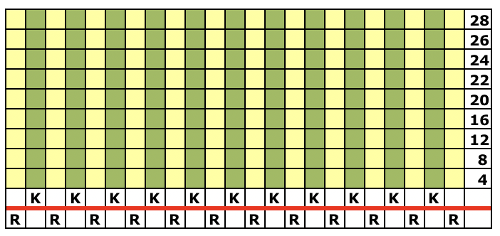
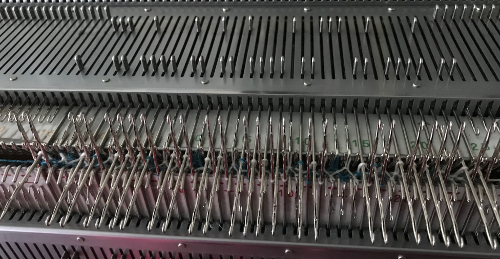
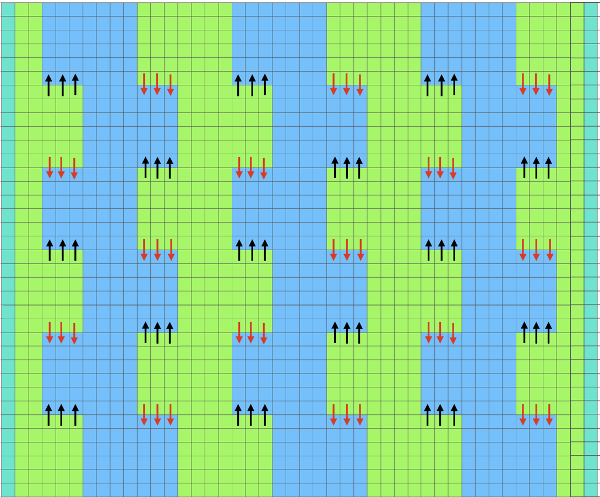
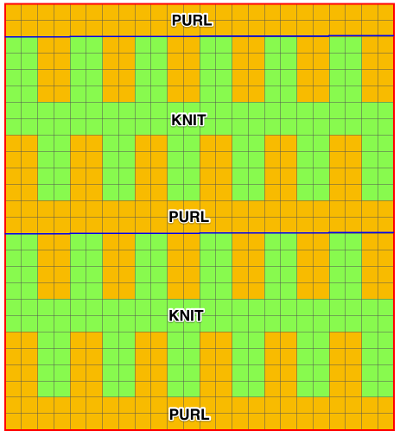
Adjustments to the needle rule may be needed depending on the fabric. If only one bed is knitting while the other is tucking, having the first and the last needle in work on the knitting bed. In English (aka half fisherman’s rib) only one (either) bed tucks. Directions marked with green #6 on left are from the Brother Ribber techniques. The remaining images are for the single-color racked checkerboard pattern from Brother Punchcard Pattern book #5. No pattern card is involved, every other needle arrangement suggested on the right accommodates slightly thicker yarns. A half-pitch setting is used.
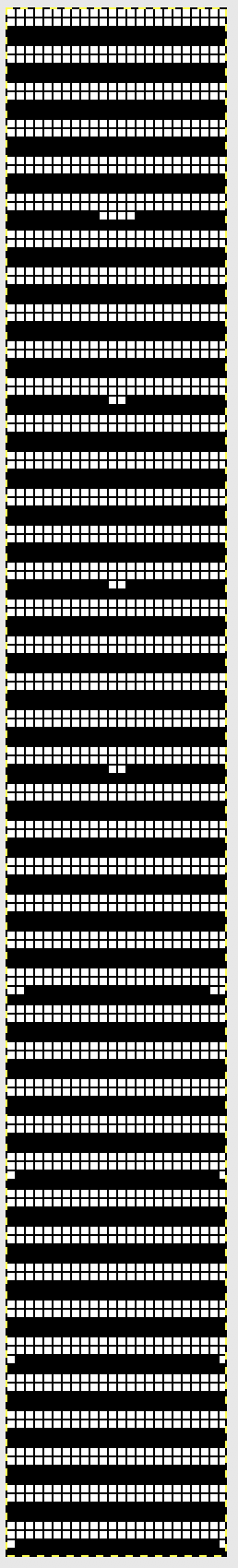
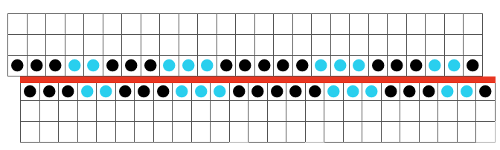
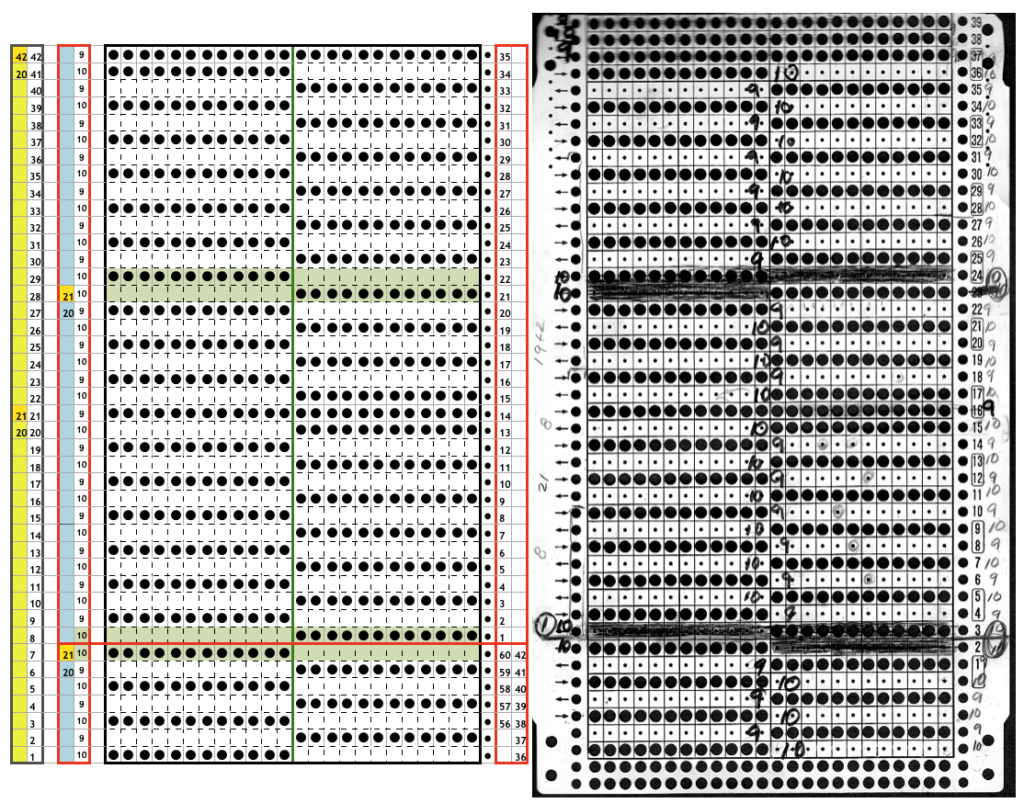
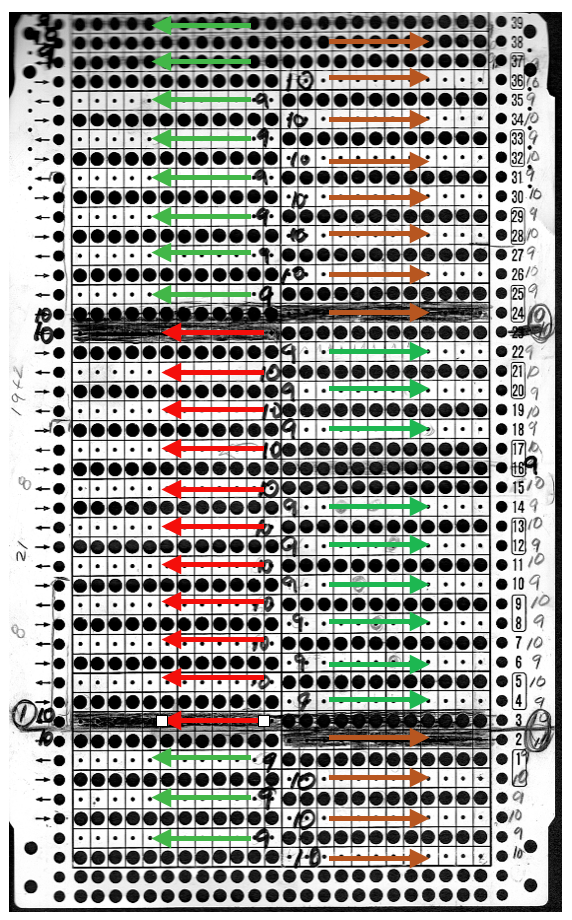
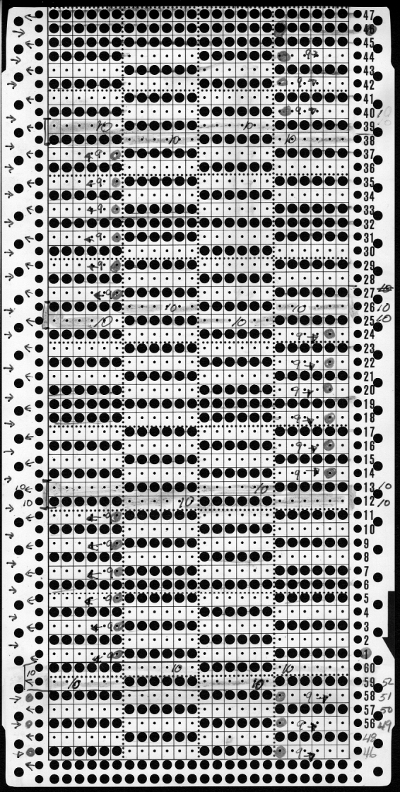
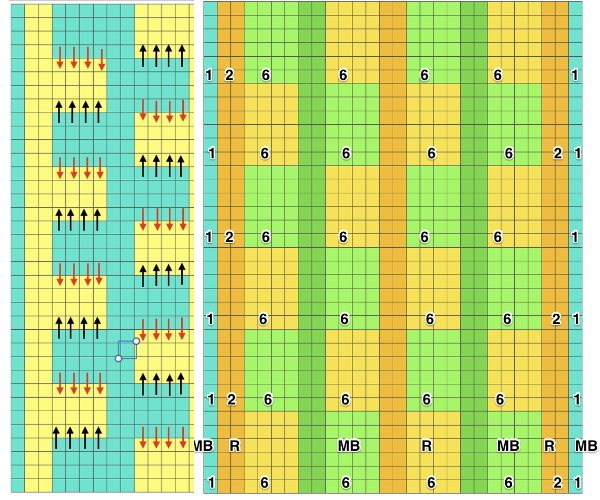
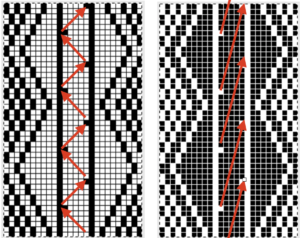
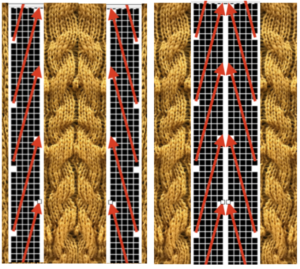
In the above instance, the main bed is not performing any patterning function, it is knitting on every needle in the work position. On a punch card machine, a card may be used to track racking positions. With the carriage set as usual for patterning and needle selection but with no cam buttons pushed in, the main bed will continue to knit stocking stitch. No rows are punched, and the numbers on the card in the colored columns indicate the racking position for corresponding rows. The “card” on the left is designed to match racking positions and carriage travel directions (colored arrows) to mirror those in the publications. Since a 36-row minimum is recommended for continuous punchcard use, the “card” on the right has added a 4-row segment for each segment of racking directions. The full repeat is now 40 rows rather than 32 in height. The numbered columns on the far right are as they would appear on standard blank Brother punchcards. The number one is at the level of the first visible row while the card reader drum is actually selecting the first design row. End needle selection is canceled (KCII on electronics). The first move as indicated by arrows is to the right, so the first row is preselected from right to left. The card is then set to advance normally and released. If any errors are made treat card adjustments as you would in any other fabric.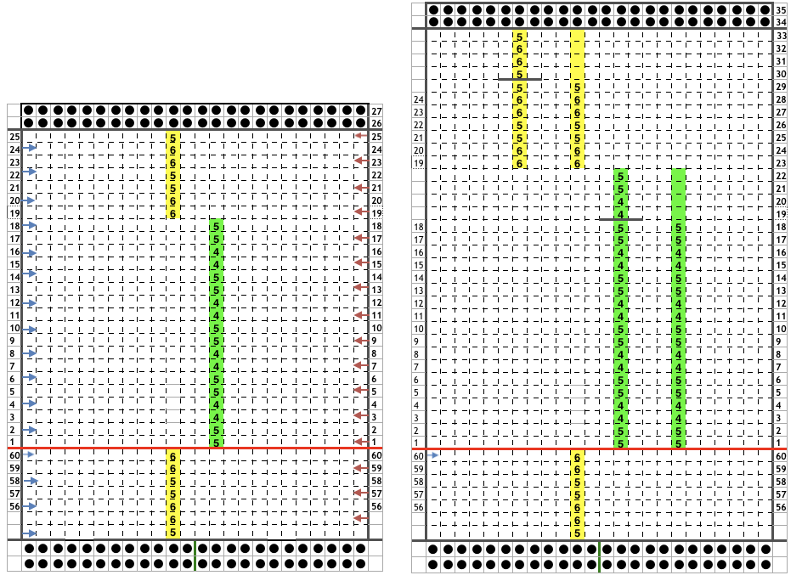
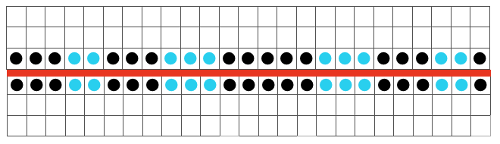
Adding main bed needle selection for selective patterning: the actual punchcard here includes annotated changes in racking sequences from 5/4 pitch positions at its start to 5/6 racking positions for the top half of the completed repeat on its left side. It may be used as-is or set to double length either for use with a single color or combined with color changes every 2 rows.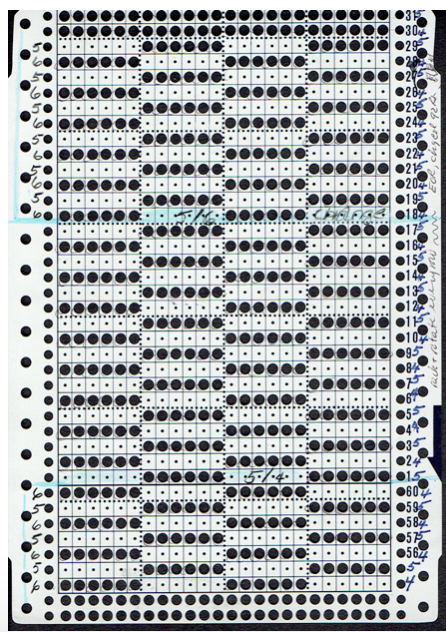
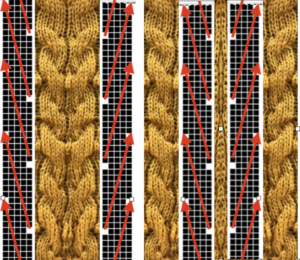
The card as punched may be used in many ways. In past experiments, I have shown that not changing the racking pitch for a single row while keeping the two alternating pitches constant created scale-like textures rather than checkerboard patterns
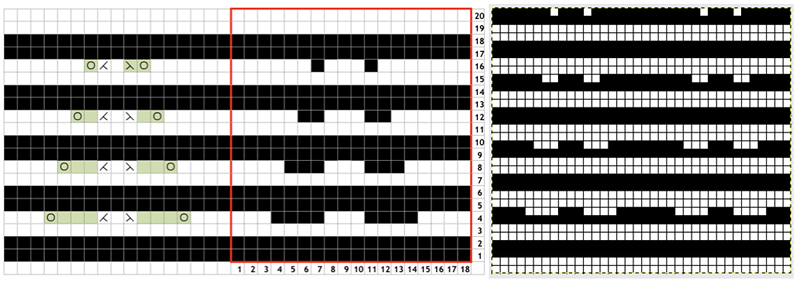
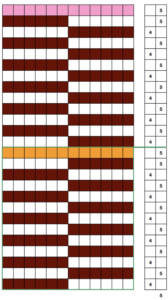 here again for a 16-row sequence
here again for a 16-row sequence
On fabrics with racking enlarge the stitch size by 1/2 to one full number to accommodate the stretch needed in racking the stitches.
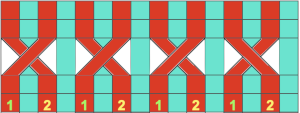
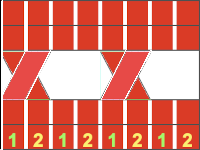
Color changes: fabrics made in full fisherman rib are reversible, while those in half fisherman are not. In full fisherman rib in order to knit a specific color, that color must be knit for two rows and tucked for 2 rows alternately. In Passap AX with pushers and arrow keys must be used, in Brother, ribber needles would need to be hand-selected to the proper position on every row.
The yarns used should be soft and have some stretch. Every other needle patterning may be used with slightly thicker yarns.
Racking in the same pairs of pitches ie. 4-5, 4-5 with no added actions taken, produces vertical columns, akin to results in any fabric that repeats the same functions in the same locations on the needle bed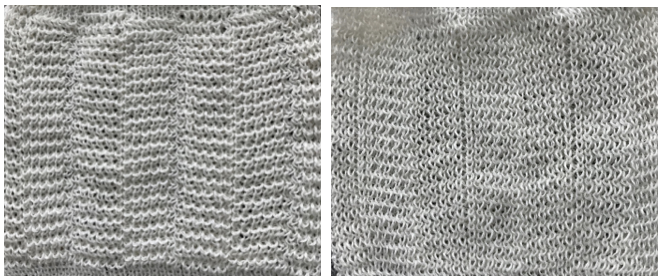
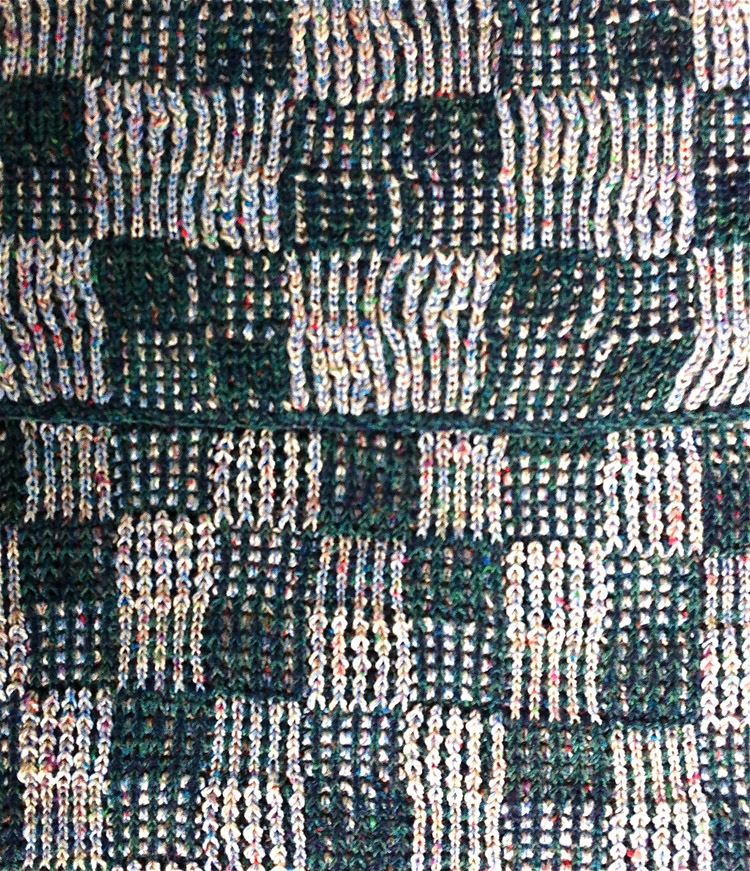
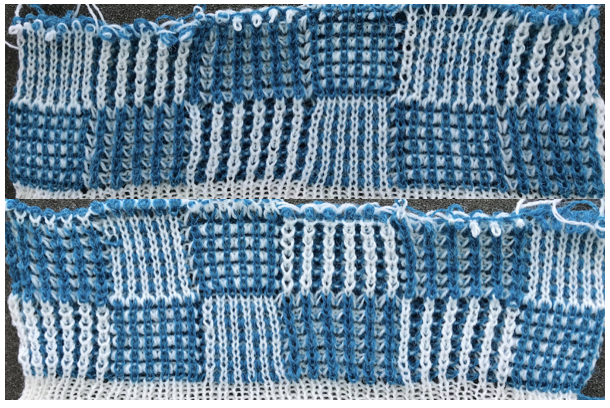
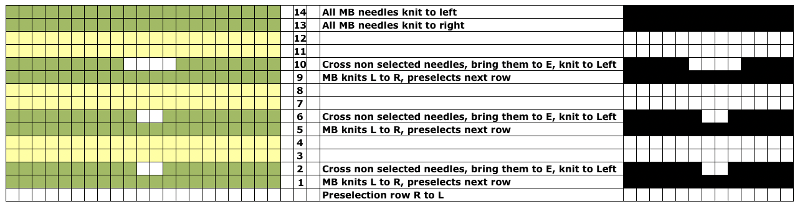
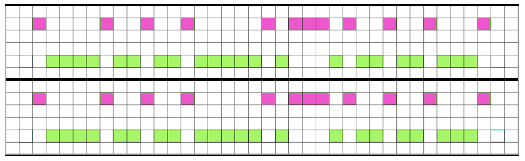
I knit my first “checks” sample on a 930 electronic programming a single repeat to match the card used double length. The goal: the check sample pictured in punchcard pattern book 5 
In programs or machines that allow for memos that correspond to design rows for each repeat, enter the racking pitch number beginning with design row number 1, and continue to 32 or more as needed. The racking sequence is changed at the halfway point of the full repeat.
Added experiments: using the same electronic repeat above, here I worked *20 rows racking every row between positions 4 and 5. One row was then knit on all stitches on the top bed** (I pushed needles out manually rather than changing cam settings), repeated * to**. The fabric reminds me of racked herringbone, the “checkers” are distorted 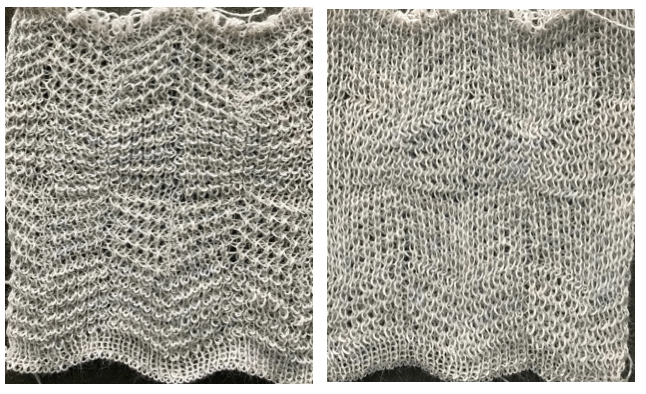 Changing color every 2 rows shows the same lean in the fabric. I have had intermittent problems with my ribber, stitches begin to simply not be picked up by the main bed and are dropped for no apparent reason
Changing color every 2 rows shows the same lean in the fabric. I have had intermittent problems with my ribber, stitches begin to simply not be picked up by the main bed and are dropped for no apparent reason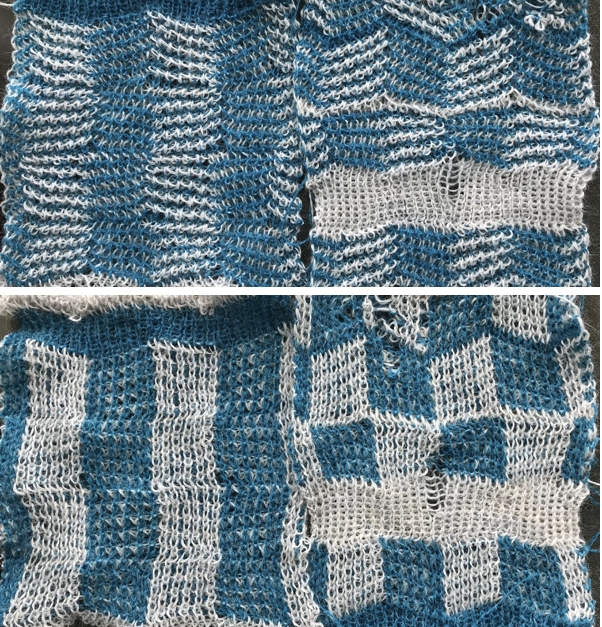  A very different fabric is created using the repeat and instructions below
A very different fabric is created using the repeat and instructions below
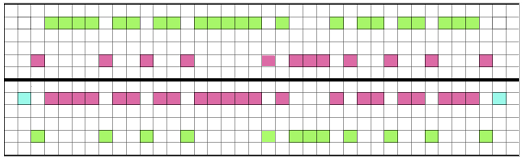
 *Knit 2 rows, rack 1 pitch to left; knit 2 rows, rack 1 pitch to right to RC 20 (or preferred row count); knit 1 row continuing in pattern to the opposite side without racking**. Repeat * to**. One repeat of the 2 sequences is 42 rows in height. At row 1 of each new (here 21 rows) sequence, the carriage starts on the opposite side
*Knit 2 rows, rack 1 pitch to left; knit 2 rows, rack 1 pitch to right to RC 20 (or preferred row count); knit 1 row continuing in pattern to the opposite side without racking**. Repeat * to**. One repeat of the 2 sequences is 42 rows in height. At row 1 of each new (here 21 rows) sequence, the carriage starts on the opposite side 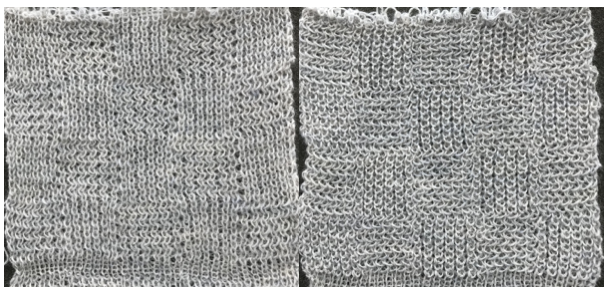 Changing colors every 2 rows is possible. The racking will begin with the carriages on alternate sides of the machine after the single-row knit without racking. In segment 1 racking occurs on the left, color changer side, and in segment 2 racking occurs on the right, opposite the color changer.
Changing colors every 2 rows is possible. The racking will begin with the carriages on alternate sides of the machine after the single-row knit without racking. In segment 1 racking occurs on the left, color changer side, and in segment 2 racking occurs on the right, opposite the color changer. 
“Full” fisherman rib with patterning on both beds: on Passap the back bed is capable of many more patterning choices than in Japanese machines, and strippers help hold loops in place on the needle beds. The Passap “needle rule” places the first needle in work on the front bed, and the last on the back bed. This is also variable depending on the fabric being knitted. Using the repeat
tech 129: (black square tuck for single row) on the front bed. Set up back bed after prep rows, making sure pushers are in the same work/rest position as on the front bed  *Knit 2 rows, rack to left, knit 2 rows, rack to right to preferred row count ie RC 20; knit 1 row still in the pattern, without racking**. Repeat * to**. One repeat of the 2 sequences is 42 rows in height. The resulting pattern is reversible.” This swatch was knit with the bottom 3 blocks using 6X6, both arrow keys on the back lock, and N in front. The back bed pusher setup is doing the patterning. The top 3 blocks are set to pattern selection on both beds, using AX, arrow keys, and KX on the front lock. Using technique 130 will double the height of the repeat, working each row twice.
*Knit 2 rows, rack to left, knit 2 rows, rack to right to preferred row count ie RC 20; knit 1 row still in the pattern, without racking**. Repeat * to**. One repeat of the 2 sequences is 42 rows in height. The resulting pattern is reversible.” This swatch was knit with the bottom 3 blocks using 6X6, both arrow keys on the back lock, and N in front. The back bed pusher setup is doing the patterning. The top 3 blocks are set to pattern selection on both beds, using AX, arrow keys, and KX on the front lock. Using technique 130 will double the height of the repeat, working each row twice.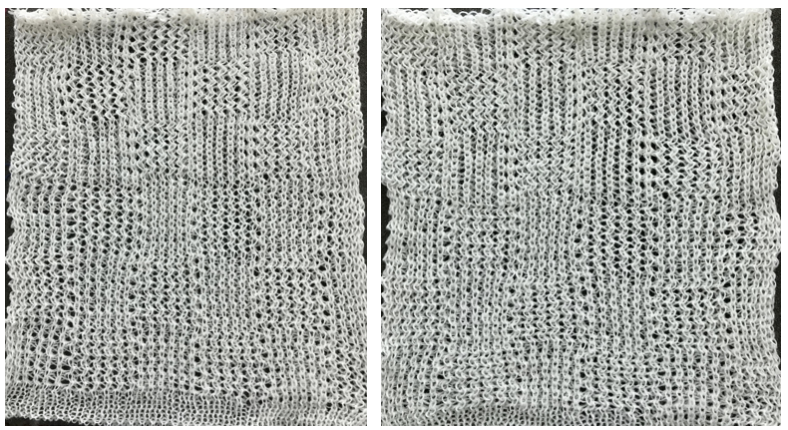
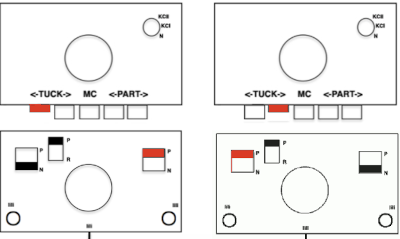
On Brother, the second bed selected needles will face tucking needles on the main bed. This creates a knit stitch on one bed, holding down the tuck loops on the other, allowing for side-by-side tuck loops on opposing beds. Such selections would need to be made on the ribber manually. Both beds are set to tuck, both arrow keys. The needles on the ribber immediately below the ones tucked on the main bed are brought to the E position and face the tuck needles on the main bed, while its non-selected needles will tuck. Rack before pushing those needles (black dots) that will be knit up to the E position. 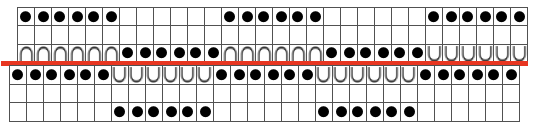 The Brother settings for full fisherman suggested in their Ribber Techniques Book and manuals produce a “circular” tuck stitch, with each bed tucking and alternately knitting on all stitches in opposite directions, so the cam button setup is different than when one is planning textures in varied patterns
The Brother settings for full fisherman suggested in their Ribber Techniques Book and manuals produce a “circular” tuck stitch, with each bed tucking and alternately knitting on all stitches in opposite directions, so the cam button setup is different than when one is planning textures in varied patterns 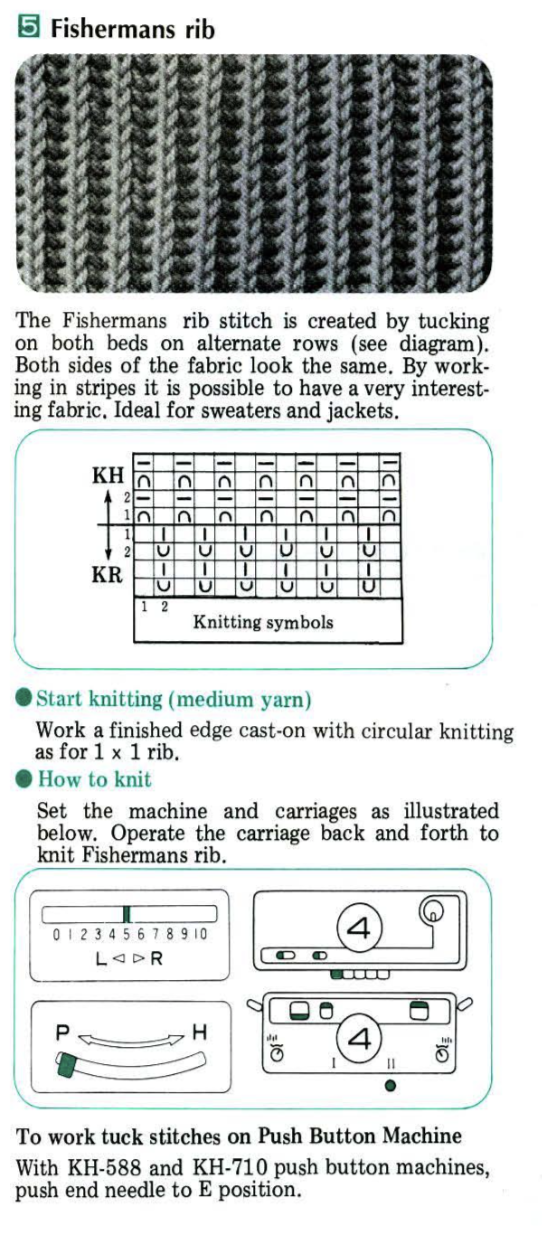 It is also possible to produce “checks” without any racking at all. On the Passap, this sample was produced eliminating racking completely. The front lock was set to knit throughout / N, the back lock alone did the work. Pushers were selected 6 up, 6 down, the back lock set to AX with left arrow key for even multiple rows divisible by 4. I used 24-32 to get a sense of scale. The arrow key was canceled for the next 2 rows AX 0 to switch the pushers. The working repeat became *32 rows 6X6, left arrow key, 2 rows AX 0*with the front bed programmed
It is also possible to produce “checks” without any racking at all. On the Passap, this sample was produced eliminating racking completely. The front lock was set to knit throughout / N, the back lock alone did the work. Pushers were selected 6 up, 6 down, the back lock set to AX with left arrow key for even multiple rows divisible by 4. I used 24-32 to get a sense of scale. The arrow key was canceled for the next 2 rows AX 0 to switch the pushers. The working repeat became *32 rows 6X6, left arrow key, 2 rows AX 0*with the front bed programmed
Here the front bed is programmed for the repeat below, technique 130 (black squares tuck for 2 rows  After the initial prep on the front of the bed, prior to knitting the first pattern row, pushers were manually selected on the back bed to match the pusher work/rest position selection on the front bed. Their position will change as the back lock moves to the left. After 12 rows, the arrow key was canceled for the next 2 rows to AX 0 to switch the pushers. The working repeat became *12 rows AX, left arrow key, 2 rows AX 0* with the front bed programmed, and its lock set to KX. The back bed produces a “checkerboard”, the front bed produces checks as well, but in a vertical alignment
After the initial prep on the front of the bed, prior to knitting the first pattern row, pushers were manually selected on the back bed to match the pusher work/rest position selection on the front bed. Their position will change as the back lock moves to the left. After 12 rows, the arrow key was canceled for the next 2 rows to AX 0 to switch the pushers. The working repeat became *12 rows AX, left arrow key, 2 rows AX 0* with the front bed programmed, and its lock set to KX. The back bed produces a “checkerboard”, the front bed produces checks as well, but in a vertical alignment
A similar half-fisherman (only one-bed tucking) fabric may be produced on Brother machines by automating patterning and switching “beds”. The main bed is set to tuck in both directions, the ribber is set to knit throughout. My sample was pretty much a disaster at the start. After trying different carriages, switching out needle retainer bars on the main bed, checking alignment, and every trick I could think of I was rewarded with stitches simply not being picked up at intervals by the main bed. Time for a break for both the operator and the machine. 
a bit more success:
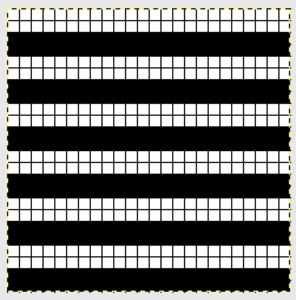
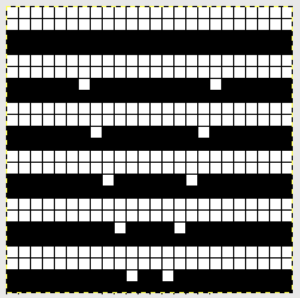
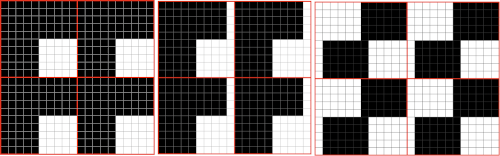
Below is my electronic repeat, 12 stitches by 56 rows in height. It is intended to mimic the work done by the pushers on the Passap. Alternate groups of 6 stitches will knit (black squares) or tuck (white squares) for 2 consecutive rows. At the center and the top of the full repeat, the two extra rows of squares result in alternate groups of stitches tucking or knitting for 4 rows, contributing to the shift in the color and texture of the checks.
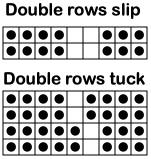
Passap specials: the idea of hand-selecting needles every row while watching multiple loops tucking on both beds and even adding racking is far too daunting to my mind. Highly textured patterns are far more easily produced in machines that allow for a greater range of patterning on both beds. To review, E6000 tuck settings:
N, EX: same on both locks, may be used without pushers or console
KX and AX: tuck in both directions
OX and DX: tubular tuck. FB: tucks right to left, free pass left to right, BB is opposite
The FX setting is incorporated into several techniques used with KX, 104, 105, 112, 113, 167, 259, and 260. Some techniques for adding back lock settings are 106, 114,145, 158, 167, 168, and 190. Techniques 259, 260, 269, and 270 use racking; 200, and 212 require manual changing of arrow keys; 284 uses the U100 transfer carriage in combination with fisherman rib for an embossed effect.
Using FX settings with pushers full fisherman rib can be combined with full needle rib or half fisherman rib on the opposite bed.
Technique 167: use FX/KX
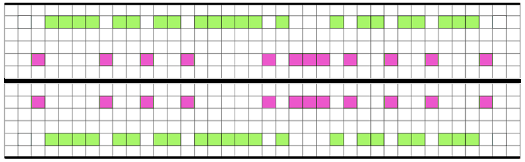
Front bed pushers are always selected up from right to left by the console independent of pattern, so they will knit. Set up pushers on the back bed in the pattern after the first row of the pattern, and make certain they are in the opposite arrangement of work/rest positions on the front bed. EX knits on all needles from left to right. Black squares represent knit stitches and white tuck ones. Making lock changes at the start of the repeat: knit 14 rows,* Knit 2 rows FX <–/KX, followed by 12 rows FX 0/KX** Repeat* to ** One full repeat of the 2 sequences is 28 rows. The original BW building block is 6 stitches wide, 7 rows high, pairs of each form the unit used to form the larger repeat blocks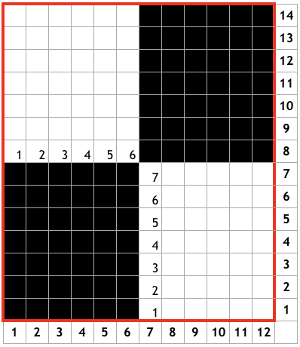
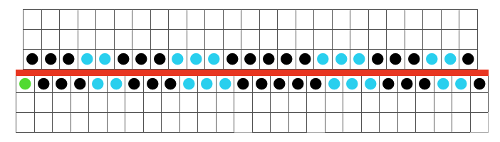
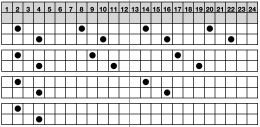
My chart for my full working repeat test sample: dots represent pushers, green highlights rows with lock changes for pusher reversal. The latter are made here on RC13 and 14 rather than RC 1 and 2
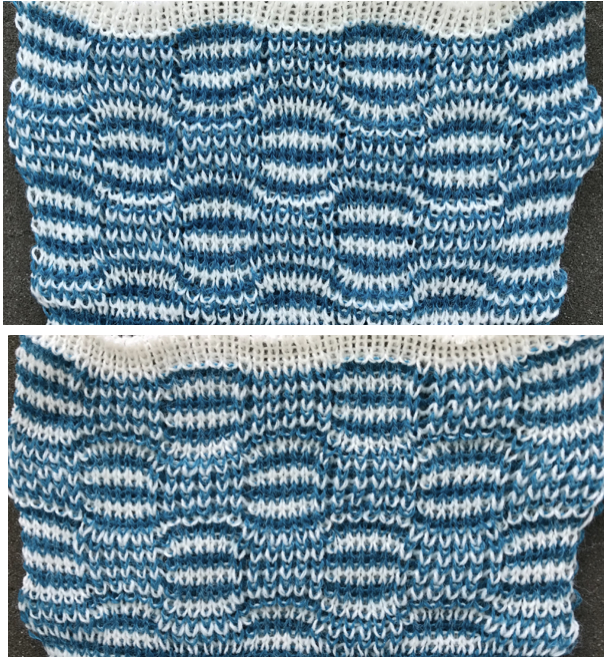
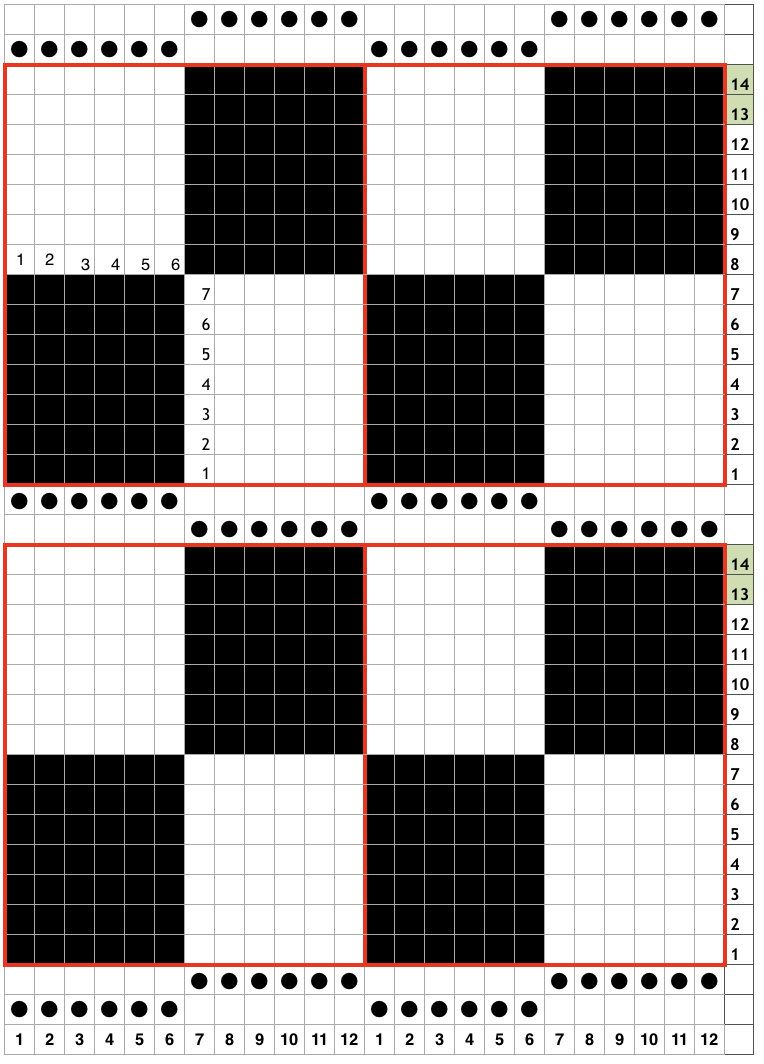

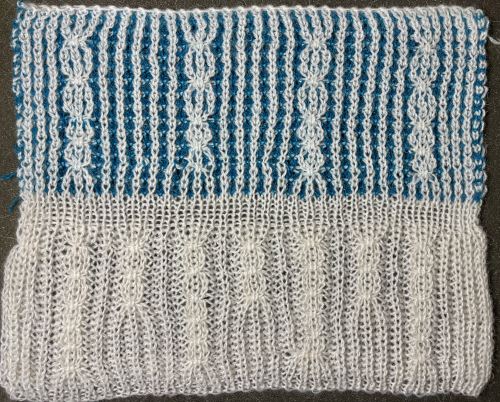
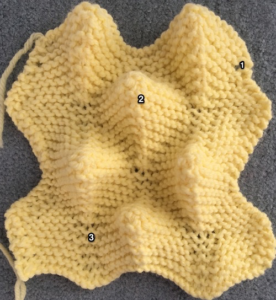
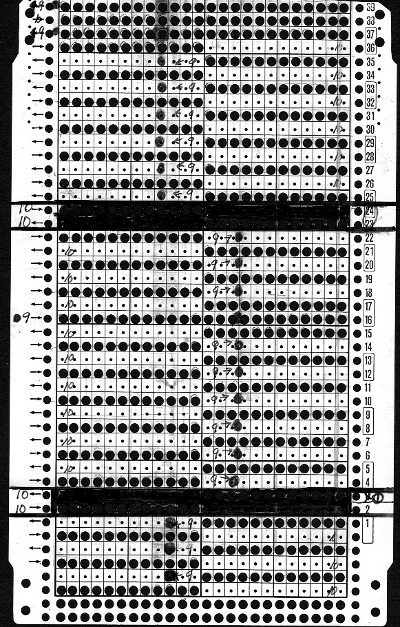
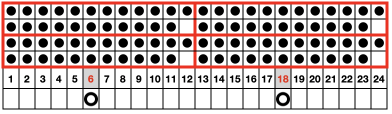
Getting back to that scarf and reversible checks, I finally sorted out the how-to and a repeat in a different number of stitches and rows. Technique 180: disregard console directions. Set up with 1 extra needle and pusher on the back bed at each side. Pusher selection on the back bed as described below matches half the number of stitches in the full repeat starting on the right side of the back bed. End with a single pusher on the far left in the opposite work/rest position of pushers in the group to its immediate right. Reset the front lock row counter manually at the end of each full repeat (24 for mine) back to 000. As an option one may choose to knit half a repeat at the top and bottom of the piece. My first swatch is testing one full repeat + a few rows. My full checkerboard repeat is 24 stitches wide by 24 rows high, composed in turn of a set of 4 blocks 12 stitches wide by 12 rows high. The AX setting changes pusher selection every 2 rows, and the AX 0 rows reverse pusher selection, resulting in the shift in the patterning on the back bed. Knit the first 24 rows (full repeat #) with no lock change, I found it easier to reset the arrow key at the start of the repeat on RC 1 and 2, rather than RC 23-24. The single BW building units are 6 stitches wide by 6 high with blocks 4 producing the 12W X12H repeat segments  A working chart for the full repeat: Black dots = pushers in their work/rest positions, numbers on right = full repeat in rows
A working chart for the full repeat: Black dots = pushers in their work/rest positions, numbers on right = full repeat in rows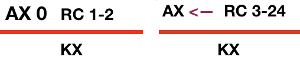
 I like to chart out my repeats and plans for executing fabrics, along with ideas for possibly varying them in ways other than suggested, this was my beginning
I like to chart out my repeats and plans for executing fabrics, along with ideas for possibly varying them in ways other than suggested, this was my beginning 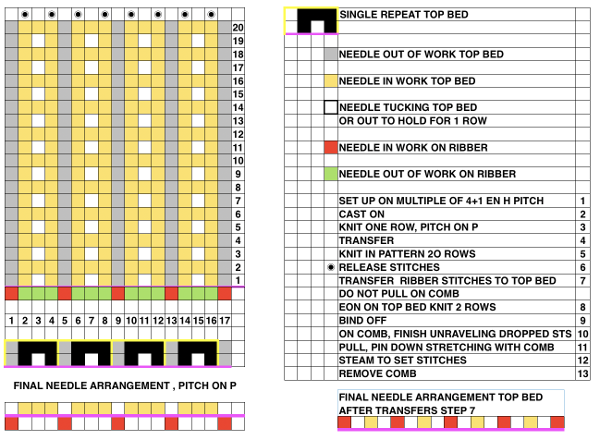 The sequence in photos, beginning with the cast on, 2/24 acrylic yarn, zigzag row with inserted ribber comb, half-pitch
The sequence in photos, beginning with the cast on, 2/24 acrylic yarn, zigzag row with inserted ribber comb, half-pitch  1 row is knit across all stitches to complete cast on,
1 row is knit across all stitches to complete cast on,  knit one more row to return to the opposite side
knit one more row to return to the opposite side  the setting is changed to full pitch, stitches are transferred between beds to match diagrams
the setting is changed to full pitch, stitches are transferred between beds to match diagrams  the center needle in each group of 3 is brought out to hold for one row, knit one row to return to the other side
the center needle in each group of 3 is brought out to hold for one row, knit one row to return to the other side  center needles are pushed back to D position in order to be knit on return pass to the opposite side
center needles are pushed back to D position in order to be knit on return pass to the opposite side  this tool makes that needle selection faster and easier
this tool makes that needle selection faster and easier  when the 20 rows had been knit in pattern drop stitches on each side of center stitch
when the 20 rows had been knit in pattern drop stitches on each side of center stitch  transfer ribber stitches up to main bed
transfer ribber stitches up to main bed  I knit 3 rows rather than 2, to return to right side for bind off
I knit 3 rows rather than 2, to return to right side for bind off  here is the swatch, still on comb for “setting stitches”
here is the swatch, still on comb for “setting stitches”

 knit back to the opposite side, transfer each of the side stitches on the top bed onto the center needle in each group,
knit back to the opposite side, transfer each of the side stitches on the top bed onto the center needle in each group,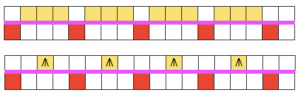 bring those needles out to hold for easier knitting on the next pass
bring those needles out to hold for easier knitting on the next pass  knit one row back to the right, making sure stitches have knit off properly. When you have returned to the right side, set the carriage to tuck from right to left only (left tuck button), RC000
knit one row back to the right, making sure stitches have knit off properly. When you have returned to the right side, set the carriage to tuck from right to left only (left tuck button), RC000 loops will be formed on the center needles as they would have been formed over the needles as if holding was in use
loops will be formed on the center needles as they would have been formed over the needles as if holding was in use when the 20 rows are completed the carriages will once again be on the right, all stitches will have been knit on the previous row
when the 20 rows are completed the carriages will once again be on the right, all stitches will have been knit on the previous row  transfer all ribber stitches to top bed, knit 2 rows, bind off. None of my swatches were blocked other than by some tugging, particularly along the bottom edge. The spacing between stitches is narrower because ladders created by single needles left out of work are formed by yarn lengths that are shorter than those that happen when stitches are knit and then in turn dropped. The height of the swatch is also affected, and the half fisherman texture in the wool swatch, in particular, is more evident.
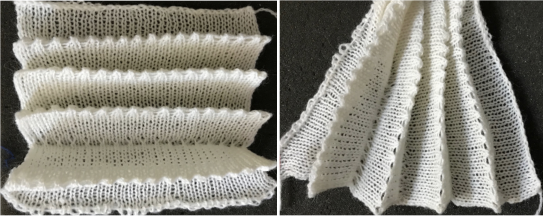
transfer all ribber stitches to top bed, knit 2 rows, bind off. None of my swatches were blocked other than by some tugging, particularly along the bottom edge. The spacing between stitches is narrower because ladders created by single needles left out of work are formed by yarn lengths that are shorter than those that happen when stitches are knit and then in turn dropped. The height of the swatch is also affected, and the half fisherman texture in the wool swatch, in particular, is more evident.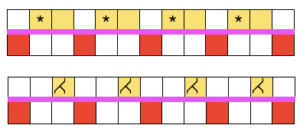 When the work is removed from the machine, stretch cast on outwards, then give each “scallop” a really good pull downwards. Steam lightly over the scallops to set them. Variations of the double bed trims may be worked on the single bed as well.
When the work is removed from the machine, stretch cast on outwards, then give each “scallop” a really good pull downwards. Steam lightly over the scallops to set them. Variations of the double bed trims may be worked on the single bed as well.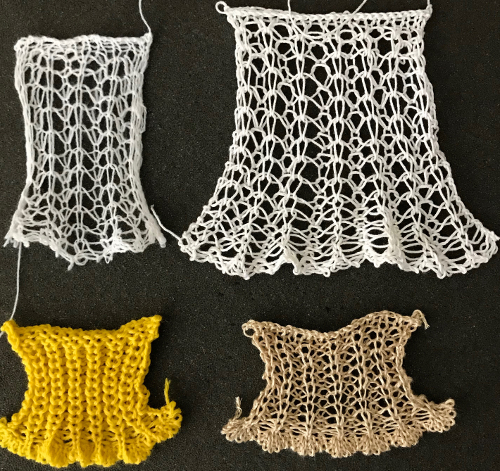



 Working it on Brother becomes a bit fiddly. Whether working on a punchcard or electronic KM, it is possible to introduce patterning on either or both beds as seen below. I preferred the look obtained with the racked cast on at the start. Setting up the Brother machine: program the repeat, half pitch for every needle rib, air knit to place the pattern on the bed so that the first needle on the left (or right if you prefer) is preselected forward and will produce a knit stitch on the first row knit. The yarn used is a 2/24 acrylic
Working it on Brother becomes a bit fiddly. Whether working on a punchcard or electronic KM, it is possible to introduce patterning on either or both beds as seen below. I preferred the look obtained with the racked cast on at the start. Setting up the Brother machine: program the repeat, half pitch for every needle rib, air knit to place the pattern on the bed so that the first needle on the left (or right if you prefer) is preselected forward and will produce a knit stitch on the first row knit. The yarn used is a 2/24 acrylic 
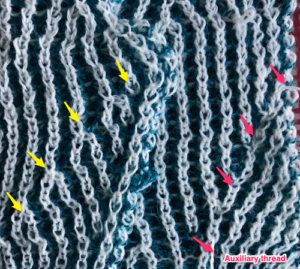
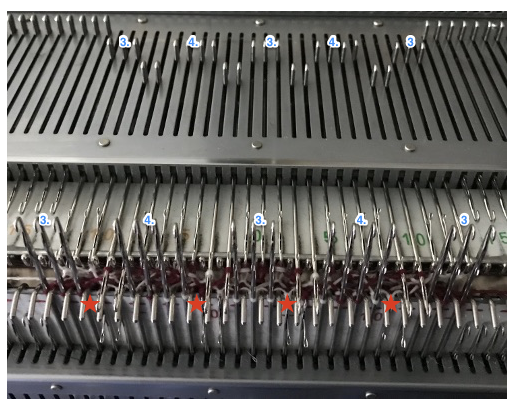
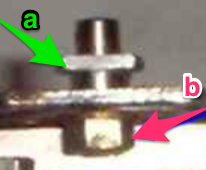
 now another needle on the ribber is brought in to work on the far left, it will tuck with lili selection when moving from left to right
now another needle on the ribber is brought in to work on the far left, it will tuck with lili selection when moving from left to right  remember the ribber rule with lili buttons: an even number of needles must be in work, this shows the start and end of selection on the ribber on alternate needle tape markings, as required
remember the ribber rule with lili buttons: an even number of needles must be in work, this shows the start and end of selection on the ribber on alternate needle tape markings, as required 



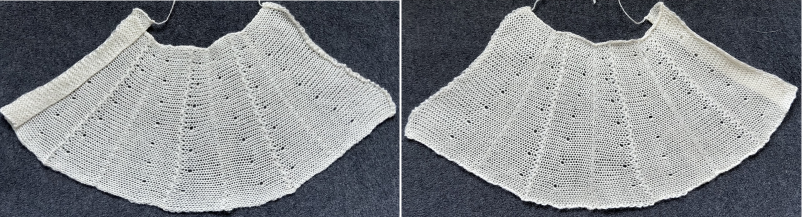
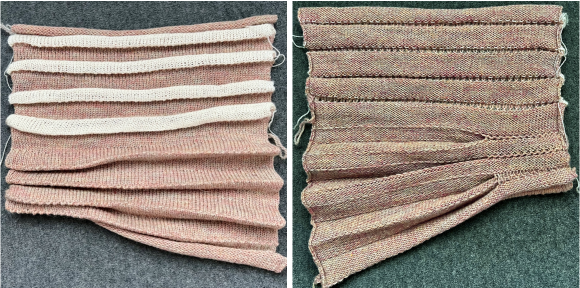
 Both pieces compared for width and rippling
Both pieces compared for width and rippling


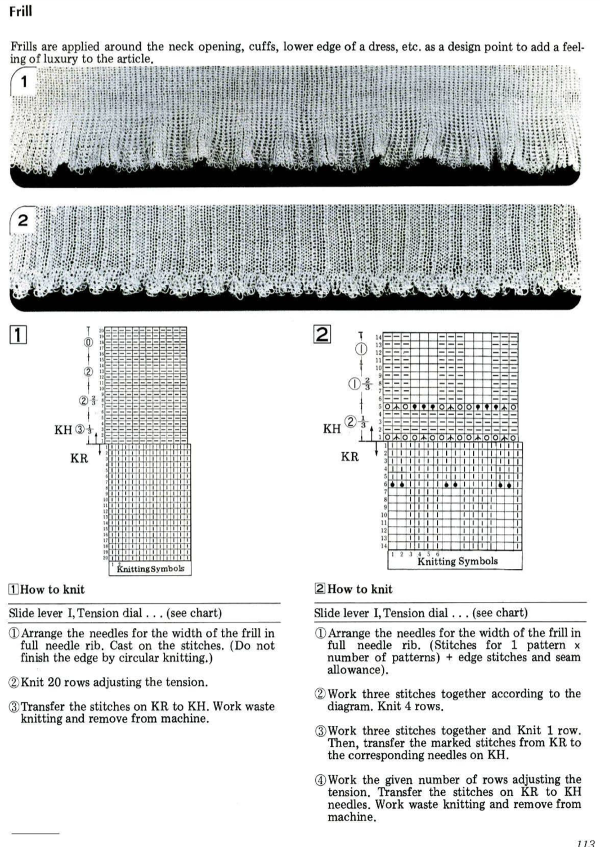
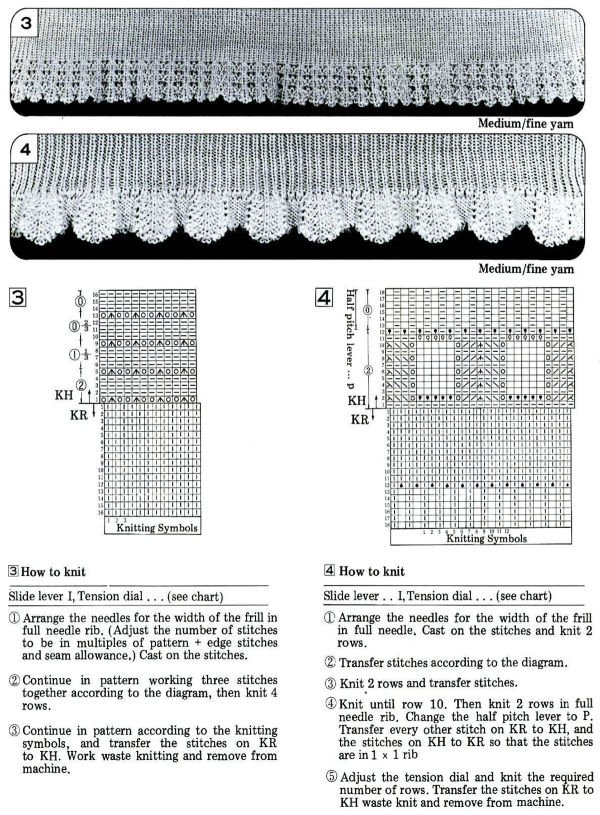
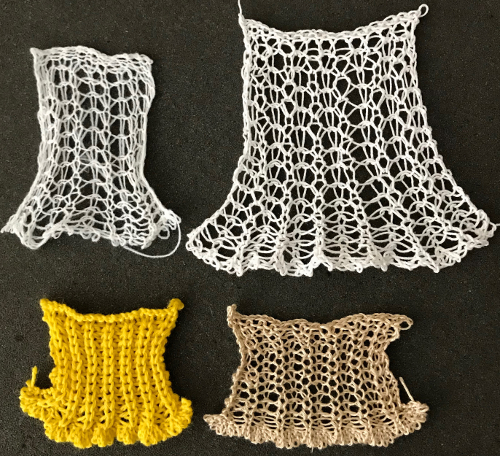
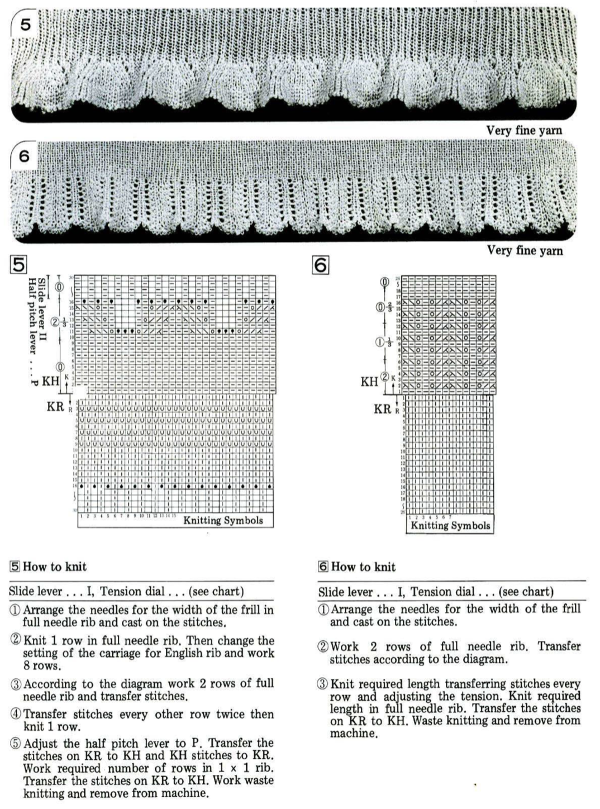 An intro to scallops: p.120
An intro to scallops: p.120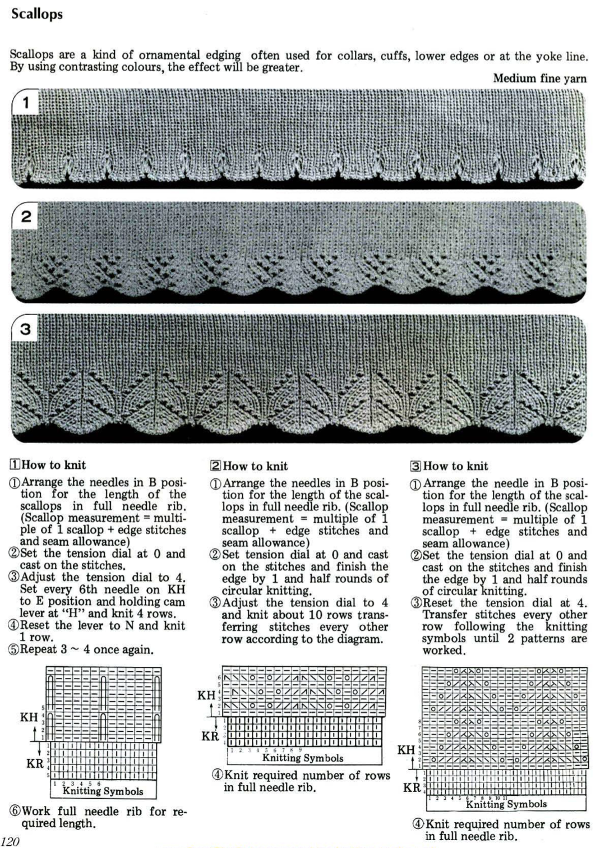
 Fisherman, aka full fisherman rib, is a tubular tuck with each bed tucking in one direction, knitting in the other
Fisherman, aka full fisherman rib, is a tubular tuck with each bed tucking in one direction, knitting in the other


 Can plaiting give me 2 colors the “easy” way?
Can plaiting give me 2 colors the “easy” way? 
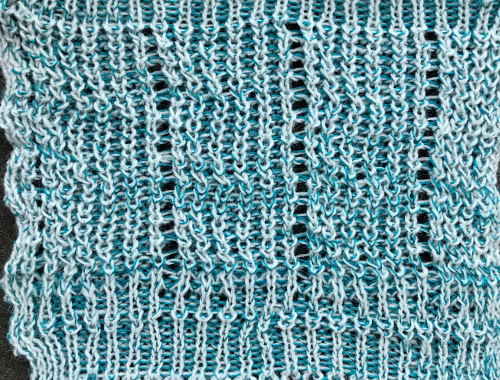
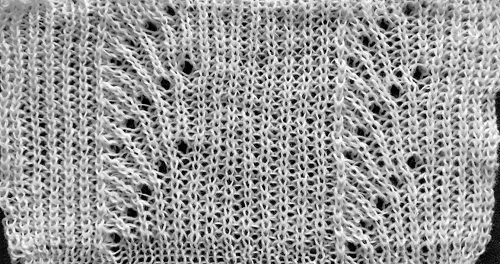














 its reverse side :
its reverse side :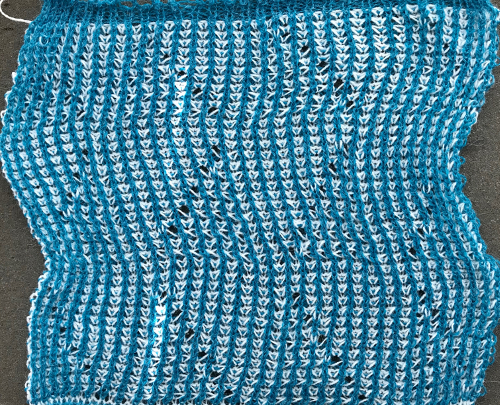



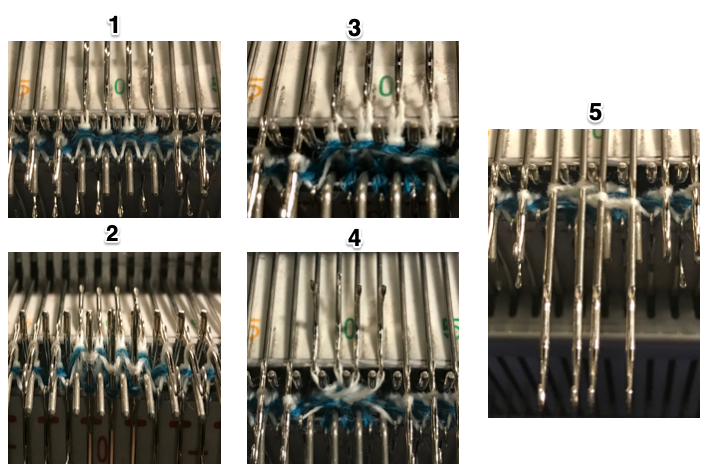
 This is what happens when a new design is being tested, and the lili buttons “accidentally” happen to be engaged on the ribber
This is what happens when a new design is being tested, and the lili buttons “accidentally” happen to be engaged on the ribber 
 Each of the 2 colors tucks for 2 rows and in turn, knits for 2 rows alternately. Settings are changed manually as shown below after every 2 rows knit, following each color change on the left.
Each of the 2 colors tucks for 2 rows and in turn, knits for 2 rows alternately. Settings are changed manually as shown below after every 2 rows knit, following each color change on the left. 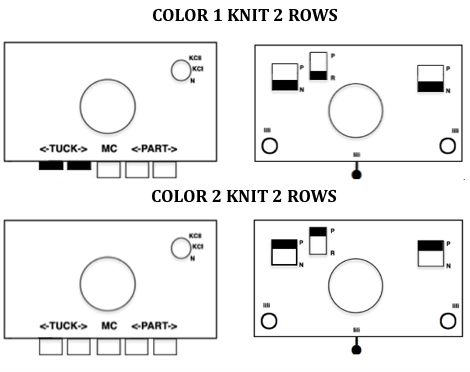 Making things a little easier: the top bed may be programmed on any machine, including punchcard models to avoid cam button changes in the knit carriage every 2 rows. With the main bed set to tuck <– —> throughout, black squares will knit for 2 rows, white squares will tuck, also for 2 rows. The first preselection row is toward the color changer. When no needles are selected on the top bed (white squares) the top bed will tuck every needle, the ribber is set to knit.
Making things a little easier: the top bed may be programmed on any machine, including punchcard models to avoid cam button changes in the knit carriage every 2 rows. With the main bed set to tuck <– —> throughout, black squares will knit for 2 rows, white squares will tuck, also for 2 rows. The first preselection row is toward the color changer. When no needles are selected on the top bed (white squares) the top bed will tuck every needle, the ribber is set to knit. 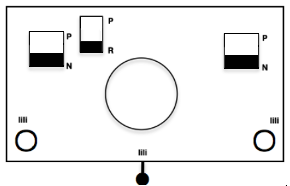



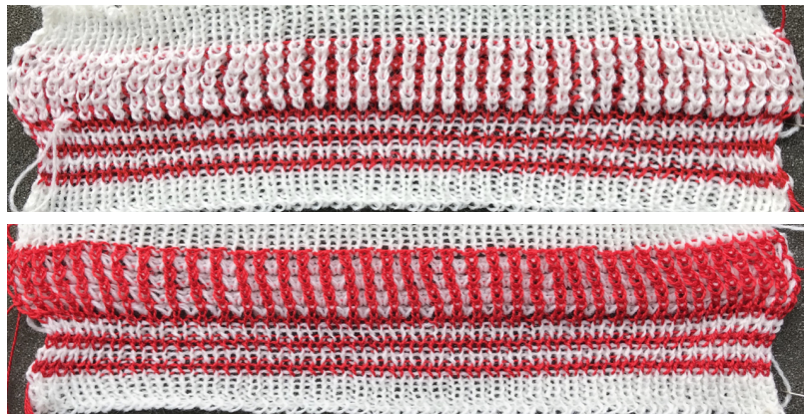
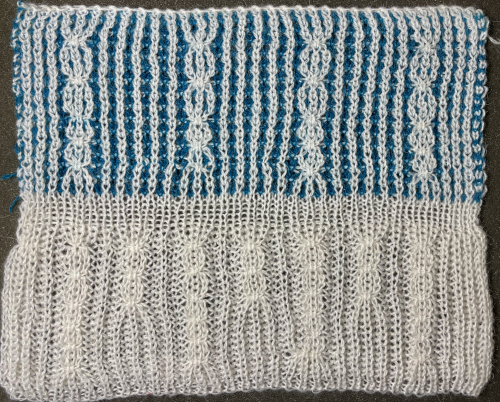
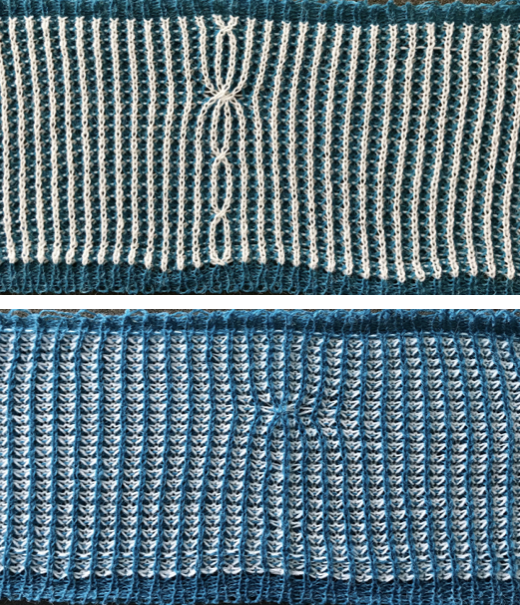
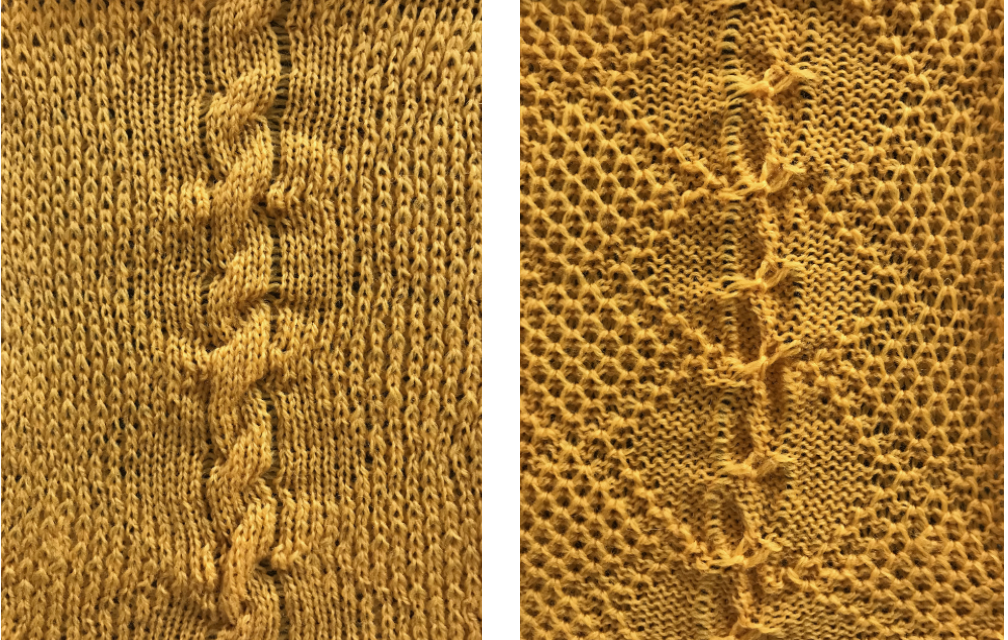
 Another attempt at cabling, 1X1 and 2X2. That white line in the bottom image on the right was caused by the color changer picking up and knitting both colors for part of the row before I noticed it. I got rid of the “wrong” color from the feeder and continued on. The wider 2X2 cables require “special handling” and eyelets are formed on columns aside from them after transfers are made.
Another attempt at cabling, 1X1 and 2X2. That white line in the bottom image on the right was caused by the color changer picking up and knitting both colors for part of the row before I noticed it. I got rid of the “wrong” color from the feeder and continued on. The wider 2X2 cables require “special handling” and eyelets are formed on columns aside from them after transfers are made. 




 The situation is different when working on single bed vertically striped fair isle designs. One of my ancient machine-knit demo FI swatches:
The situation is different when working on single bed vertically striped fair isle designs. One of my ancient machine-knit demo FI swatches: 
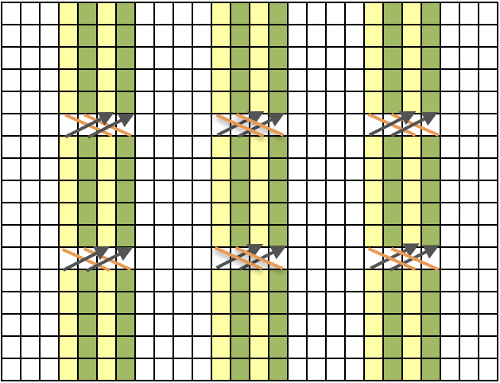
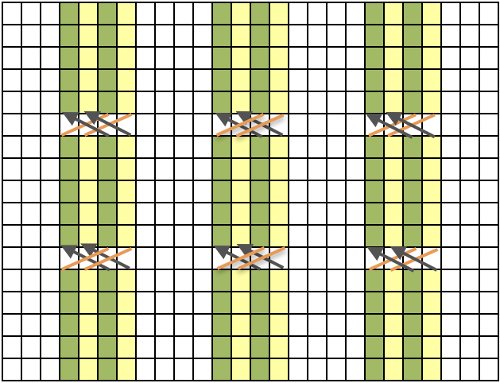
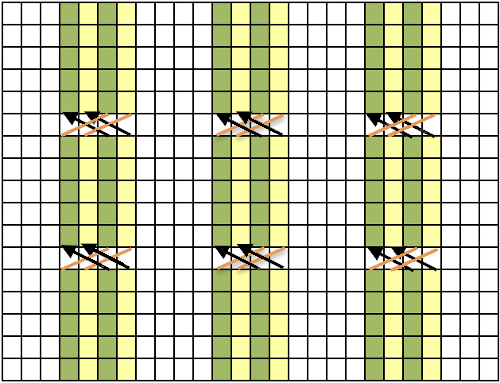

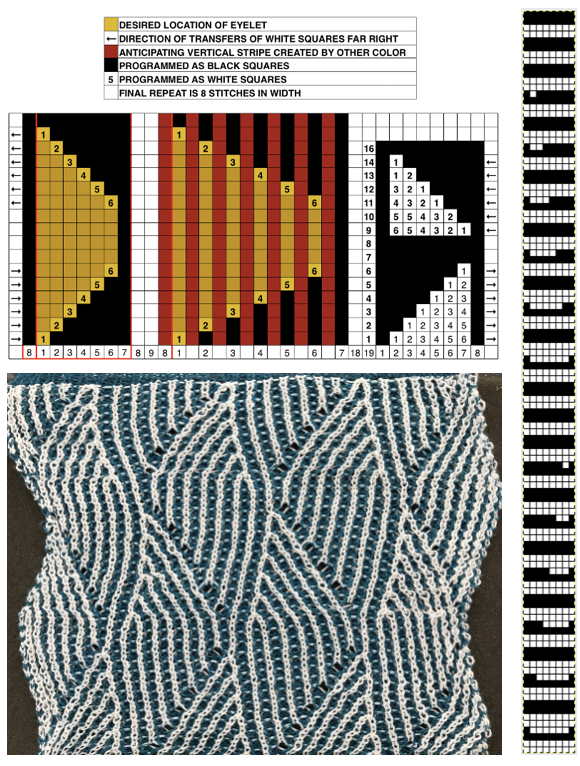
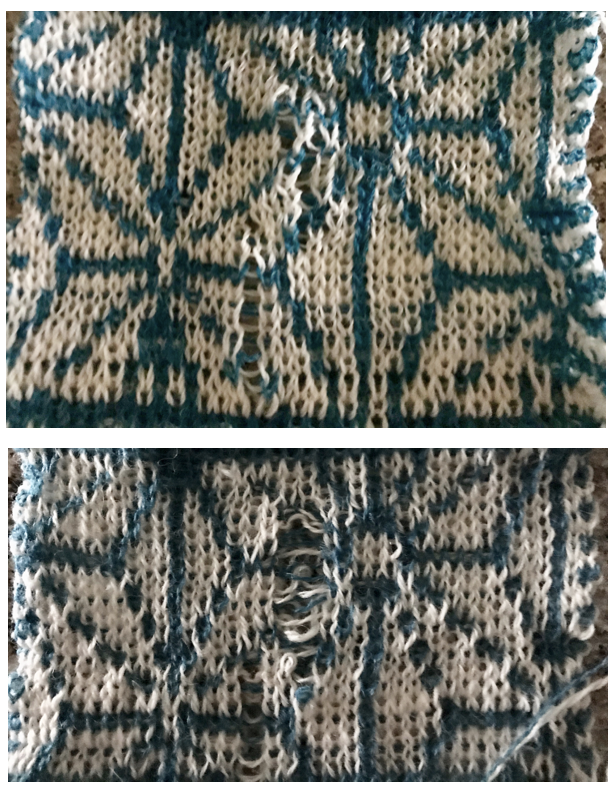
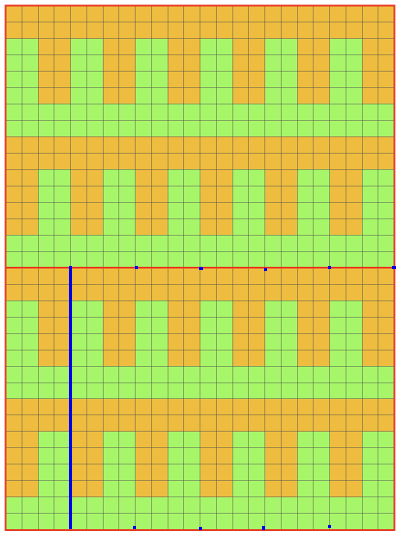
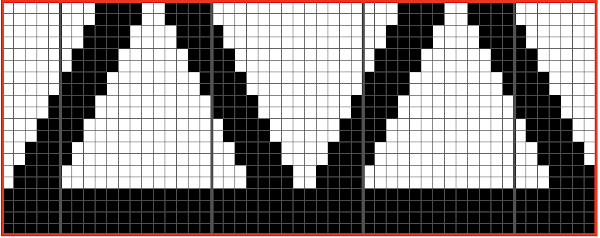
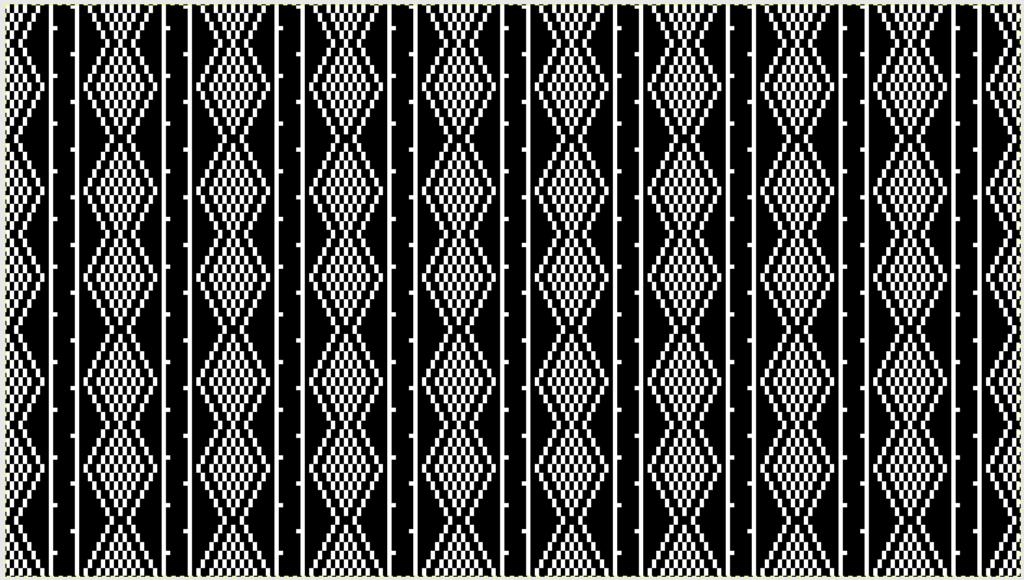
 The charted repeat on the left below when tiled shows the area of a patterning error, on the right with the missing blank rows added the problem is shown to be resolved, the repeat is now 24 X 84.
The charted repeat on the left below when tiled shows the area of a patterning error, on the right with the missing blank rows added the problem is shown to be resolved, the repeat is now 24 X 84. 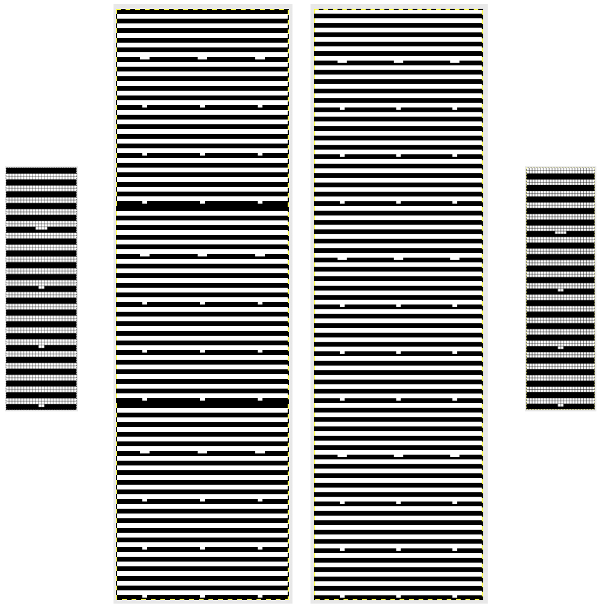


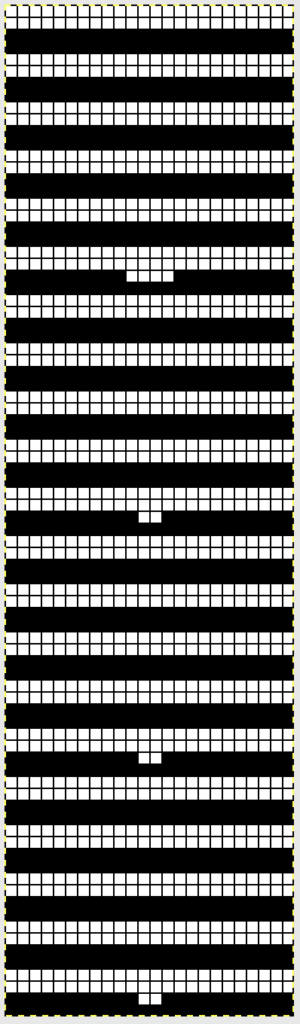
 Adding complexity, there is the possibility of
Adding complexity, there is the possibility of 
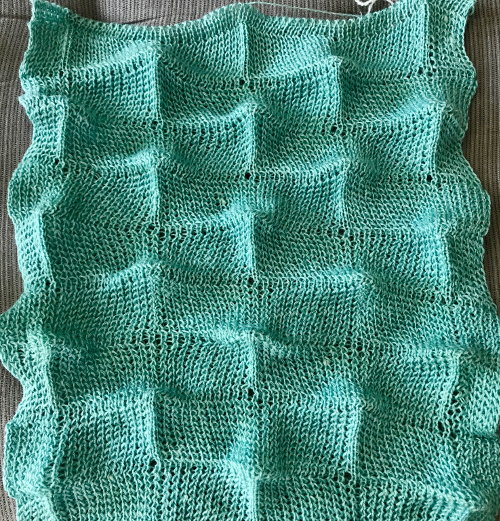
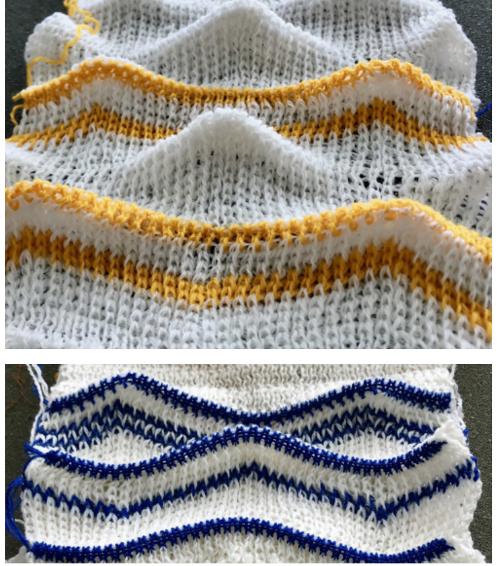
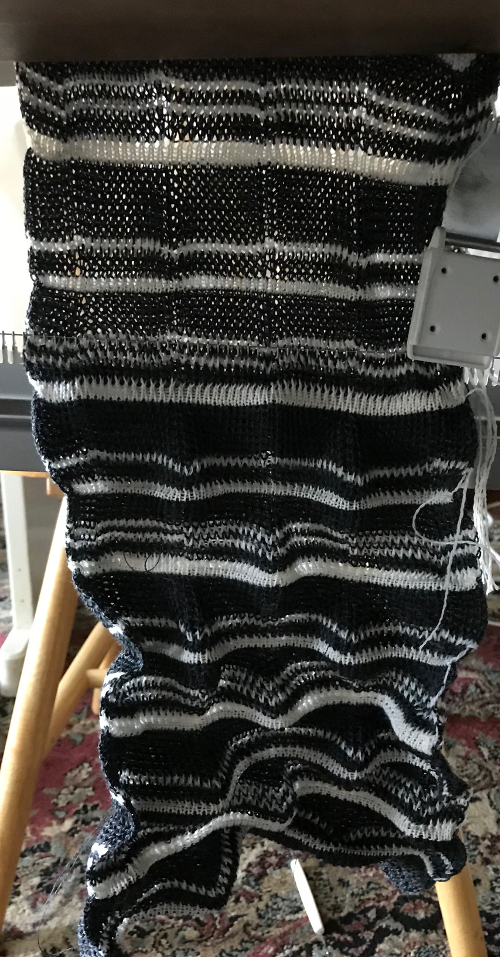
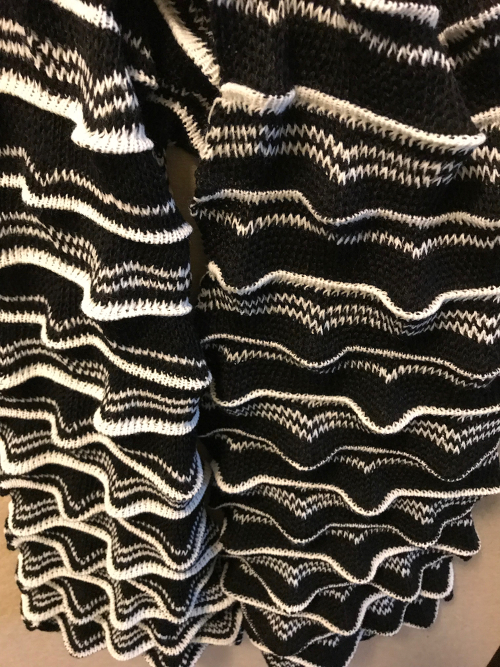
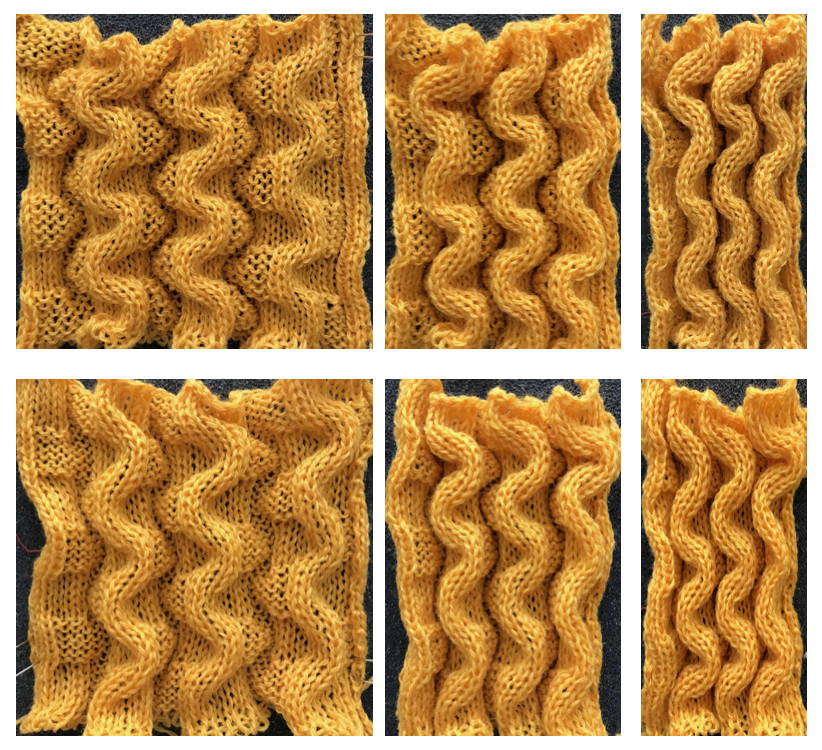




































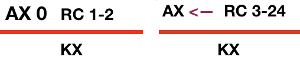

























































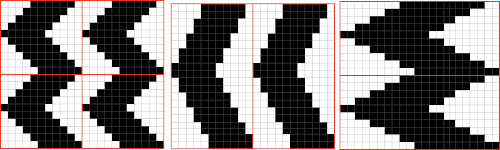
 and my small test swatch. The fold on each side and the swing in the pattern appear crisper and better defined to me
and my small test swatch. The fold on each side and the swing in the pattern appear crisper and better defined to me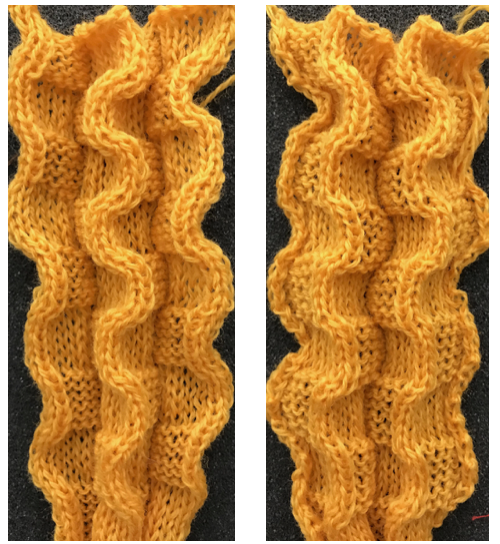
 an attempt at a side view
an attempt at a side view  an earlier
an earlier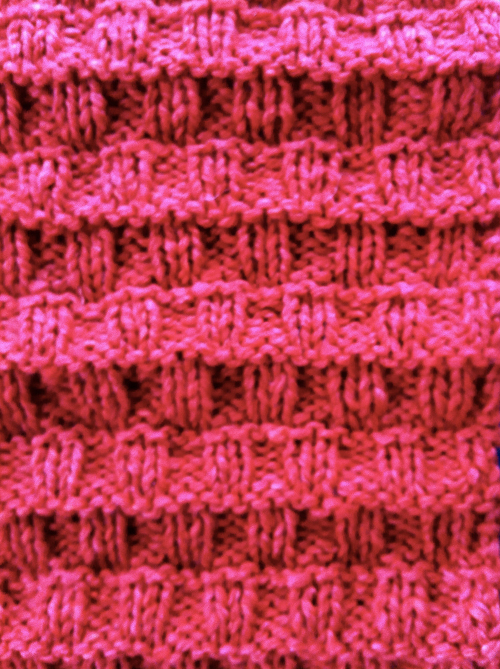  Another handknit swatch in worsted weight, perhaps suitable for G carriage
Another handknit swatch in worsted weight, perhaps suitable for G carriage 



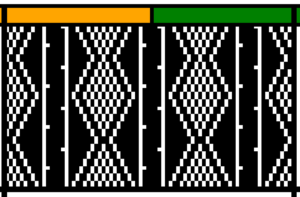
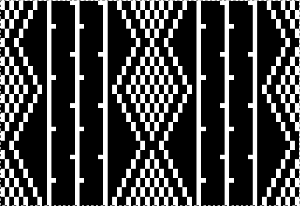
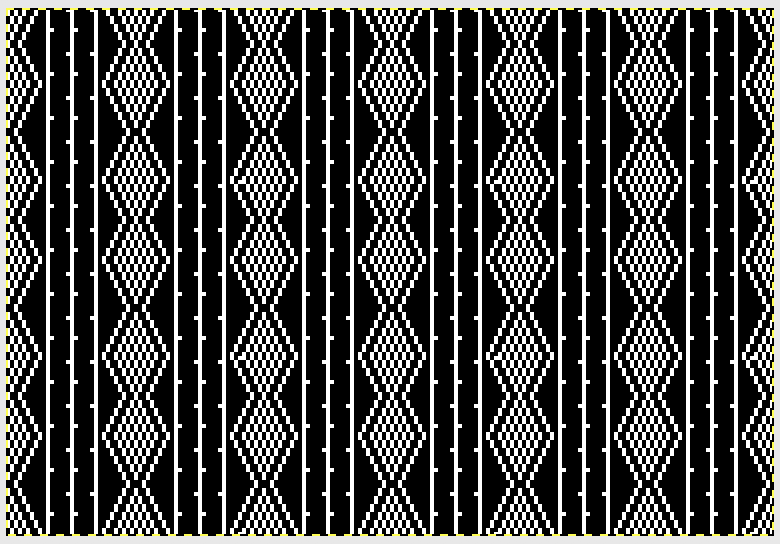
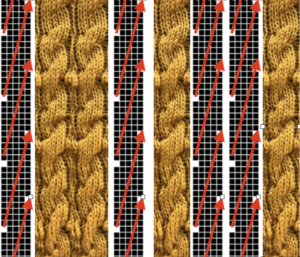
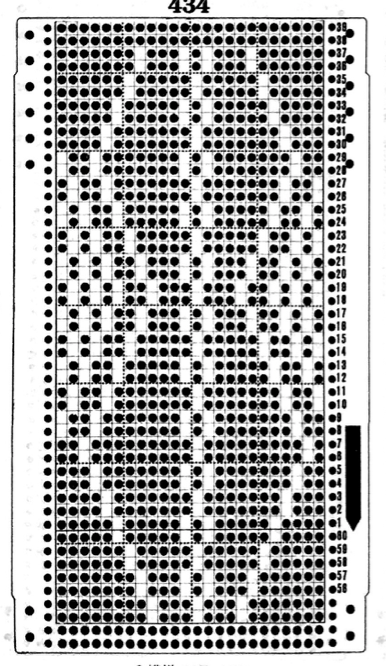 The card is cropped to the 24 X 44 stitch in width and height for the repeat to be worked in electronics. The area colored blue on the far right indicates possible all knit rows for hooking up “cables” during knitting, mustard color indicates ladders created by an out of work needle on each side of the central, all knit column. The ladders make it easier to identify each all knit column. The tape over holes idea does not work for masking a punchcard since that blue area would need to be all punched holes. The tape over would result in “unpunched” ones.
The card is cropped to the 24 X 44 stitch in width and height for the repeat to be worked in electronics. The area colored blue on the far right indicates possible all knit rows for hooking up “cables” during knitting, mustard color indicates ladders created by an out of work needle on each side of the central, all knit column. The ladders make it easier to identify each all knit column. The tape over holes idea does not work for masking a punchcard since that blue area would need to be all punched holes. The tape over would result in “unpunched” ones.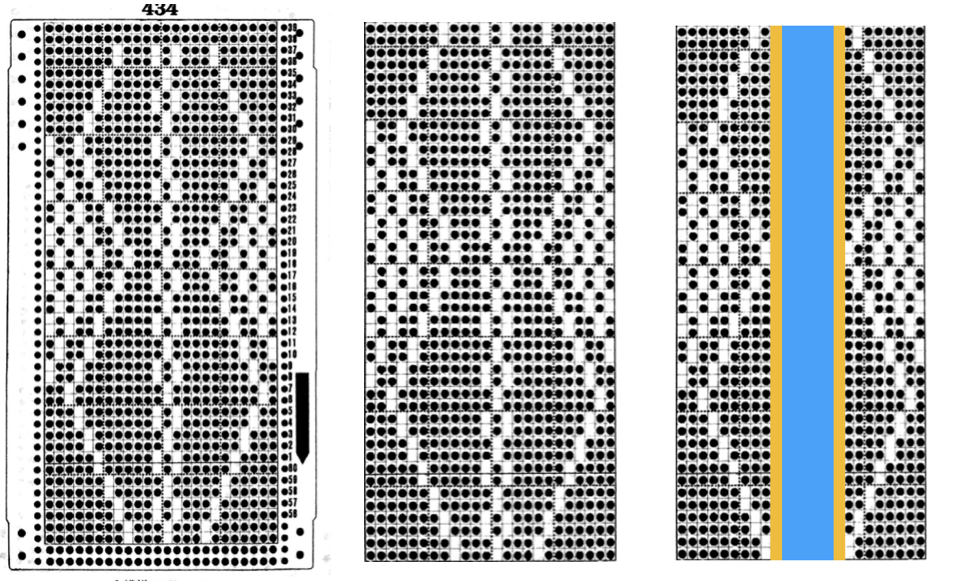 This takes the revised card single repeat and indicates some quick possibilities for altering it
This takes the revised card single repeat and indicates some quick possibilities for altering it 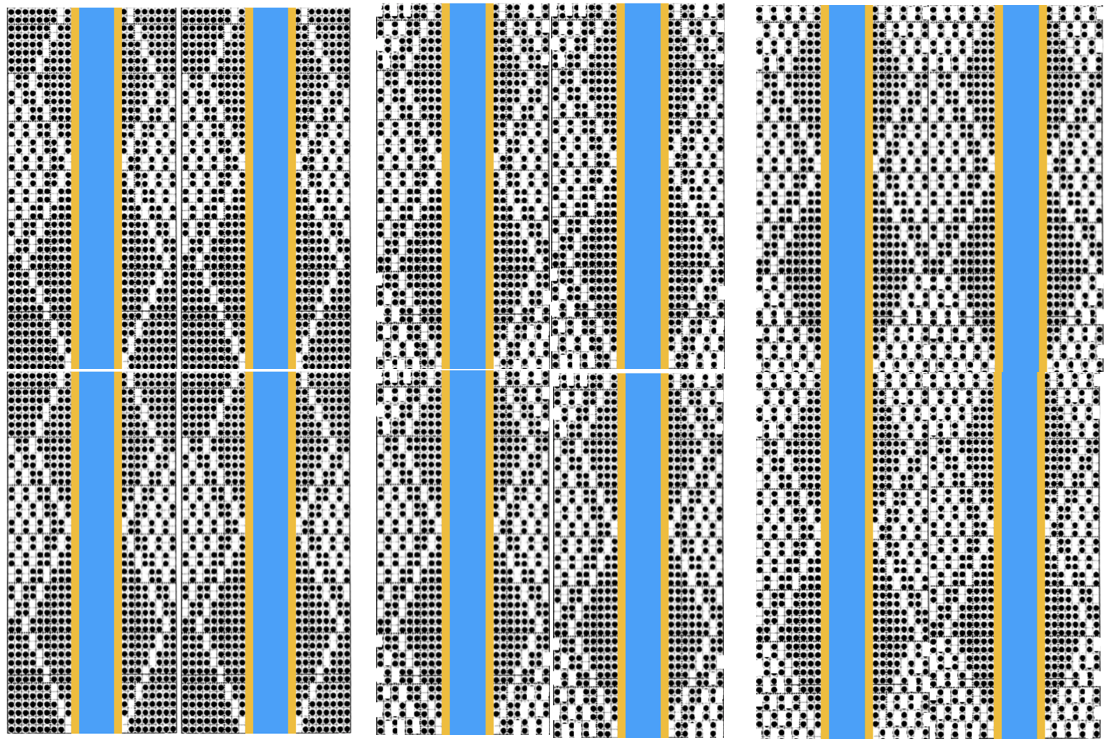
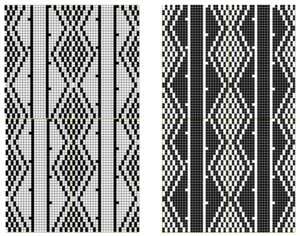
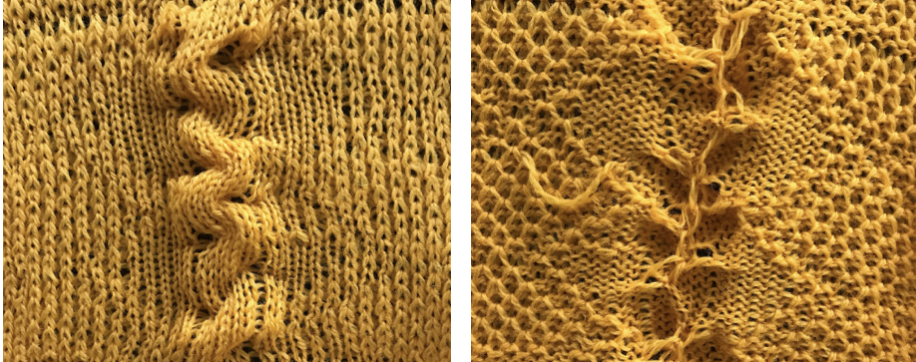







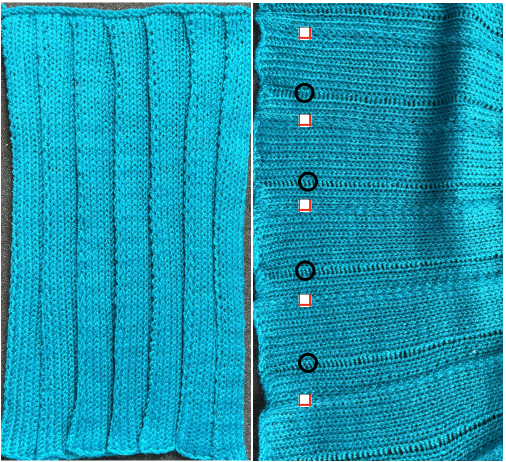
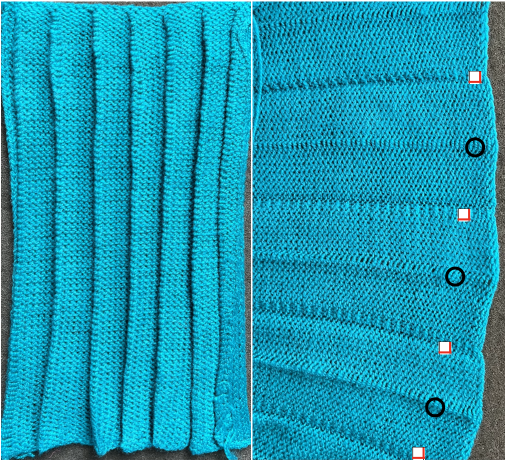


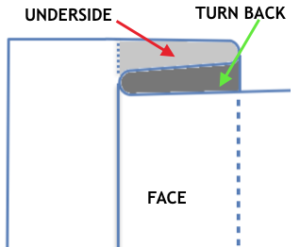

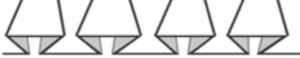
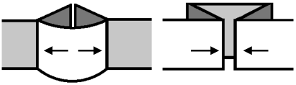
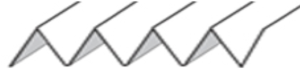

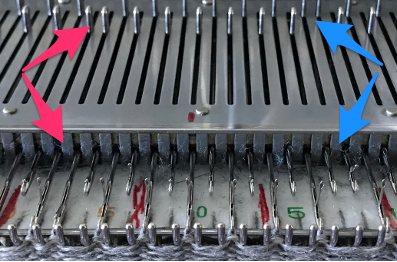 The fabric narrows considerably as it is stretched lengthwise to set the stitches. Several panels would be required for a garment such as a skirt. Such an item would need to be pulled into shape, pinned, and hot pressed. Fiber content will determine the crispness of the pleats after blocking, and their retention after cleaning. The swatch below is turned sideways for the sake of space.
The fabric narrows considerably as it is stretched lengthwise to set the stitches. Several panels would be required for a garment such as a skirt. Such an item would need to be pulled into shape, pinned, and hot pressed. Fiber content will determine the crispness of the pleats after blocking, and their retention after cleaning. The swatch below is turned sideways for the sake of space.  More variations with folds can be made by varying the “rules” commonly recognized for creases. Working sideways once more: on a punchcard machine, using card # 1 locked, cast on making certain every other needle as well as the first and last are selected.
More variations with folds can be made by varying the “rules” commonly recognized for creases. Working sideways once more: on a punchcard machine, using card # 1 locked, cast on making certain every other needle as well as the first and last are selected. Cancel the slip setting, complete the next knit section, and transfer every other needle to the adjacent one on either the right or left.
Cancel the slip setting, complete the next knit section, and transfer every other needle to the adjacent one on either the right or left.  The needles holding 2 stitches may be brought out to the hold position as each transfer is made, or pushed out to hold after the fact to insure the stitches have been transferred and will knit off properly. The number of needles in work remains constant.
The needles holding 2 stitches may be brought out to the hold position as each transfer is made, or pushed out to hold after the fact to insure the stitches have been transferred and will knit off properly. The number of needles in work remains constant. 


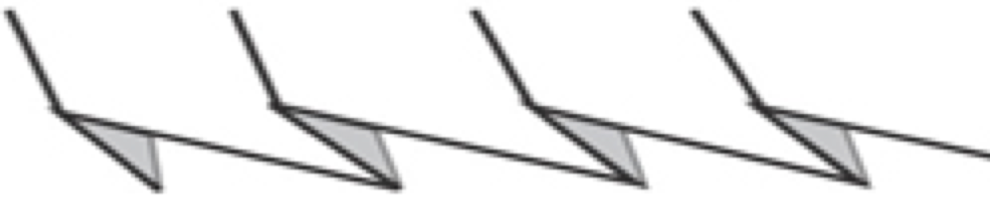
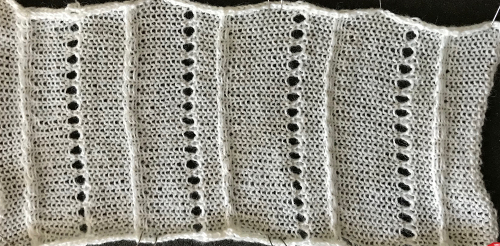 The slipped stitches form the inside folds in the pressed swatch, while eyelets and tuck stitches fold a picot edge to the outside.
The slipped stitches form the inside folds in the pressed swatch, while eyelets and tuck stitches fold a picot edge to the outside.