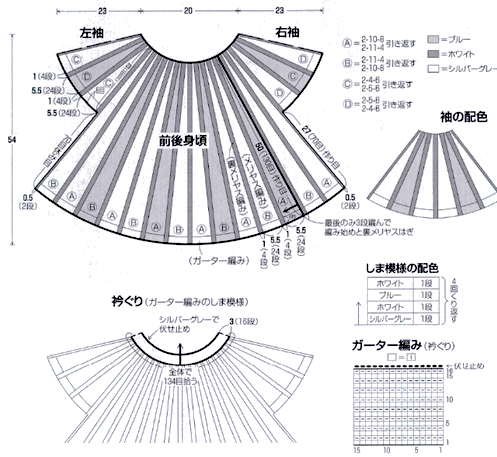
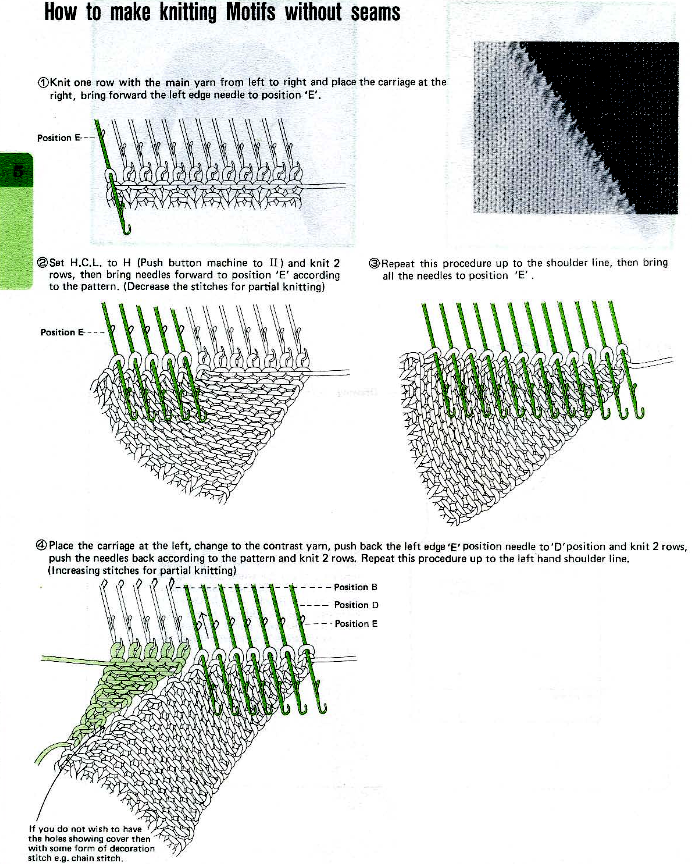
There are generators online for many generators to aid with knitting design.
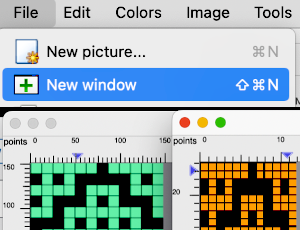
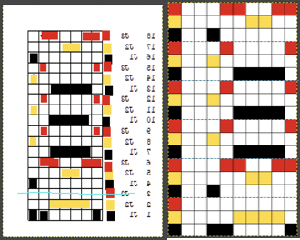
In 2015 I published a post on working with generated mazes: Gimp charting 1
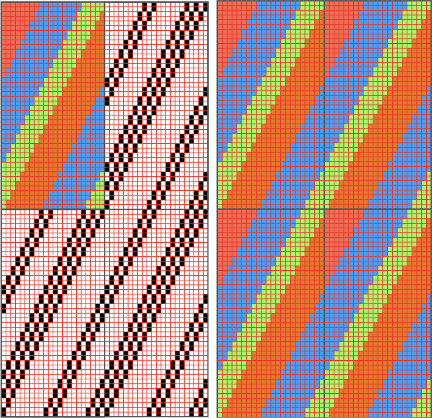
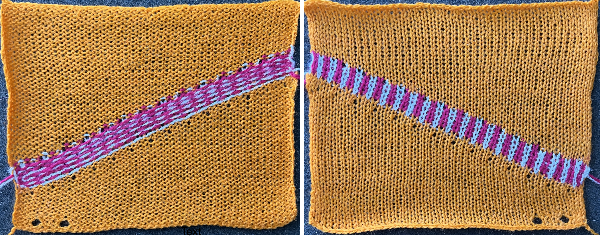
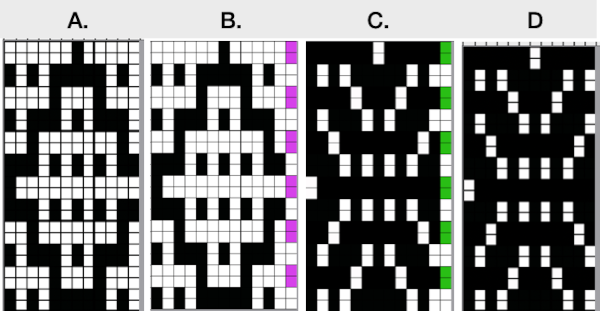
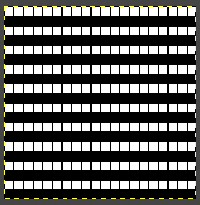
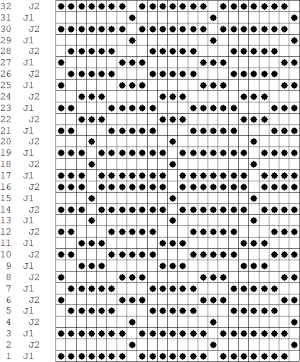
The long lines of black or white cells make them unsuitable for traditional fair isle knitting.
There are many ways to achieve the same goals. One option for converting small-scale repeats is to begin with a file previously used and separated, magnified to 1800X.
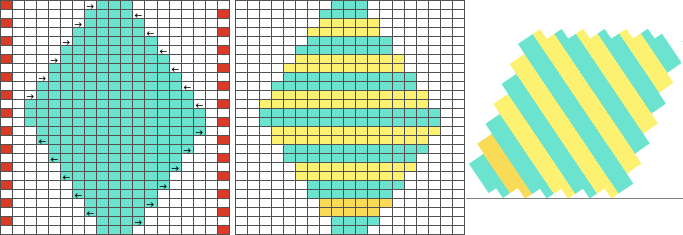
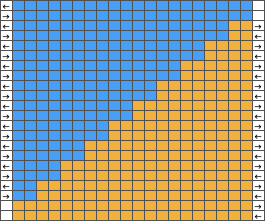
1. using the rectangle select tool, begin on row 1, extending the handle outside the image, I work from left to right
2. hold down the shift key and continue selecting every other row. As each row is selected, it is outlined with dots. The handles to the right and left of that row serve as guides as to the last row worked, moving up as separation progresses. Clicking on the rectangle select tool at any point fixes the layer, and the dotted lines will disappear.  The process could be performed in steps, with guides placed before color inverting the previous steps in the sequence and moving on to the next.
The process could be performed in steps, with guides placed before color inverting the previous steps in the sequence and moving on to the next.  The guides remain until they are removed by clicking on the check mark beside show guides,
The guides remain until they are removed by clicking on the check mark beside show guides, ![]() or with the / / command.
or with the / / command.
This method may be more error-prone than using layers or colors to make rows transparent when developing large designs.
3. after each pertinent row has been selected, choose the color invert option and save the resulting file. The first steps in the separation are completed.
The final file must be color-inverted and lengthened X2 before knitting. The result matches the separation in the previous post. 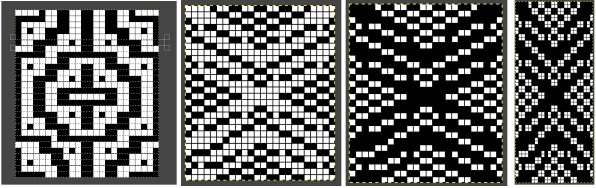 Holding down the shift key when using the pencil tool on any image produces very different results.
Holding down the shift key when using the pencil tool on any image produces very different results.  My samples continue to be knit on the 930 using img2track, a download program I find reliable and easy to use. The only errors in programming I have encountered were due to operator errors, not software ones.
My samples continue to be knit on the 930 using img2track, a download program I find reliable and easy to use. The only errors in programming I have encountered were due to operator errors, not software ones.
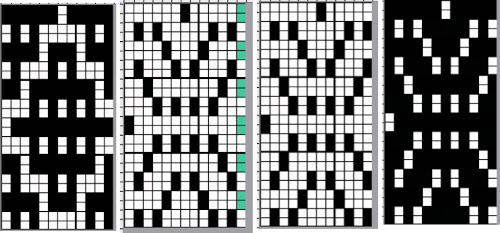
Since 2015 working with larger images has become far less daunting as my methods for color separations of mazes and mosaics have evolved.
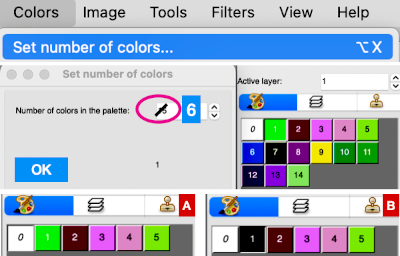
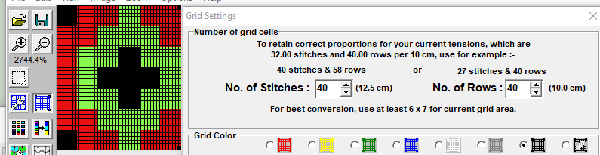
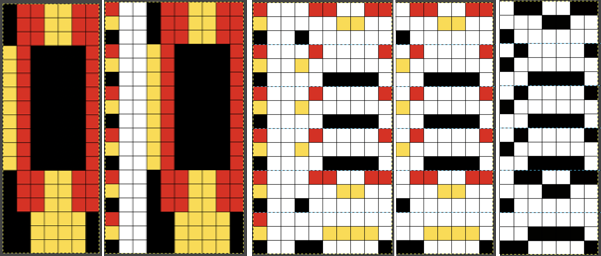
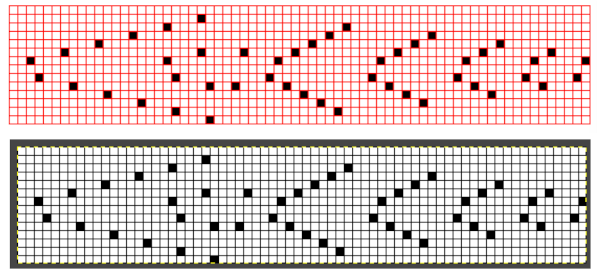
Laura Kroegler’s online Mosaic Pattern Generator is still available. Returning to it, and using these parameters  the pngs were downloaded both in red and then again in black and white.
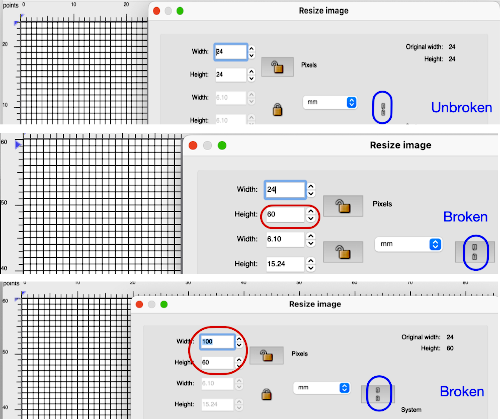
the pngs were downloaded both in red and then again in black and white.  A 38X38 stitch repeat was isolated, and using Layer/Transparency/Color to Alpha a knittable mosaic design was obtained which, when knit, would require elongation X2 for color changing every 2 rows
A 38X38 stitch repeat was isolated, and using Layer/Transparency/Color to Alpha a knittable mosaic design was obtained which, when knit, would require elongation X2 for color changing every 2 rows ![]()
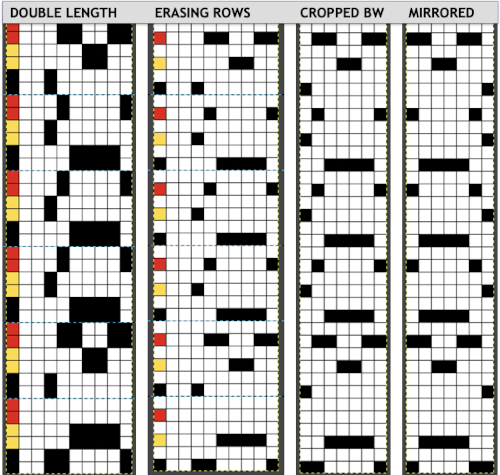
 The last file, doubled in length to 76 rows in height, requires no further processing
The last file, doubled in length to 76 rows in height, requires no further processing ![]() The separations are achieved now in just minutes.
The separations are achieved now in just minutes.
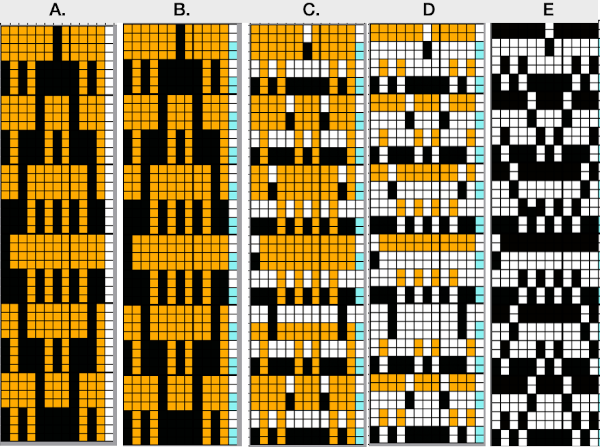
The proof of concept swatch: when using repeats that are so much wider, one must commit to far larger swatches to test them. In addition, the placement in the final piece may matter with shifting the pattern to highlight a preferred center, here the machine was allowed to place the design as a simple overall one on 78 stitches by 116 rows.  There are droves of inspiring large-scale mosaic crochet images published nowadays, which led me to wonder about DIY similar large graphic mosaics in machine knitting.
There are droves of inspiring large-scale mosaic crochet images published nowadays, which led me to wonder about DIY similar large graphic mosaics in machine knitting.
They can be built from scratch, or published designs may be used and converted for use in machine knitting.
A follow-up post on DIY Figurative designs in mosaic knitting
As a start, I performed the first color separation with shortcuts, mirroring the cleaned-up repeat, did not verify each step with tiling, and committed to knitting a test swatch.
A 68X136 repeat X2 in width and at least 40 more rows in height produced a 16X24-inch test swatch, on which a couple of missing pixels became noticeable.
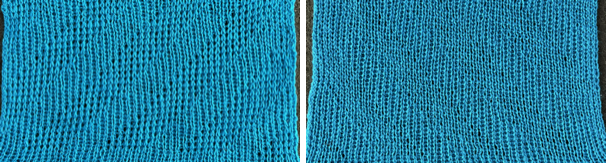
The swatch was also knit using slip in both directions on the main bed, which produces a narrow, short fabric in contrast to wide and short when using the tuck setting,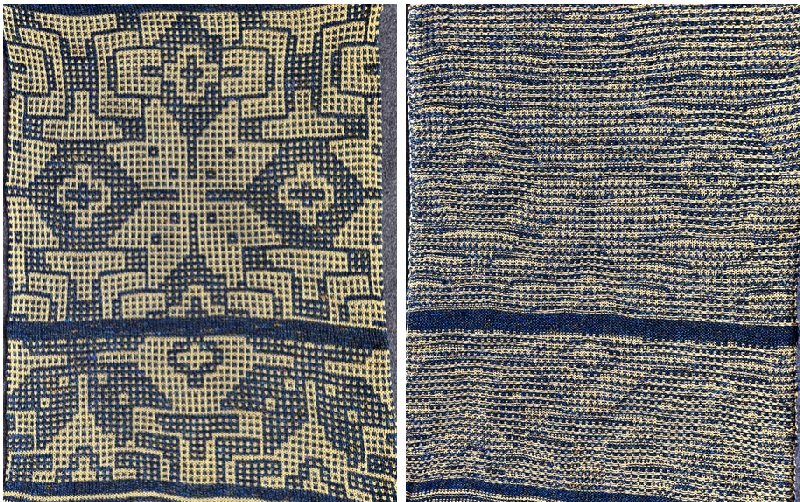 back to the drawing board.
back to the drawing board.
DIY: The initial approach is similar to that used in creating mock filet crochet shapes on the machine.
With present tools ie Gimp begin with choosing any symmetrical design where the shaping of the motif occurs in single rows, this one measures 23X23 ![]()
 scale the file X3 in both directions to 69X69
scale the file X3 in both directions to 69X69 
 save this brush to use later for bucket-fill the design.
save this brush to use later for bucket-fill the design.  Choose fuzzy select by color/black, each shape will be surrounded by a dotted line
Choose fuzzy select by color/black, each shape will be surrounded by a dotted line  bucket fill the selections with the saved pattern
bucket fill the selections with the saved pattern  click on rectangle select to fix the layer, work on and clean up the repeat, and check a magnified version for any missing or misplaced pixels.
click on rectangle select to fix the layer, work on and clean up the repeat, and check a magnified version for any missing or misplaced pixels.  Save the png. for reference before continuing to work.
Save the png. for reference before continuing to work.  Make one of 2 choices. If the goal is to place a motif and to add borders or horizontal additional design stripes, create a new canvas, larger than the above, fill it with the same pattern, and then Colors/Invert. Click on the rectangle tool to fix the layer.
Make one of 2 choices. If the goal is to place a motif and to add borders or horizontal additional design stripes, create a new canvas, larger than the above, fill it with the same pattern, and then Colors/Invert. Click on the rectangle tool to fix the layer.  Change the white color to alpha in the previously processed snowflake, click on the rectangle tool again
Change the white color to alpha in the previously processed snowflake, click on the rectangle tool again  copy and paste the file onto the color-reversed grid, and click on the rectangle tool. Check the pasted image visually, and continue adding any other designs.
copy and paste the file onto the color-reversed grid, and click on the rectangle tool. Check the pasted image visually, and continue adding any other designs.  If the goal is to produce an all-over design, crop the shape on the dotted ground, and save it as a 69X69 repeat. Pasting the original on an equal-sized color reversed dotted ground does not work.
If the goal is to produce an all-over design, crop the shape on the dotted ground, and save it as a 69X69 repeat. Pasting the original on an equal-sized color reversed dotted ground does not work.  Tiling the result of the cropped repeat will show the need for cropping it by one row at the top and one column to the right.
Tiling the result of the cropped repeat will show the need for cropping it by one row at the top and one column to the right.  The resulting repeat, 68X68
The resulting repeat, 68X68  tiled X3 in each direction for a visual check.
tiled X3 in each direction for a visual check.  Using the process previously described
Using the process previously described
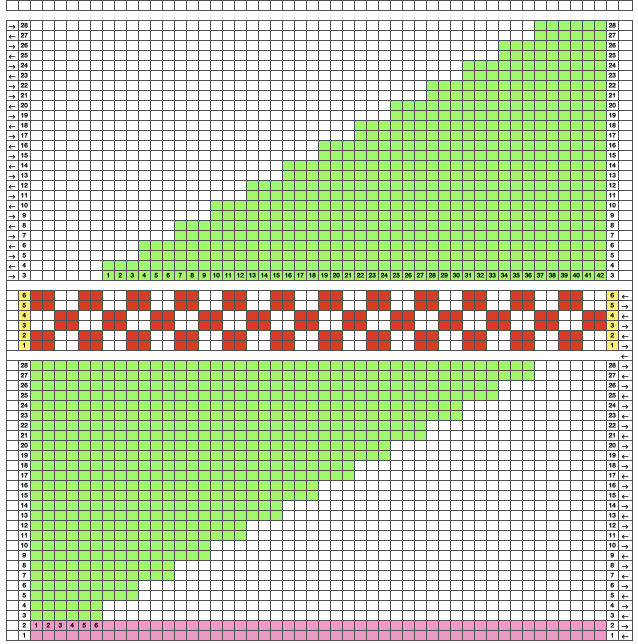
1. open the 68-stitch file in Gimp, and magnify it to at least 800X for a visible grid
2. open file/new, equal size and magnification
3. copy and paste 1 on 2, click on the rectangle select tool
Colors/invert, click again on the rectangle tool or anywhere in the work window  4: magnify further if needed. Using the pencil tool fill in every other row beginning with row 2 in a contrasting palette color, and click on the rectangle tool
4: magnify further if needed. Using the pencil tool fill in every other row beginning with row 2 in a contrasting palette color, and click on the rectangle tool  5. Layer, transparency, color to alpha, as described in the last post, click on rectangle tool
5. Layer, transparency, color to alpha, as described in the last post, click on rectangle tool  6. Copy and paste this result onto the 68-stitch file in the first window, there will be lots of dotted lines onscreen
6. Copy and paste this result onto the 68-stitch file in the first window, there will be lots of dotted lines onscreen  Click on the rectangle select tool to paste the image in place.
Click on the rectangle select tool to paste the image in place. 
 Since those large areas of white will be knitted in a tuck or slip fabric, the above result needs to be color inverted. If used as is, set the machine’s built-in double-length function.
Since those large areas of white will be knitted in a tuck or slip fabric, the above result needs to be color inverted. If used as is, set the machine’s built-in double-length function. 
 Doubling the length of the file before the download to km
Doubling the length of the file before the download to km  Added info on the technique may be found in the post on More separations for various knits using Gimp, color to alpha
Added info on the technique may be found in the post on More separations for various knits using Gimp, color to alpha
Another approach with sequential files provided to test in DIY experiments  begin with the 68X68 image
begin with the 68X68 image  color invert it
color invert it  open a new file, 2 rows high with an added color, and save it to the clipboard, white color to alpha
open a new file, 2 rows high with an added color, and save it to the clipboard, white color to alpha ![]() use the brush to fill the color inverted image,
use the brush to fill the color inverted image,  red color to alpha
red color to alpha  and paste the resulting image on the original
and paste the resulting image on the original double the file in length for knitting as mosaic, results matching the previous experiment
double the file in length for knitting as mosaic, results matching the previous experiment  Part of the view on the img2track screen for the 68X136 file is ready for download.
Part of the view on the img2track screen for the 68X136 file is ready for download.  Committing to proving the concept:
Committing to proving the concept:  Inspiration drawn from a published design, color-separating the repeat as seen in ArahPaint in knit design 6: color separations
Inspiration drawn from a published design, color-separating the repeat as seen in ArahPaint in knit design 6: color separations
 The full repeat is 100 stitches X 200 rows. The yarns are 2/8 wools, the maximum thickness for tuck stitch on a 4.5mm machine.
The full repeat is 100 stitches X 200 rows. The yarns are 2/8 wools, the maximum thickness for tuck stitch on a 4.5mm machine.
The swatch, knit on 61 stitches and for 109 rows, measures 10.25X16.5 inches. The dark loops on the side were due to yarn being caught on gate pegs, the few spots on the knit side that may appear as errors are light color stitches that did not knit off properly due to that fact.  Knitting the original design as DBJ using the built-in KRC function and the birdseye setting to produce a flat knit with “no floats” is possible.
Knitting the original design as DBJ using the built-in KRC function and the birdseye setting to produce a flat knit with “no floats” is possible.
An even number of needles must be used on the ribber.
The first preselection row is made from left to right, the knit carriage is set to slip in both directions before continuing to knit from the right. The ribber is also set to slip in both directions, using lili buttons.
The patterning errors in the swatch result from needles with bent latches, posing a strong argument for always testing a design at least once at a minimum of the full width before committing to a final piece. 
Large-scale mosaics can be planned by tripling the size of a previously tested pattern
1. the original 12X18 ![]() 2. is tripled in height and width X3 to 36X54.
2. is tripled in height and width X3 to 36X54.![]() To begin with, the process involves using multiple colors.
To begin with, the process involves using multiple colors.
Working in ArahPaint, save 2 brushes, each 2X2 pixels 3. 36X54 new image in a new window is filled with the bottom brush
3. 36X54 new image in a new window is filled with the bottom brush![]() 4. the black and white #2 is copied and pasted in place on #3 after rendering the black color transparent
4. the black and white #2 is copied and pasted in place on #3 after rendering the black color transparent ![]() 5. in a new window fill a new 36X54 image with the top bush
5. in a new window fill a new 36X54 image with the top bush ![]() 6. copy and paste #4 on #5 after rendering the white transparent
6. copy and paste #4 on #5 after rendering the white transparent ![]() check tiling
check tiling  7. convert the color repeat to BW indexed
7. convert the color repeat to BW indexed ![]()
 The patterns at this stage of the process may be knit double-bed as DBJ using the birdseye backing, as already shown, or as a “fantasy fair isle” with no further separation.
The patterns at this stage of the process may be knit double-bed as DBJ using the birdseye backing, as already shown, or as a “fantasy fair isle” with no further separation.
Download the repeat on an electronic machine, program it for the number of needles in use on the top bed, and select the KRC separation button.
The first preselection row is made from left to right.
After the carriages have reached the right, the main bed is set to tuck in both directions, the ribber to N in both directions.
Because the fabric is being knit using every needle on both beds, each main bed tuck loop will have a knit stitch on the opposite bed anchoring it down. Those rows will appear more compressed, producing narrower horizontal lines.
The knit is reversible, wide, and drapes well.
I recommend starting double bed fabrics with waste yarn and ravel cord, testing color changes, and checking that stitches are formed properly.
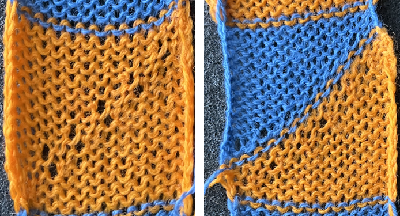
I missed several dropped stitches at the start of this piece, in areas marked with cyan arrows.
Because ribber fabrics sit hiding between the beds, dropped stitches or patterning errors may not be seen until several inches of fabric have been knit.
The test swatch, knit on 72 stitches, and testing partial repeat height, measures 17.5 inches in width.  Performing the color separation for knitting the design in the traditional single-bed method
Performing the color separation for knitting the design in the traditional single-bed method
the starting file ![]() color-inverted
color-inverted ![]() new file, stripe brush-filled
new file, stripe brush-filled 
![]() copy and paste it on the color reversed image after rendering the purple transparent
copy and paste it on the color reversed image after rendering the purple transparent ![]() copy and paste the result on the original file after rendering cyan transparent,
copy and paste the result on the original file after rendering cyan transparent, ![]() double the result in length, 36X108
double the result in length, 36X108![]()
 color invert, the 36X108 file, check that it is in indexed BW mode before saving.
color invert, the 36X108 file, check that it is in indexed BW mode before saving.
![]() The proof-of-concept swatch uses the tuck setting. It was knit using 2/8 wool on 72 stitches X 120 rows and measures 10.5X11.75 inches.
The proof-of-concept swatch uses the tuck setting. It was knit using 2/8 wool on 72 stitches X 120 rows and measures 10.5X11.75 inches.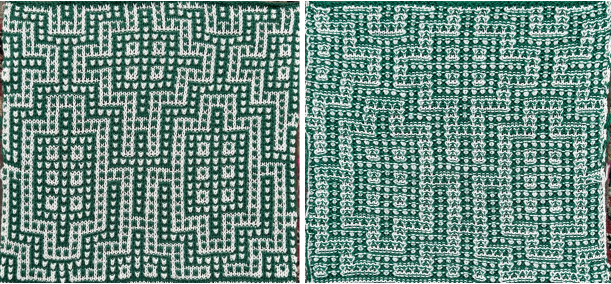
A file creating different shapes to play with, 32X86![]() tiled as is
tiled as is  color reversed
color reversed  For color separation see ArahPaint in knit design 6
For color separation see ArahPaint in knit design 6
The final repeat, 32X172 rows ![]() The test swatch was knit on 60 stitches and for 182 rows, measured 9X11.25 inches
The test swatch was knit on 60 stitches and for 182 rows, measured 9X11.25 inches  A larger BW design was processed using no modification of the original 75X71 motif. When using Gimp/File/Save, the result is a .xcf document similar to PSD files in Photoshop. It will store layers, transparency settings, and more information associated with and parts of the same project.
A larger BW design was processed using no modification of the original 75X71 motif. When using Gimp/File/Save, the result is a .xcf document similar to PSD files in Photoshop. It will store layers, transparency settings, and more information associated with and parts of the same project. 
 Note to self: before deleting the .xcf, ensure the final PNG has been saved.
Note to self: before deleting the .xcf, ensure the final PNG has been saved.
If determined to use the particular flower, the starting file 96X90 is copied and pasted on a new brush-filled ground with the black rendered transparent, adjusting placement, cleaning up edges
is copied and pasted on a new brush-filled ground with the black rendered transparent, adjusting placement, cleaning up edges  a new color is used to outline the outer shape of the flower and the petals for better definition
a new color is used to outline the outer shape of the flower and the petals for better definition  it is copied and pasted on a new brush-filled ground after the white is rendered transparent
it is copied and pasted on a new brush-filled ground after the white is rendered transparent  the colors converted to BW, playing with placement in any final piece
the colors converted to BW, playing with placement in any final piece

If one is familiar with image processing and fond of the maze appearance in designs, there is a font to try: Mazeletter
The downloadable associated documentation and source for inspiration: http://mazeletter.xyz/Mazeletter.pdf.
A sample text:  in a 129X32 BW version with no pixel clean-up
in a 129X32 BW version with no pixel clean-up ![]() Mosaic4way, is potentially usable for single bed fair isle or dbj.
Mosaic4way, is potentially usable for single bed fair isle or dbj.  The BW file, 199X32
The BW file, 199X32
![]() When scaling designs containing more than 2 colors, there is a variable loss of detail or added random pixels. ArahPaint’s guess weave from the grid tool is the best I have found for scaling such samples to knittable sizes.
When scaling designs containing more than 2 colors, there is a variable loss of detail or added random pixels. ArahPaint’s guess weave from the grid tool is the best I have found for scaling such samples to knittable sizes.















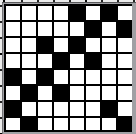

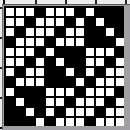
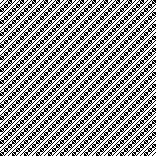
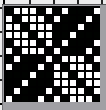



























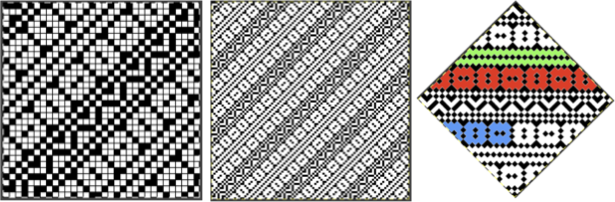


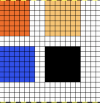
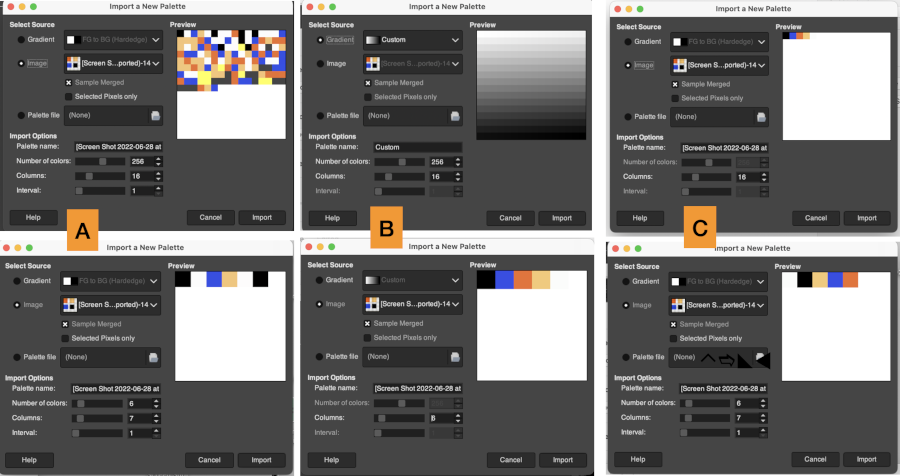







 Designing for fair isle, or when attempting to visualize and illustrate slip and tuck fabrics with frequent color changes, more colors may be required even though the final download will be in black and white. There is a quick way to add random colors assigned by the program and based on the initial palette:
Designing for fair isle, or when attempting to visualize and illustrate slip and tuck fabrics with frequent color changes, more colors may be required even though the final download will be in black and white. There is a quick way to add random colors assigned by the program and based on the initial palette: 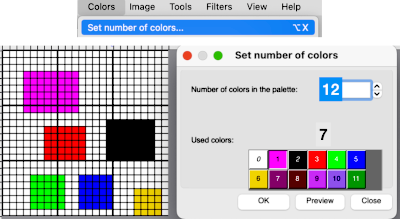
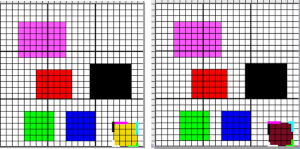
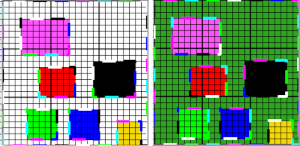









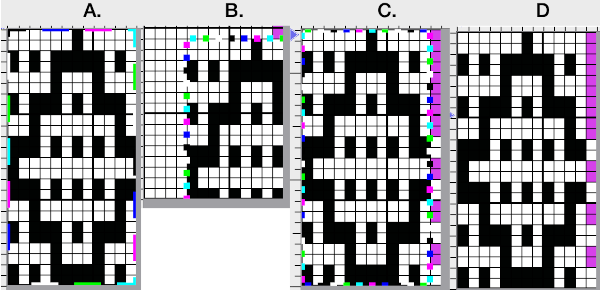











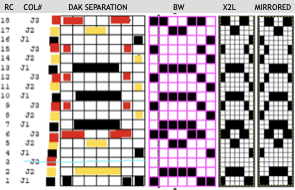



 Here it is shown modified, with rows containing fewer than 3 colors marked.
Here it is shown modified, with rows containing fewer than 3 colors marked. 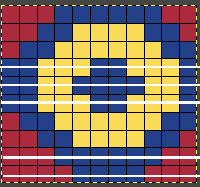



 The repeats for designs may be self-separated to suit.
The repeats for designs may be self-separated to suit.
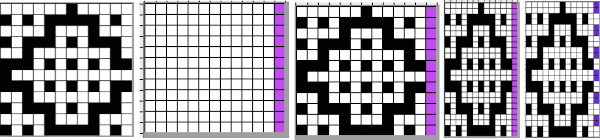
 Three variations of the final png files are shared
Three variations of the final png files are shared  This is the appearance when a different design was entered in img2track. The separated file 3 color file in BW is not shared.
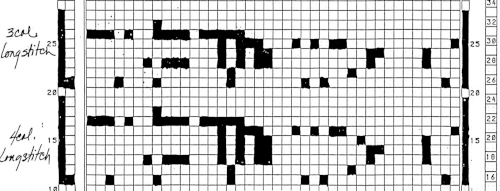
This is the appearance when a different design was entered in img2track. The separated file 3 color file in BW is not shared. 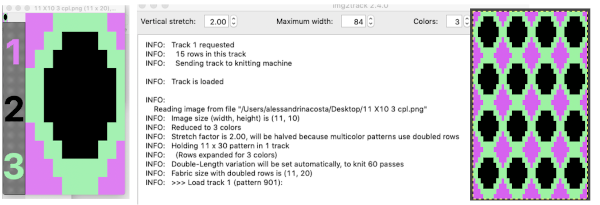 The method for knitting the pattern: the long stitches are formed by loops that are created on the top bed and dropped on the following row.
The method for knitting the pattern: the long stitches are formed by loops that are created on the top bed and dropped on the following row.



 The second carriage, C2 is set to KCII as well. It will be advancing the design with each pass as well and will drop loops on the first pass, preselect for the subsequent pattern row on the next
The second carriage, C2 is set to KCII as well. It will be advancing the design with each pass as well and will drop loops on the first pass, preselect for the subsequent pattern row on the next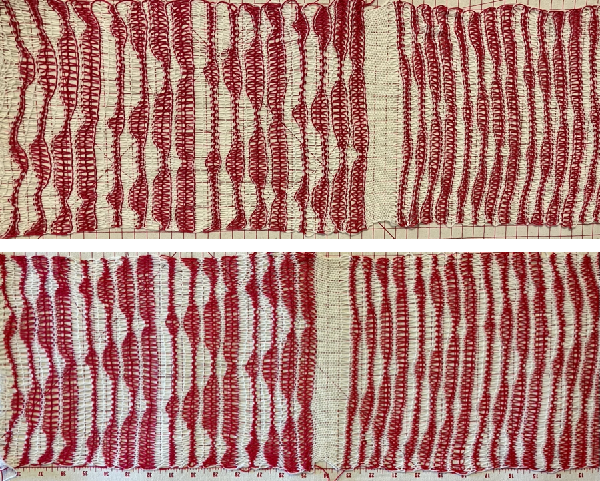
 The elongated stitches allow objects behind them to peek through
The elongated stitches allow objects behind them to peek through 
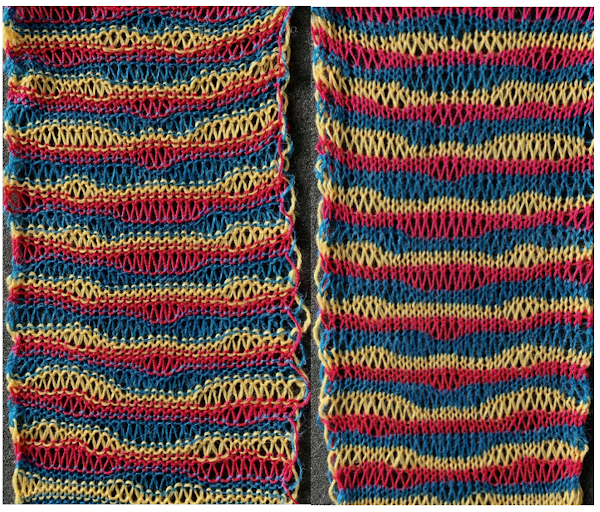
 Here the goal is to use the img2 track separation, maintaining the same color change rotation in each piece.
Here the goal is to use the img2 track separation, maintaining the same color change rotation in each piece.
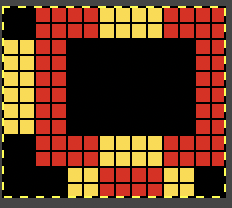
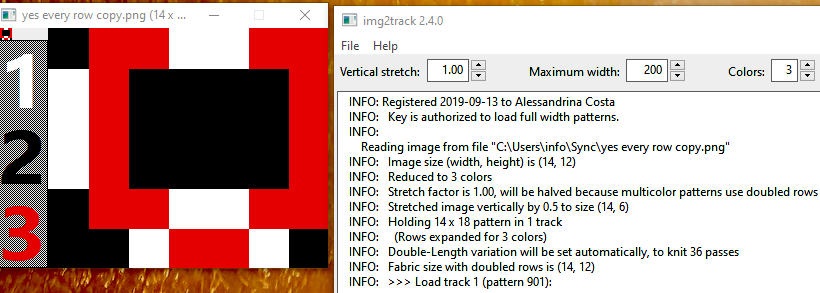 The tiled potential appearance as a dbj fabric:
The tiled potential appearance as a dbj fabric: In the first sample three carriages are used:
In the first sample three carriages are used: What of end release? because all 3 colors are present in every row, the design is suitable. The first preselection row is from right to left.
What of end release? because all 3 colors are present in every row, the design is suitable. The first preselection row is from right to left.


 Any published or self-drawn separation for 3 colors per row patterning including every color in every row of the original design may be used, programmed as a single bed design, and knit for end release.
Any published or self-drawn separation for 3 colors per row patterning including every color in every row of the original design may be used, programmed as a single bed design, and knit for end release.
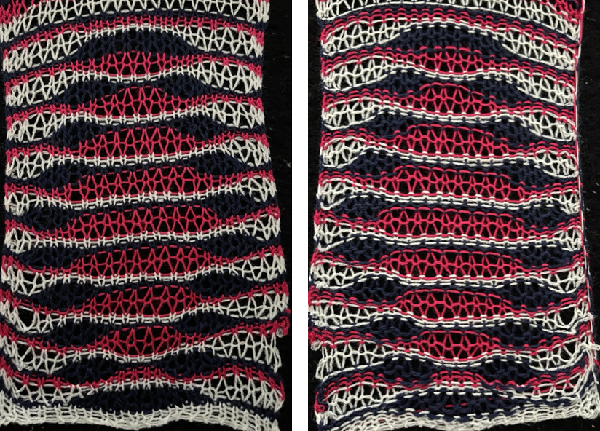

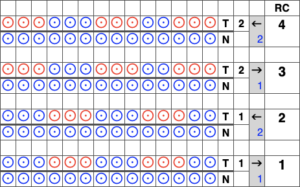



 In Fantasy Fairisle knitting using 187 with alternating up and down pushers on the back bed and AX with 2 arrow keys would match Brother ribber knitting with lili buttons used on an even number of needles set to tuck.
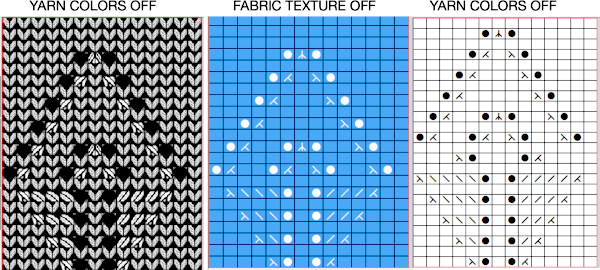
In Fantasy Fairisle knitting using 187 with alternating up and down pushers on the back bed and AX with 2 arrow keys would match Brother ribber knitting with lili buttons used on an even number of needles set to tuck. For the 1-pixel grid in Gimp to be visible on an editable image, a magnification of at least 800 is required. The options offered by default
For the 1-pixel grid in Gimp to be visible on an editable image, a magnification of at least 800 is required. The options offered by default can be changed to suit by simply typing in a new number.
can be changed to suit by simply typing in a new number.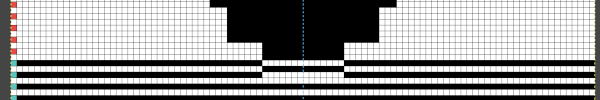
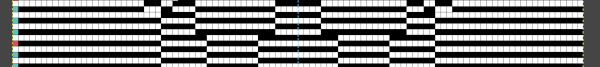 the processed image
the processed image 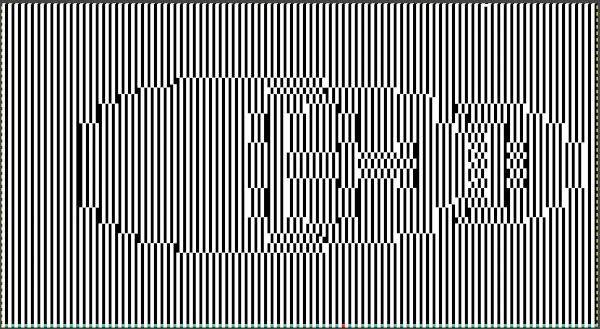 the trimmed 98X182 png
the trimmed 98X182 png  doubled in length once more to 98X364
doubled in length once more to 98X364 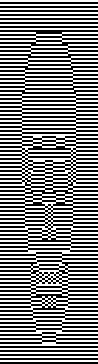 Knitting process on a 930 using img2track:
Knitting process on a 930 using img2track: A reminder: in my experience, the Brother cast-on combs are usually chrome-colored, Studio grey, and Passap, and I believe Superba ones were traditionally green. The first 2 were designed for 4.5 mm machines, the latter for 5mm. The different mm spacing does not make the 5 mm combs suitable for casting on on Brother, but they can be poked through the knit in progress. I like to leave the first comb and weights on, insert the new comb closer to the beds, and then move the weight up, and then remove the lower position comb.
A reminder: in my experience, the Brother cast-on combs are usually chrome-colored, Studio grey, and Passap, and I believe Superba ones were traditionally green. The first 2 were designed for 4.5 mm machines, the latter for 5mm. The different mm spacing does not make the 5 mm combs suitable for casting on on Brother, but they can be poked through the knit in progress. I like to leave the first comb and weights on, insert the new comb closer to the beds, and then move the weight up, and then remove the lower position comb.
 In the Brother model, sometimes the yarn is left in the wrong place below eye level rather than its own individual one corresponding to its button, and both yarns are picked up with the next color change.
In the Brother model, sometimes the yarn is left in the wrong place below eye level rather than its own individual one corresponding to its button, and both yarns are picked up with the next color change. 
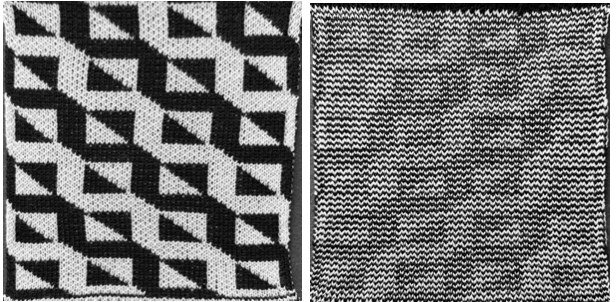
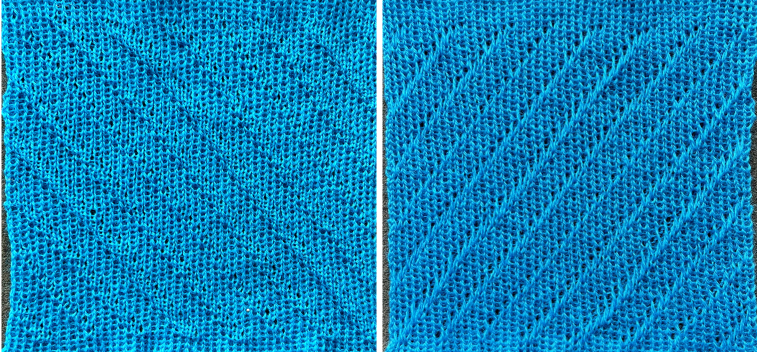
 a close-up of the texture at an angle
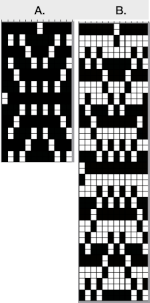
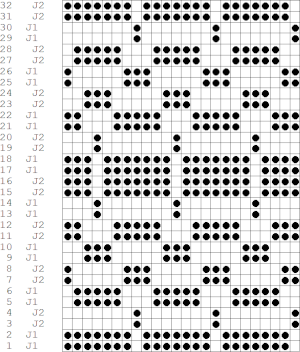
a close-up of the texture at an angle  Claudia Scarpa developed a skull variation using only layers in Gimp
Claudia Scarpa developed a skull variation using only layers in Gimp  and has been kind enough to create a
and has been kind enough to create a 
 It is possible to work some repeats on some machines with the ribber also set to tuck both ways with EON needle selection.
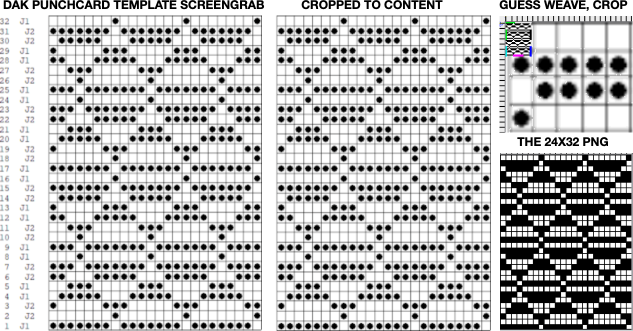
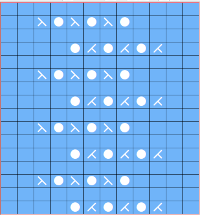
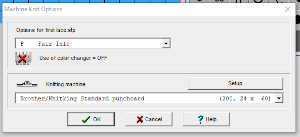
It is possible to work some repeats on some machines with the ribber also set to tuck both ways with EON needle selection. When using the Dak stitch design module, the color separation is automated. Choose any design repeat. This happens to be a 20X20 one, chosen from the thumbnail assortment, so not suitable for punchcard models. “Printing” the template using choosing the option of using dots rather than squares to represent knit stitches makes the resulting print screengrab easier to trace.
When using the Dak stitch design module, the color separation is automated. Choose any design repeat. This happens to be a 20X20 one, chosen from the thumbnail assortment, so not suitable for punchcard models. “Printing” the template using choosing the option of using dots rather than squares to represent knit stitches makes the resulting print screengrab easier to trace.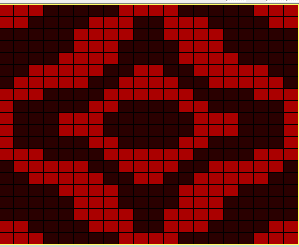 the 20X20 repeat as a BW png
the 20X20 repeat as a BW png  The result is screengrabbed, opened in Gimp, converted to BW mode, and scaled to the 20X40 expanded design size. Unless the double-length function in the machine is also used, it will need scaling again to double length prior to download.
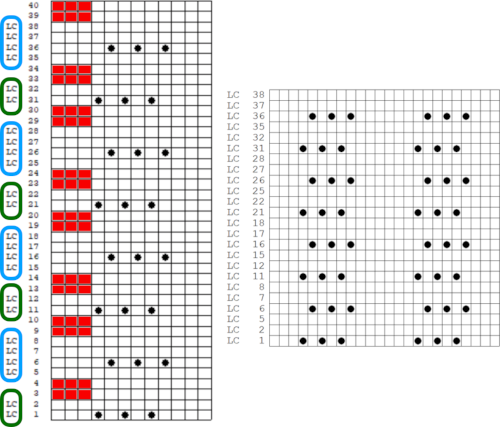
The result is screengrabbed, opened in Gimp, converted to BW mode, and scaled to the 20X40 expanded design size. Unless the double-length function in the machine is also used, it will need scaling again to double length prior to download. The final image double length, showing the difference between the separation using the template, and that using layers as in Claudia’s video, which appears different but is actually the same repeat, color reversed.
The final image double length, showing the difference between the separation using the template, and that using layers as in Claudia’s video, which appears different but is actually the same repeat, color reversed. 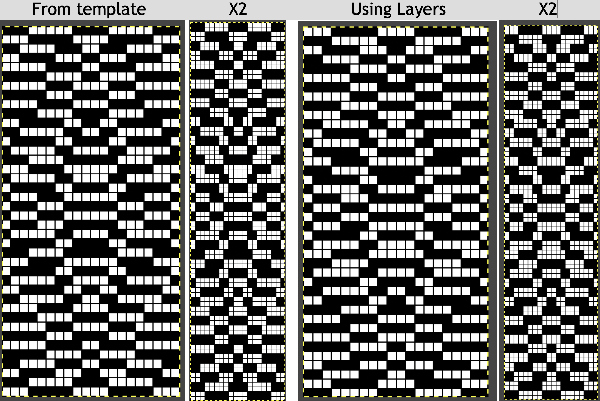 Using bucket fill for the ground in the second layer, as described in the video, the captured clipboard image can be very small
Using bucket fill for the ground in the second layer, as described in the video, the captured clipboard image can be very small 
 Alternately, the initial design may be scaled X4 to 20 X 80 pixels
Alternately, the initial design may be scaled X4 to 20 X 80 pixels 
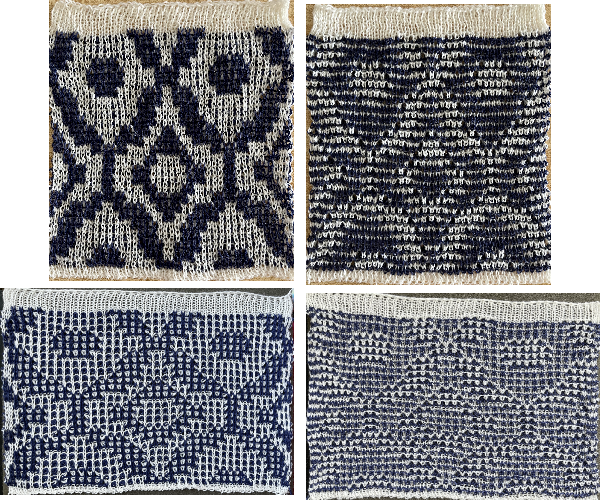


 bring the ribber needles up into work between them
bring the ribber needles up into work between them 
 drop the ribber
drop the ribber 




 As for more than 2 colors per row, performing the color separations may be achieved
As for more than 2 colors per row, performing the color separations may be achieved 
 stitch and row counts should match, and save the stp
stitch and row counts should match, and save the stp 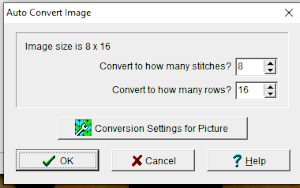
 The separation methods in DAK:
The separation methods in DAK:
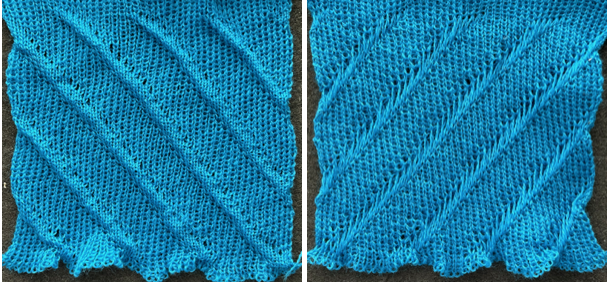
 Yarn choice and design make a big difference. Here the yarn is far too thin, and the repeat too narrow in width, but the possible result is illustrated. The main bed is set to slip in both directions throughout. The ribber setting needs to slip in both directions for every other pair of rows. When the ribber slips, the main bed will knit the color that will create the pockets, where there are many single stitches selected here, the KC was set to KC1. When the color is changed and the ribber is set to knit again, stitches in that color will knit on both beds, sealing the fabric in those areas and forming a solid color background on the reverse side. Here the white forms the pockets, and the floats after a pair of passes are seen in this photo.
Yarn choice and design make a big difference. Here the yarn is far too thin, and the repeat too narrow in width, but the possible result is illustrated. The main bed is set to slip in both directions throughout. The ribber setting needs to slip in both directions for every other pair of rows. When the ribber slips, the main bed will knit the color that will create the pockets, where there are many single stitches selected here, the KC was set to KC1. When the color is changed and the ribber is set to knit again, stitches in that color will knit on both beds, sealing the fabric in those areas and forming a solid color background on the reverse side. Here the white forms the pockets, and the floats after a pair of passes are seen in this photo.  Because the yarn is so thin there is a considerable grin through on both sides, the areas marked with arrows indicate where the white pockets were lightly stuffed with yarn ends
Because the yarn is so thin there is a considerable grin through on both sides, the areas marked with arrows indicate where the white pockets were lightly stuffed with yarn ends 
 If pngs are created outside the program, they may be doubled in length unless the repeat is designed that way.
If pngs are created outside the program, they may be doubled in length unless the repeat is designed that way. 
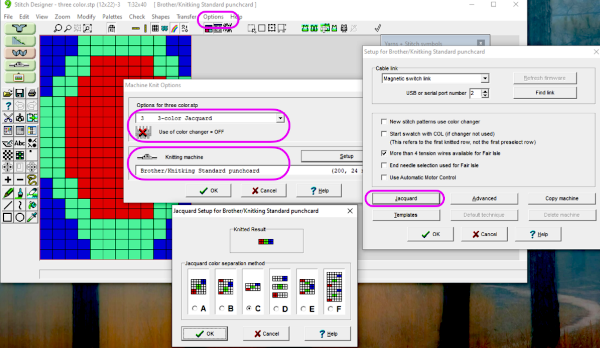 How the different jacquard setups process the specific repeats:
How the different jacquard setups process the specific repeats: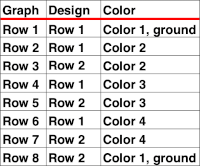
 Passap card reader techniques saved from long ago experiments.
Passap card reader techniques saved from long ago experiments. 
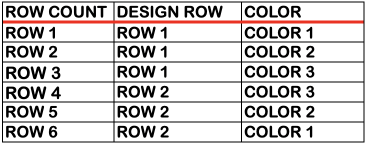
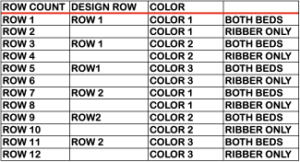
 Processing the template using numbers: a table is created twice the length of the 8X16 triangle repeat, followed by hiding the 32 odd-numbered rows, positioned in front of the scaled punchcard template, stitch markings are traced
Processing the template using numbers: a table is created twice the length of the 8X16 triangle repeat, followed by hiding the 32 odd-numbered rows, positioned in front of the scaled punchcard template, stitch markings are traced 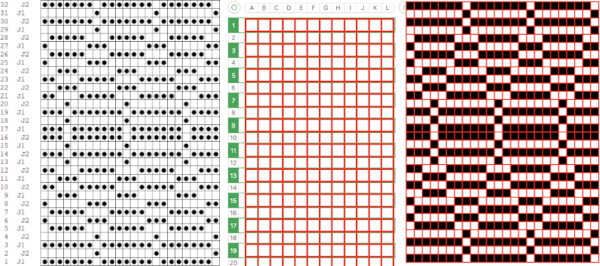 the rows are then unhidden, the repeat is checked, matched here to the F jacquard separation in Dak
the rows are then unhidden, the repeat is checked, matched here to the F jacquard separation in Dak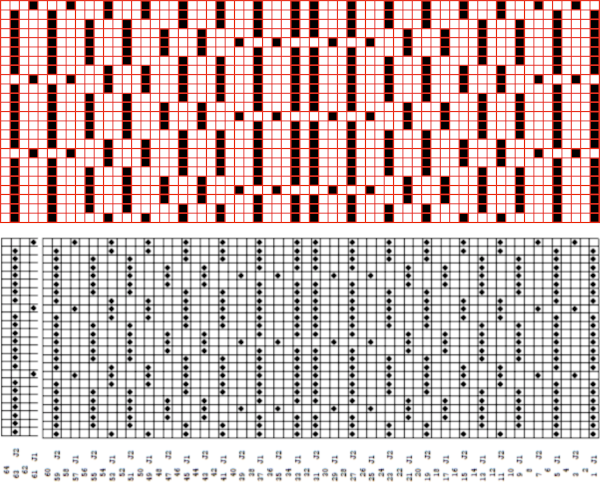 The numbers table is processed in Gimp to obtain the png for knitting the now 24X64 pattern
The numbers table is processed in Gimp to obtain the png for knitting the now 24X64 pattern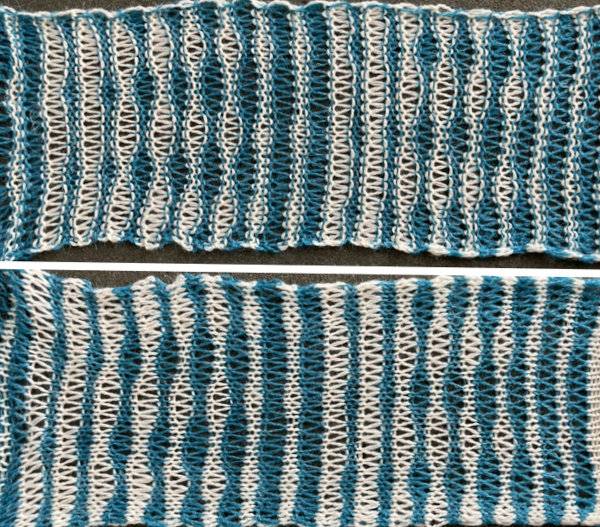  and the pattern executed as a tubular FI knit: I had yarn issues, hence the dropped stitches. Both swatches were knit to approximately the same point in the pattern repeats, there are obvious quality differences in width and length. In tubular knits, there are differences in the width and height of the knit on each side. The front is a slip stitch with floats, drawing the fabric in, while the ribber knits every stitch every other row. With a good choice of yarn and pattern, loosening the tension on the top bed may ease this problem. As often happens, casting on and binding off need special considerations ie to allow for any fabric stretch when off the machine or to leave a tubular knit open at either or both ends if that is the goal.
and the pattern executed as a tubular FI knit: I had yarn issues, hence the dropped stitches. Both swatches were knit to approximately the same point in the pattern repeats, there are obvious quality differences in width and length. In tubular knits, there are differences in the width and height of the knit on each side. The front is a slip stitch with floats, drawing the fabric in, while the ribber knits every stitch every other row. With a good choice of yarn and pattern, loosening the tension on the top bed may ease this problem. As often happens, casting on and binding off need special considerations ie to allow for any fabric stretch when off the machine or to leave a tubular knit open at either or both ends if that is the goal.  DAK has been a purchase made out of curiosity, and my use of it has been very limited since my designing needs are met by using other programs that are free to users and generate and accept files in multiple formats, while the Brother Knitleader or even simple use of the magic formula solves knitting any desired shape in any gauge.
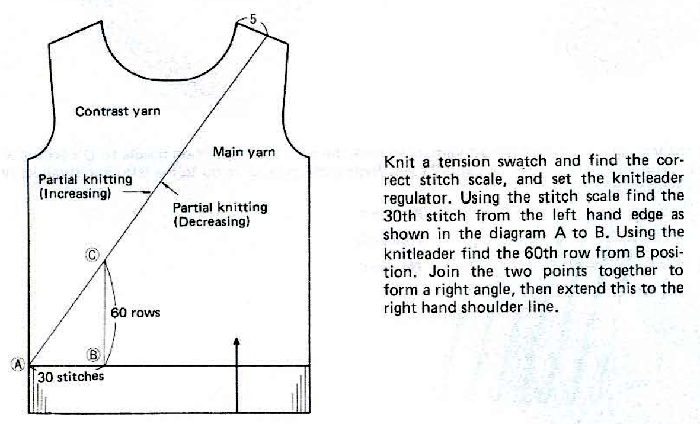
DAK has been a purchase made out of curiosity, and my use of it has been very limited since my designing needs are met by using other programs that are free to users and generate and accept files in multiple formats, while the Brother Knitleader or even simple use of the magic formula solves knitting any desired shape in any gauge.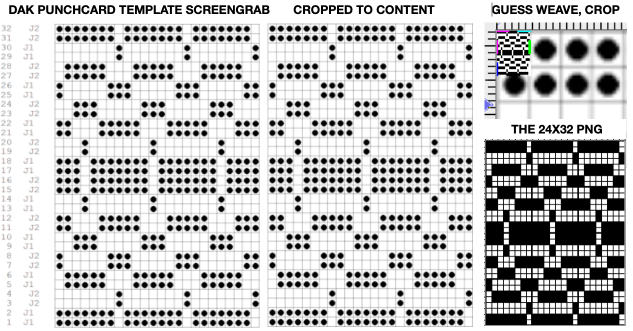
 When automating the repeat edits are possible and very easy using the lace module, these first drafts were created in Numbers,
When automating the repeat edits are possible and very easy using the lace module, these first drafts were created in Numbers, 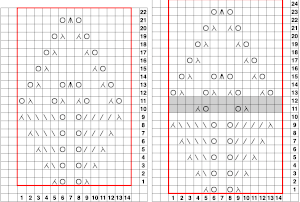 I have to admit the first time I tried to knit both the associated png, mirrored and not, I experienced patterning errors. Whether due to operator fatigue, static, or any other possible cause, on a different day both designs knit successfully, and my appreciation of the module is growing steadily. The results for this, a complex shape, are quick and awesome when compared to the amount of time it would take to draft the pattern outside the program.
I have to admit the first time I tried to knit both the associated png, mirrored and not, I experienced patterning errors. Whether due to operator fatigue, static, or any other possible cause, on a different day both designs knit successfully, and my appreciation of the module is growing steadily. The results for this, a complex shape, are quick and awesome when compared to the amount of time it would take to draft the pattern outside the program.
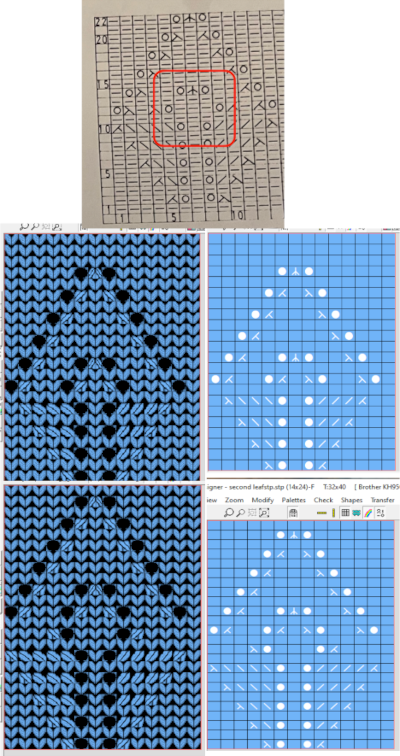
 An stp was created, the template is marked 74 rows in height, filled in as the stp was generated, right side facing
An stp was created, the template is marked 74 rows in height, filled in as the stp was generated, right side facing  Numbers and Gimp reduced the template to a png 14 stitches wide by 52 rows long, needed to be mirrored using the number one button on the 930 for successful knitting,
Numbers and Gimp reduced the template to a png 14 stitches wide by 52 rows long, needed to be mirrored using the number one button on the 930 for successful knitting, 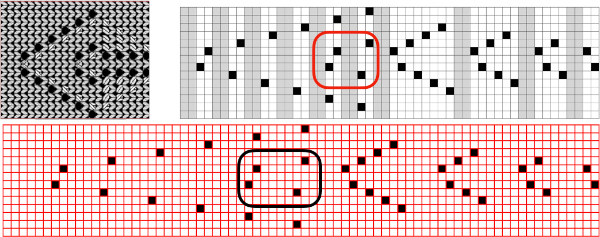
 matches the original illustration. Dak makes slight modifications very easy. The untested brick repeat, 28X104, developed using Arah followed by its png
matches the original illustration. Dak makes slight modifications very easy. The untested brick repeat, 28X104, developed using Arah followed by its png 
 The amended design drawn in repeat in dak visualizing the knit,
The amended design drawn in repeat in dak visualizing the knit,  The print preview template:
The print preview template: 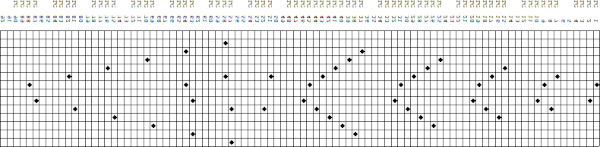
 the resulting png, 14 stitches by 68 rows, also knit using the number one button on the 930
the resulting png, 14 stitches by 68 rows, also knit using the number one button on the 930  The brick repeat developed in Arah, now 28 stitches by 136 rows,
The brick repeat developed in Arah, now 28 stitches by 136 rows, 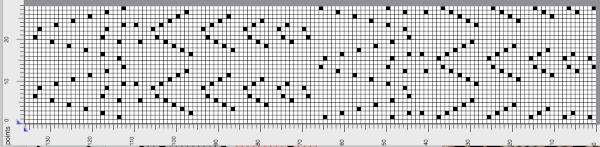 its png
its png  A test for the second brick repeat, here visualizing results with a screengrab of the stp.
A test for the second brick repeat, here visualizing results with a screengrab of the stp. 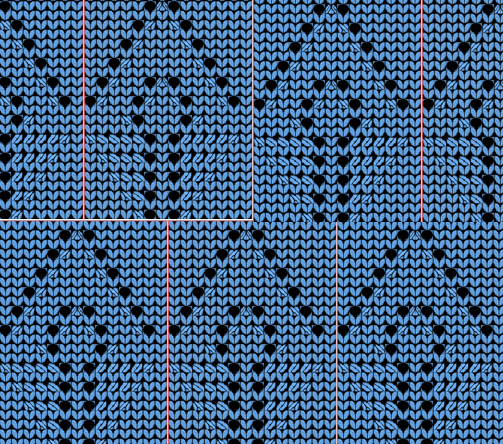 The test swatch is for a single repeat width, the initial yarn used ran out, hence the color change, the second yarn was thinner and broke, but there is enough to get a sense as to how the overall alignment of the knit shapes will appear, including that horizontal chevron between the shifting leaves. The png required mirroring when used on the 930.
The test swatch is for a single repeat width, the initial yarn used ran out, hence the color change, the second yarn was thinner and broke, but there is enough to get a sense as to how the overall alignment of the knit shapes will appear, including that horizontal chevron between the shifting leaves. The png required mirroring when used on the 930. 
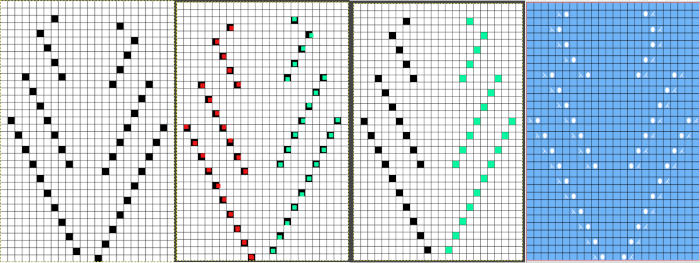

 it would need to be drawn eliminating the pairs of blank rows between transfers to match the original repeat because all those carriage passes are consecutive. Drafts with no blank rows between alternating transfers are not accepted by the program and ruled out in any template preview as well.
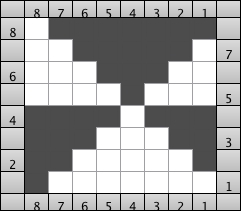
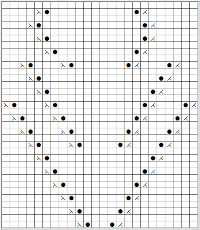
it would need to be drawn eliminating the pairs of blank rows between transfers to match the original repeat because all those carriage passes are consecutive. Drafts with no blank rows between alternating transfers are not accepted by the program and ruled out in any template preview as well. 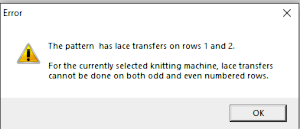 The complexity of working with a “simple” repeat: over the years I accumulated a notebook full of copies from Japanese magazine pages with what I believed to offer interesting potential, this repeat happened to be one. The markings for the knit rows on the right, and the two blank rows at the bottom identify it as suitable for Studio punchcard machines, and it would appear to be easy to translate for knitting on Brother thanks to those 2 blank rows between transfer cell markings.
The complexity of working with a “simple” repeat: over the years I accumulated a notebook full of copies from Japanese magazine pages with what I believed to offer interesting potential, this repeat happened to be one. The markings for the knit rows on the right, and the two blank rows at the bottom identify it as suitable for Studio punchcard machines, and it would appear to be easy to translate for knitting on Brother thanks to those 2 blank rows between transfer cell markings. 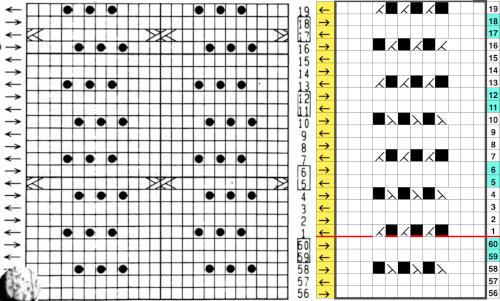 Developing the Brother repeat in Numbers for beginning with transfers to the left. The repeat is recognizable as a mesh variant, more information for mesh design repeats may be found in the
Developing the Brother repeat in Numbers for beginning with transfers to the left. The repeat is recognizable as a mesh variant, more information for mesh design repeats may be found in the  the repeat on the right was created in Gimp.
the repeat on the right was created in Gimp. 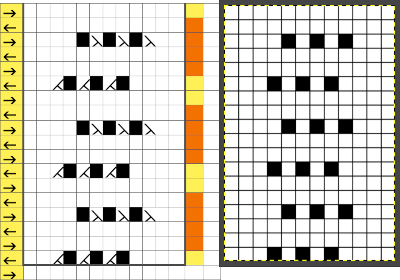 The 12X18 png
The 12X18 png  Creating the stp: the size of the png was used to create the image file, which required cropping, in Dak this would be the menu language after activating the proper tools. the stp size is 12X16,
Creating the stp: the size of the png was used to create the image file, which required cropping, in Dak this would be the menu language after activating the proper tools. the stp size is 12X16, 
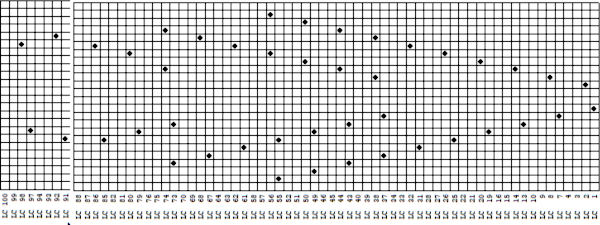
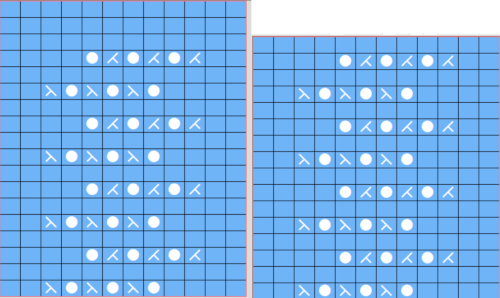 The template generated for a Brother punchcard machine illustrates the problems and some of the confusion if the template repeat is used for actual knitting, especially on the punchcard machines. Drawing the eyelet and dragging the mouse one cell to the left is the intuitive way to draw for transfers to the left. The symbols appear to be right-side facing by default and if they are in turn mirrored by the program prior to saving, when the templates are generated, the intent for use of the design would match. The numbers on the left are in the punchcard template, adjusted by cropping the two extra rows in the Brother electronic template by the software, do not reflect the actual design row numbers. The starting row is wrong for the Brother lace carriage operation from the left to produce the first row transfers to the left in actual knitting. As far as determining sequences for knit row placement, that is left up to the punchcard knitter’s experimentation. The minimum repeat for a punchcard to roll continuously is 36 rows, that fact needs to be considered if punching cards. The repeat shift for the first transfers to happen toward the left is illustrated on the right.
The template generated for a Brother punchcard machine illustrates the problems and some of the confusion if the template repeat is used for actual knitting, especially on the punchcard machines. Drawing the eyelet and dragging the mouse one cell to the left is the intuitive way to draw for transfers to the left. The symbols appear to be right-side facing by default and if they are in turn mirrored by the program prior to saving, when the templates are generated, the intent for use of the design would match. The numbers on the left are in the punchcard template, adjusted by cropping the two extra rows in the Brother electronic template by the software, do not reflect the actual design row numbers. The starting row is wrong for the Brother lace carriage operation from the left to produce the first row transfers to the left in actual knitting. As far as determining sequences for knit row placement, that is left up to the punchcard knitter’s experimentation. The minimum repeat for a punchcard to roll continuously is 36 rows, that fact needs to be considered if punching cards. The repeat shift for the first transfers to happen toward the left is illustrated on the right.  As initially given, with the lace carriage starting on the left, the first transfer row would be to the right. In many cases, this may not matter, but in this instance, where the knit rows happen after 2 or 4 LC passes respectively, the template offers another instance of the fact that the knitter using it needs to have previous understanding and experience in creating the particular stitch type. This version does not have an accompanying swatch.
As initially given, with the lace carriage starting on the left, the first transfer row would be to the right. In many cases, this may not matter, but in this instance, where the knit rows happen after 2 or 4 LC passes respectively, the template offers another instance of the fact that the knitter using it needs to have previous understanding and experience in creating the particular stitch type. This version does not have an accompanying swatch.  Analyzing the electronic template for interactive knitting: it is correct in marking rows for LC operation from the left with the first transfer row made to the right, matching the above chart.
Analyzing the electronic template for interactive knitting: it is correct in marking rows for LC operation from the left with the first transfer row made to the right, matching the above chart. 
 For good measure, the repeat is also drawn as stitches and produced the punchcard template with a first blank row identical to that generated when using symbols
For good measure, the repeat is also drawn as stitches and produced the punchcard template with a first blank row identical to that generated when using symbols 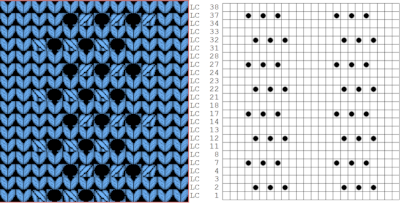 Using the pencil tool to draw the transfers differently resulted in a series of error alerts, so not an option.
Using the pencil tool to draw the transfers differently resulted in a series of error alerts, so not an option.


 When manuals are chosen in any module, there is an option offered to download the associated pdf
When manuals are chosen in any module, there is an option offered to download the associated pdf  by clicking on the arrow key
by clicking on the arrow key  Update:
Update:  The lace module is an extremely attractive solution for speeding up the lace design process whether from published charts or DIY. The left mouse button is used to draw as usual, but the right mouse button is used when drawing shared transfers in fine lace on Brother, or simple lace in Studio km.
The lace module is an extremely attractive solution for speeding up the lace design process whether from published charts or DIY. The left mouse button is used to draw as usual, but the right mouse button is used when drawing shared transfers in fine lace on Brother, or simple lace in Studio km.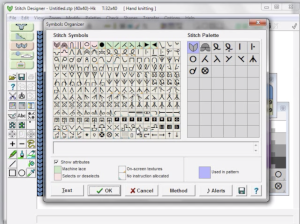
 The designer may enter patterns on this view as well, but I prefer to work with symbols
The designer may enter patterns on this view as well, but I prefer to work with symbols It is best to begin testing with a small repeat when exploring new techniques, find his format easier to use than drawing on “stitches”. There are several options for the canvas ground color, the default is in blue. As a first step, saved as an stp, Dak opened my saved file as pictured in this view.
It is best to begin testing with a small repeat when exploring new techniques, find his format easier to use than drawing on “stitches”. There are several options for the canvas ground color, the default is in blue. As a first step, saved as an stp, Dak opened my saved file as pictured in this view. 
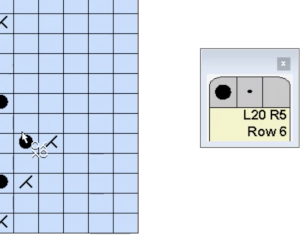
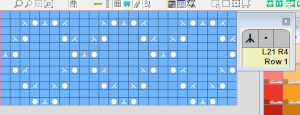 DAK row numbers do not refer to design rows, they reference row counts as would be seen in any row counter registering carriage passes
DAK row numbers do not refer to design rows, they reference row counts as would be seen in any row counter registering carriage passes
 If a symbol is missing from the drawing, the program alerts the knitter to the error. Here there are no eyelets represented.
If a symbol is missing from the drawing, the program alerts the knitter to the error. Here there are no eyelets represented. 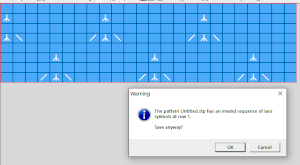 There was no warning for the error in the last row of the test stp, where in the last row two stitches were being moved in opposite directions on the same row. If the content is considered accurate, this window will appear, the safe button will be highlighted, click OK
There was no warning for the error in the last row of the test stp, where in the last row two stitches were being moved in opposite directions on the same row. If the content is considered accurate, this window will appear, the safe button will be highlighted, click OK 
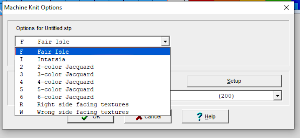
 wrong side facing is chosen for the purl side view.
wrong side facing is chosen for the purl side view.  Stitch pattern print previews, using default settings for layout:
Stitch pattern print previews, using default settings for layout: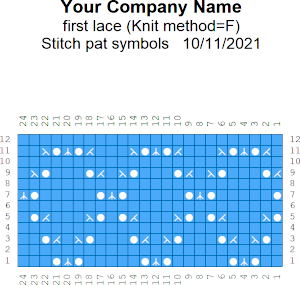
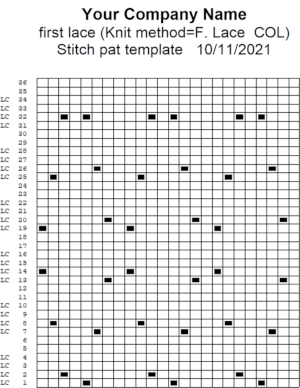

 This stp pattern was also created using the pencil tool in combination with symbols. In the print preview, there were 2 errors in the Dak printouts, the three blank rows rather than 2 in the outlined section between transfers, and transfers in 2 different directions occurring on the same row with the same carriage pass. I have no way to test whether the same issue would occur in interactive knitting using my own stp file. My repeat, drawn in Numbers on the right, is numbered in design rows.
This stp pattern was also created using the pencil tool in combination with symbols. In the print preview, there were 2 errors in the Dak printouts, the three blank rows rather than 2 in the outlined section between transfers, and transfers in 2 different directions occurring on the same row with the same carriage pass. I have no way to test whether the same issue would occur in interactive knitting using my own stp file. My repeat, drawn in Numbers on the right, is numbered in design rows. 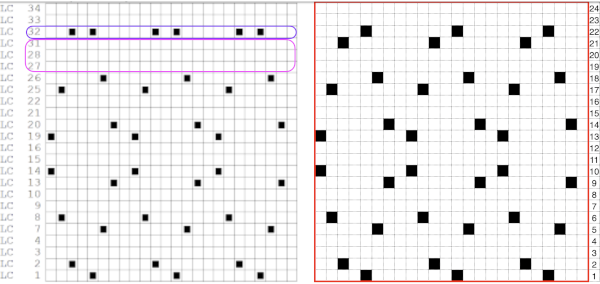
 choices can also be made on how to represent stitch units If the plan is to create a punchcard template and the repeat is too wide, an error message appears
choices can also be made on how to represent stitch units If the plan is to create a punchcard template and the repeat is too wide, an error message appears 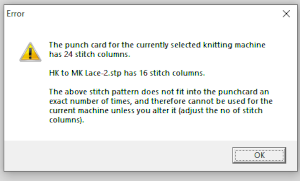 Paper size measurements in page set up other than US letter
Paper size measurements in page set up other than US letter other associated menu choices
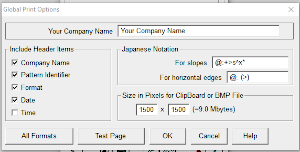
other associated menu choices  It is possible to save the template as a bmp of the full image. The size of the file is shown to the right of the pixel count number settings for the clipboard or bmp file, which will vary in proportion to the stitch and row count. Click on the floppy disk icon to save.
It is possible to save the template as a bmp of the full image. The size of the file is shown to the right of the pixel count number settings for the clipboard or bmp file, which will vary in proportion to the stitch and row count. Click on the floppy disk icon to save. 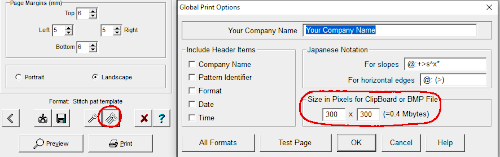

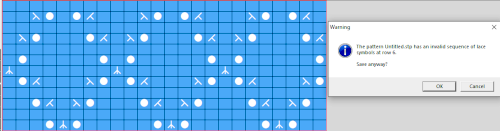

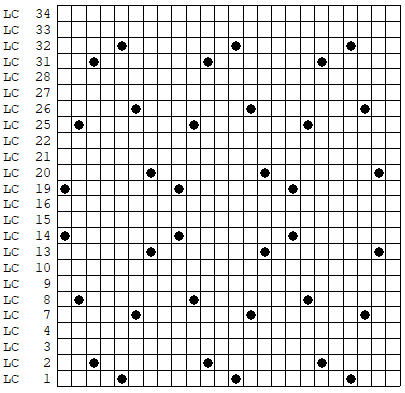 As an additional lace template test, I repeated the process on a portion of an stp file shared generously shared by a DAK FB group knitter along with photos of a completed, lovely lace sweater using it. The results are shown sideways because of the repeat length. The 950i template places four rows at the end of each lace sequence, while as seen in the published repeat of a different lace beside it, there should only be 2. The carriage passes made by the KC in traditional lace knitting though they advance the row counter, do not advance the pattern unless it is selecting needles as well, ie in trims that combine lace with the slip stitch setting. Exceptions to the 2 blank rows rule occur when the lace shape reverses direction such as in zig-zags, or when plain knit or pattern rows are planned deliberately to mix and interact with the lace design.
As an additional lace template test, I repeated the process on a portion of an stp file shared generously shared by a DAK FB group knitter along with photos of a completed, lovely lace sweater using it. The results are shown sideways because of the repeat length. The 950i template places four rows at the end of each lace sequence, while as seen in the published repeat of a different lace beside it, there should only be 2. The carriage passes made by the KC in traditional lace knitting though they advance the row counter, do not advance the pattern unless it is selecting needles as well, ie in trims that combine lace with the slip stitch setting. Exceptions to the 2 blank rows rule occur when the lace shape reverses direction such as in zig-zags, or when plain knit or pattern rows are planned deliberately to mix and interact with the lace design. 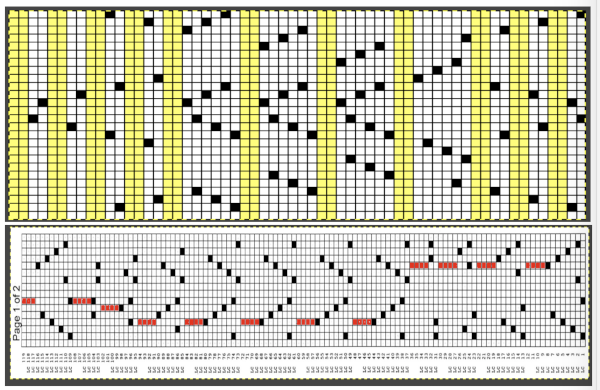 Please see the previous
Please see the previous 
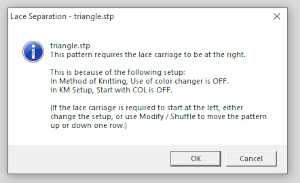 The electronic preview continues to have a series of 4 blank rows between transfer segments. The punchcard template has 2 blank rows between each transfer segment and matches the published pattern with a 3-row exception toward the top of the card. The renderings below begin with the DAK punchcard template on the left with its confused numbering, the extra empty row at the bottom of the repeat was eliminated. The overall repeat is mirrored. It is followed by the published pattern associated with the chart, pixels are then marked for left and right transfers, followed by my amended final repeat, which when knit on the 930 required mirroring.
The electronic preview continues to have a series of 4 blank rows between transfer segments. The punchcard template has 2 blank rows between each transfer segment and matches the published pattern with a 3-row exception toward the top of the card. The renderings below begin with the DAK punchcard template on the left with its confused numbering, the extra empty row at the bottom of the repeat was eliminated. The overall repeat is mirrored. It is followed by the published pattern associated with the chart, pixels are then marked for left and right transfers, followed by my amended final repeat, which when knit on the 930 required mirroring. 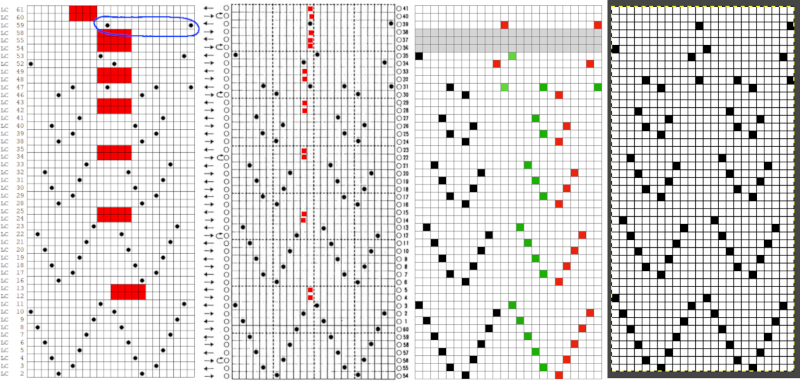 Lace tool use instructions begin on page 299 of the third module user manual, Stitch designer. From the manual: when the Lace tool is clicked, lace patterns can be created by using the LMB or RMB to click and hold on the stitch cell where the eyelet needs to be, after which the mouse can be dragged in the required transfer direction and let go on the stitch that needs the corresponding decrease. Intermediate transfer stitches will be added automatically where appropriate. If the button is clicked and the stitch pattern has a method that is incompatible with lace, the warning that is shown on the right will be displayed. The Wrong side facing texture is probably the most natural choice because this is generally considered the normal method of knitting on Japanese knitting machines. Sections of Lace and Fair Isle may be used in the same stitch pattern and either Fair Isle or Wrong side facing texture are good choices when working with lace patterns.
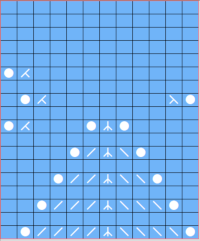
Lace tool use instructions begin on page 299 of the third module user manual, Stitch designer. From the manual: when the Lace tool is clicked, lace patterns can be created by using the LMB or RMB to click and hold on the stitch cell where the eyelet needs to be, after which the mouse can be dragged in the required transfer direction and let go on the stitch that needs the corresponding decrease. Intermediate transfer stitches will be added automatically where appropriate. If the button is clicked and the stitch pattern has a method that is incompatible with lace, the warning that is shown on the right will be displayed. The Wrong side facing texture is probably the most natural choice because this is generally considered the normal method of knitting on Japanese knitting machines. Sections of Lace and Fair Isle may be used in the same stitch pattern and either Fair Isle or Wrong side facing texture are good choices when working with lace patterns.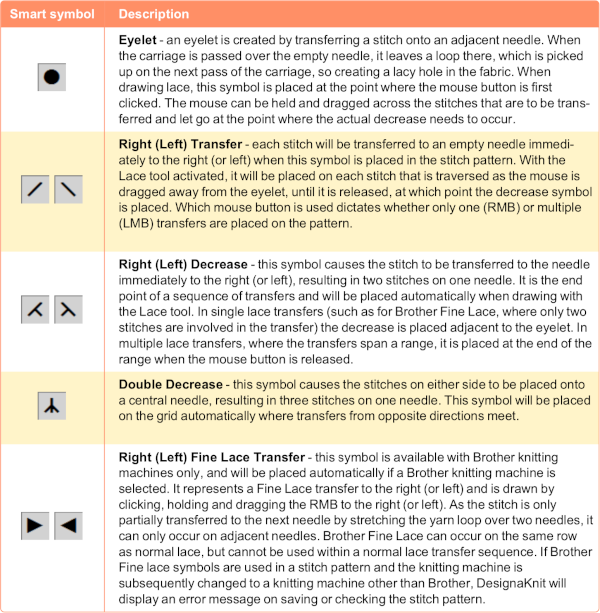
 The associated template preview for the punchcard nearly matched the one that was obtained with the pencil tool chart, but had some differences: the previous image was mirrored although no dak settings were changed. As in all punchcard template numbering, the knit row numbers are skipped in the sequence on the left, so they will not match design row numbers, and the small flower motif is placed differently
The associated template preview for the punchcard nearly matched the one that was obtained with the pencil tool chart, but had some differences: the previous image was mirrored although no dak settings were changed. As in all punchcard template numbering, the knit row numbers are skipped in the sequence on the left, so they will not match design row numbers, and the small flower motif is placed differently 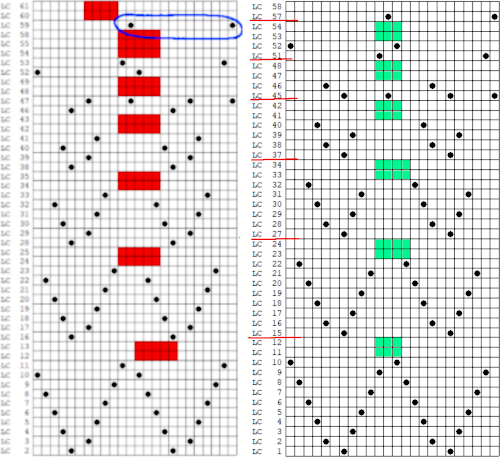
 A wider swatch
A wider swatch When attempting to use this repeat for a continuous one, unless the total number of rows is an even number, the second repeat will reverse the direction of the transfers, resulting in mispatterning and multiple side-by-side empty needles. Changing the total repeat to 48 rows by adding another blank row places all transfers properly. The 12X48 png
When attempting to use this repeat for a continuous one, unless the total number of rows is an even number, the second repeat will reverse the direction of the transfers, resulting in mispatterning and multiple side-by-side empty needles. Changing the total repeat to 48 rows by adding another blank row places all transfers properly. The 12X48 png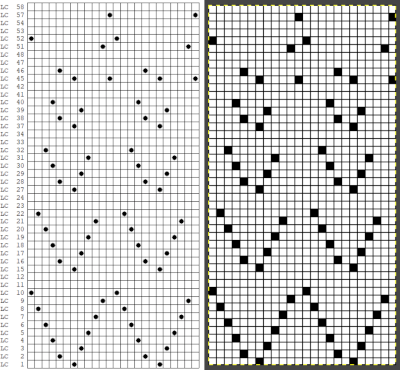
 A half drop repeat is also possible. To achieve this test of a repeat drawn in a paint program, I knit 2 rows after the last “flower” eyelet and had to flip the repeat horizontally before continuing for the top half of the repeat, producing a very different look.
A half drop repeat is also possible. To achieve this test of a repeat drawn in a paint program, I knit 2 rows after the last “flower” eyelet and had to flip the repeat horizontally before continuing for the top half of the repeat, producing a very different look.  There is a transfer error in the knit swatch on the right where I “repaired” a dropped stitch. Edits would be needed if one is determined to make this pattern automated as a continuous design.
There is a transfer error in the knit swatch on the right where I “repaired” a dropped stitch. Edits would be needed if one is determined to make this pattern automated as a continuous design.


 my edit in a spreadsheet, the yellow cells mark rows missing in order to get the lace carriage back to the left side before the next pair of all knit rows.
my edit in a spreadsheet, the yellow cells mark rows missing in order to get the lace carriage back to the left side before the next pair of all knit rows. 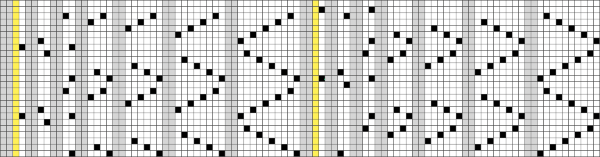
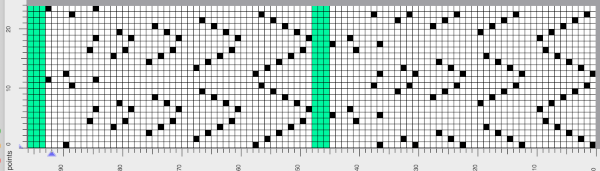 the Arah image was saved as a png, knit on my 930 using img2 track, and mirroring
the Arah image was saved as a png, knit on my 930 using img2 track, and mirroring

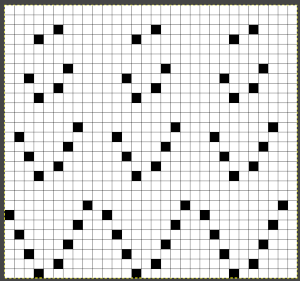

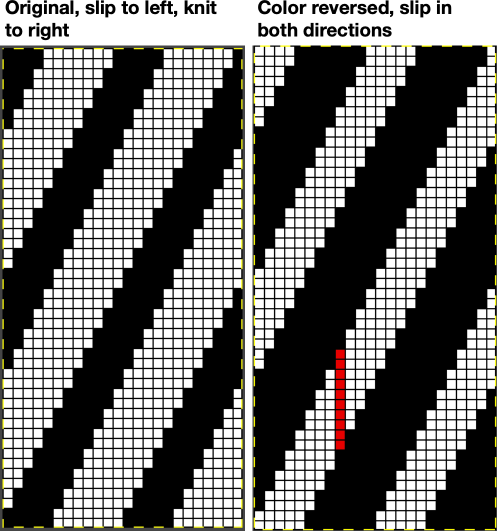
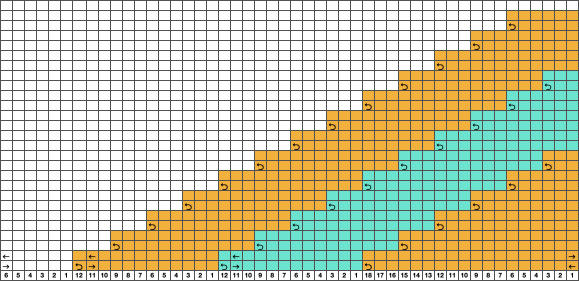
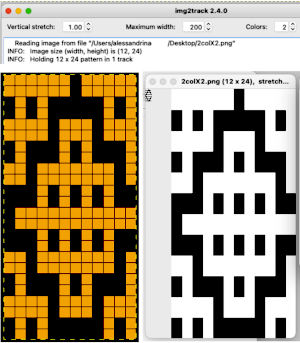
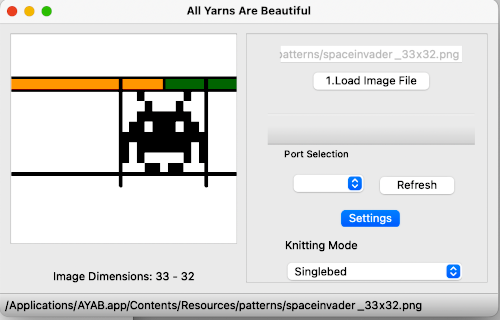
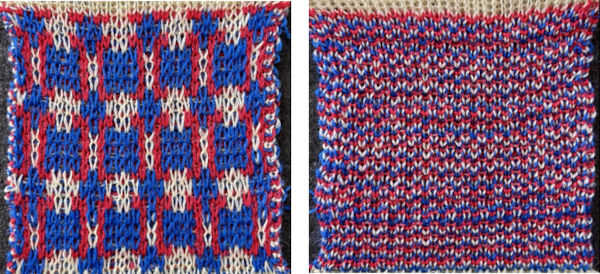
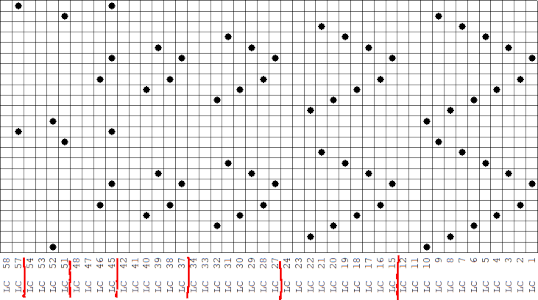
 Nearly all my previous dbj pieces have been knit on a Passap E6000. The 930 experience for such repeats is new to me. With some help from Tanya Cunnigham in reviewing the steps required when using img2track, I returned to cellular automata repeat saved years ago.
Nearly all my previous dbj pieces have been knit on a Passap E6000. The 930 experience for such repeats is new to me. With some help from Tanya Cunnigham in reviewing the steps required when using img2track, I returned to cellular automata repeat saved years ago. That provided an opportunity to decide I preferred the reverse color placement as well as wanting a thicker ply for the white, resulting in twice the fun with 2 colors, and another scrapped sample
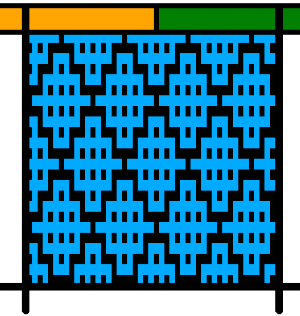
That provided an opportunity to decide I preferred the reverse color placement as well as wanting a thicker ply for the white, resulting in twice the fun with 2 colors, and another scrapped sample 
 I was able to achieve a reasonable repair on the knit side, but the birdseye pattern on the reverse is a bit scrambled.
I was able to achieve a reasonable repair on the knit side, but the birdseye pattern on the reverse is a bit scrambled. 
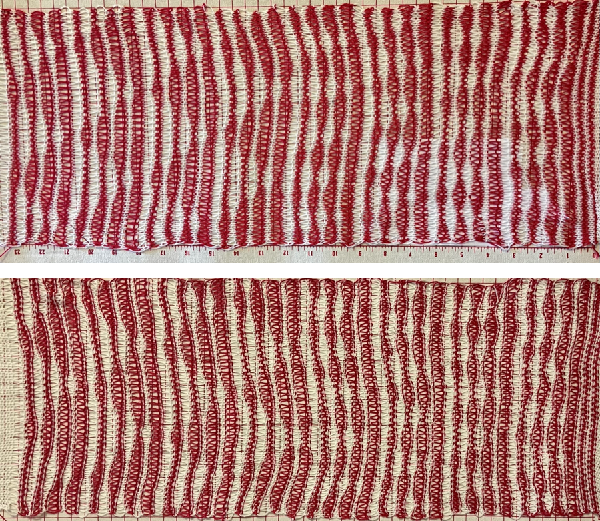
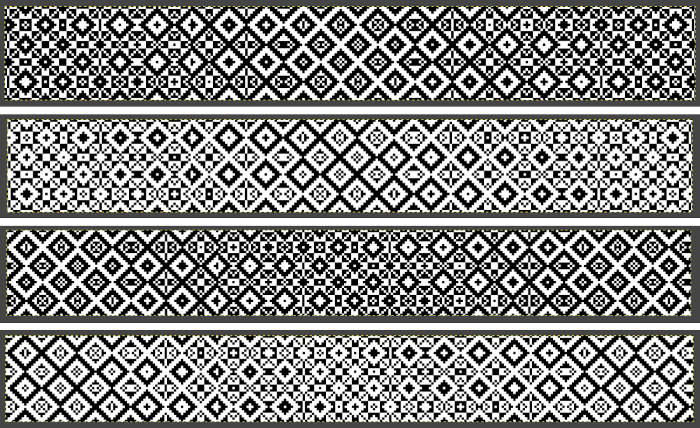 There is also potential for exchanging colors to get a sense of how the pattern might appear in different colorways
There is also potential for exchanging colors to get a sense of how the pattern might appear in different colorways 